The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed by Grady Booch, Ivar Jacobson and James Rumbaugh at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996.
In 1997 UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG), and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005 UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as an approved ISO standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML.
History
History of object-oriented methods and notation
Before UML 1.0
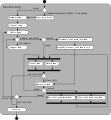
UML has been evolving since the second half of the 1990s and has its roots in the object-oriented programming
methods developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The timeline (see
image) shows the highlights of the history of object-oriented modeling
methods and notation.
It is originally based on the notations of the Booch method, the object-modeling technique (OMT) and object-oriented software engineering (OOSE), which it has integrated into a single language.
Rational Software Corporation hired James Rumbaugh from General Electric
in 1994 and after that the company became the source for two of the
most popular object-oriented modeling approaches of the day: Rumbaugh's object-modeling technique (OMT) and Grady Booch's method. They were soon assisted in their efforts by Ivar Jacobson, the creator of the object-oriented software engineering (OOSE) method, who joined them at Rational in 1995.
UML 1.x
Under the technical leadership of those three (Rumbaugh, Jacobson and Booch), a consortium called the UML Partners was organized in 1996 to complete the Unified Modeling Language (UML)
specification, and propose it to the Object Management Group (OMG) for
standardisation. The partnership also contained additional interested
parties (for example HP, DEC, IBM and Microsoft).
The UML Partners' UML 1.0 draft was proposed to the OMG in January 1997
by the consortium. During the same month the UML Partners formed a
group, designed to define the exact meaning of language constructs,
chaired by Cris Kobryn
and administered by Ed Eykholt, to finalize the specification and
integrate it with other standardization efforts. The result of this
work, UML 1.1, was submitted to the OMG in August 1997 and adopted by
the OMG in November 1997.
After the first release a task force was formed to improve the language, which released several minor revisions, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5.
The standards it produced (as well as the original standard) have been noted as being ambiguous and inconsistent.
Cardinality notation
As with database Chen, Bachman, and ISO ER diagrams, class models are specified to use "look-across" cardinalities, even though several authors (Merise, Elmasri, and Navathe, amongst others) prefer same-side or "look-here" for roles and both minimum and maximum cardinalities. Recent researchers (Feinerer, Dullea et al.) have shown that the "look-across" technique used by UML and ER diagrams is less effective and less coherent when applied to n-ary relationships of order strictly greater than 2.
Feinerer says: "Problems arise if we operate under the look-across semantics as used for UML associations. Hartmann
investigates this situation and shows how and why different
transformations fail.", and: "As we will see on the next few pages, the
look-across interpretation introduces several difficulties which prevent
the extension of simple mechanisms from binary to n-ary associations."
UML 2
UML 2.0
major revision replaced version 1.5 in 2005, which was developed with an
enlarged consortium to improve the language further to reflect new
experience on usage of its features.
Although UML 2.1 was never released as a formal specification,
versions 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 appeared in 2007, followed by UML 2.2 in
February 2009. UML 2.3 was formally released in May 2010. UML 2.4.1 was formally released in August 2011. UML 2.5 was released in October 2012 as an "In progress" version and was officially released in June 2015. Formal version 2.5.1 was adopted in December 2017.
There are four parts to the UML 2.x specification:
- The Superstructure that defines the notation and semantics for diagrams and their model elements;
- The Infrastructure that defines the core metamodel on which the Superstructure is based;
- The Object Constraint Language (OCL) for defining rules for model elements;
- The UML Diagram Interchange that defines how UML 2 diagram layouts are exchanged.
The current versions of these standards are:
- UML Superstructure version 2.4.1;
- UML Infrastructure version 2.4.1;
- OCL version 2.3.1;
- UML Diagram Interchange version 1.0.
It continues to be updated and improved by the revision task force, who resolve any issues with the language.
Design
UML offers a way to visualize a system's architectural blueprints in a diagram, including elements such as:
- any activities (jobs);
- individual components of the system;
- and how they can interact with other software components;
- how the system will run;
- how entities interact with others (components and interfaces);
- external user interface.
Although originally intended for object-oriented design
documentation, UML has been extended to a larger set of design
documentation (as listed above), and been found useful in many contexts.
Software development methods
UML is not a development method by itself;
however, it was designed to be compatible with the leading
object-oriented software development methods of its time, for example OMT, Booch method, Objectory and especially RUP that it was originally intended to be used with when work began at Rational Software.
Modeling
It is
important to distinguish between the UML model and the set of diagrams
of a system. A diagram is a partial graphic representation of a system's
model. The set of diagrams need not completely cover the model and
deleting a diagram does not change the model. The model may also contain
documentation that drives the model elements and diagrams (such as
written use cases).
UML diagrams represent two different views of a system model:
- Static (or structural) view: emphasizes the static structure of the system using objects, attributes, operations and relationships. It includes class diagrams and composite structure diagrams;
- Dynamic (or behavioral) view: emphasizes the dynamic behavior of the system by showing collaborations among objects and changes to the internal states of objects. This view includes sequence diagrams, activity diagrams and state machine diagrams.
UML models can be exchanged among UML tools by using the XML Metadata Interchange (XMI) format.
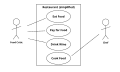
In UML, one of the key tools for behavior modelling is the use-case model, caused by OOSE.
Use cases are a way of specifying required usages of a system.
Typically, they are used to capture the requirements of a system, that
is, what a system is supposed to do.
Diagrams
UML 2 has many types of diagrams, which are divided into two categories. Some types represent structural information, and the rest represent general types of behavior, including a few that represent different aspects of interactions. These diagrams can be categorized hierarchically as shown in the following class diagram:
These diagrams may all contain comments or notes explaining usage, constraint, or intent.
Structure diagrams
Structure
diagrams emphasize the things that must be present in the system being
modeled. Since structure diagrams represent the structure, they are used
extensively in documenting the software architecture of software systems. For example, the component diagram describes how a software system is split up into components and shows the dependencies among these components.
Behavior diagrams
Behavior
diagrams emphasize what must happen in the system being modeled. Since
behavior diagrams illustrate the behavior of a system, they are used
extensively to describe the functionality of software systems. As an
example, the activity diagram describes the business and operational step-by-step activities of the components in a system.
Interaction diagrams
Interaction
diagrams, a subset of behavior diagrams, emphasize the flow of control
and data among the things in the system being modeled. For example, the sequence diagram shows how objects communicate with each other regarding a sequence of messages.
Metamodeling
Illustration of the Meta-Object Facility
The Object Management Group (OMG) has developed a metamodeling architecture to define the UML, called the Meta-Object Facility.
MOF is designed as a four-layered architecture, as shown in the image
at right. It provides a meta-meta model at the top, called the M3 layer.
This M3-model is the language used by Meta-Object Facility to build
metamodels, called M2-models.
The most prominent example of a Layer 2 Meta-Object Facility
model is the UML metamodel, which describes the UML itself. These
M2-models describe elements of the M1-layer, and thus M1-models. These
would be, for example, models written in UML. The last layer is the
M0-layer or data layer. It is used to describe runtime instances of the
system.
The meta-model can be extended using a mechanism called stereotyping. This has been criticised as being insufficient/untenable by Brian Henderson-Sellers and Cesar Gonzalez-Perez in "Uses and Abuses of the Stereotype Mechanism in UML 1.x and 2.0".
Adoption
UML has been marketed for many contexts.
It has been treated, at times, as a design silver bullet,
which leads to problems. UML misuse includes overuse (designing every
part of the system with it, which is unnecessary) and assuming that
novices can design with it.
It is considered a large language, with many constructs. Some people (including Jacobson) feel that UML's size hinders learning (and therefore, using) it.