| |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 0.7–2.3 h |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.927 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H11NO |
| Molar mass | 149.19 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
Cathinone /ˈkæθɪnoʊn/ (also known as benzoylethanamine, or β-keto-amphetamine) is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines. It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other phenethylamines that share this structure include the stimulants methcathinone, MDPV, mephedrone and the antidepressant bupropion.
History
Discovery
Khat
has been cultivated in the Horn of Africa and Arabian Peninsula region
of the world for thousands of years. It is most commonly chewed for the euphoric effect it produces. The active ingredient was first proposed in 1930, when cathine was identified as a predominant alkaloid in the plant.
Cathine was thought to be the main active ingredient in khat until the
1960s, when it was found that the amount of cathine in the khat leaves
is insufficient to produce the effects observed. In 1975, the United
Nations Narcotic Laboratory analyzed khat leaves from Yemen, Kenya and Madagascar and found the presence of a different alkaloid, cathinone.
Cathinone is a similar molecule to cathine, but is much more abundant
in younger plants. This finding caused scientists to speculate about
whether cathinone was the true active ingredient in khat.
A study was conducted in 1994 to test the effects of cathinone.
Six volunteers who had never chewed khat were given an active khat
sample and a cathinone-free placebo sample.
The researchers analyzed the participants’ moods, activity levels and
blood pressure before and after consuming the khat or placebo. This
analysis showed that cathinone produced amphetamine-like symptoms,
leading the researchers to confirm that cathinone, not cathine, is the
active ingredient in khat leaves.
Cultural significance
Man chewing khat
Over 20 million people in the Arabian Peninsula and East Africa chew khat leaves daily. It is an important piece of the culture and economy in this region, especially in Ethiopia (where khat is said to have originated), Kenya, Djibouti,
and Yemen. Men usually chew it during parties or other social
gatherings while smoking cigarettes and drinking tea. Farmers and other
workers also use khat in the afternoon to reduce fatigue and hunger as
the day goes on. It functions like the caffeine
in a strong cup of coffee as an anti-fatigue drug. Students and
drivers have been known to use it to stay alert for longer periods of
time.
In order to produce its desired effects, khat leaves should be
chewed fresh. The fresh leaves have a higher concentration of
cathinone. Waiting too long after cultivation to chew the leaf will
allow the cathinone to break down into its less potent form, cathine.
Because of the need for quick chewing, it is a habit that has
historically been prevalent only where the plant grows. However, in the
recent years with improvements in road and air transport, khat chewing
has spread to all corners of the world.
The cultivation of khat in Yemen is a highly profitable industry
for farmers. Khat plants will grow differently depending on the climate
they are grown in and each one will produce different amounts of
cathinone.
It generally doesn’t grow as well as in coastal, hot climates. In
Yemen, the khat plant is named after the region in which it is grown.
The Nehmi khat plant has the highest known concentration of cathinone,
342.5 mg/100g.
Legality
Internationally, cathinone is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Circa 1993, the DEA added cathinone to the Controlled Substances Act's Schedule I.
The sale of khat is legal in some jurisdictions, but illegal in others). Substituted cathinones were also often used as the key ingredient of recreational drug mixes commonly known as "bath salts" in the United States.
The table below shows the legality of khat and cathinone in various countries:
| Region | Regulation |
|---|---|
| Eritrea | Illegal |
| Ethiopia | Legal |
| Somalia | Legal |
| Djibouti | Legal |
| Kenya | Khat is legal but cathinone and cathine are classified as Class C substances |
| South Africa | Khat is a protected plant |
| China | Illegal |
| Israel | Legal – The khat plant leaves are allowed to be chewed and beverages containing khat are legal, but it is illegal to sell pills based on cathinone extracts |
| Malaysia | Illegal |
| Saudi Arabia | Illegal |
| Yemen | Khat is legal but the cultivation and selling of the plant is regulated by the government |
| Denmark | Illegal |
| Finland | Illegal |
| France | Khat is prohibited as a stimulant |
| Germany | Khat is illegal but a derivative of cathinone is available upon prescription |
| Ireland | Illegal unless authorized |
| Netherlands | Cathinone and cathine have been illegal but khat was announced as illegal in 2012 |
| Norway | Illegal |
| Poland | Illegal |
| Sweden | Illegal |
| Switzerland | Illegal |
| United Kingdom | Illegal |
| Canada | Illegal to obtain unless approved by a medical practitioner |
| United States | Illegal |
| Australia | Khat is regulated under the Australian Customs Service and a special permit is needed to import it for personal use |
| New Zealand | Illegal |
| Georgia | The khat plant itself is allowed to be sold and chewed, but it is illegal to sell or make beverages containing khat |
| Bulgaria | Illegal under List I - "Plants and substances with a high risk to the public health due to their harmful effect of misuse, prohibited for use in human and veterinary medicine" |
Biological effects
Mechanism of action
Cathinone has been found to stimulate the release of dopamine and inhibit the reuptake of epinephrine, norepinephrine and serotonin in the central nervous system (CNS). These neurotransmitters are all considered monoamines and share the general structure of an aromatic ring and an amine group attached by a two-carbon separator. Because cathinone is a hydrophobic molecule, it can easily cross cell membranes and other barriers, including the blood-brain barrier. This property allows it to interact with the monoamine transporters in the synaptic cleft between neurons. Cathinone induces the release of dopamine from brain striatal preparations that are prelabelled either with dopamine or its precursors.
The metabolites of cathinone, cathine and norephedrine also possess CNS stimulation, but create much weaker effects. The effects of cathinone on the body can be countered by a preceding administration of a dopamine-receptor antagonist.
The antagonist will keep the neuron at its resting state, so the
cathinone cannot cause extraneous release of dopamine or other
neurotransmitters.
Cathinone can also affect the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) by blocking adrenergic receptors and inhibiting smooth muscle contraction. It can also induce dry mouth, blurred vision and increased blood pressure and heart rate.
Pharmacology
Khat
leaves are removed from the plant stalk and are kept in a ball in the
cheek and chewed. Chewing releases juices from the leaves, which include
the alkaloid cathinone. The absorption of cathinone has two phases: one
in the buccal mucosa and one in the stomach and small intestine. The stomach and small intestine are very important in the absorption of ingested alkaloids.
At approximately 2.3 hours after chewing khat leaves, the maximum
concentration of cathinone in blood plasma is reached. The mean
residence time is 5.2 ± 3.4 hours. The elimination half-life of cathinone is 1.5 ± 0.8 hours.
A two-compartment model for absorption and elimination best describes
this data. However, at most, only 7% of the ingested cathinone is
recovered in the urine.
This indicates that the cathinone is being broken down in the body.
Cathinone has been shown to selectively metabolize into
R,S-(-)-norephedrine and cathine. The reduction of the ketone
group in cathinone will produce cathine. This reduction is catalyzed by
enzymes in the liver. The spontaneous breakdown of cathinone is the
reason it must be chewed fresh after cultivation.
Effects on health
The
first documentation of the khat plant being used in medicine was in a
book published by an Arabian physician in the 10th century. It was used as an antidepressant
because it led to feelings of happiness and excitement. Chronic khat
chewing can also create drug dependence, as shown by animal studies.
In such studies, monkeys were trained to push a lever to receive the
drug reward. As the monkeys' dependence increased, they pressed the
lever at an increasing frequency.
Khat chewing and the effects of cathinone on the body differ from
person to person, but there is a general pattern of behavior that
emerges after ingesting fresh cathinone:
- Feelings of euphoria that last for one to two hours
- Discussion of serious issues and increased irritability
- The chewer's imagination is very active
- Depressive stage
- Irritability, loss of appetite and insomnia
There are other effects not related to the CNS. The chewer can develop constipation and heartburn after a khat session. Long-term effects of cathinone can include gum disease or oral cancer, cardiovascular disease and depression. The withdrawal symptoms of cathinone include, hot flashes, lethargy and a great urge to use the drug for at least the first two days.
Chemistry
Biosynthesis
Mechanism of the Non-Beta Oxidation pathway for the biosynthesis of S-Cathinone in the Khat plant
The synthesis of cathinone in khat begins with L-phenylalanine and
the first step is carried out by L-phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL),
which cleaves off an ammonia group and creates a carbon-carbon double
bond, forming cinnamic acid.
After this, the molecule can either go through a beta-oxidative
pathway or a non-beta-oxidative pathway. The beta-oxidative pathway
produces benzoyl-CoA while the non-beta-oxidative pathway produces benzoic acid. Both of these molecules can be converted to 1-phenylpropane-1,2-dione by a condensation reaction catalyzed by a ThDP-dependent enzyme (Thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzyme) with pyruvate and producing CO2.
1-phenylpropane-1,2-dione goes through a transaminase reaction to
replace a ketone with an ammonia group to form (S)-cathinone.
(S)-Cathinone can then undergo a reduction reaction to produce the less
potent but structurally similar cathine or norephedrine, which are also
found in the plant.
Aside from the beta- and non-beta-oxidative pathways, the
biosynthesis of cathinone can proceed through a CoA-dependent pathway.
The CoA-dependent pathway is actually a mix between the two main
pathways as it starts like the beta-oxidative pathway and then when it
loses CoA, it finishes the synthesis in the non-beta-oxidative pathway.
In this pathway, the trans-cinnamic acid produced from L-phenylalanine
is ligated to a Coenzyme A (CoA), just like the beginning of the beta-oxidative pathway. It then undergoes hydration at the double bond. This product then loses the CoA to produce benzaldehyde,
an intermediate of the non-beta-oxidative pathway. Benzaldehyde is
converted into benzoic acid and proceeds through the rest of the
synthesis.
Synthetic production
Cathinone can be synthetically produced from propiophenone through a Friedel-Crafts Acylation of propionic acid and benzene. The resulting propiophenone
can be brominated, and the bromine can be substituted with ammonia to
produce a racemic mixture of cathinone. A different synthetic strategy
must be employed to produce enantiomerically pure (S)-cathinone. This
synthetic route starts out with the N-acetylation of the optically active amino acid, S-alanine. Then, phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is used to chlorinate the carboxylic acid
forming an acyl chloride. At the same time, a Friedel-Crafts acylation
is preformed on benzene with aluminum chloride catalyst. Finally, the acetyl protecting group is removed by heating with hydrochloric acid to form enantiomerically pure S-(-)-cathinone.
Structure
Bupropion: a cathinone derivative
Cathinone can be extracted from Catha edulis, or synthesized from α-bromopropiophenone (which is easily made from propiophenone). Because cathinone is both a primary amine and a ketone, it is very likely to dimerize, especially as a free base isolated from plant matter.
The structure of cathinone is very similar to that of other
molecules. By reducing the ketone, it becomes cathine if it retains its
stereochemistry, or norephedrine if its stereochemistry is inverted.
Cathine is a less potent version of cathinone and cathinone's
spontaneous reduction is the reason that older khat plants are not as
stimulating as younger ones. Cathinone and amphetamine are closely
related in that amphetamine is only lacking the ketone C=O group. Cathinone is structurally related to methcathinone, in much the same way as amphetamine is related to methamphetamine. Cathinone differs from amphetamine by possessing a ketone oxygen atom (C=O) on the β (beta) position of the side chain. The corresponding alcohol, cathine, is a less powerful stimulant. The biophysiological conversion from cathinone to cathine is to blame for the depotentiation of khat
leaves over time. Fresh leaves have a greater ratio of cathinone to
cathine than dried ones, therefore having more psychoactive effects.
There are many cathinone derivatives that include the addition of
an R group to the amino end of the molecule. Some of these derivatives
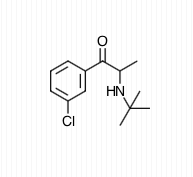
have medical uses as well. Bupropion
is one of the most commonly prescribed antidepressants and its
structure is Cathinone with a tertiary butyl group attached to the
nitrogen and chlorine attached to the benzene ring meta- (chemistry) to the main carbon chain.