| Human eye | |
|---|---|
 The human eye of the right side of the face, showing a white sclera with some blood vessels, a green iris, and the black pupil. | |
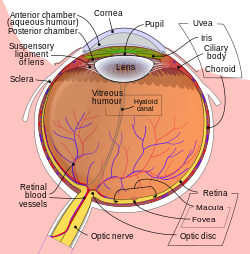
 1. vitreous body 2. ora serrata 3. ciliary muscle 4. ciliary zonules 5. Schlemm's canal 6. pupil 7. anterior chamber 8. cornea 9. iris 10. lens cortex 11. lens nucleus 12. ciliary process 13. conjunctiva 14. inferior oblique muscle 15. inferior rectus muscle 16. medial rectus muscle 17. retinal arteries and veins 18. optic disc 19. dura mater 20. central retinal artery 21. central retinal vein 22. optic nerve 23. vorticose vein 24. bulbar sheath 25. macula 26. fovea 27. sclera 28. choroid 29. superior rectus muscle 30. retina | |
| Details | |
| System | Visual system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Oculi Hominum |
| Greek | ἀνθρώπινος ὀφθαλμός |
| MeSH | D005123 |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.007 A15.2.00.001 |
| TA2 | 113, 6734 |
| FMA | 54448 |
The human eye is a sense organ that reacts to light and allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina are photoreceptive cells which are able to detect visible light and convey this information to the brain. Eyes signal information which is used by the brain to elicit the perception of colour, shape, depth, movement, and other features. The eye is part of the sensory nervous system.
Similar to the eyes of other mammals, the human eye's non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion cells in the retina receive light signals which affect adjustment of the size of the pupil, regulation and suppression of the hormone melatonin, and entrainment of the circadian rhythm.
Structure
Humans have two eyes, situated on the left and the right of the face. The eyes sit in bony cavities called the orbits, in the skull. There are six extraocular muscles that control eye movements. The front visible part of the eye is made up of the whitish sclera, a coloured iris, and the pupil. A thin layer called the conjunctiva sits on top of this. The front part is also called the anterior segment of the eye.
The eye is not shaped like a perfect sphere, rather it is a fused two-piece unit, composed of an anterior (front) segment and the posterior (back) segment. The anterior segment is made up of the cornea, iris and lens. The cornea is transparent and more curved, and is linked to the larger posterior segment, composed of the vitreous, retina, choroid and the outer white shell called the sclera. The cornea is typically about 11.5 mm (0.45 in) in diameter, and 0.5 mm (500 μm) in thickness near its center. The posterior chamber constitutes the remaining five-sixths; its diameter is typically about 24 mm (0.94 in). The cornea and sclera are connected by an area termed the limbus. The iris is the pigmented circular structure concentrically surrounding the center of the eye, the pupil, which appears to be black. The size of the pupil, which controls the amount of light entering the eye, is adjusted by the iris' dilator and sphincter muscles.
Light energy enters the eye through the cornea, through the pupil and then through the lens. The lens shape is changed for near focus (accommodation) and is controlled by the ciliary muscle. Photons of light falling on the light-sensitive cells of the retina (photoreceptor cones and rods) are converted into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain by the optic nerve and interpreted as sight and vision.
Size
The size of the eye differs among adults by only one or two millimetres. The eyeball is generally less tall than it is wide. The sagittal vertical (height) of a human adult eye is approximately 23.7 mm (0.93 in), the transverse horizontal diameter (width) is 24.2 mm (0.95 in) and the axial anteroposterior size (depth) averages 22.0–24.8 mm (0.87–0.98 in) with no significant difference between sexes and age groups. Strong correlation has been found between the transverse diameter and the width of the orbit (r = 0.88). The typical adult eye has an anterior to posterior diameter of 24 mm (0.94 in), and a volume of 6 cubic centimetres (0.37 cu in).
The eyeball grows rapidly, increasing from about 16–17 mm (0.63–0.67 in) diameter at birth to 22.5–23 mm (0.89–0.91 in) by three years of age. By age 12, the eye attains its full size.
Components
The eye is made up of three coats, or layers, enclosing various anatomical structures. The outermost layer, known as the fibrous tunic, is composed of the cornea and sclera, which provide shape to the eye and support the deeper structures. The middle layer, known as the vascular tunic or uvea, consists of the choroid, ciliary body, pigmented epithelium and iris. The innermost is the retina, which gets its oxygenation from the blood vessels of the choroid (posteriorly) as well as the retinal vessels (anteriorly).
The spaces of the eye are filled with the aqueous humour anteriorly, between the cornea and lens, and the vitreous body, a jelly-like substance, behind the lens, filling the entire posterior cavity. The aqueous humour is a clear watery fluid that is contained in two areas: the anterior chamber between the cornea and the iris, and the posterior chamber between the iris and the lens. The lens is suspended to the ciliary body by the suspensory ligament (Zonule of Zinn), made up of hundreds of fine transparent fibers which transmit muscular forces to change the shape of the lens for accommodation (focusing). The vitreous body is a clear substance composed of water and proteins, which give it a jelly-like and sticky composition.
Structures surrounding the eye
Extraocular muscles
Each eye has six muscles that control its movements: the lateral rectus, the medial rectus, the inferior rectus, the superior rectus, the inferior oblique, and the superior oblique. When the muscles exert different tensions, a torque is exerted on the globe that causes it to turn, in almost pure rotation, with only about one millimeter of translation. Thus, the eye can be considered as undergoing rotations about a single point in the center of the eye.
Normal anatomy of the human eye and orbit, anterior view
Vision
Field of view
The approximate field of view of an individual human eye (measured from the fixation point, i.e., the point at which one's gaze is directed) varies by facial anatomy, but is typically 30° superior (up, limited by the brow), 45° nasal (limited by the nose), 70° inferior (down), and 100° temporal (towards the temple). For both eyes combined (Binocular vision) visual field is approximately 100° vertical and a maximum 190° horizontal, approximately 120° of which makes up the binocular field of view (seen by both eyes) flanked by two uniocular fields (seen by only one eye) of approximately 40 degrees. It is an area of 4.17 steradians or 13700 square degrees for binocular vision. When viewed at large angles from the side, the iris and pupil may still be visible by the viewer, indicating the person has peripheral vision possible at that angle.
About 15° temporal and 1.5° below the horizontal is the blind spot created by the optic nerve nasally, which is roughly 7.5° high and 5.5° wide.
Dynamic range
The retina has a static contrast ratio of around 100:1 (about 6.5 f-stops). As soon as the eye moves rapidly to acquire a target (saccades), it re-adjusts its exposure by adjusting the iris, which adjusts the size of the pupil. Initial dark adaptation takes place in approximately four seconds of profound, uninterrupted darkness; full adaptation through adjustments in retinal rod photoreceptors is 80% complete in thirty minutes. The process is nonlinear and multifaceted, so an interruption by light exposure requires restarting the dark adaptation process over again.
The human eye can detect a luminance range of 1014, or one hundred trillion (100,000,000,000,000) (about 46.5 f-stops), from 10−6 cd/m2, or one millionth (0.000001) of a candela per square meter to 108 cd/m2 or one hundred million (100,000,000) candelas per square meter. This range does not include looking at the midday sun (109 cd/m2) or lightning discharge.
At the low end of the range is the absolute threshold of vision for a steady light across a wide field of view, about 10−6 cd/m2 (0.000001 candela per square meter). The upper end of the range is given in terms of normal visual performance as 108 cd/m2 (100,000,000 or one hundred million candelas per square meter).
The eye includes a lens similar to lenses found in optical instruments such as cameras and the same physics principles can be applied. The pupil of the human eye is its aperture; the iris is the diaphragm that serves as the aperture stop. Refraction in the cornea causes the effective aperture (the entrance pupil) to differ slightly from the physical pupil diameter. The entrance pupil is typically about 4 mm in diameter, although it can range from 2 mm (f/8.3) in a brightly lit place to 8 mm (f/2.1) in the dark. The latter value decreases slowly with age; older people's eyes sometimes dilate to not more than 5–6mm in the dark, and may be as small as 1mm in the light.
Eye movement
The visual system in the human brain is too slow to process information if images are slipping across the retina at more than a few degrees per second. Thus, to be able to see while moving, the brain must compensate for the motion of the head by turning the eyes. Frontal-eyed animals have a small area of the retina with very high visual acuity, the fovea centralis. It covers about 2 degrees of visual angle in people. To get a clear view of the world, the brain must turn the eyes so that the image of the object of regard falls on the fovea. Any failure to make eye movements correctly can lead to serious visual degradation.
Having two eyes allows the brain to determine the depth and distance of an object, called stereovision, and gives the sense of three-dimensionality to the vision. Both eyes must point accurately enough that the object of regard falls on corresponding points of the two retinas to stimulate stereovision; otherwise, double vision might occur. Some persons with congenitally crossed eyes tend to ignore one eye's vision, thus do not suffer double vision, and do not have stereovision. The movements of the eye are controlled by six muscles attached to each eye, and allow the eye to elevate, depress, converge, diverge and roll. These muscles are both controlled voluntarily and involuntarily to track objects and correct for simultaneous head movements.
Rapid eye movement
Rapid eye movement, REM, typically refers to the sleep stage during which the most vivid dreams occur. During this stage, the eyes move rapidly.
Saccades
Saccades are quick, simultaneous movements of both eyes in the same direction controlled by the frontal lobe of the brain.
Fixational Eye Movements
Even when looking intently at a single spot, the eyes drift around. This ensures that individual photosensitive cells are continually stimulated in different degrees. Without changing input, these cells would otherwise stop generating output.
Eye movements include drift, ocular tremor, and microsaccades. Some irregular drifts, movements smaller than a saccade and larger than a microsaccade, subtend up to one tenth of a degree. Researchers vary in their definition of microsaccades by amplitude. Martin Rolfs states that 'the majority of microsaccades observed in a variety of tasks have amplitudes smaller than 30 min-arc'. However, others state that the "current consensus has largely consolidated around a definition of microsaccades that includes magnitudes up to 1°."
Vestibulo-ocular reflexes
The vestibulo-ocular reflex is a reflex eye movement that stabilizes images on the retina during head movement by producing an eye movement in the direction opposite to head movement in response to neural input from the vestibular system of the inner ear, thus maintaining the image in the center of the visual field. For example, when the head moves to the right, the eyes move to the left. This applies for head movements up and down, left and right, and tilt to the right and left, all of which give input to the ocular muscles to maintain visual stability.
Smooth pursuit movement
Eyes can also follow a moving object around. This tracking is less accurate than the vestibulo-ocular reflex, as it requires the brain to process incoming visual information and supply feedback. Following an object moving at constant speed is relatively easy, though the eyes will often make saccades to keep up. The smooth pursuit movement can move the eye at up to 100°/s in adult humans.
It is more difficult to visually estimate speed in low light conditions or while moving, unless there is another point of reference for determining speed.
Optokinetic reflex
The Optokinetic reflex (or optokinetic nystagmus) stabilizes the image on the retina through visual feedback. It is induced when the entire visual scene drifts across the retina, eliciting eye rotation in the same direction and at a velocity that minimizes the motion of the image on the retina. When the gaze direction deviates too far from the forward heading, a compensatory saccade is induced to reset the gaze to the centre of the visual field.
For example, when looking out of the window at a moving train, the eyes can focus on a moving train for a short moment (by stabilizing it on the retina), until the train moves out of the field of vision. At this point, the eye is moved back to the point where it first saw the train (through a saccade).
Near response
The adjustment to close-range vision involves three processes to focus an image on the retina.
Vergence movement
When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the projection of the image is in the centre of the retina in both eyes. To look at a nearby object, the eyes rotate 'towards each other' (convergence), while for an object farther away they rotate 'away from each other' (divergence).
Pupil constriction
Lenses cannot refract light rays at their edges as well as closer to the center. The image produced by any lens is therefore somewhat blurry around the edges (spherical aberration). It can be minimized by screening out peripheral light rays and looking only at the better-focused center. In the eye, the pupil serves this purpose by constricting while the eye is focused on nearby objects. Small apertures also give an increase in depth of field, allowing a broader range of "in focus" vision. In this way the pupil has a dual purpose for near vision: to reduce spherical aberration and increase depth of field.
Accommodation of the lens
Changing the curvature of the lens is carried out by the ciliary muscles surrounding the lens; this process is known as "accommodation". Accommodation narrows the inner diameter of the ciliary body, which actually relaxes the fibers of the suspensory ligament attached to the periphery of the lens, and also allows the lens to relax into a more convex, or globular, shape. A more convex lens refracts light more strongly and focuses divergent light rays from near objects onto the retina, allowing closer objects to be brought into better focus.
Clinical significance
Eye care professionals
The human eye contains enough complexity to warrant specialized attention and care beyond the duties of a general practitioner. These specialists, or eye care professionals, serve different functions in different countries. Eye care professionals can have overlap in their patient care privileges. For example, both an ophthalmologist (M.D.) and optometrist (O.D.) are professionals who diagnoses eye disease and can prescribe lenses to correct vision. However, typically only ophthalmologists are licensed to perform surgical procedures. Ophthalmologists may also specialize within a surgical area, such as cornea, cataracts, laser, retina, or oculoplastics.
Eye care professionals include:
Eye irritation
Eye irritation has been defined as "the magnitude of any stinging, scratching, burning, or other irritating sensation from the eye". It is a common problem experienced by people of all ages. Related eye symptoms and signs of irritation are discomfort, dryness, excess tearing, itching, grating, foreign body sensation, ocular fatigue, pain, scratchiness, soreness, redness, swollen eyelids, and tiredness, etc. These eye symptoms are reported with intensities from mild to severe. It has been suggested that these eye symptoms are related to different causal mechanisms, and symptoms are related to the particular ocular anatomy involved.
Several suspected causal factors in our environment have been studied so far. One hypothesis is that indoor air pollution may cause eye and airway irritation. Eye irritation depends somewhat on destabilization of the outer-eye tear film, i.e. the formation of dry spots on the cornea, resulting in ocular discomfort. Occupational factors are also likely to influence the perception of eye irritation. Some of these are lighting (glare and poor contrast), gaze position, reduced blink rate, limited number of breaks from visual tasking, and a constant combination of accommodation, musculoskeletal burden, and impairment of the visual nervous system. Another factor that may be related is work stress. In addition, psychological factors have been found in multivariate analyses to be associated with an increase in eye irritation among VDU users. Other risk factors, such as chemical toxins/irritants (e.g. amines, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acrolein, N-decane, VOCs, ozone, pesticides and preservatives, allergens, etc.) might cause eye irritation as well.
Certain volatile organic compounds that are both chemically reactive and airway irritants may cause eye irritation. Personal factors (e.g. use of contact lenses, eye make-up, and certain medications) may also affect destabilization of the tear film and possibly result in more eye symptoms. Nevertheless, if airborne particles alone should destabilize the tear film and cause eye irritation, their content of surface-active compounds must be high. An integrated physiological risk model with blink frequency, destabilization, and break-up of the eye tear film as inseparable phenomena may explain eye irritation among office workers in terms of occupational, climate, and eye-related physiological risk factors.
There are two major measures of eye irritation. One is blink frequency which can be observed by human behavior. The other measures are break up time, tear flow, hyperemia (redness, swelling), tear fluid cytology, and epithelial damage (vital stains) etc., which are human beings' physiological reactions. Blink frequency is defined as the number of blinks per minute and it is associated with eye irritation. Blink frequencies are individual with mean frequencies of < 2–3 to 20–30 blinks/minute, and they depend on environmental factors including the use of contact lenses. Dehydration, mental activities, work conditions, room temperature, relative humidity, and illumination all influence blink frequency. Break-up time (BUT) is another major measure of eye irritation and tear film stability. It is defined as the time interval (in seconds) between blinking and rupture. BUT is considered to reflect the stability of the tear film as well. In normal persons, the break-up time exceeds the interval between blinks, and, therefore, the tear film is maintained. Studies have shown that blink frequency is correlated negatively with break-up time. This phenomenon indicates that perceived eye irritation is associated with an increase in blink frequency since the cornea and conjunctiva both have sensitive nerve endings that belong to the first trigeminal branch. Other evaluating methods, such as hyperemia, cytology etc. have increasingly been used to assess eye irritation.
There are other factors that are related to eye irritation as well. Three major factors that influence the most are indoor air pollution, contact lenses and gender differences. Field studies have found that the prevalence of objective eye signs is often significantly altered among office workers in comparisons with random samples of the general population. These research results might indicate that indoor air pollution has played an important role in causing eye irritation. There are more and more people wearing contact lens now and dry eyes appear to be the most common complaint among contact lens wearers. Although both contact lens wearers and spectacle wearers experience similar eye irritation symptoms, dryness, redness, and grittiness have been reported far more frequently among contact lens wearers and with greater severity than among spectacle wearers. Studies have shown that incidence of dry eyes increases with age, especially among women. Tear film stability (e.g. tear break-up time) is significantly lower among women than among men. In addition, women have a higher blink frequency while reading. Several factors may contribute to gender differences. One is the use of eye make-up. Another reason could be that the women in the reported studies have done more VDU work than the men, including lower grade work. A third often-quoted explanation is related to the age-dependent decrease of tear secretion, particularly among women after 40 years of age.
In a study conducted by UCLA, the frequency of reported symptoms in industrial buildings was investigated. The study's results were that eye irritation was the most frequent symptom in industrial building spaces, at 81%. Modern office work with use of office equipment has raised concerns about possible adverse health effects. Since the 1970s, reports have linked mucosal, skin, and general symptoms to work with self-copying paper. Emission of various particulate and volatile substances has been suggested as specific causes. These symptoms have been related to sick building syndrome (SBS), which involves symptoms such as irritation to the eyes, skin, and upper airways, headache and fatigue.
Many of the symptoms described in SBS and multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) resemble the symptoms known to be elicited by airborne irritant chemicals. A repeated measurement design was employed in the study of acute symptoms of eye and respiratory tract irritation resulting from occupational exposure to sodium borate dusts. The symptom assessment of the 79 exposed and 27 unexposed subjects comprised interviews before the shift began and then at regular hourly intervals for the next six hours of the shift, four days in a row. Exposures were monitored concurrently with a personal real time aerosol monitor. Two different exposure profiles, a daily average and short term (15 minute) average, were used in the analysis. Exposure-response relations were evaluated by linking incidence rates for each symptom with categories of exposure.
Acute incidence rates for nasal, eye, and throat irritation, and coughing and breathlessness were found to be associated with increased exposure levels of both exposure indices. Steeper exposure-response slopes were seen when short term exposure concentrations were used. Results from multivariate logistic regression analysis suggest that current smokers tended to be less sensitive to the exposure to airborne sodium borate dust.
Several actions can be taken to prevent eye irritation—
- trying to maintain normal blinking by avoiding room temperatures that are too high; avoiding relative humidities that are too high or too low, because they reduce blink frequency or may increase water evaporation.
- trying to maintain an intact film of tears by the following actions:
- Blinking and short breaks may be beneficial for VDU users. Increasing these two actions might help maintain the tear film.
- Downward gazing is recommended to reduce ocular surface area and water evaporation.
- The distance between the VDU and keyboard should be kept as short as possible to minimize evaporation from the ocular surface area by a low direction of the gaze, and
- Blink training can be beneficial.
In addition, other measures are proper lid hygiene, avoidance of eye rubbing, and proper use of personal products and medication. Eye make-up should be used with care.
Eye disease
1. Lens, 2. Zonule of Zinn or Ciliary zonule, 3. Posterior chamber and 4. Anterior chamber with 5. Aqueous humour flow; 6. Pupil, 7. Corneosclera or Fibrous tunic with 8. Cornea, 9. Trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal. 10. Corneal limbus and 11. Sclera; 12. Conjunctiva, 13. Uvea with 14. Iris, 15. Ciliary body (with a: pars plicata and b: pars plana) and 16. Choroid); 17. Ora serrata, 18. Vitreous humor with 19. Hyaloid canal/(old artery), 20. Retina with 21. Macula or macula lutea, 22. Fovea and 23. Optic disc → blind spot; 24. Optical axis of the eye. 25. Axis of eye, 26. Optic nerve with 27. Dural sheath, 28. Tenon's capsule or bulbar sheath, 29. Tendon.
30. Anterior segment, 31. Posterior segment.
32. Ophthalmic artery, 33. Artery and central retinal vein → 36. Blood vessels of the retina; Ciliary arteries (34. Short posterior ones, 35. Long posterior ones and 37. Anterior ones), 38. Lacrimal artery, 39. Ophthalmic vein, 40. Vorticose vein.
41. Ethmoid bone, 42. Medial rectus muscle, 43. Lateral rectus muscle, 44. Sphenoid bone.
There are many diseases, disorders, and age-related changes that may affect the eyes and surrounding structures.
As the eye ages, certain changes occur that can be attributed solely to the aging process. Most of these anatomic and physiologic processes follow a gradual decline. With aging, the quality of vision worsens due to reasons independent of diseases of the aging eye. While there are many changes of significance in the non-diseased eye, the most functionally important changes seem to be a reduction in pupil size and the loss of accommodation or focusing capability (presbyopia). The area of the pupil governs the amount of light that can reach the retina. The extent to which the pupil dilates decreases with age, leading to a substantial decrease in light received at the retina. In comparison to younger people, it is as though older persons are constantly wearing medium-density sunglasses. Therefore, for any detailed visually guided tasks on which performance varies with illumination, older persons require extra lighting. Certain ocular diseases can come from sexually transmitted diseases such as herpes and genital warts. If contact between the eye and area of infection occurs, the STD can be transmitted to the eye.
With aging, a prominent white ring develops in the periphery of the cornea called arcus senilis. Aging causes laxity, downward shift of eyelid tissues and atrophy of the orbital fat. These changes contribute to the etiology of several eyelid disorders such as ectropion, entropion, dermatochalasis, and ptosis. The vitreous gel undergoes liquefaction (posterior vitreous detachment or PVD) and its opacities — visible as floaters — gradually increase in number.
Various eye care professionals, including ophthalmologists (eye doctors/surgeons), optometrists, and opticians, are involved in the treatment and management of ocular and vision disorders. A Snellen chart is one type of eye chart used to measure visual acuity. At the conclusion of a complete eye examination, the eye doctor might provide the patient with an eyeglass prescription for corrective lenses. Some disorders of the eyes for which corrective lenses are prescribed include myopia (near-sightedness), hyperopia (far-sightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia (the loss of focusing range during aging).
Macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is especially prevalent in the U.S. and affects roughly 1.75 million Americans each year. Having lower levels of lutein and zeaxanthin within the macula may be associated with an increase in the risk of age-related macular degeneration. < Lutein and zeaxanthin act as antioxidants that protect the retina and macula from oxidative damage from high-energy light waves. As the light waves enter the eye they excite electrons that can cause harm to the cells in the eye, but they can cause oxidative damage that may lead to macular degeneration or cataracts. Lutein and zeaxanthin bind to the electron free radical and are reduced rendering the electron safe. There are many ways to ensure a diet rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, the best of which is to eat dark green vegetables including kale, spinach, broccoli and turnip greens. Nutrition is an important aspect of the ability to achieve and maintain proper eye health. Lutein and zeaxanthin are two major carotenoids, found in the macula of the eye, that are being researched to identify their role in the pathogenesis of eye disorders such as age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.