
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies".
Sex assignment at birth usually aligns with a child's anatomical sex and phenotype. The number of births with ambiguous genitals is in the range of 1:4500–1:2000 (0.02%–0.05%). Other conditions involve atypical chromosomes, gonads, or hormones. Some persons may be assigned and raised as a girl or boy but then identify with another gender later in life, while most continue to identify with their assigned sex. A systematic review by Tiffany Jones states that the number of people with intersex conditions are estimated to be between 1.7% and 4%. Anne Fausto-Sterling and her co-authors suggest that the prevalence of "nondimorphic sexual development" might be as high as 1.7%. A study published by Leonard Sax reports that this figure includes conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome (XXY) which most clinicians do not recognize as intersex, and that if the term is understood to mean only "conditions in which chromosomal sex is inconsistent with phenotypic sex, or in which the phenotype is not classifiable as either male or female", the prevalence of intersex is about 0.018%.
Terms used to describe intersex people are contested, and change over time and place. Intersex people were previously referred to as "hermaphrodites" or "congenital eunuchs". In the 19th and 20th centuries, some medical experts devised new nomenclature in an attempt to classify the characteristics that they had observed, the first attempt to create a taxonomic classification system of intersex conditions. Intersex people were categorized as either having "true hermaphroditism", "female pseudohermaphroditism", or "male pseudohermaphroditism". These terms are no longer used, and terms including the word "hermaphrodite" are considered to be misleading, stigmatizing, and scientifically specious in reference to humans. In biology, the term "hermaphrodite" is used to describe an organism that can produce both male and female gametes. Some people with intersex traits use the term "intersex", and some prefer other language. In clinical settings, the term "disorders of sex development" (DSD) has been used since 2006, a shift in language considered controversial since its introduction.
Intersex people face stigmatization and discrimination from birth, or following the discovery of intersex traits at stages of development such as puberty. Intersex people may face infanticide, abandonment, and stigmatization from their families. Globally, some intersex infants and children, such as those with ambiguous outer genitalia, are surgically or hormonally altered to create more socially acceptable sex characteristics. This is considered controversial, with no firm evidence of favorable outcomes. Such treatments may involve sterilization. Adults, including elite female athletes, have also been subjects of such treatment. Increasingly, these issues are considered human rights abuses, with statements from international and national human rights and ethics institutions. Intersex organizations have also issued statements about human rights violations, including the 2013 Malta declaration of the third International Intersex Forum. In 2011, Christiane Völling became the first intersex person known to have successfully sued for damages in a case brought for non-consensual surgical intervention. In April 2015, Malta became the first country to outlaw non-consensual medical interventions to modify sex anatomy, including that of intersex people.
Terminology
There is no clear consensus definition of intersex and no clear delineation of which specific conditions qualify an individual as intersex. The World Health Organization's International Classification of Diseases (ICD), the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), and many medical journals classify intersex traits or conditions among disorders of sex development (DSD).
A common adjective for people with disorders of sex development (DSD) is "intersex".
Etymology and definitions
In 1917, Richard Goldschmidt created the term "intersexuality" to refer to a variety of physical sex ambiguities. However, according to The SAGE Encyclopedia of LGBTQ Studies, it was not until Anne Fausto Sterling published her article "The Five Sexes: Why Male and Female Are Not Enough" in 1993 that the term reached popularity.

According to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights:
Intersex people are born with sex characteristics (including genitals, gonads and chromosome patterns) that do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies. Intersex is an umbrella term used to describe a wide range of natural bodily variations.
Attitudes towards the term
Some intersex organizations reference "intersex people" and "intersex variations or traits" while others use more medicalized language such as "people with intersex conditions", or people "with intersex conditions or DSDs (differences of sex development)" and "children born with variations of sex anatomy". In May 2016, interACT published a statement recognizing "increasing general understanding and acceptance of the term 'intersex'".
Australian sociological research on 272 "people born with atypical sex characteristics", published in 2016, found that 60% of respondents used the term "intersex" to self-describe their sex characteristics, including people identifying themselves as intersex, describing themselves as having an intersex variation or, in smaller numbers, having an intersex condition. Respondents also commonly used diagnostic labels and referred to their sex chromosomes, with word choices depending on audience.
Research on 202 respondents by the Lurie Children's Hospital, Chicago, and the AIS-DSD Support Group (now known as InterConnect Support Group) published in 2017 found that 80% of Support Group respondents "strongly liked, liked or felt neutral about intersex" as a term, while caregivers were less supportive. The hospital reported that the use of the term "disorders of sex development" may negatively affect care.
Another study by a group of children's hospitals in the United States found that 53% of 133 parent and adolescent participants recruited at five clinics did not like the term "intersex". Participants who were members of support groups were more likely to dislike the term. A "dsd-LIFE" study in 2020 found that around 43% of 179 participants thought the term "intersex" was bad, 20% felt neutral about the term, while the rest thought the term was good.
The term "hermaphrodite"
Historically, the term "hermaphrodite" was used in law to refer to people whose sex was in doubt. The 12th-century Decretum Gratiani states that "Whether an hermaphrodite may witness a testament, depends on which sex prevails" ("Hermafroditus an ad testamentum adhiberi possit, qualitas sexus incalescentis ostendit."). Similarly, the 17th-century English jurist and judge Edward Coke (Lord Coke), wrote in his Institutes of the Lawes of England on laws of succession stating, "Every heire is either a male, a female, or an hermaphrodite, that is both male and female. And an hermaphrodite (which is also called Androgynus) shall be heire, either as male or female, according to that kind of sexe which doth prevaile."
During the Victorian era, medical authors attempted to ascertain whether or not humans could be hermaphrodites, adopting a precise biological definition for the term, and making distinctions between "male pseudohermaphrodite", "female pseudohermaphrodite" and especially "true hermaphrodite". These terms, which reflected histology (microscopic appearance) of the gonads, are no longer used.] Until the mid-20th century, "hermaphrodite" was used synonymously with "intersex". Medical terminology shifted in the early 21st century, not only due to concerns about language, but also a shift to understandings based on genetics. The term "hermaphrodite" is also controversial as it implies the existence of someone fully male and fully female. This is a fantasy by certain people who seek "hermaphrodite" sex partners; in the Intersex movement, such people are called "wannafucks." As such the term "hermaphrodite" is often seen as degrading and offensive, although many intersex activists use it as a direct form of self empowerment and critique such as in the ISNA's first newsletter "Hermaphrodites with Attitude."'
The Intersex Society of North America has stated that hermaphrodites should not be confused with intersex people and that using "hermaphrodite" to refer to intersex individuals is considered to be stigmatizing and misleading.
Prevalence

Estimates of the number of people who are intersex vary, depending on which conditions are counted as intersex. The now-defunct Intersex Society of North America stated that:
If you ask experts at medical centers how often a child is born so noticeably atypical in terms of genitalia that a specialist in sex differentiation is called in, the number comes out to about 1 in 1500 to 1 in 2000 births [0.07–0.05%]. But a lot more people than that are born with subtler forms of sex anatomy variations, some of which won't show up until later in life.
Anne Fausto-Sterling and her co-authors broadly said in 2000 that "[a]dding the estimates of all known causes of nondimorphic sexual development suggests that approximately 1.7% of all live births do not conform to a Platonic ideal of absolute sex chromosome, gonadal, genital, and hormonal dimorphism"; these publications have been widely quoted by intersex activists. Of the 1.7%, 1.5% points (88% of those considered "nondimorphic sexual development" in this figure) consist of individuals with late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia (LOCAH) which may be asymptomatic but can present after puberty and cause infertility.
In response to Fausto-Sterling, Leonard Sax estimated that the prevalence of intersex was about 0.018% of the world's population, after discounting several conditions including LOCAH, Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY), Turner syndrome (45,X), the chromosomal variants of 47,XYY and 47,XXX, and vaginal agenesis. Sax reasons that in these conditions chromosomal sex is consistent with phenotypic sex and phenotype is classifiable as either male or female.
In a 2003 letter to the editor, political scientist Carrie Hull analyzed the data used by Fausto-Sterling and said the estimated intersex rate should instead have been 0.37%, due to many errors. In a response letter published simultaneously, Fausto-Sterling welcomed the additional analysis and said "I am not invested in a particular final estimate, only that there BE an estimate". A 2018 review reported that the number of births with ambiguous genitals is in the range of 0.02% to 0.05%.
Intersex Human Rights Australia says it maintains 1.7% as its preferred upper limit "despite its flaws", stating both that the estimate "encapsulates the entire population of people who are stigmatized – or risk stigmatization – due to innate sex characteristics," and that Sax's definitions exclude individuals who experience such stigma and who have helped to establish the intersex movement.
The following summarizes prevalences of traits that have been called intersex:
| Intersex condition | Sex specificity | Approximate prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia (nonclassical forms) | Female (males are generally asymptomatic) | One in 50–1,000 births (0.1–0.2% up to 1–2% depending on population) |
| Hypospadias | Male | One in 200–10,000 male births (0.01%–0.5%), prevalence estimates vary considerably |
| Klinefelter syndrome | Male | One in 500–1,000 male births (0.1–0.2%) |
| Trisomy X | Female | One in 1,000 female births (0.10%) |
| Turner syndrome | Female | One in 2,500 female births (0.04%) |
| Müllerian agenesis (of vagina, i.e., MRKH Syndrome) | Female | One in 4,500 female births (0.022%) |
| Vaginal atresia | Female | One in 5,000 female births (0.02%) |
| 45,X/46,XY mosaicism | Male | One in 6,666 births (0.015%) |
| XYY syndrome | Male | One in 7,000 male births (0.0142%) |
| Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (classical forms) | None (but virilization of female infants) | One in 10,000–20,000 births (0.01–0.02%) |
| XXYY syndrome | Male | One in 18,000–40,000 male births (0.0025%–0.0055%) |
| XX male syndrome | Male | One in 20,000 male births (0.005%) |
| True hermaphroditism | None | One in 20,000 births (0.005%) |
| XY gonadal dysgenesis | Phenotypic female | One in 80,000 births (0.0013%) |
| Androgen insensitivity syndrome (complete and partial phenotypes) | Genetic male | One in 99,000 births (0.001%) |
| Idiopathic (no discernable medical cause) | None | One in 110,000 births (0.0009%) |
| Iatrogenic (caused by medical treatment, e.g., progestogen administered to pregnant mother) | None | No estimate |
| 5-alpha-reductase deficiency | Male | No estimate |
| Aromatase excess syndrome | None | No estimate |
| Anorchia | Male | No estimate |
| Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome | Male | No estimate |
Prevalences of specific conditions can vary across regions. In the Dominican Republic, 5-alpha-reductase deficiency is not uncommon in the town of Las Salinas, resulting in social acceptance of the intersex trait. Men with the trait are called "güevedoces" (Spanish for "eggs at twelve"). 12 out of 13 families had one or more male family members that carried the gene. The overall incidence for the town was 1 in every 90 males were carriers, with other males either non-carriers or non-affected carriers.
History


From early history, societies have been aware of intersex people. Some of the earliest evidence is found in mythology: the Greek historian Diodorus Siculus wrote of the mythological Hermaphroditus in the first century BC, who was "born with a physical body which is a combination of that of a man and that of a woman", and reputedly possessed supernatural properties. He also recounted the lives of Diophantus of Abae and Callon of Epidaurus. Ardhanarishvara, an androgynous composite form of male deity Shiva and female deity Parvati, originated in Kushan culture as far back as the first century AD. A statue depicting Ardhanarishvara is included in India's Meenakshi Temple; this statue clearly shows both male and female bodily elements.
Hippocrates (c. 460 – c. 370 BC Greek physician) and Galen (129 – c. 200/216 AD Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher) both viewed sex as a spectrum between men and women, with "many shades in between, including hermaphrodites, a perfect balance of male and female". Pliny the Elder (AD 23/24–79) the Roman naturalist described "those who are born of both sexes, whom we call hermaphrodites, at one time androgyni" (from the Greek andr-, "man," and gyn-, "woman"). Augustine (354 – 28 August 430 AD) the influential Catholic theologian wrote in The Literal Meaning of Genesis that humans were created in two sexes, despite "as happens in some births, in the case of what we call androgynes".
In medieval and early modern European societies, Roman law, post-classical canon law, and later common law, referred to a person's sex as male, female or hermaphrodite, with legal rights as male or female depending on the characteristics that appeared most dominant. The 12th century Decretum Gratiani states that "Whether an hermaphrodite may witness a testament, depends on which sex prevails". The foundation of common law, the 17th Century Institutes of the Lawes of England described how a hermaphrodite could inherit "either as male or female, according to that kind of sexe which doth prevaile." Legal cases have been described in canon law and elsewhere over the centuries.
Some non-European societies have sex or gender systems that recognize more than the two categories of male/man and female/woman. Some of these cultures, for instance the South-Asian Hijra communities, may include intersex people in a third gender category. Although–according to Morgan Holmes–early Western anthropologists categorized such cultures "primitive," Holmes has argued that analyses of these cultures have been simplistic or romanticized and fail to take account of the ways that subjects of all categories are treated.
During the Victorian era, medical authors introduced the terms "true hermaphrodite" for an individual who has both ovarian and testicular tissue, "male pseudo-hermaphrodite" for a person with testicular tissue, but either female or ambiguous sexual anatomy, and "female pseudo-hermaphrodite" for a person with ovarian tissue, but either male or ambiguous sexual anatomy. Some later shifts in terminology have reflected advances in genetics, while other shifts are suggested to be due to pejorative associations.
The term "intersexuality" was coined by Richard Goldschmidt in 1917. The first suggestion to replace the term "hermaphrodite" with "intersex" was made by Cawadias in the 1940s.
Since the rise of modern medical science, some intersex people with ambiguous external genitalia have had their genitalia surgically modified to resemble either female or male genitals. Surgeons pinpointed intersex babies as a "social emergency" when born. An 'optimal gender policy', initially developed by John Money, stated that early intervention helped avoid gender identity confusion, but this lacks evidence. Early interventions have adverse consequences for psychological and physical health. Since advances in surgery have made it possible for intersex conditions to be concealed, many people are not aware of how frequently intersex conditions arise in human beings or that they occur at all.
Dialogue between what were once antagonistic groups of activists and clinicians has led to only slight changes in medical policies and how intersex patients and their families are treated in some locations. In 2011, Christiane Völling became the first intersex person known to have successfully sued for damages in a case brought for non-consensual surgical intervention. In April 2015, Malta became the first country to outlaw non-consensual medical interventions to modify sex anatomy, including that of intersex people. Many civil society organizations and human rights institutions now call for an end to unnecessary "normalizing" interventions, including in the Malta declaration.
Human rights and legal issues

Human rights institutions are placing increasing scrutiny on harmful practices and issues of discrimination against intersex people. These issues have been addressed by a rapidly increasing number of international institutions including, in 2015, the Council of Europe, the United Nations Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights and the World Health Organization (WHO). These developments have been accompanied by International Intersex Forums and increased cooperation amongst civil society organizations. However, the implementation, codification, and enforcement of intersex human rights in national legal systems remains slow.
Physical integrity and bodily autonomy
Stigmatization and discrimination from birth may include infanticide, abandonment, and the stigmatization of families. The birth of an intersex child was often viewed as a curse or a sign of a witch mother, especially in parts of Africa. Abandonments and infanticides have been reported in Uganda, Kenya, South Asia, and China.
Infants, children and adolescents also experience "normalising" interventions on intersex persons that are medically unnecessary and the pathologisation of variations in sex characteristics. In countries where the human rights of intersex people have been studied, medical interventions to modify the sex characteristics of intersex people have still taken place without the consent of the intersex person. Interventions have been described by human rights defenders as a violation of many rights, including (but not limited to) bodily integrity, non-discrimination, privacy, and experimentation. These interventions have frequently been performed with the consent of the intersex person's parents, when the person is legally too young to consent. Such interventions have been criticized by the WHO, other UN bodies such as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, and an increasing number of regional and national institutions due to their adverse consequences, including trauma, impact on sexual function and sensation, and violation of rights to physical and mental integrity. The UN organizations decided that infant intervention should not be allowed, in favor of waiting for the child to mature enough to be a part of the decision-making – this allows for a decision to be made with total consent. In April 2015, Malta became the first country to outlaw surgical intervention without consent. In the same year, the Council of Europe became the first institution to state that intersex people have the right not to undergo sex affirmation interventions.
Anti-discrimination and equal treatment

People born with intersex bodies are seen as different. Intersex infants, children, adolescents and adults "are often stigmatized and subjected to multiple human rights violations", including discrimination in education, healthcare, employment, sport, and public services. Several countries have so far explicitly protected intersex people from discrimination, with landmarks including South Africa, Australia, and, most comprehensively, Malta.
Remedies and claims for compensation
Claims for compensation and remedies for human rights abuses include the 2011 case of Christiane Völling in Germany. A second case was adjudicated in Chile in 2012, involving a child and his parents. A further successful case in Germany, taken by Michaela Raab, was reported in 2015. In the United States, the Minor Child (M.C. v Aaronson) lawsuit was "a medical malpractice case related to the informed consent for a surgery performed on the Crawford's adopted child (known as M.C.) at [Medical University of South Carolina] in April 2006". The case was one of the first lawsuit of its kind to challenge "legal, ethical, and medical issues regarding genital-normalizing surgery" in minors, and was eventually settled out of court by the Medical University of South Carolina for $440,000 in 2017.
Information and support
Access to information, medical records, peer and other counselling and support. With the rise of modern medical science in Western societies, a secrecy-based model was also adopted, in the belief that this was necessary to ensure normal physical and psychosocial development.
Legal recognition
The Asia Pacific Forum of National Human Rights Institutions states that legal recognition is firstly "about intersex people who have been issued a male or a female birth certificate being able to enjoy the same legal rights as other men and women." In some regions, obtaining any form of birth certification may be an issue. A Kenyan court case in 2014 established the right of an intersex boy, "Baby A", to a birth certificate.
Like all individuals, some intersex individuals may be raised as a certain sex (male or female) but then identify with another later in life, while most do not. Recognition of third sex or gender classifications occurs in several countries, However, it is controversial when it becomes assumed or coercive, as is the case with some German infants. Sociological research in Australia, a country with a third 'X' sex classification, shows that 19% of people born with atypical sex characteristics selected an "X" or "other" option, while 75% of survey respondents self-described as male or female (52% as women, 23% as men), and 6% as unsure.
LGBT and LGBTI


Intersex conditions can be contrasted with transgender gender identities and the attached gender dysphoria a transgender person may feel, wherein their gender identity does not match their assigned sex. However, some people are both intersex and transgender; though intersex people by definition have variable sex characteristics that do not align with either typically male or female, this may be considered separate to an individual's assigned gender, the way they are raised and perceived, and their internal gender identity. A 2012 clinical review paper found that between 8.5% and 20% of people with intersex variations experienced gender dysphoria. In an analysis of the use of preimplantation genetic diagnosis to eliminate intersex traits, Behrmann and Ravitsky state: "Parental choice against intersex may ... conceal biases against same-sex attractedness and gender nonconformity."
The relationship of intersex people and communities to LGBTQ communities is complex, but intersex people are often added to the LGBT acronym, resulting in the acronym LGBTI. Emi Koyama describes how inclusion of intersex in LGBTI can fail to address intersex-specific human rights issues, including creating false impressions "that intersex people's rights are protected" by laws protecting LGBT people, and failing to acknowledge that many intersex people are not LGBT. Organisation Intersex International Australia states that some intersex individuals are homosexual, and some are heterosexual, but "LGBTI activism has fought for the rights of people who fall outside of expected binary sex and gender norms." Julius Kaggwa of SIPD Uganda has written that, while the gay community "offers us a place of relative safety, it is also oblivious to our specific needs". Mauro Cabral has written that transgender people and organizations "need to stop approaching intersex issues as if they were trans issues", including use of intersex conditions and people as a means of explaining being transgender; "we can collaborate a lot with the intersex movement by making it clear how wrong that approach is".
In society
Fiction, literature and media

An intersex character is the narrator in Jeffrey Eugenides' Pulitzer Prize-winning novel Middlesex.
The memoir, Born Both: An Intersex Life (Hachette Books, 2017), by intersex author and activist Hida Viloria, received strong praise from The New York Times Book Review, The Washington Post, Rolling Stone, People Magazine, and Psychology Today, was one of School Library Journal's 2017 Top Ten Adult Books for Teens, and was a 2018 Lambda Literary Award nominee.
Television works about intersex and films about intersex are scarce. The Spanish-language film XXY won the Critics' Week grand prize at the 2007 Cannes Film Festival and the ACID/CCAS Support Award. Faking It is notable for providing both the first intersex main character in a television show, and television's first intersex character played by an intersex actor.
Civil society institutions
Intersex peer support and advocacy organizations have existed since at least 1985, with the establishment of the Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Support Group Australia in 1985. The Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Support Group (UK) was established in 1988. The Intersex Society of North America (ISNA) may have been one of the first intersex civil society organizations to have been open to people regardless of diagnosis; it was active from 1993 to 2008.
Events
Intersex Awareness Day is an internationally observed civil awareness day designed to highlight the challenges faced by intersex people, occurring annually on 26 October. It marks the first public demonstration by intersex people, which took place in Boston on 26 October 1996, outside a venue where the American Academy of Pediatrics was holding its annual conference.
Intersex Day of Remembrance, also known as Intersex Solidarity Day, is an internationally observed civil awareness day designed to highlight issues faced by intersex people, occurring annually on 8 November. It marks the birthday of Herculine Barbin, a French intersex person whose memoirs were later published by Michel Foucault in Herculine Barbin: Being the Recently Discovered Memoirs of a Nineteenth-century French Hermaphrodite.
Flag

The intersex flag was created in July 2013 by Morgan Carpenter of Intersex Human Rights Australia to create a flag "that is not derivative, but is yet firmly grounded in meaning". The circle is described as "unbroken and unornamented, symbolising wholeness and completeness, and our potentialities. We are still fighting for bodily autonomy and genital integrity, and this symbolises the right to be who and how we want to be."
Religion
In Judaism, the Talmud contains extensive discussion concerning the status of two types of intersex people in Jewish law; namely, the androgynous, who exhibit both male and female external sexual organs, and the tumtum, who exhibit neither. In the 1970s and 1980s, the treatment of intersex babies started to be discussed in Orthodox Jewish medical halacha by prominent rabbinic leaders, such as Eliezer Waldenberg and Moshe Feinstein.
Sport

Erik Schinegger, Foekje Dillema, Maria José Martínez-Patiño and Santhi Soundarajan were subject to adverse sex verification testing resulting in ineligibility to compete in organised competitive competition. Stanisława Walasiewicz was posthumously ruled ineligible to have competed.
The South African middle-distance runner Caster Semenya won gold at the World Championships in the women's 800 metres and won silver in the 2012 Summer Olympics. When Semenya won gold in the World Championships, the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) requested sex verification tests. The results were not released. Semenya was ruled eligible to compete.
Katrina Karkazis, Rebecca Jordan-Young, Georgiann Davis and Silvia Camporesi have claimed that IAAF policies on "hyperandrogenism" in female athletes are "significantly flawed", arguing that the policy does not protect against breaches of privacy, requires athletes to undergo unnecessary treatment in order to compete, and intensifies "gender policing", and recommended that athletes be able to compete in accordance with their legally-recognised gender.
In April 2014, the BMJ reported that four elite women athletes with XY chromosomes and 5-ARD were subjected to sterilization and "partial clitoridectomies" in order to compete in sport. The authors noted that partial clitoridectomy was "not medically indicated" and "does not relate to real or perceived athletic 'advantage'." Intersex advocates regarded this intervention as "a clearly coercive process". In 2016, the United Nations Special Rapporteur on health, Dainius Pūras, criticized "current and historic" sex verification policies, describing how "a number of athletes have undergone gonadectomy (removal of reproductive organs) and partial clitoridectomy (a form of female genital mutilation) in the absence of symptoms or health issues warranting those procedures."
Biology
The notion of intersex individuals can be understood in the context of sexual system biology that varies across different types of organisms. Most animal species (~95%, including humans) are gonochoric, in which individuals are of either a female or male sex. Hermaphroditic species (some animals and most flowering plants) are represented by individuals that can express both sexes simultaneously or sequentially during their lifetimes. Intersex individuals in a number of gonochoric species, who express both female and male phenotypic characters to some degree, are known to exist at very low prevalences.
Although "hermaphrodite" and "intersex" have been used synonymously in humans, a hermaphrodite is specifically an individual capable of producing female and male gametes. While there are reports of individuals that seemed to have the potential to produce both types of gamete, in more recent years the term hermaphrodite as applied to humans has fallen out of favor, since female and male reproductive functions have not been observed together in the same individual.
Medical
Research in the late 20th century led to a growing medical consensus that diverse intersex bodies are normal, but relatively rare, forms of human biology. Clinician and researcher Milton Diamond stresses the importance of care in the selection of language related to intersex people:
Foremost, we advocate use of the terms "typical", "usual", or "most frequent" where it is more common to use the term "normal." When possible avoid expressions like maldeveloped or undeveloped, errors of development, defective genitals, abnormal, or mistakes of nature. Emphasize that all of these conditions are biologically understandable while they are statistically uncommon.
Medical classifications
Sexual differentiation
The common pathway of sexual differentiation, where a productive human female has an XX chromosome pair, and a productive male has an XY pair, is relevant to the development of intersex conditions.
During fertilization, the sperm adds either an X (female) or a Y (male) chromosome to the X in the ovum. This determines the genetic sex of the embryo. During the first weeks of development, genetic male and female fetuses are "anatomically indistinguishable", with primitive gonads beginning to develop during approximately the sixth week of gestation. The gonads, in a bipotential state, may develop into either testes (the male gonads) or ovaries (the female gonads), depending on the consequent events. Up until and including the seventh week, genetically female and genetically male fetuses appear identical.
At around eight weeks of gestation, the gonads of an XY embryo differentiate into functional testes, secreting testosterone. Ovarian differentiation, for XX embryos, does not occur until approximately week 12 of gestation. In typical female differentiation, the Müllerian duct system develops into the uterus, Fallopian tubes, and inner third of the vagina. In males, the Müllerian duct-inhibiting hormone MIH causes this duct system to regress. Next, androgens cause the development of the Wolffian duct system, which develops into the vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory ducts. By birth, the typical fetus has been completely sexed male or female, meaning that the genetic sex (XY-male or XX-female) corresponds with the phenotypical sex; that is to say, genetic sex corresponds with internal and external gonads, and external appearance of the genitals.
Signs
There are a variety of symptoms that can occur. Ambiguous genitalia is the most common sign. There can be micropenis, clitoromegaly, partial labial fusion, electrolyte abnormalities, delayed or absent puberty, unexpected changes at puberty, hypospadias, labial or inguinal (groin) masses (which may turn out to be testes) in girls and undescended testes (which may turn out to be ovaries) in boys.
Ambiguous genitalia
Ambiguous genitalia may appear as a large clitoris or as a small penis.
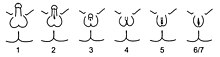
Because there is variation in all of the processes of the development of the sex organs, a child can be born with a sexual anatomy that is typically female or feminine in appearance with a larger-than-average clitoris (clitoral hypertrophy) or typically male or masculine in appearance with a smaller-than-average penis that is open along the underside. The appearance may be quite ambiguous, describable as female genitals with a very large clitoris and partially fused labia, or as male genitals with a very small penis, completely open along the midline ("hypospadic"), and empty scrotum. Fertility is variable.
Measurement systems for ambiguous genitalia
The orchidometer is a medical instrument to measure the volume of the testicles. It was developed by Swiss pediatric endocrinologist Andrea Prader. The Prader scale and Quigley scale are visual rating systems that measure genital appearance. These measurement systems were satirized in the Phall-O-Meter, created by the (now defunct) Intersex Society of North America.
Other signs
In order to help in classification, methods other than a genitalia inspection can be performed. For instance, a karyotype display of a tissue sample may determine which of the causes of intersex is prevalent in the case. Additionally, electrolyte tests, endoscopic exam, ultrasound and hormone stimulation tests can be done.
Causes
Intersex can be divided into four categories which are: 46, XX intersex; 46, XY intersex; true gonadal intersex; and complex or undetermined intersex.
46, XX intersex
This condition used to be called "female pseudohermaphroditism". Persons with this condition have female internal genitalia and karyotype (XX) and various degree of external genitalia virilization. External genitalia is masculinized congenitally when female fetus is exposed to excess androgenic environment. Hence, the chromosome of the person is of a woman, the ovaries of a woman, but external genitals that appear like a male. The labia fuse, and the clitoris enlarges to appear like a penis. The causes of this can be male hormones taken during pregnancy, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, male-hormone-producing tumors in the mother and aromatase deficiency.
46, XY intersex
This condition used to be called "male pseudohermaphroditism". This is defined as incomplete masculinization of the external genitalia. Thus, the person has male chromosomes, but the external genitals are incompletely formed, ambiguous, or clearly female. This condition is also called 46, XY with undervirilization. 46, XY intersex has many possible causes, which can be problems with the testes and testosterone formation. Also, there can be problems with using testosterone. Some people lack the enzyme needed to convert testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, which is a cause of 5-alpha-reductase deficiency. Androgen insensitivity syndrome is the most common cause of 46, XY intersex.
True gonadal intersex
This condition used to be called "true hermaphroditism". This is defined as having asymmetrical gonads with ovarian and testicular differentiation on either sides separately or combined as ovotestis. In most cases, the cause of this condition is unknown.
Complex or undetermined intersex
This is the condition of having any chromosome configurations rather than 46, XX or 46, XY intersex. This condition does not result in an imbalance between internal and external genitalia. However, there may be problems with sex hormone levels, overall sexual development, and altered numbers of sex chromosomes.
Conditions
There are a variety of opinions on what conditions or traits are and are not intersex, dependent on the definition of intersex that is used. Current human rights based definitions stress a broad diversity of sex characteristics that differ from expectations for male or female bodies. During 2015, the Council of Europe, the European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights and Inter-American Commission on Human Rights have called for a review of medical classifications on the basis that they presently impede enjoyment of the right to health; the Council of Europe expressed concern that "the gap between the expectations of human rights organisations of intersex people and the development of medical classifications has possibly widened over the past decade".
Medical interventions

Rationales
Medical interventions take place to address physical health concerns and psychosocial risks. Both types of rationale are the subject of debate, particularly as the consequences of surgical (and many hormonal) interventions are lifelong and irreversible. Questions regarding physical health include accurately assessing risk levels, necessity, and timing. Psychosocial rationales are particularly susceptible to questions of necessity as they reflect social and cultural concerns.
There remains no clinical consensus about an evidence base, surgical timing, necessity, type of surgical intervention, and degree of difference warranting intervention. Such surgeries are the subject of significant contention due to consequences that include trauma, impact on sexual function and sensation, and violation of rights to physical and mental integrity. This includes community activism, and multiple reports by international human rights and health institutions and national ethics bodies.
In the cases where gonads may pose a cancer risk, as in some cases of androgen insensitivity syndrome, concern has been expressed that treatment rationales and decision-making regarding cancer risk may encapsulate decisions around a desire for surgical "normalization".





