| Theobroma cacao | |
|---|---|

| |
| Cacao fruits on the tree | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Malvales |
| Family: | Malvaceae |
| Genus: | Theobroma |
| Species: |
T. cacao
|
| Binomial name | |
| Theobroma cacao | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Closed and open blossom and fruits on the trunk of Theobroma cacao (ÖBG Bayreuth)
Theobroma cacao, also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, is a small (4–8 m (13–26 ft) tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae, native to the deep tropical regions of Mesoamerica. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make chocolate liquor, cocoa solids, cocoa butter and chocolate. The largest producer of cocoa beans in 2018 was Ivory Coast, with 37% of the world total.
Description
Leaves are alternate, entire, unlobed, 10–40 cm (3.9–15.7 in) long and 5–20 cm (2.0–7.9 in) broad.
The flowers are produced in clusters directly on the trunk and older branches; this is known as cauliflory. The flowers are small, 1–2 cm (0.39–0.79 in) diameter, with pink calyx. The floral formula, used to represent the structure of a flower using numbers, is ✶ K5 C5 A(5°+5²) G(5). While many of the world's flowers are pollinated by bees (Hymenoptera) or butterflies/moths (Lepidoptera), cacao flowers are pollinated by tiny flies, Forcipomyia midges in the subfamily Forcipomyiinae. Using the natural pollinator Forcipomyia midges for Theobroma cacao was shown to have more fruit production than using artificial pollinators. The fruit,
called a cacao pod, is ovoid, 15–30 cm (5.9–11.8 in) long and 8–10 cm
(3.1–3.9 in) wide, ripening yellow to orange, and weighs about 500 g
(1.1 lb) when ripe. The pod contains 20 to 60 seeds, usually called "beans", embedded in a white pulp. The seeds are the main ingredient of chocolate, while the pulp is used in some countries to prepare refreshing juice, smoothies, jelly, and cream. Usually discarded until practices changed in the 21st century, the fermented pulp may be distilled into an alcoholic beverage. Each seed contains a significant amount of fat (40–50%) as cocoa butter. The fruit's active constituent is the stimulant theobromine, a compound similar to caffeine.
Taxonomy and nomenclature
Cacao (Theobroma cacao) belongs to the genus Theobroma classified under the subfamily Byttnerioideae of the mallow family Malvaceae. Cacao is one of 17 species of Theobroma.
In 2008, researchers proposed a new classification based upon morphological, geographic, and genomic criteria: 10 groups have been named according to their geographic origin or the traditional cultivar name. These groups are: Amelonado, Criollo, Nacional, Contamana, Curaray, Cacao guiana, Iquitos, Marañon, Nanay, and Purús.
The generic name is derived from the Greek for "food of the gods"; from θεός (theos), meaning 'god', and βρῶμα (broma), meaning 'food'. The specific name cacao is the Hispanization of the name of the plant in indigenous Mesoamerican languages. The cacao was known as kakaw in Tzeltal, Kʼicheʼ and Classic Maya; kagaw in Sayula Popoluca; and cacahuatl in Nahuatl as "bean of the cocoa-tree".
Distribution and domestication
T. cacao is widely distributed from southeastern Mexico to the Amazon basin. There were originally two hypotheses about its domestication; one said that there were two foci for domestication, one in the Lacandon Jungle area of Mexico and another in lowland South America. More recent studies of patterns of DNA diversity, however, suggest that this is not the case. One study sampled 1241 trees and classified them into 10 distinct genetic clusters. This study also identified areas, for example around Iquitos in modern Peru and Ecuador, where representatives of several genetic clusters originated more than 5000 years ago, leading to development of the variety, Nacional cocoa bean. This result suggests that this is where T. cacao
was originally domesticated, probably for the pulp that surrounds the
beans, which is eaten as a snack and fermented into a mildly alcoholic
beverage.
Using the DNA sequences and comparing them with data derived from
climate models and the known conditions suitable for cacao, one study
refined the view of domestication, linking the area of greatest cacao
genetic diversity to a bean-shaped area that encompasses Ecuador, the border between Brazil and Peru and the southern part of the Colombian-Brazilian border. Climate models indicate that at the peak of the last ice age 21,000 years ago, when habitat suitable for cacao was at its most reduced, this area was still suitable, and so provided a refugium for the species.
Cacao trees grow well as understory
plants in humid forest ecosystems. This is equally true of abandoned
cultivated trees, making it difficult to distinguish truly wild trees
from those whose parents may originally have been cultivated.
Currency system
Cacao beans constituted both a ritual beverage and a major currency system in pre-Columbian Mesoamerican civilizations. At one point, the Aztec empire received a yearly tribute of 980 loads (xiquipil in Nahuatl) of cacao, in addition to other goods. Each load represented exactly 8,000 beans.
The buying power of quality beans was such that 80–100 beans could buy a
new cloth mantle. The use of cacao beans as currency is also known to
have spawned counterfeiters during the Aztec empire.
Cultivation
In 2016, cocoa beans were cultivated on roughly 10,196,725 hectares (25,196,660 acres) worldwide.
Cocoa beans are grown by large agroindustrial plantations and small
producers, the bulk of production coming from millions of farmers with
small plots.
A tree begins to bear when it is four or five years old. A mature tree
may have 6,000 flowers in a year, yet only about 20 pods. About 1,200
seeds (40 pods) are required to produce 1 kg (2.2 lb) of cocoa paste.
Historically, chocolate makers have recognized three main cultivar groups of cacao beans used to make cocoa and chocolate: Forastero, Criollo and Trinitario. The most prized, rare, and expensive is the Criollo group, the cocoa bean used by the Maya.
Only 10% of chocolate is made from Criollo, which is arguably less
bitter and more aromatic than any other bean. In November 2000, the
cacao beans coming from Chuao were awarded an appellation of origin under the title "Cacao de Chuao" (from Spanish-cacao of Chuao).
The cacao bean in 80% of chocolate is made using beans of the
Forastero group, the main and most ubiquitous variety being the
Amenolado variety, while the arriba variety (such as the Nacional
variety) are less commonly found in Forastero produce. Forastero trees
are significantly hardier and more disease-resistant than Criollo trees,
resulting in cheaper cacao beans.
Major cocoa bean processors include Hershey's, Nestlé and Mars, all of which purchase cocoa beans via various sources. Chocolate can be made from T. cacao through a process of steps that involve harvesting, fermenting of T. cacao pulp, drying, harvesting, and then extraction. Roasting T. cacao
by using superheated steam was found to be better than conventional
roasting (use of ovens) because it resulted in same quality of cocoa
beans in a shorter amount of time.
| Cocoa bean production – 2018 | |
|---|---|
| Country | (tonnes) |
Production
In 2018, world production of cocoa beans was 5.3 million tons, led by Ivory Coast with 37% of the total. Other major producers were Ghana (18%) and Indonesia (11%).
Conservation
Cacao flowers
Theobroma cacao
The pests and diseases to which cacao is subject, along with climate
change, mean that new varieties will be needed to respond to these
challenges. Breeders rely on the genetic diversity conserved in field genebanks to create new varieties, because cacao has recalcitrant seeds that cannot be stored in a conventional genebank.
In an effort to improve the diversity available to breeders, and ensure
the future of the field genebanks, experts have drawn up A Global
Strategy for the Conservation and Use of Cacao Genetic Resources, as the
Foundation for a Sustainable Cocoa Economy.
The strategy has been adopted by the cacao producers and their clients,
and seeks to improve the characterization of cacao diversity, the
sustainability and diversity of the cacao collections, the usefulness of
the collections, and to ease access to better information about the
conserved material. Some natural areas of cacao diversity are protected
by various forms of conservation, for example national parks. However, a
recent study of genetic diversity and predicted climates suggests that many of those protected areas will no longer be suitable for cacao by 2050. It also identifies an area around Iquitos in Peru
that will remain suitable for cacao and that is home to considerable
genetic diversity, and recommends that this area be considered for
protection. Other projects, such as the International Cocoa Quarantine Centre, aim to combat cacao diseases and preserve genetic diversity.
Phytopathogens (parasitic organisms) cause much damage to Theobroma cacao
plantations around the world. Many of those phytopathogens, which
include many of the pests named below, were analyzed using mass
spectrometry and allow for guiding on the correct approaches to get rid
of the specific phytopathogens. This method was found to be quick,
reproducible, and accurate showing promising results in the future to
prevent damage to Theobroma cacao by various phytopathogens.
A specific type of bacteria Streptomyces camerooniansis was found to be beneficial for T. cacao by helping plant growth by accelerating seed germination of T. cacao,
inhibiting growth of various types of microorganisms (such as different
oomycetes, fungi, and bacteria), and preventing rotting by Phytophthora megakarya.
Pests
Various plant pests and diseases can cause serious problems for cacao production.
- Insects
- Cocoa mirids or capsids worldwide (but especially Sahlbergella singularis and Distantiella theobroma in West Africa and Helopeltis spp. in Southeast Asia)
- Conopomorpha cramerella (cocoa pod borer – in Southeast Asia)
- Fungi
- Moniliophthora roreri (frosty pod rot)
- Moniliophthora perniciosa (witches' broom)
- Ceratocystis cacaofunesta (mal de machete) or (Ceratocystis wilt)
- Verticillium dahliae
- Oncobasidium theobromae (vascular streak dieback)
- Oomycetes
- Phytophthora spp. (black pod) especially Phytophthora megakarya in West Africa
- Viruses
- Mistletoe
- Rats and other vertebrate pests (squirrels, woodpeckers, etc.)
Genome
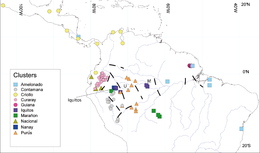
Map showing genetic clusters of Theobroma cacao
| |
| NCBI genome ID | 572 |
|---|---|
| Ploidy | diploid |
| Genome size | 345.99 Mb |
| Number of chromosomes | 10 pairs |
| Year of completion | 2010 |
The genome of T. cacao is diploid, its size is 430 Mbp, and it comprises 10 chromosome pairs (2n=2x=20). In September 2010, a team of scientists announced a draft sequence of the cacao genome (Matina1-6 genotype). In a second, unrelated project, the International Cocoa Genome Sequencing Consortium-ICGS, co-ordinated by CIRAD, first published
in December 2010 (online, paper publication in January 2011), the
sequence of the cacao genome, of the Criollo cacao (of a landrace from
Belize, B97-61/B2). In their publication, they reported a detailed
analysis of the genomic and genetic data.
The sequence of the cacao genome identified 28,798 protein-coding
genes, compared to the roughly 23,000 protein-coding genes of the human genome. About 20% of the cacao genome consists of transposable elements, a low proportion compared to other plant species. Many genes were identified as coding for flavonoids, aromatic terpenes, theobromine and many other metabolites involved in cocoa flavor and quality traits, among which a relatively high proportion code for polyphenols, which constitute up to 8% of cacao pods dry weight. The cacao genome appears close to the hypothetical hexaploid ancestor of all dicotyledonous plants,
and it is proposed as an evolutionary mechanism by which the 21
chromosomes of the dicots' hypothetical hexaploid ancestor underwent
major fusions leading to cacao's 10 chromosome pairs.
The genome sequence enables cacao molecular biology and breeding
for elite varieties through marker-assisted selection, in particular for
genetic resistance to fungal,
oomycete and viral diseases responsible for huge yield losses each
year. In 2017–18, due to concerns about survivability of cacao plants in
an era of global warming in which climates become more extreme in the narrow band of latitudes where cacao is grown (20 degrees north and south of the equator), the commercial company, Mars, Incorporated and the University of California, Berkeley are using CRISPR to adjust DNA for improved hardiness of cacao in hot climates.
History of cultivation
Cultivation, use, and cultural elaboration of cacao were early and extensive in Mesoamerica.
Ceramic vessels with residues from the preparation of cacao beverages
have been found at archaeological sites dating back to the Early Formative (1900–900 BC) period. For example, one such vessel found at an Olmec archaeological site on the Gulf Coast of Veracruz, Mexico dates cacao's preparation by pre-Olmec peoples as early as 1750 BC. On the Pacific coast of Chiapas, Mexico, a Mokaya archaeological site provides evidence of cacao beverages dating even earlier, to 1900 BC.
The initial domestication was probably related to the making of a fermented, thus alcoholic, beverage.
In 2018, researchers who analysed the genome of cultivated cacao trees
concluded that the domesticated cacao trees all originated from a single
domestication event that occurred about 3,600 years ago somewhere in
Central America.
Several mixtures of cacao are described in ancient texts, for
ceremonial or medicinal, as well as culinary, purposes. Some mixtures
included maize, chili, vanilla (Vanilla planifolia), and honey. Archaeological evidence for use of cacao, while relatively sparse, has come from the recovery of whole cacao beans at Uaxactun, Guatemala and from the preservation of wood fragments of the cacao tree at Belize sites including Cuello and Pulltrouser Swamp. In addition, analysis of residues from ceramic vessels has found traces of theobromine and caffeine in early formative vessels from Puerto Escondido, Honduras (1100–900 BC) and in middle formative vessels from Colha, Belize
(600–400 BC) using similar techniques to those used to extract
chocolate residues from four classic period (around 400 AD) vessels from
a tomb at the Maya archaeological site of Rio Azul. As cacao is the only known commodity from Mesoamerica containing both of these alkaloid compounds, it seems likely these vessels were used as containers for cacao drinks. In addition, cacao is named in a hieroglyphic
text on one of the Rio Azul vessels. Cacao is also believed to have
been ground by the Aztecs and mixed with tobacco for smoking purposes. Cocoa was being domesticated by the Mayo Chinchipe of the upper Amazon around 3,000 BC.
Modern history
Toasted cacao beans
The first European knowledge about chocolate came in the form of a
beverage which was first introduced to the Spanish at their meeting with
Moctezuma in the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan in 1519. Cortés
and others noted the vast quantities of this beverage the Aztec emperor
consumed, and how it was carefully whipped by his attendants
beforehand. Examples of cacao beans, along with other agricultural
products, were brought back to Spain at that time, but it seems the
beverage made from cacao was introduced to the Spanish court in 1544 by
Kekchi Maya nobles brought from the New World to Spain by Dominican friars to meet Prince Philip. Within a century, chocolate had spread to France, England and elsewhere in Western Europe. Demand for this beverage led the French to establish cacao plantations in the Caribbean, while Spain subsequently developed their cacao plantations in their Venezuelan and Philippine colonies (Bloom 1998, Coe 1996). A painting by Dutch Golden Age artist Albert Eckhout shows a wild cacao tree in mid-seventeenth century Dutch Brazil. The Nahuatl-derived Spanish word cacao entered scientific nomenclature in 1753 after the Swedish naturalist Linnaeus published his taxonomic binomial system and coined the genus and species Theobroma cacao. Traditional pre-Hispanic beverages made with cacao are still consumed in Mesoamerica. These include the Oaxacan beverage known as tejate.
Mythology
The Maya believed the kakaw (cacao) was discovered by the gods in a mountain that also contained other delectable foods to be used by them. According to Maya mythology, the Plumed Serpent gave cacao to the Maya after humans were created from maize by divine grandmother goddess Xmucane. The Maya celebrated an annual festival in April to honor their cacao god, Ek Chuah, an event that included the sacrifice of a dog
with cacao-colored markings, additional animal sacrifices, offerings of
cacao, feathers and incense, and an exchange of gifts. In a similar
creation story, the Mexica (Aztec) god Quetzalcoatl discovered cacao (cacahuatl: "bitter water"), in a mountain filled with other plant foods. Cacao was offered regularly to a pantheon of Mexica deities and the Madrid Codex
depicts priests lancing their ear lobes (autosacrifice) and covering
the cacao with blood as a suitable sacrifice to the gods. The cacao
beverage was used as a ritual only by men, as it was believed to be an intoxicating food unsuitable for women and children.




