| |
| General | |
|---|---|
| Symbol | 3He |
| Names | helium-3, He-3, tralphium (obsolete) |
| Protons | 2 |
| Neutrons | 1 |
| Nuclide data | |
| Natural abundance | 0.000137% (% He on Earth) 0.001% (% He in Solar System) |
| Half-life | stable |
| Parent isotopes | 3H (beta decay of tritium) |
| Isotope mass | 3.0160293 u |
| Spin | 1⁄2 |
| Isotopes of helium Complete table of nuclides | |
Helium-3 (3He see also helion) is a light, stable isotope of helium with two protons and one neutron (the most common isotope, helium-4, having two protons and two neutrons in contrast). Other than protium (ordinary hydrogen), helium-3 is the only stable isotope of any element with more protons than neutrons. Helium-3 was discovered in 1939.
Helium-3 occurs as a primordial nuclide, escaping from Earth's crust into its atmosphere and into outer space over millions of years. Helium-3 is also thought to be a natural nucleogenic and cosmogenic nuclide, one produced when lithium is bombarded by natural neutrons, which can be released by spontaneous fission and by nuclear reactions with cosmic rays. Some of the helium-3 found in the terrestrial atmosphere is also an artifact of atmospheric and underwater nuclear weapons testing.
Much speculation has been made over the possibility of helium-3 as a future energy source. Unlike most nuclear fission reactions, the fusion of helium-3 atoms releases large amounts of energy without causing the surrounding material to become radioactive. However, the temperatures required to achieve helium-3 fusion reactions are much higher than in traditional fusion reactions, and the process may unavoidably create other reactions that themselves would cause the surrounding material to become radioactive.
The abundance of helium-3 is thought to be greater on the Moon than on Earth, having been embedded in the upper layer of regolith by the solar wind over billions of years, though still lower in abundance than in the Solar System's gas giants.
History
The existence of helium-3 was first proposed in 1934 by the Australian nuclear physicist Mark Oliphant while he was working at the University of Cambridge Cavendish Laboratory. Oliphant had performed experiments in which fast deuterons collided with deuteron targets (incidentally, the first demonstration of nuclear fusion). Isolation of helium-3 was first accomplished by Luis Alvarez and Robert Cornog in 1939. Helium-3 was thought to be a radioactive isotope until it was also found in samples of natural helium, which is mostly helium-4, taken both from the terrestrial atmosphere and from natural gas wells.
Physical properties
Because of its low atomic mass of 3.02 atomic mass units, helium-3 has some physical properties different from those of helium-4, with a mass of 4.00 atomic mass units. Because of the weak, induced dipole–dipole interaction between the helium atoms, their microscopic physical properties are mainly determined by their zero-point energy. Also, the microscopic properties of helium-3 cause it to have a higher zero-point energy than helium-4. This implies that helium-3 can overcome dipole–dipole interactions with less thermal energy than helium-4 can.
The quantum mechanical effects on helium-3 and helium-4 are significantly different because with two protons, two neutrons, and two electrons, helium-4 has an overall spin of zero, making it a boson, but with one fewer neutron, helium-3 has an overall spin of one half, making it a fermion.
Helium-3 boils at 3.19 K compared with helium-4 at 4.23 K, and its critical point is also lower at 3.35 K, compared with helium-4 at 5.2 K. Helium-3 has less than half the density of helium-4 when it is at its boiling point: 59 g/L compared to 125 g/L of helium-4 at a pressure of one atmosphere. Its latent heat of vaporization is also considerably lower at 0.026 kJ/mol compared with the 0.0829 kJ/mol of helium-4.
Natural abundance
Terrestrial abundance
3He is a primordial substance in the Earth's mantle, considered to have become entrapped within the Earth during planetary formation. The ratio of 3He to 4He within the Earth's crust and mantle is less than that for assumptions of solar disk composition as obtained from meteorite and lunar samples, with terrestrial materials generally containing lower 3He/4He ratios due to ingrowth of 4He from radioactive decay.
3He has a cosmological ratio of 300 atoms per million atoms of 4He (at. ppm), leading to the assumption that the original ratio of these primordial gases in the mantle was around 200-300 ppm when Earth was formed. A lot of 4He was generated by alpha-particle decay of uranium and thorium, and now the mantle has only around 7% primordial helium, lowering the total 3He/4He ratio to around 20 ppm. Ratios of 3He/4He in excess of atmospheric are indicative of a contribution of 3He from the mantle. Crustal sources are dominated by the 4He which is produced by the decay of radioactive elements in the crust and mantle.
The ratio of helium-3 to helium-4 in natural Earth-bound sources varies greatly. Samples of the lithium ore spodumene from Edison Mine, South Dakota were found to contain 12 parts of helium-3 to a million parts of helium-4. Samples from other mines showed 2 parts per million.
Helium is also present as up to 7% of some natural gas sources, and large sources have over 0.5% (above 0.2% makes it viable to extract). The fraction of 3He in helium separated from natural gas in the U.S. was found to range from 70 to 242 parts per billion. Hence the US 2002 stockpile of 1 billion normal m3 would have contained about 12 to 43 kilograms of helium-3. According to American physicist Richard Garwin, about 26 m3 or almost 5 kg of 3He is available annually for separation from the US natural gas stream. If the process of separating out the 3He could employ as feedstock the liquefied helium typically used to transport and store bulk quantities, estimates for the incremental energy cost range from US$34 to $300 per liter NTP, excluding the cost of infrastructure and equipment. Algeria's annual gas production is assumed to contain 100 million normal cubic metres and this would contain between 7 and 24 m3 of helium-3 (about 1 to 4 kilograms) assuming a similar 3He fraction.
3He is also present in the Earth's atmosphere. The natural abundance of 3He in naturally occurring helium gas is 1.38×10−6 (1.38 parts per million). The partial pressure of helium in the Earth's atmosphere is about 0.52 Pa, and thus helium accounts for 5.2 parts per million of the total pressure (101325 Pa) in the Earth's atmosphere, and 3He thus accounts for 7.2 parts per trillion of the atmosphere. Since the atmosphere of the Earth has a mass of about 5.14×1015 tonnes, the mass of 3He in the Earth's atmosphere is the product of these numbers, or about 37,000 tonnes of 3He. (In fact the effective figure is ten times smaller, since the above ppm are ppmv and not ppmw. One must multiply by 3 (the molecular mass of Helium-3) and divide by 29 (the mean molecular mass of the atmosphere), resulting in 3,828 tonnes of helium-3 in the earth's atmosphere.)
3He is produced on Earth from three sources: lithium spallation, cosmic rays, and beta decay of tritium (3H). The contribution from cosmic rays is negligible within all except the oldest regolith materials, and lithium spallation reactions are a lesser contributor than the production of 4He by alpha particle emissions.
The total amount of helium-3 in the mantle may be in the range of 0.1–1 million tonnes. However, most of the mantle is not directly accessible. Some helium-3 leaks up through deep-sourced hotspot volcanoes such as those of the Hawaiian Islands, but only 300 grams per year is emitted to the atmosphere. Mid-ocean ridges emit another 3 kilograms per year. Around subduction zones, various sources produce helium-3 in natural gas deposits which possibly contain a thousand tonnes of helium-3 (although there may be 25 thousand tonnes if all ancient subduction zones have such deposits). Wittenberg estimated that United States crustal natural gas sources may have only half a tonne total. Wittenberg cited Anderson's estimate of another 1200 metric tonnes in interplanetary dust particles on the ocean floors. In the 1994 study, extracting helium-3 from these sources consumes more energy than fusion would release.
Lunar surface
Solar nebula (primordial) abundance
One early estimate of the primordial ratio of 3He to 4He in the solar nebula has been the measurement of their ratio in the atmosphere of Jupiter, measured by the mass spectrometer of the Galileo atmospheric entry probe. This ratio is about 1:10,000, or 100 parts of 3He per million parts of 4He. This is roughly the same ratio of the isotopes as in lunar regolith, which contains 28 ppm helium-4 and 2.8 ppb helium-3 (which is at the lower end of actual sample measurements, which vary from about 1.4 to 15 ppb). However, terrestrial ratios of the isotopes are lower by a factor of 100, mainly due to enrichment of helium-4 stocks in the mantle by billions of years of alpha decay from uranium and thorium.
Human production
Tritium decay
Virtually all helium-3 used in industry today is produced from the radioactive decay of tritium, given its very low natural abundance and its very high cost.
Production, sales and distribution of helium-3 in the United States are managed by the US Department of Energy (DOE) Isotope Program.
While tritium has several different experimentally determined values of its half-life, NIST lists 4,500 ± 8 days (12.32 ± 0.02 years). It decays into helium-3 by beta decay as in this nuclear equation:
Among the total released energy of 18.6 keV, the part taken by electron's kinetic energy varies, with an average of 5.7 keV, while the remaining energy is carried off by the nearly undetectable electron antineutrino. Beta particles from tritium can penetrate only about 6.0 mm of air, and they are incapable of passing through the dead outermost layer of human skin. The unusually low energy released in the tritium beta decay makes the decay (along with that of rhenium-187) appropriate for absolute neutrino mass measurements in the laboratory (the most recent experiment being KATRIN).
The low energy of tritium's radiation makes it difficult to detect tritium-labeled compounds except by using liquid scintillation counting.
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen and is typically produced by bombarding lithium-6 with neutrons in a nuclear reactor. The lithium nucleus absorbs a neutron and splits into helium-4 and tritium. Tritium decays into helium-3 with a half-life of 12.3 years, so helium-3 can be produced by simply storing the tritium until it undergoes radioactive decay.
Tritium is a critical component of nuclear weapons and historically it was produced and stockpiled primarily for this application. The decay of tritium into helium-3 reduces the explosive power of the fusion warhead, so periodically the accumulated helium-3 must be removed from warhead reservoirs and tritium in storage. Helium-3 removed during this process is marketed for other applications.
For decades this has been, and remains, the principal source of the world's helium-3. However, since the signing of the START I Treaty in 1991 the number of nuclear warheads that are kept ready for use has decreased This has reduced the quantity of helium-3 available from this source. Helium-3 stockpiles have been further diminished by increased demand, primarily for use in neutron radiation detectors and medical diagnostic procedures. US industrial demand for helium-3 reached a peak of 70,000 liters (approximately 8 kg) per year in 2008. Price at auction, historically about $100/liter, reached as high as $2000/liter. Since then, demand for helium-3 has declined to about 6000 liters per year due to the high cost and efforts by the DOE to recycle it and find substitutes.
The DOE recognized the developing shortage of both tritium and helium-3, and began producing tritium by lithium irradiation at the Tennessee Valley Authority's Watts Bar Nuclear Generating Station in 2010. In this process tritium-producing burnable absorber rods (TPBARs) containing lithium in a ceramic form are inserted into the reactor in place of the normal boron control rods Periodically the TPBARs are replaced and the tritium extracted.
Currently only one reactor is used for tritium production but the process could, if necessary, be vastly scaled up to meet any conceivable demand simply by utilizing more of the nation's power reactors. Substantial quantities of tritium and helium-3 could also be extracted from the heavy water moderator in CANDU nuclear reactors.
Uses
Neutron detection
Helium-3 is an important isotope in instrumentation for neutron detection. It has a high absorption cross section for thermal neutron beams and is used as a converter gas in neutron detectors. The neutron is converted through the nuclear reaction
- n + 3He → 3H + 1H + 0.764 MeV
into charged particles tritium ions (T, 3H) and Hydrogen ions, or protons (p, 1H) which then are detected by creating a charge cloud in the stopping gas of a proportional counter or a Geiger–Müller tube.
Furthermore, the absorption process is strongly spin-dependent, which allows a spin-polarized helium-3 volume to transmit neutrons with one spin component while absorbing the other. This effect is employed in neutron polarization analysis, a technique which probes for magnetic properties of matter.
The United States Department of Homeland Security had hoped to deploy detectors to spot smuggled plutonium in shipping containers by their neutron emissions, but the worldwide shortage of helium-3 following the drawdown in nuclear weapons production since the Cold War has to some extent prevented this. As of 2012, DHS determined the commercial supply of boron-10 would support converting its neutron detection infrastructure to that technology.
Cryogenics
A helium-3 refrigerator uses helium-3 to achieve temperatures of 0.2 to 0.3 kelvin. A dilution refrigerator uses a mixture of helium-3 and helium-4 to reach cryogenic temperatures as low as a few thousandths of a kelvin.
An important property of helium-3, which distinguishes it from the more common helium-4, is that its nucleus is a fermion since it contains an odd number of spin 1⁄2 particles. Helium-4 nuclei are bosons, containing an even number of spin 1⁄2 particles. This is a direct result of the addition rules for quantized angular momentum. At low temperatures (about 2.17 K), helium-4 undergoes a phase transition: A fraction of it enters a superfluid phase that can be roughly understood as a type of Bose–Einstein condensate. Such a mechanism is not available for helium-3 atoms, which are fermions. However, it was widely speculated that helium-3 could also become a superfluid at much lower temperatures, if the atoms formed into pairs analogous to Cooper pairs in the BCS theory of superconductivity. Each Cooper pair, having integer spin, can be thought of as a boson. During the 1970s, David Lee, Douglas Osheroff and Robert Coleman Richardson discovered two phase transitions along the melting curve, which were soon realized to be the two superfluid phases of helium-3. The transition to a superfluid occurs at 2.491 millikelvins on the melting curve. They were awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery. Alexei Abrikosov, Vitaly Ginzburg, and Tony Leggett won the 2003 Nobel Prize in Physics for their work on refining understanding of the superfluid phase of helium-3.
In a zero magnetic field, there are two distinct superfluid phases of 3He, the A-phase and the B-phase. The B-phase is the low-temperature, low-pressure phase which has an isotropic energy gap. The A-phase is the higher temperature, higher pressure phase that is further stabilized by a magnetic field and has two point nodes in its gap. The presence of two phases is a clear indication that 3He is an unconventional superfluid (superconductor), since the presence of two phases requires an additional symmetry, other than gauge symmetry, to be broken. In fact, it is a p-wave superfluid, with spin one, S=1, and angular momentum one, L=1. The ground state corresponds to total angular momentum zero, J=S+L=0 (vector addition). Excited states are possible with non-zero total angular momentum, J>0, which are excited pair collective modes. Because of the extreme purity of superfluid 3He (since all materials except 4He have solidified and sunk to the bottom of the liquid 3He and any 4He has phase separated entirely, this is the most pure condensed matter state), these collective modes have been studied with much greater precision than in any other unconventional pairing system.
Medical imaging
Helium-3 nuclei have an intrinsic nuclear spin of 1⁄2, and a relatively high magnetogyric ratio. Helium-3 can be hyperpolarized using non-equilibrium means such as spin-exchange optical pumping. During this process, circularly polarized infrared laser light, tuned to the appropriate wavelength, is used to excite electrons in an alkali metal, such as caesium or rubidium inside a sealed glass vessel. The angular momentum is transferred from the alkali metal electrons to the noble gas nuclei through collisions. In essence, this process effectively aligns the nuclear spins with the magnetic field in order to enhance the NMR signal. The hyperpolarized gas may then be stored at pressures of 10 atm, for up to 100 hours. Following inhalation, gas mixtures containing the hyperpolarized helium-3 gas can be imaged with an MRI scanner to produce anatomical and functional images of lung ventilation. This technique is also able to produce images of the airway tree, locate unventilated defects, measure the alveolar oxygen partial pressure, and measure the ventilation/perfusion ratio. This technique may be critical for the diagnosis and treatment management of chronic respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, cystic fibrosis, and asthma.
Radio energy absorber for tokamak plasma experiments
Both MIT's Alcator C-Mod tokamak and the Joint European Torus (JET) have experimented with adding a little He-3 to a H-D plasma to increase the absorption of radio-frequency (RF) energy to heat the H & D ions, a "three-ion" effect.
Nuclear fuel
| Reactants |
|
Products | Q | n/MeV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-generation fusion fuels | ||||
| 2D + 2D | → | 3He + 1 0n |
3.268 MeV | 0.306 |
| 2D + 2D | → | 3T + 1 1p |
4.032 MeV | 0 |
| 2D + 3T | → | 4He + 1 0n |
17.571 MeV | 0.057 |
| Second-generation fusion fuel | ||||
| 2D + 3He | → | 4He + 1 1p |
18.354 MeV | 0 |
| Third-generation fusion fuels | ||||
| 3He + 3He | → | 4He+ 21 1p |
12.86 MeV | 0 |
| 11B + 1 1p |
→ | 3 4He | 8.68 MeV | 0 |
| Net result of D burning (sum of first 4 rows) | ||||
| 6 D | → | 2(4He + n + p) | 43.225 MeV | 0.046 |
| Current nuclear fuel | ||||
| 235U + n | → | 2 FP+ 2.5n | ~200 MeV | 0.0075 |
3He can be produced by the low temperature fusion of → 3He + γ + 4.98 MeV. If the fusion temperature is below that for the helium nuclei to fuse, the reaction produces a high energy alpha particle which quickly acquires an electron producing a stable light helium ion which can be utilized directly as a source of electricity without producing dangerous neutrons.
3He can be used in fusion reactions by either of the reactions 2H + 3He → 4He + 1p + 18.3 MeV, or 3He + 3He → 4He + 2 1p+ 12.86 MeV.
The conventional deuterium + tritium ("D-T") fusion process produces energetic neutrons which render reactor components radioactive with activation products. The appeal of helium-3 fusion stems from the aneutronic nature of its reaction products. Helium-3 itself is non-radioactive. The lone high-energy by-product, the proton, can be contained using electric and magnetic fields. The momentum energy of this proton (created in the fusion process) will interact with the containing electromagnetic field, resulting in direct net electricity generation.
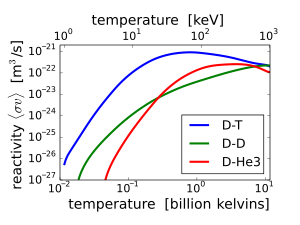
Because of the higher Coulomb barrier, the temperatures required for 2H + 3He fusion are much higher than those of conventional D-T fusion. Moreover, since both reactants need to be mixed together to fuse, reactions between nuclei of the same reactant will occur, and the D-D reaction (2H + 2H) does produce a neutron. Reaction rates vary with temperature, but the D-3He reaction rate is never greater than 3.56 times the D-D reaction rate (see graph). Therefore, fusion using D-3He fuel at the right temperature and a D-lean fuel mixture, can produce a much lower neutron flux than D-T fusion, but is not clean, negating some of its main attraction.
The second possibility, fusing 3He with itself (3He + 3He), requires even higher temperatures (since now both reactants have a +2 charge), and thus is even more difficult than the D-3He reaction. However, it does offer a possible reaction that produces no neutrons; the charged protons produced can be contained using electric and magnetic fields, which in turn results in direct electricity generation. 3He + 3He fusion is feasible as demonstrated in the laboratory and has immense advantages, but commercial viability is many years in the future.
The amounts of helium-3 needed as a replacement for conventional fuels are substantial by comparison to amounts currently available. The total amount of energy produced in the 2D + 3He reaction is 18.4 MeV, which corresponds to some 493 megawatt-hours (4.93×108 W·h) per three grams (one mole) of 3He If the total amount of energy could be converted to electrical power with 100% efficiency (a physical impossibility), it would correspond to about 30 minutes of output of a gigawatt electrical plant per mole of 3He. Thus, a year's production (at 6 grams for each operation hour) would require 52.5 kilograms of helium-3. The amount of fuel needed for large-scale applications can also be put in terms of total consumption: electricity consumption by 107 million U.S. households in 2001totaled 1,140 billion kW·h (1.14×1015 W·h). Again assuming 100% conversion efficiency, 6.7 tonnes per year of helium-3 would be required for that segment of the energy demand of the United States, 15 to 20 tonnes per year given a more realistic end-to-end conversion efficiency.
A second-generation approach to controlled fusion power involves combining helium-3 and deuterium (2D). This reaction produces a helium-4 ion (4He) (like an alpha particle, but of different origin) and a high-energy proton (positively charged hydrogen ion). The most important potential advantage of this fusion reaction for power production as well as other applications lies in its compatibility with the use of electrostatic fields to control fuel ions and the fusion protons. High speed protons, as positively charged particles, can have their kinetic energy converted directly into electricity, through use of solid-state conversion materials as well as other techniques. Potential conversion efficiencies of 70% may be possible, as there is no need to convert proton energy to heat in order to drive a turbine-powered electrical generator.
There have been many claims about the capabilities of helium-3 power plants. According to proponents, fusion power plants operating on deuterium and helium-3 would offer lower capital and operating costs than their competitors due to less technical complexity, higher conversion efficiency, smaller size, the absence of radioactive fuel, no air or water pollution, and only low-level radioactive waste disposal requirements. Recent estimates suggest that about $6 billion in investment capital will be required to develop and construct the first helium-3 fusion power plant. Financial break even at today's wholesale electricity prices (5 US cents per kilowatt-hour) would occur after five 1-gigawatt plants were on line, replacing old conventional plants or meeting new demand.
The reality is not so clear-cut. The most advanced fusion programs in the world are inertial confinement fusion (such as National Ignition Facility) and magnetic confinement fusion (such as ITER and Wendelstein 7-X). In the case of the former, there is no solid roadmap to power generation. In the case of the latter, commercial power generation is not expected until around 2050. In both cases, the type of fusion discussed is the simplest: D-T fusion. The reason for this is the very low Coulomb barrier for this reaction; for D+3He, the barrier is much higher, and it is even higher for 3He–3He. The immense cost of reactors like ITER and National Ignition Facility are largely due to their immense size, yet to scale up to higher plasma temperatures would require reactors far larger still. The 14.7 MeV proton and 3.6 MeV alpha particle from D–3He fusion, plus the higher conversion efficiency, means that more electricity is obtained per kilogram than with D-T fusion (17.6 MeV), but not that much more. As a further downside, the rates of reaction for helium-3 fusion reactions are not particularly high, requiring a reactor that is larger still or more reactors to produce the same amount of electricity.
To attempt to work around this problem of massively large power plants that may not even be economical with D-T fusion, let alone the far more challenging D–3He fusion, a number of other reactors have been proposed – the Fusor, Polywell, Focus fusion, and many more, though many of these concepts have fundamental problems with achieving a net energy gain, and generally attempt to achieve fusion in thermal disequilibrium, something that could potentially prove impossible, and consequently, these long-shot programs tend to have trouble garnering funding despite their low budgets. Unlike the "big", "hot" fusion systems, however, if such systems were to work, they could scale to the higher barrier "aneutronic" fuels, and therefore their proponents tend to promote p-B fusion, which requires no exotic fuels such as helium-3.
Extraterrestrial mining
Lunar surface
Materials on the Moon's surface contain helium-3 at concentrations between 1.4 and 15 ppb in sunlit areas, and may contain concentrations as much as 50 ppb in permanently shadowed regions. A number of people, starting with Gerald Kulcinski in 1986, have proposed to explore the Moon, mine lunar regolith and use the helium-3 for fusion. Because of the low concentrations of helium-3, any mining equipment would need to process extremely large amounts of regolith (over 150 tonnes of regolith to obtain one gram of helium-3), and some proposals have suggested that helium-3 extraction be piggybacked onto a larger mining and development operation.
The primary objective of Indian Space Research Organisation's first lunar probe called Chandrayaan-1, launched on October 22, 2008, was reported in some sources to be mapping the Moon's surface for helium-3-containing minerals. However, no such objective is mentioned in the project's official list of goals, although many of its scientific payloads have noted helium-3-related applications.
Cosmochemist and geochemist Ouyang Ziyuan from the Chinese Academy of Sciences who is now in charge of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program has already stated on many occasions that one of the main goals of the program would be the mining of helium-3, from which operation "each year, three space shuttle missions could bring enough fuel for all human beings across the world."
In January 2006, the Russian space company RKK Energiya announced that it considers lunar helium-3 a potential economic resource to be mined by 2020, if funding can be found.
Not all writers feel the extraction of lunar helium-3 is feasible, or even that there will be a demand for it for fusion. Dwayne Day, writing in The Space Review in 2015, characterises helium-3 extraction from the moon for use in fusion, as magical/religious thinking, and questions the feasibility of lunar extraction when compared to production on Earth.