An ideal Fermi gas is a phase of matter which is an ensemble of a large number of non-interacting fermions. Fermions are particles that obey Fermi–Dirac statistics, like electrons, protons and neutrons, and in general, particles with half-integer spin. These statistics determine the energy distribution of fermions in a Fermi gas in thermal equilibrium, and is characterized by their number density, temperature, and the set of available energy states. The model is named after the Italian physicist Enrico Fermi.
This physical model can be accurately applied to many systems with a large number of fermions. Some key examples are the behaviour of charge carriers in a metal, nucleons in an atomic nucleus, neutrons in a neutron star, and electrons in a white dwarf.
This physical model can be accurately applied to many systems with a large number of fermions. Some key examples are the behaviour of charge carriers in a metal, nucleons in an atomic nucleus, neutrons in a neutron star, and electrons in a white dwarf.
Description
Illustration of the energy states: Energy-occupation diagram for a system with 7 energy levels, the energy Ei is degenerate Di times and has an occupancy given by Ni, with i=1,2,3,4,5,6,7. By the Pauli exclusion principle, up to Di fermions can occupy a level of energy Ei of the system.
An ideal Fermi gas or free Fermi gas is a physical model assuming a collection of non-interacting fermions in a constant potential well. It is the quantum mechanical version of an ideal gas, for the case of fermionic particles.
By the Pauli exclusion principle, no quantum state can be occupied by more than one fermion with an identical set of quantum numbers. Thus a non-interacting Fermi gas, unlike a Bose gas, concentrates a small number of particles per energy. Thus a Fermi gas is prohibited from condensing into a Bose–Einstein condensate, although weakly-interacting Fermi gases might. The total energy of the Fermi gas at absolute zero is larger than the sum of the single-particle ground states because the Pauli principle implies a sort of interaction or pressure that keeps fermions separated and moving. For this reason, the pressure of a Fermi gas is non-zero even at zero temperature, in contrast to that of a classical ideal gas. For example, this so-called degeneracy pressure stabilizes a neutron star (a Fermi gas of neutrons) or a white dwarf star (a Fermi gas of electrons) against the inward pull of gravity, which would ostensibly collapse the star into a black hole. Only when a star is sufficiently massive to overcome the degeneracy pressure can it collapse into a singularity.
It is possible to define a Fermi temperature below which the gas can be considered degenerate (its pressure derives almost exclusively from the Pauli principle). This temperature depends on the mass of the fermions and the density of energy states.
The main assumption of the free electron model to describe the delocalized electrons in a metal can be derived from the Fermi gas. Since interactions are neglected due to screening effect, the problem of treating the equilibrium properties and dynamics of an ideal Fermi gas reduces to the study of the behaviour of single independent particles. In these systems the Fermi temperature is generally many thousands of kelvins, so in human applications the electron gas can be considered degenerate. The maximum energy of the fermions at zero temperature is called the Fermi energy. The Fermi energy surface in momentum space is known as the Fermi surface.
The nearly free electron model adapts the Fermi gas model to consider the crystal structure of metals and semiconductors. Where electrons in a crystal lattice are substituted by Bloch waves with a corresponding crystal momentum. As such, periodic systems are still relatively tractable and the model forms the starting point for more advanced theories that deal with interactions, e.g., using the perturbation theory.
Illustration of the Fermi energy for a one-dimensional well
The one-dimensional infinite square well of length L is a model for a one-dimensional box. It is a standard model-system in quantum mechanics for which the solution for a single particle is well known. The levels are labelled by a single quantum number n and the energies are given bySuppose now that instead of one particle in this box we have N particles in the box and that these particles are fermions with spin-½. Then not more than two particles can have the same energy, i.e., two particles can have the energy of , two other particles can have energy and so forth. The reason that two particles can have the same energy is that a particle can have a spin of ½ (spin up) or a spin of −½ (spin down), leading to two states for each energy level. In the configuration for which the total energy is lowest (the ground state), all the energy levels up to n = N/2 are occupied and all the higher levels are empty.
Defining the reference for the Fermi energy to be , the Fermi energy is therefore given by
Three-dimensional case
A model of the atomic nucleus showing it as a compact bundle of the two types of nucleons:
protons (red) and neutrons (blue). As a first approximation, the
nucleus can be treated as composed of non-interacting proton and neutron
gases.
The three-dimensional isotropic and non-relativistic case is known as the Fermi sphere.
Let us now consider a three-dimensional infinite square well, that is, a cubical box that has a side length L. The states are now labelled by three quantum numbers nx, ny, and nz. The single particle energies are
- ,
If we introduce a vector then each quantum state corresponds to a point in 'n-space' with energy
The free fermions that occupy the lowest energy states form a sphere in momentum space. The surface of this sphere is the Fermi surface.
The factor of two is found again because there are two spin states, while the factor of 1/8 is because only 1/8 of the sphere lies in the region where all n are positive. We find
Related quantities
Using this definition of Fermi energy, various related quantities can be useful. The Fermi temperature is defined as:Other quantities defined in this context are Fermi momentum
- ,
- .
These quantities are not well-defined in cases where the Fermi surface is non-spherical.
Thermodynamic quantities
Degeneracy pressure
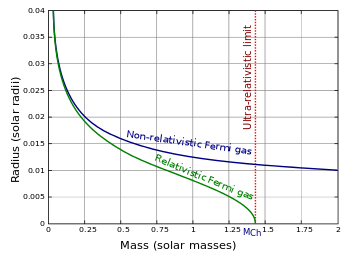
As we showed above, a Fermi gas has a non-zero total energy even at zero temperature. By using the first law of thermodynamics, we can associate a pressure to this internal energy, that isStandard stars avoid collapse by balancing thermal pressure (plasma and radiation) against gravitational forces. At the end of the star lifetime, when thermal processes are weaker, some stars may become white dwarfs, which are only sustained against gravity by electron degeneracy pressure. Using the Fermi gas as a model, it is possible to calculate the Chandrasekhar limit, i.e. the maximum mass any star may acquire (without significant thermally generated pressure) before collapsing into a black hole or a neutron star. The latter, is a star mainly composed of neutrons, where the collapse is also avoided by neutron degeneracy pressure.
For the case of metals, the electron degeneracy pressure contributes to the compressibility or bulk modulus of the material.
Chemical potential
Assuming that the concentration of fermions does not change with temperature, then the total chemical potential µ (Fermi level) of the three-dimensional ideal Fermi gas is related to the zero temperature Fermi energy EF by a Sommerfeld expansion (assuming ):- ,
Hence, the internal chemical potential, µ-E0, is approximately equal to the Fermi energy at temperatures that are much lower than the characteristic Fermi temperature TF. This characteristic temperature is on the order of 105 K for a metal, hence at room temperature (300 K), the Fermi energy and internal chemical potential are essentially equivalent.
Density of states
Figure 3: Density of states (DOS) of a Fermi gas in 3-dimensions
For the three dimensional case, with fermions of spin-½, we can obtain the number of particles as a function of the energy by substituting the Fermi energy by a variable energy :
- ,
- .
Arbitrary-dimensional case
Using a volume integral on dimensions, we can find the state density:A particular result is obtained for , where the density of states becomes a constant (does not depend on the energy):
- .
Typical values
Metals
Under the free electron model, the electrons in a metal can be considered to form a Fermi gas. The number density of conduction electrons in metals ranges between approximately 1028 and 1029 electrons/m3, which is also the typical density of atoms in ordinary solid matter. This number density produces a Fermi energy of the order:- ,
White dwarfs
Stars known as white dwarfs have mass comparable to our Sun, but have about a hundredth of its radius. The high densities mean that the electrons are no longer bound to single nuclei and instead form a degenerate electron gas. The number density of electrons in a white dwarf is of the order of 1036 electrons/m3. This means their Fermi energy is:Nucleus
Another typical example is that of the particles in a nucleus of an atom. The radius of the nucleus is roughly:The number density of nucleons in a nucleus is therefore:
So the Fermi energy of a nucleus is about:
- ,
The radius of the nucleus admits deviations around the value mentioned above, so a typical value for the Fermi energy is usually given as 38 MeV.
Extensions to the model
Relativistic Fermi gas
Radius–mass relations for a model white dwarf, relativistic relation vs non-relativistic. The Chandrasekhar limit is indicated as MCh.
For the whole article, we have only discussed the case where particles have a parabolic relation between energy and momentum, as is the case in non-relativistic mechanics. For particles with energies close to their respective rest mass, we have to use the equations of special relativity. Where single-particle energy is given by:
- .
- ,
- .


































![{\displaystyle N(E)={\frac {V}{3\pi ^{2}}}\left[{\frac {2m}{\hbar ^{2}}}(E-E_{0})\right]^{3/2}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/36a48ee4dfa8d3825e92710746a8b2e8512d939b)