From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/El_Ni%C3%B1o
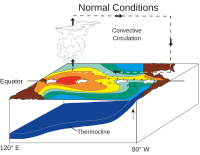
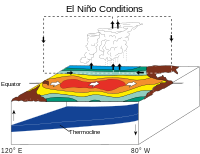
El Niño (/ɛl ˈniːnjoʊ/ el NEEN-yoh, Spanish: [el ˈniɲo]; lit. 'The Boy') is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date Line and 120°W), including the area off the Pacific coast of South America. The ENSO is the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
El Niño is accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific. El Niño phases are known to last close to four years; however, records demonstrate that the cycles have lasted between two and seven years. During the development of El Niño, rainfall develops between September–November. The cool phase of ENSO is La Niña, 'The Girl', with sea surface temperatures (SSTs) in the eastern Pacific below average, and air pressure high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific. The ENSO cycle, including both El Niño and La Niña, causes global changes in temperature and rainfall.
Developing countries that depend on their own agriculture and fishing, particularly those bordering the Pacific Ocean, are usually most affected. In this phase of the Oscillation, the pool of warm water in the Pacific near South America is often at its warmest about Christmas. The original phrase, El Niño de Navidad, arose centuries ago, when Peruvian fishermen named the weather phenomenon after the newborn Christ.
Concept
Originally, the term El Niño applied to an annual weak warm ocean current that ran southwards along the coast of Peru and Ecuador at about Christmas time. However, over time the term has evolved and now refers to the warm and negative phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and is the warming of the ocean surface or above-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. This warming causes a shift in the atmospheric circulation with rainfall becoming reduced over Indonesia, India and northern Australia, while rainfall and tropical cyclone formation increases over the tropical Pacific Ocean. The low-level surface trade winds, which normally blow from east to west along the equator, either weaken or start blowing from the other direction.

It is believed that El Niño has occurred for thousands of years. For example, it is thought that El Niño affected the Moche in modern-day Peru. Scientists have also found chemical signatures of warmer sea surface temperatures and increased rainfall caused by El Niño in coral specimens that are around 13,000 years old. Around 1525, when Francisco Pizarro made landfall in Peru, he noted rainfall in the deserts, the first written record of the impacts of El Niño. Modern day research and reanalysis techniques have managed to find at least 26 El Niño events since 1900, with the 1982–83, 1997–98 and 2014–16 events among the strongest on record.
Currently, each country has a different threshold for what constitutes an El Niño event, which is tailored to their specific interests. For example, the Australian Bureau of Meteorology looks at the trade winds, Southern Oscillation Index, weather models and sea surface temperatures in the Niño 3 and 3.4 regions, before declaring an El Niño. The United States Climate Prediction Center (CPC) and the International Research Institute for Climate and Society (IRI) looks at the sea surface temperatures in the Niño 3.4 region, the tropical Pacific atmosphere and forecasts that NOAA's Oceanic Niño Index will equal or exceed +.5 °C (0.90 °F) for several seasons in a row. However, the Japan Meteorological Agency declares that an El Niño event has started when the average five month sea surface temperature deviation for the Niño 3 region, is over 0.5 °C (0.90 °F) warmer for six consecutive months or longer. The Peruvian government declares that a coastal El Niño is under way if the sea surface temperature deviation in the Niño 1+2 regions equal or exceed 0.4 °C (0.72 °F) for at least three months.
There is no consensus on whether climate change will have any influence on the strength or duration of El Niño events, as research alternately supports El Niño events becoming stronger and weaker, longer and shorter. However, recent scholarship has found that climate change is increasing the frequency of extreme El Niño events.
Occurrences

El Niño events are thought to have been occurring for thousands of years. For example, it is thought that El Niño affected the Moche in modern-day Peru, who sacrificed humans in order to try to prevent the rains.
It is thought that there have been at least 30 El Niño events since 1900, with the 1982–83, 1997–98 and 2014–16 events among the strongest on record. Since 2000, El Niño events have been observed in 2002–03, 2004–05, 2006–07, 2009–10, 2014–16, 2018–19, and beginning in 2023.
Major ENSO events were recorded in the years 1790–93, 1828, 1876–78, 1891, 1925–26, 1972–73, 1982–83, 1997–98, and 2014–16.
Typically, this anomaly happens at irregular intervals of two to seven years, and lasts nine months to two years. The average period length is five years. When this warming occurs for seven to nine months, it is classified as El Niño "conditions"; when its duration is longer, it is classified as an El Niño "episode".
During strong El Niño episodes, a secondary peak in sea surface temperature across the far eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean sometimes follows the initial peak.
Cultural history and prehistoric information
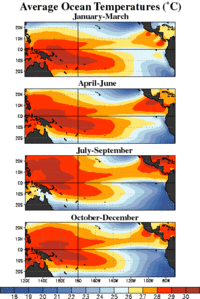
ENSO conditions have occurred at two- to seven-year intervals for at least the past 300 years, but most of them have been weak. Evidence is also strong for El Niño events during the early Holocene epoch 10,000 years ago.
El Niño may have led to the demise of the Moche and other pre-Columbian Peruvian cultures. A recent study suggests a strong El Niño effect between 1789 and 1793 caused poor crop yields in Europe, which in turn helped touch off the French Revolution. The extreme weather produced by El Niño in 1876–77 gave rise to the most deadly famines of the 19th century. The 1876 famine alone in northern China killed up to 13 million people.
An early recorded mention of the term "El Niño" to refer to climate occurred in 1892, when Captain Camilo Carrillo told the geographical society congress in Lima that Peruvian sailors named the warm south-flowing current "El Niño" because it was most noticeable around Christmas. Although pre-Columbian societies were certainly aware of the phenomenon, the indigenous names for it have been lost to history. The phenomenon had long been of interest because of its effects on the guano industry and other enterprises that depend on biological productivity of the sea. It is recorded that as early as 1822, cartographer Joseph Lartigue, of the French frigate La Clorinde under Baron Mackau, noted the "counter-current" and its usefulness for traveling southward along the Peruvian coast.
Charles Todd, in 1888, suggested droughts in India and Australia tended to occur at the same time; Norman Lockyer noted the same in 1904. An El Niño connection with flooding was reported in 1894 by Victor Eguiguren (1852–1919) and in 1895 by Federico Alfonso Pezet (1859–1929). In 1924, Gilbert Walker (for whom the Walker circulation is named) coined the term "Southern Oscillation". He and others (including Norwegian-American meteorologist Jacob Bjerknes) are generally credited with identifying the El Niño effect.
The major 1982–83 El Niño led to an upsurge of interest from the scientific community. The period 1990–95 was unusual in that El Niños have rarely occurred in such rapid succession. An especially intense El Niño event in 1998 caused an estimated 16% of the world's reef systems to die. The event temporarily warmed air temperature by 1.5 °C, compared to the usual increase of 0.25 °C associated with El Niño events. Since then, mass coral bleaching has become common worldwide, with all regions having suffered "severe bleaching".
Diversity
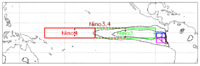
It is thought that there are several different types of El Niño events, with the canonical eastern Pacific and the Modoki central Pacific types being the two that receive the most attention. These different types of El Niño events are classified by where the tropical Pacific sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies are the largest. For example, the strongest sea surface temperature anomalies associated with the canonical eastern Pacific event are located off the coast of South America. The strongest anomalies associated with the Modoki central Pacific event are located near the International Date Line. However, during the duration of a single event, the area with the greatest sea surface temperature anomalies can change.
The traditional Niño, also called Eastern Pacific (EP) El Niño, involves temperature anomalies in the Eastern Pacific. However, in the last two decades, atypical El Niños were observed, in which the usual place of the temperature anomaly (Niño 1 and 2) is not affected, but an anomaly arises in the central Pacific (Niño 3.4). The phenomenon is called Central Pacific (CP) El Niño, "dateline" El Niño (because the anomaly arises near the International Date Line), or El Niño "Modoki" (Modoki is Japanese for "similar, but different").
The effects of the CP El Niño are different from those of the traditional EP El Niño—e.g., the recently discovered El Niño leads to more frequent Atlantic hurricanes.
There is also a scientific debate on the very existence of this "new" ENSO. Indeed, a number of studies dispute the reality of this statistical distinction or its increasing occurrence, or both, either arguing the reliable record is too short to detect such a distinction, finding no distinction or trend using other statistical approaches, or that other types should be distinguished, such as standard and extreme ENSO.
The first recorded El Niño that originated in the central Pacific and moved toward the east was in 1986. Recent Central Pacific El Niños happened in 1986–87, 1991–92, 1994–95, 2002–03, 2004–05 and 2009–10. Furthermore, there were "Modoki" events in 1957–59, 1963–64, 1965–66, 1968–70, 1977–78 and 1979–80. Some sources say that the El Niños of 2006-07 and 2014-16 were also Central Pacific El Niños.
Effects on the global climate

El Niño affects the global climate and disrupts normal weather patterns, which as a result can lead to intense storms in some places and droughts in others.
Tropical cyclones
Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving into the main belt of the Westerlies. Areas west of Japan and Korea tend to experience many fewer September–November tropical cyclone impacts during El Niño and neutral years. During El Niño years, the break in the subtropical ridge tends to lie near 130°E, which would favor the Japanese archipelago.
Within the Atlantic Ocean vertical wind shear is increased, which inhibits tropical cyclone genesis and intensification, by causing the westerly winds in the atmosphere to be stronger. The atmosphere over the Atlantic Ocean can also be drier and more stable during El Niño events, which can also inhibit tropical cyclone genesis and intensification. Within the Eastern Pacific basin: El Niño events contribute to decreased easterly vertical wind shear and favours above-normal hurricane activity. However, the impacts of the ENSO state in this region can vary and are strongly influenced by background climate patterns. The Western Pacific basin experiences a change in the location of where tropical cyclones form during El Niño events, with tropical cyclone formation shifting eastward, without a major change in how many develop each year. As a result of this change, Micronesia is more likely to be affected by tropical cyclones, while China has a decreased risk of being affected by tropical cyclones. A change in the location of where tropical cyclones form also occurs within the Southern Pacific Ocean between 135°E and 120°W, with tropical cyclones more likely to occur within the Southern Pacific basin than the Australian region. As a result of this change tropical cyclones are 50% less likely to make landfall on Queensland, while the risk of a tropical cyclone is elevated for island nations like Niue, French Polynesia, Tonga, Tuvalu, and the Cook Islands.
Remote influence on tropical Atlantic Ocean
A study of climate records has shown that El Niño events in the equatorial Pacific are generally associated with a warm tropical North Atlantic in the following spring and summer. About half of El Niño events persist sufficiently into the spring months for the Western Hemisphere Warm Pool to become unusually large in summer. Occasionally, El Niño's effect on the Atlantic Walker circulation over South America strengthens the easterly trade winds in the western equatorial Atlantic region. As a result, an unusual cooling may occur in the eastern equatorial Atlantic in spring and summer following El Niño peaks in winter. Cases of El Niño-type events in both oceans simultaneously have been linked to severe famines related to the extended failure of monsoon rains.
Regional impacts
Observations of El Niño events since 1950 show that impacts associated with El Niño events depend on the time of year. However, while certain events and impacts are expected to occur during events, it is not certain or guaranteed that they will occur. The impacts that generally do occur during most El Niño events include below-average rainfall over Indonesia and northern South America, while above average rainfall occurs in southeastern South America, eastern equatorial Africa, and the southern United States.
Africa
In Africa, East Africa—including Kenya, Tanzania, and the White Nile basin—experiences, in the long rains from March to May, wetter-than-normal conditions. Conditions are also drier than normal from December to February in south-central Africa, mainly in Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and Botswana.
Antarctica
Many ENSO linkages exist in the high southern latitudes around Antarctica. Specifically, El Niño conditions result in high-pressure anomalies over the Amundsen and Bellingshausen Seas, causing reduced sea ice and increased poleward heat fluxes in these sectors, as well as the Ross Sea. The Weddell Sea, conversely, tends to become colder with more sea ice during El Niño. The exact opposite heating and atmospheric pressure anomalies occur during La Niña. This pattern of variability is known as the Antarctic dipole mode, although the Antarctic response to ENSO forcing is not ubiquitous.
Asia
As warm water spreads from the west Pacific and the Indian Ocean to the east Pacific, it takes the rain with it, causing extensive drought in the western Pacific and rainfall in the normally dry eastern Pacific. Singapore experienced the driest February in 2010 since records began in 1869, with only 6.3 mm of rain falling in the month and temperatures hitting as high as 35 °C on 26 February. The years 1968 and 2005 had the next driest Februaries, when 8.4 mm of rain fell.
Australia and the Southern Pacific
During El Niño events, the shift in rainfall away from the Western Pacific may mean that rainfall across Australia is reduced. Over the southern part of the continent, warmer than average temperatures can be recorded as weather systems are more mobile and fewer blocking areas of high pressure occur. The onset of the Indo-Australian Monsoon in tropical Australia is delayed by two to six weeks, which as a consequence means that rainfall is reduced over the northern tropics. The risk of a significant bushfire season in south-eastern Australia is higher following an El Niño event, especially when it is combined with a positive Indian Ocean Dipole event. During an El Niño event, New Zealand tends to experience stronger or more frequent westerly winds during their summer, which leads to an elevated risk of drier than normal conditions along the east coast. There is more rain than usual though on New Zealand's West Coast, because of the barrier effect of the North Island mountain ranges and the Southern Alps.
Fiji generally experiences drier than normal conditions during an El Niño, which can lead to drought becoming established over the Islands. However, the main impacts on the island nation is felt about a year after the event becomes established. Within the Samoan Islands, below average rainfall and higher than normal temperatures are recorded during El Niño events, which can lead to droughts and forest fires on the islands. Other impacts include a decrease in the sea level, possibility of coral bleaching in the marine environment and an increased risk of a tropical cyclone affecting Samoa.
Europe
El Niño's effects on Europe are controversial, complex and difficult to analyse, as it is one of several factors that influence the weather over the continent and other factors can overwhelm the signal.
North America

Over North America, the main temperature and precipitation impacts of El Niño generally occur in the six months between October and March. In particular, the majority of Canada generally has milder than normal winters and springs, with the exception of eastern Canada where no significant impacts occur. Within the United States, the impacts generally observed during the six-month period include wetter-than-average conditions along the Gulf Coast between Texas and Florida, while drier conditions are observed in Hawaii, the Ohio Valley, Pacific Northwest and the Rocky Mountains.
Historically, El Niño was not understood to affect U.S. weather patterns until Christensen et al. (1981) used entropy minimax pattern discovery based on information theory to advance the science of long range weather prediction. Previous computer models of weather were based on persistence alone and reliable to only 5–7 days into the future. Long range forecasting was essentially random. Christensen et al. demonstrated the ability to predict the probability that precipitation will be below or above average with modest but statistically significant skill one, two and even three years into the future.
Study of more recent weather events over California and the southwestern United States indicate that there is a variable relationship between El Niño and above-average precipitation, as it strongly depends on the strength of the El Niño event and other factors. Though it has been historically associated with high rainfall in California, the effects of El Niño depend more strongly on the "flavor" of El Niño than its presence or absence, as only "persistent El Niño" events lead to consistently high rainfall.
The synoptic condition for the Tehuano wind, or "Tehuantepecer", is associated with a high-pressure area forming in Sierra Madre of Mexico in the wake of an advancing cold front, which causes winds to accelerate through the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. Tehuantepecers primarily occur during the cold season months for the region in the wake of cold fronts, between October and February, with a summer maximum in July caused by the westward extension of the Azores High. Wind magnitude is greater during El Niño years than during La Niña years, due to the more frequent cold frontal incursions during El Niño winters. Its effects can last from a few hours to six days. Some El Niño events were recorded in the isotope signals of plants, and that had helped scientists to study his impact.
South America
Because El Niño's warm pool feeds thunderstorms above, it creates increased rainfall across the east-central and eastern Pacific Ocean, including several portions of the South American west coast. The effects of El Niño in South America are direct and stronger than in North America. An El Niño is associated with warm and very wet weather months in April–October along the coasts of northern Peru and Ecuador, causing major flooding whenever the event is strong or extreme. The effects during the months of February, March, and April may become critical along the west coast of South America, El Niño reduces the upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water that sustains large fish populations, which in turn sustain abundant sea birds, whose droppings support the fertilizer industry. The reduction in upwelling leads to fish kills off the shore of Peru.
The local fishing industry along the affected coastline can suffer during long-lasting El Niño events. The world's largest fishery collapsed due to overfishing during the 1972 El Niño Peruvian anchoveta reduction. During the 1982–83 event, jack mackerel and anchoveta populations were reduced, scallops increased in warmer water, but hake followed cooler water down the continental slope, while shrimp and sardines moved southward, so some catches decreased while others increased. Horse mackerel have increased in the region during warm events. Shifting locations and types of fish due to changing conditions create challenges for the fishing industry. Peruvian sardines have moved during El Niño events to Chilean areas. Other conditions provide further complications, such as the government of Chile in 1991 creating restrictions on the fishing areas for self-employed fishermen and industrial fleets.
The ENSO variability may contribute to the great success of small, fast-growing species along the Peruvian coast, as periods of low population removes predators in the area. Similar effects benefit migratory birds that travel each spring from predator-rich tropical areas to distant winter-stressed nesting areas.
Southern Brazil and northern Argentina also experience wetter than normal conditions, but mainly during the spring and early summer. Central Chile receives a mild winter with large rainfall, and the Peruvian-Bolivian Altiplano is sometimes exposed to unusual winter snowfall events. Drier and hotter weather occurs in parts of the Amazon River Basin, Colombia, and Central America.
Galapagos Islands
The Galapagos Islands are a chain of volcanic islands, nearly 600 miles west of Ecuador, South America. Located in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, these islands are home to a wide diversity of terrestrial and marine species including sharks, birds, iguanas, turtles, penguins, and seals. This robust ecosystem is fueled by the normal trade winds which influence upwelling of cold, nutrient rich waters to the islands. During an El Niño an event where the trade winds weaken and sometimes push from west to east. This causes the Equatorial current to weaken, thus raising surface water temperatures and decreasing nutrients in waters surrounding the Galapagos. El Niño causes a trophic cascade which impacts entire ecosystems starting with primary producers and ending with critical animals such as sharks, penguins, and seals. The effects of El Niño can become detrimental to populations that often starve and die off during these years. Rapid evolutionary adaptations are displayed amongst animal groups during El Niño years to mitigate El Niño conditions.
Socio-ecological effects for humanity and nature
Economic effects

When El Niño conditions last for many months, extensive ocean warming and the reduction in easterly trade winds limits upwelling of cold nutrient-rich deep water, and its economic effect on local fishing for an international market can be serious.
More generally, El Niño can affect commodity prices and the macroeconomy of different countries. It can constrain the supply of rain-driven agricultural commodities; reduce agricultural output, construction, and services activities; create food-price and generalised inflation; and may trigger social unrest in commodity-dependent poor countries that primarily rely on imported food. A University of Cambridge Working Paper shows that while Australia, Chile, Indonesia, India, Japan, New Zealand and South Africa face a short-lived fall in economic activity in response to an El Niño shock, other countries may actually benefit from an El Niño weather shock (either directly or indirectly through positive spillovers from major trading partners), for instance, Argentina, Canada, Mexico and the United States. Furthermore, most countries experience short-run inflationary pressures following an El Niño shock, while global energy and non-fuel commodity prices increase. The IMF estimates a significant El Niño can boost the GDP of the United States by about 0.5% (due largely to lower heating bills) and reduce the GDP of Indonesia by about 1.0%.
Health and social impacts
Extreme weather conditions related to the El Niño cycle correlate with changes in the incidence of epidemic diseases. For example, the El Niño cycle is associated with increased risks of some of the diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, such as malaria, dengue fever, and Rift Valley fever. Cycles of malaria in India, Venezuela, Brazil, and Colombia have now been linked to El Niño. Outbreaks of another mosquito-transmitted disease, Australian encephalitis (Murray Valley encephalitis—MVE), occur in temperate south-east Australia after heavy rainfall and flooding, which are associated with La Niña events. A severe outbreak of Rift Valley fever occurred after extreme rainfall in north-eastern Kenya and southern Somalia during the 1997–98 El Niño.
ENSO conditions have also been related to Kawasaki disease incidence in Japan and the west coast of the United States, via the linkage to tropospheric winds across the north Pacific Ocean.
ENSO may be linked to civil conflicts. Scientists at The Earth Institute of Columbia University, having analyzed data from 1950 to 2004, suggest ENSO may have had a role in 21% of all civil conflicts since 1950, with the risk of annual civil conflict doubling from 3% to 6% in countries affected by ENSO during El Niño years relative to La Niña years.
Ecological consequences
In terrestrial ecosystems, rodent outbreaks were observed in northern Chile and along the Peruvian coastal desert following the 1972-73 El Niño event. While some nocturnal primates (western tarsiers Tarsius bancanus and slow loris Nycticebus coucang) and the Malayan sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) were locally extirpate or suffered drastic reduction in numbers within these burned forests. Lepidoptera outbreaks were documented in Panamá and Costa Rica. During the 1982–83, 1997–98 and 2015–16 ENSO events, large extensions of tropical forests experienced a prolonged dry period that resulted in widespread fires, and drastic changes in forest structure and tree species composition in Amazonian and Bornean forests.
Their impacts do not restrict only vegetation, since declines in insect populations were observed after extreme drought and terrible fires during El Niño 2015–16. Declines in habitat-specialist and disturbance-sensitive bird species and in large-frugivorous mammals were also observed in Amazonian burned forests, while temporary extirpation of more than 100 lowland butterfly species occurred at a burned forest site in Borneo.
Most critically, global mass bleaching events were recorded in 1997-98 and 2015–16, when around 75-99% losses of live coral were registered across the world. Considerable attention was also given to the collapse of Peruvian and Chilean anchovy populations that led to a severe fishery crisis following the ENSO events in 1972–73, 1982–83, 1997–98 and, more recently, in 2015–16. In particular, increased surface seawater temperatures in 1982-83 also lead to the probable extinction of two hydrocoral species in Panamá, and to a massive mortality of kelp beds along 600 km of coastline in Chile, from which kelps and associated biodiversity slowly recovered in the most affected areas even after 20 years. All these findings enlarge the role of ENSO events as a strong climatic force driving ecological changes all around the world – particularly in tropical forests and coral reefs.
In seasonally dry tropical forests, which are more drought tolerant, researchers found that El Niño induced drought increased seedling mortality. In a research published in October 2022, researchers studied seasonally dry tropical forests in a national park in Chiang Mai in Thailand for 7 years and observed that El Niño increased seedling mortality even in seasonally dry tropical forests and may impact entire forests in long run.