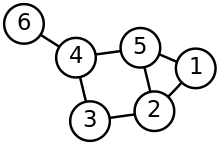
A drawing of a graph.
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of vertices (also called nodes or points) which are connected by edges (also called links or lines). A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically; see Graph (discrete mathematics)
for more detailed definitions and for other variations in the types of
graph that are commonly considered. Graphs are one of the prime objects
of study in discrete mathematics.
Refer to the glossary of graph theory for basic definitions in graph theory.
Definitions
Definitions in graph theory vary. The following are some of the more basic ways of defining graphs and related mathematical structures.
Graph
A graph with three vertices and three edges.
In one restricted but very common sense of the term, a graph is an ordered pair G = (V, E) comprising:
- V a set of vertices (also called nodes or points);
- E ⊆ {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} a set of edges (also called links or lines), which are unordered pairs of vertices (that is, an edge is associated with two distinct vertices).
To avoid ambiguity, this type of object may be called precisely an undirected simple graph.
In the edge {x, y}, the vertices x and y are called the endpoints of the edge. The edge is said to join x and y and to be incident on x and on y. A vertex may exist in a graph and not belong to an edge. Multiple edges are two or more edges that join the same two vertices.
In one more general sense of the term allowing multiple edges,[3][4] a graph is an ordered triple G = (V, E, ϕ) comprising:
- V a set of vertices (also called nodes or points);
- E a set of edges (also called links or lines);
- ϕ: E → {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} an incidence function mapping every edge to an unordered pair of vertices (that is, an edge is associated with two distinct vertices).
To avoid ambiguity, this type of object may be called precisely an undirected multigraph.
A loop
is an edge that joins a vertex to itself. Graphs as defined in the two
definitions above cannot have loops, because a loop joining a vertex x is the edge (for an undirected simple graph) or is incident on (for an undirected multigraph) {x, x} = {x} which is not in {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y}. So to allow loops the definitions must be expanded. For undirected simple graphs, E ⊆ {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} should become E ⊆ {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2}. For undirected multigraphs, ϕ: E → {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} should become ϕ: E → {{x, y} | (x, y) ∈ V2}. To avoid ambiguity, these types of objects may be called precisely an undirected simple graph permitting loops and an undirected multigraph permitting loops respectively.
V and E are usually taken to be finite, and many of the well-known results are not true (or are rather different) for infinite graphs because many of the arguments fail in the infinite case. Moreover, V is often assumed to be non-empty, but E is allowed to be the empty set. The order of a graph is |V|, its number of vertices. The size of a graph is |E|, its number of edges. The degree or valency of a vertex is the number of edges that are incident to it, where a loop is counted twice.
In an undirected simple graph of order n, the maximum degree of each vertex is n − 1 and the maximum size of the graph is n(n − 1)/2.
The edges of an undirected simple graph permitting loops G induce a symmetric homogeneous relation ~ on the vertices of G that is called the adjacency relation of G. Specifically, for each edge {x, y}, its endpoints x and y are said to be adjacent to one another, which is denoted x ~ y.
Directed graph
A directed graph with three vertices and four directed edges (the double arrow represents an edge in each direction).
A directed graph or digraph is a graph in which edges have orientations.
In one restricted but very common sense of the term, a directed graph is an ordered pair G = (V, E) comprising:
- V a set of vertices (also called nodes or points);
- E ⊆ {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} a set of edges (also called directed edges, directed links, directed lines, arrows or arcs) which are ordered pairs of distinct vertices (i.e., an edge is associated with two distinct vertices).
To avoid ambiguity, this type of object may be called precisely a directed simple graph.
In the edge (x, y) directed from x to y, the vertices x and y are called the endpoints of the edge, x the tail of the edge and y the head of the edge. The edge (y, x) is called the inverted edge of (x, y). The edge is said to join x and y and to be incident on x and on y. A vertex may exist in a graph and not belong to an edge. Multiple edges are two or more edges with both the same tail and the same head.
In one more general sense of the term allowing multiple edges, a directed graph is an ordered triple G = (V, E, ϕ) comprising:
- V a set of vertices (also called nodes or points);
- E a set of edges (also called directed edges, directed links, directed lines, arrows or arcs);
- ϕ: E → {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} an incidence function mapping every edge to an ordered pair of distinct vertices (i.e., an edge is associated with two distinct vertices).
To avoid ambiguity, this type of object may be called precisely a directed multigraph.
A loop
is an edge that joins a vertex to itself. Directed graphs as defined in
the two definitions above cannot have loops, because a loop joining a
vertex x is the edge (for a directed simple graph) or is incident on (for a directed multigraph) (x, x) which is not in {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y}. So to allow loops the definitions must be expanded. For directed simple graphs, E ⊆ {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} should become E ⊆ {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2}. For directed multigraphs, ϕ: E → {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2 ∧ x ≠ y} should become ϕ: E → {(x, y) | (x, y) ∈ V2}. To avoid ambiguity, these types of objects may be called precisely a directed simple graph permitting loops and a directed multigraph permitting loops (or a quiver) respectively.
The edges of a directed simple graph permitting loops G is a homogeneous relation ~ on the vertices of G that is called the adjacency relation of G. Specifically, for each edge (x, y), its endpoints x and y are said to be adjacent to one another, which is denoted x ~ y.
Applications
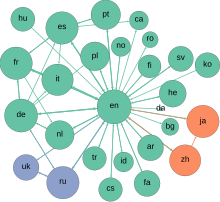
The
network graph formed by Wikipedia editors (edges) contributing to
different Wikipedia language versions (vertices) during one month in
summer 2013.
Graphs can be used to model many types of relations and processes in physical, biological,
social and information systems. Many practical problems can be
represented by graphs. Emphasizing their application to real-world
systems, the term network is sometimes defined to mean a graph in
which attributes (e.g. names) are associated with the vertices and
edges, and the subject that expresses and understands the real-world
systems as a network is called network science.
Computer science
In computer science,
graphs are used to represent networks of communication, data
organization, computational devices, the flow of computation, etc. For
instance, the link structure of a website can be represented by a directed graph, in which the vertices represent web pages and directed edges represent links from one page to another. A similar approach can be taken to problems in social media, travel, biology, computer chip design, mapping the progression of neuro-degenerative diseases, and many other fields. The development of algorithms to handle graphs is therefore of major interest in computer science. The transformation of graphs is often formalized and represented by graph rewrite systems. Complementary to graph transformation systems focusing on rule-based in-memory manipulation of graphs are graph databases geared towards transaction-safe, persistent storing and querying of graph-structured data.
Linguistics
Graph-theoretic methods, in various forms, have proven particularly useful in linguistics, since natural language often lends itself well to discrete structure. Traditionally, syntax and compositional semantics follow tree-based structures, whose expressive power lies in the principle of compositionality, modeled in a hierarchical graph. More contemporary approaches such as head-driven phrase structure grammar model the syntax of natural language using typed feature structures, which are directed acyclic graphs.
Within lexical semantics,
especially as applied to computers, modeling word meaning is easier
when a given word is understood in terms of related words; semantic networks are therefore important in computational linguistics. Still, other methods in phonology (e.g. optimality theory, which uses lattice graphs) and morphology (e.g. finite-state morphology, using finite-state transducers)
are common in the analysis of language as a graph. Indeed, the
usefulness of this area of mathematics to linguistics has borne
organizations such as TextGraphs, as well as various 'Net' projects, such as WordNet, VerbNet, and others.
Physics and chemistry
Graph theory is also used to study molecules in chemistry and physics. In condensed matter physics,
the three-dimensional structure of complicated simulated atomic
structures can be studied quantitatively by gathering statistics on
graph-theoretic properties related to the topology of the atoms. Also,
"the Feynman graphs and rules of calculation summarize quantum field theory in a form in close contact with the experimental numbers one wants to understand." In chemistry a graph makes a natural model for a molecule, where vertices represent atoms and edges bonds. This approach is especially used in computer processing of molecular structures, ranging from chemical editors to database searching. In statistical physics,
graphs can represent local connections between interacting parts of a
system, as well as the dynamics of a physical process on such
systems. Similarly, in computational neuroscience
graphs can be used to represent functional connections between brain
areas that interact to give rise to various cognitive processes, where
the vertices represent different areas of the brain and the edges
represent the connections between those areas. Graph theory plays an
important role in electrical modeling of electrical networks, here,
weights are associated with resistance of the wire segments to obtain
electrical properties of network structures. Graphs are also used to represent the micro-scale channels of porous media, in which the vertices represent the pores and the edges represent the smaller channels connecting the pores. Chemical graph theory uses the molecular graph
as a means to model molecules.
Graphs and networks are excellent models to study and understand phase
transitions and critical phenomena.
Removal of nodes or edges lead to a critical transition where the
network breaks into small clusters which is studied as a phase
transition. This breakdown is studied via percolation theory.
Social sciences
Graph theory is also widely used in sociology as a way, for example, to measure actors' prestige or to explore rumor spreading, notably through the use of social network analysis software. Under the umbrella of social networks are many different types of graphs.
Acquaintanceship and friendship graphs describe whether people know
each other. Influence graphs model whether certain people can influence
the behavior of others. Finally, collaboration graphs model whether two
people work together in a particular way, such as acting in a movie
together.
Biology
Likewise, graph theory is useful in biology
and conservation efforts where a vertex can represent regions where
certain species exist (or inhabit) and the edges represent migration
paths or movement between the regions. This information is important
when looking at breeding patterns or tracking the spread of disease,
parasites or how changes to the movement can affect other species.
Graphs are also commonly used in molecular biology and genomics
to model and analyse datasets with complex relationships. For example,
graph-based methods are often used to 'cluster' cells together into
cell-types in single-cell transcriptome analysis. Another use is to model genes or proteins in a pathway and study the relationships between them, such as metabolic pathways and gene regulatory networks .
Evolutionary trees, ecological networks, and hierarchical clustering of
gene expression patterns are also represented as graph structures.
Graph-based methods are pervasive that researchers in some fields of
biology and these will only become far more widespread as technology
develops to leverage this kind of high-throughout multidimensional data.
Graph theory is also used in connectomics; nervous systems can be seen as a graph, where the nodes are neurons and the edges are the connections between them.
Mathematics
In mathematics, graphs are useful in geometry and certain parts of topology such as knot theory. Algebraic graph theory has close links with group theory. Algebraic graph theory has been applied to many areas including dynamic systems and complexity.
Other topics
A graph structure can be extended by assigning a weight to each edge of the graph. Graphs with weights, or weighted graphs,
are used to represent structures in which pairwise connections have
some numerical values. For example, if a graph represents a road
network, the weights could represent the length of each road. There may
be several weights associated with each edge, including distance (as in
the previous example), travel time, or monetary cost. Such weighted
graphs are commonly used to program GPS's, and travel-planning search
engines that compare flight times and costs.
History
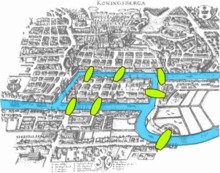
The Königsberg Bridge problem
The paper written by Leonhard Euler on the Seven Bridges of Königsberg and published in 1736 is regarded as the first paper in the history of graph theory. This paper, as well as the one written by Vandermonde on the knight problem, carried on with the analysis situs initiated by Leibniz. Euler's formula relating the number of edges, vertices, and faces of a convex polyhedron was studied and generalized by Cauchy and L'Huilier, and represents the beginning of the branch of mathematics known as topology.
More than one century after Euler's paper on the bridges of Königsberg and while Listing was introducing the concept of topology, Cayley was led by an interest in particular analytical forms arising from differential calculus to study a particular class of graphs, the trees. This study had many implications for theoretical chemistry. The techniques he used mainly concern the enumeration of graphs
with particular properties. Enumerative graph theory then arose from
the results of Cayley and the fundamental results published by Pólya between 1935 and 1937. These were generalized by De Bruijn in 1959. Cayley linked his results on trees with contemporary studies of chemical composition.
The fusion of ideas from mathematics with those from chemistry began
what has become part of the standard terminology of graph theory.
In particular, the term "graph" was introduced by Sylvester in a paper published in 1878 in Nature, where he draws an analogy between "quantic invariants" and "co-variants" of algebra and molecular diagrams:
- "[…] Every invariant and co-variant thus becomes expressible by a graph precisely identical with a Kekuléan diagram or chemicograph. […] I give a rule for the geometrical multiplication of graphs, i.e. for constructing a graph to the product of in- or co-variants whose separate graphs are given. […]" (italics as in the original).
The first textbook on graph theory was written by Dénes Kőnig, and published in 1936. Another book by Frank Harary, published in 1969, was "considered the world over to be the definitive textbook on the subject",
and enabled mathematicians, chemists, electrical engineers and social
scientists to talk to each other. Harary donated all of the royalties to
fund the Pólya Prize.
One of the most famous and stimulating problems in graph theory is the four color problem:
"Is it true that any map drawn in the plane may have its regions
colored with four colors, in such a way that any two regions having a
common border have different colors?" This problem was first posed by Francis Guthrie in 1852 and its first written record is in a letter of De Morgan addressed to Hamilton the same year. Many incorrect proofs have been proposed, including those by Cayley, Kempe, and others. The study and the generalization of this problem by Tait, Heawood, Ramsey and Hadwiger led to the study of the colorings of the graphs embedded on surfaces with arbitrary genus. Tait's reformulation generated a new class of problems, the factorization problems, particularly studied by Petersen and Kőnig. The works of Ramsey on colorations and more specially the results obtained by Turán in 1941 was at the origin of another branch of graph theory, extremal graph theory.
The four color problem remained unsolved for more than a century. In 1969 Heinrich Heesch published a method for solving the problem using computers. A computer-aided proof produced in 1976 by Kenneth Appel and Wolfgang Haken makes fundamental use of the notion of "discharging" developed by Heesch.
The proof involved checking the properties of 1,936 configurations by
computer, and was not fully accepted at the time due to its complexity. A
simpler proof considering only 633 configurations was given twenty
years later by Robertson, Seymour, Sanders and Thomas.
The autonomous development of topology from 1860 and 1930 fertilized graph theory back through the works of Jordan, Kuratowski and Whitney. Another important factor of common development of graph theory and topology came from the use of the techniques of modern algebra. The first example of such a use comes from the work of the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff, who published in 1845 his Kirchhoff's circuit laws for calculating the voltage and current in electric circuits.
The introduction of probabilistic methods in graph theory, especially in the study of Erdős and Rényi of the asymptotic probability of graph connectivity, gave rise to yet another branch, known as random graph theory, which has been a fruitful source of graph-theoretic results.
Graph drawing
Graphs are represented visually by drawing a point or circle for
every vertex, and drawing a line between two vertices if they are
connected by an edge. If the graph is directed, the direction is
indicated by drawing an arrow.
A graph drawing should not be confused with the graph itself (the
abstract, non-visual structure) as there are several ways to structure
the graph drawing. All that matters is which vertices are connected to
which others by how many edges and not the exact layout. In practice, it
is often difficult to decide if two drawings represent the same graph.
Depending on the problem domain some layouts may be better suited and
easier to understand than others.
The pioneering work of W. T. Tutte
was very influential on the subject of graph drawing. Among other
achievements, he introduced the use of linear algebraic methods to
obtain graph drawings.
Graph drawing also can be said to encompass problems that deal with the crossing number
and its various generalizations. The crossing number of a graph is the
minimum number of intersections between edges that a drawing of the
graph in the plane must contain. For a planar graph, the crossing number is zero by definition.
Drawings on surfaces other than the plane are also studied.
Graph-theoretic data structures
There are different ways to store graphs in a computer system. The data structure used depends on both the graph structure and the algorithm
used for manipulating the graph. Theoretically one can distinguish
between list and matrix structures but in concrete applications the best
structure is often a combination of both. List structures are often
preferred for sparse graphs as they have smaller memory requirements. Matrix
structures on the other hand provide faster access for some
applications but can consume huge amounts of memory. Implementations of
sparse matrix structures that are efficient on modern parallel computer
architectures are an object of current investigation.
List structures include the incidence list, an array of pairs of vertices, and the adjacency list,
which separately lists the neighbors of each vertex: Much like the
incidence list, each vertex has a list of which vertices it is adjacent
to.
Matrix structures include the incidence matrix, a matrix of 0's and 1's whose rows represent vertices and whose columns represent edges, and the adjacency matrix,
in which both the rows and columns are indexed by vertices. In both
cases a 1 indicates two adjacent objects and a 0 indicates two
non-adjacent objects. The degree matrix indicates the degree of vertices. The Laplacian matrix is a modified form of the adjacency matrix that incorporates information about the degrees of the vertices, and is useful in some calculations such as Kirchhoff's theorem on the number of spanning trees of a graph.
The distance matrix,
like the adjacency matrix, has both its rows and columns indexed by
vertices, but rather than containing a 0 or a 1 in each cell it contains
the length of a shortest path between two vertices.
Problems
Enumeration
There is a large literature on graphical enumeration: the problem of counting graphs meeting specified conditions. Some of this work is found in Harary and Palmer (1973).
Subgraphs, induced subgraphs, and minors
A common problem, called the subgraph isomorphism problem, is finding a fixed graph as a subgraph in a given graph. One reason to be interested in such a question is that many graph properties are hereditary for subgraphs, which means that a graph has the property if and only if all subgraphs have it too.
Unfortunately, finding maximal subgraphs of a certain kind is often an NP-complete problem. For example:
- Finding the largest complete subgraph is called the clique problem (NP-complete).
One special case of subgraph isomorphism is the graph isomorphism problem.
It asks whether two graphs are isomorphic. It is not known whether
this problem is NP-complete, nor whether it can be solved in polynomial
time.
A similar problem is finding induced subgraphs
in a given graph. Again, some important graph properties are hereditary
with respect to induced subgraphs, which means that a graph has a
property if and only if all induced subgraphs also have it. Finding
maximal induced subgraphs of a certain kind is also often NP-complete.
For example:
- Finding the largest edgeless induced subgraph or independent set is called the independent set problem (NP-complete).
Still another such problem, the minor containment problem, is to find a fixed graph as a minor of a given graph. A minor
or subcontraction of a graph is any graph obtained by taking a subgraph
and contracting some (or no) edges. Many graph properties are
hereditary for minors, which means that a graph has a property if and
only if all minors have it too. For example, Wagner's Theorem states:
- A graph is planar if it contains as a minor neither the complete bipartite graph K3,3 (see the Three-cottage problem) nor the complete graph K5.
A similar problem, the subdivision containment problem, is to find a fixed graph as a subdivision of a given graph. A subdivision or homeomorphism
of a graph is any graph obtained by subdividing some (or no) edges.
Subdivision containment is related to graph properties such as planarity. For example, Kuratowski's Theorem states:
- A graph is planar if it contains as a subdivision neither the complete bipartite graph K3,3 nor the complete graph K5.
Another problem in subdivision containment is the Kelmans–Seymour conjecture:
- Every 5-vertex-connected graph that is not planar contains a subdivision of the 5-vertex complete graph K5.
Another class of problems has to do with the extent to which various
species and generalizations of graphs are determined by their point-deleted subgraphs. For example:
Graph coloring
Many problems and theorems in graph theory have to do with various
ways of coloring graphs. Typically, one is interested in coloring a
graph so that no two adjacent vertices have the same color, or with
other similar restrictions. One may also consider coloring edges
(possibly so that no two coincident edges are the same color), or other
variations. Among the famous results and conjectures concerning graph
coloring are the following:
- Four-color theorem
- Strong perfect graph theorem
- Erdős–Faber–Lovász conjecture (unsolved)
- Total coloring conjecture, also called Behzad's conjecture (unsolved)
- List coloring conjecture (unsolved)
- Hadwiger conjecture (graph theory) (unsolved)
Subsumption and unification
Constraint modeling theories concern families of directed graphs related by a partial order.
In these applications, graphs are ordered by specificity, meaning that
more constrained graphs—which are more specific and thus contain a
greater amount of information—are subsumed by those that are more
general. Operations between graphs include evaluating the direction of a
subsumption relationship between two graphs, if any, and computing
graph unification. The unification of two argument graphs is defined as
the most general graph (or the computation thereof) that is consistent
with (i.e. contains all of the information in) the inputs, if such a
graph exists; efficient unification algorithms are known.
For constraint frameworks which are strictly compositional, graph unification is the sufficient satisfiability and combination function. Well-known applications include automatic theorem proving and modeling the elaboration of linguistic structure.
Route problems
- Hamiltonian path problem
- Minimum spanning tree
- Route inspection problem (also called the "Chinese postman problem")
- Seven bridges of Königsberg
- Shortest path problem
- Steiner tree
- Three-cottage problem
- Traveling salesman problem (NP-hard)
Network flow
There are numerous problems arising especially from applications that have to do with various notions of flows in networks, for example:
Visibility problems
Covering problems
Covering problems in graphs may refer to various set cover problems on subsets of vertices/subgraphs.
- Dominating set problem is the special case of set cover problem where sets are the closed neighborhoods.
- Vertex cover problem is the special case of Set cover problem where sets to cover are every edges.
- The original set cover problem, also called hitting set, can be described as a vertex cover in a hypergraph.
Decomposition problems
Decomposition,
defined as partitioning the edge set of a graph (with as many vertices
as necessary accompanying the edges of each part of the partition), has a
wide variety of question. Often, it is required to decompose a graph
into subgraphs isomorphic to a fixed graph; for instance, decomposing a
complete graph into Hamiltonian cycles. Other problems specify a family
of graphs into which a given graph should be decomposed, for instance, a
family of cycles, or decomposing a complete graph Kn into n − 1 specified trees having, respectively, 1, 2, 3, ..., n − 1 edges.
Some specific decomposition problems that have been studied include:
- Arboricity, a decomposition into as few forests as possible
- Cycle double cover, a decomposition into a collection of cycles covering each edge exactly twice
- Edge coloring, a decomposition into as few matchings as possible
- Graph factorization, a decomposition of a regular graph into regular subgraphs of given degrees
Graph classes
Many problems involve characterizing the members of various classes of graphs. Some examples of such questions are below:
- Enumerating the members of a class
- Characterizing a class in terms of forbidden substructures
- Ascertaining relationships among classes (e.g. does one property of graphs imply another)
- Finding efficient algorithms to decide membership in a class
- Finding representations for members of a class