Each shell can contain only a fixed number of electrons: The first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight (2 + 6) electrons, the third shell can hold up to 18 (2 + 6 + 10) and so on. The general formula is that the nth shell can in principle hold up to 2(n2) electrons. Since electrons are electrically attracted to the nucleus, an atom's electrons will generally occupy outer shells only if the more inner shells have already been completely filled by other electrons. However, this is not a strict requirement: atoms may have two or even three incomplete outer shells. For an explanation of why electrons exist in these shells see electron configuration.
The electrons in the outermost occupied shell (or shells) determine the chemical properties of the atom; it is called the valence shell.
Each shell consists of one or more subshells, and each subshell consists of one or more atomic orbitals.
History
The shell terminology comes from Arnold Sommerfeld's modification of the Bohr model. Sommerfeld retained Bohr's planetary model, but added mildly elliptical orbits (characterized by additional quantum numbers ℓ and m) to explain the fine spectroscopic structure of some elements. The multiple electrons with the same principal quantum number (n) had close orbits that formed a "shell" of positive thickness instead of the infinitely thin circular orbit of Bohr's model.The existence of electron shells was first observed experimentally in Charles Barkla's and Henry Moseley's X-ray absorption studies. Barkla labeled them with the letters K, L, M, N, O, P, and Q. The origin of this terminology was alphabetic. A "J" series was also suspected, though later experiments indicated that the K absorption lines are produced by the innermost electrons. These letters were later found to correspond to the n values 1, 2, 3, etc. They are used in the spectroscopic Siegbahn notation.
The physical chemist Gilbert Lewis was responsible for much of the early development of the theory of the participation of valence shell electrons in chemical bonding. Linus Pauling later generalized and extended the theory while applying insights from quantum mechanics.
Shells
The electron shells are labeled K, L, M, N, O, P, and Q; or 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7; going from innermost shell outwards. Electrons in outer shells have higher average energy and travel farther from the nucleus than those in inner shells. This makes them more important in determining how the atom reacts chemically and behaves as a conductor, because the pull of the atom's nucleus upon them is weaker and more easily broken. In this way, a given element's reactivity is highly dependent upon its electronic configuration.Subshells
Each shell is composed of one or more subshells, which are themselves composed of atomic orbitals. For example, the first (K) shell has one subshell, called 1s; the second (L) shell has two subshells, called 2s and 2p; the third shell has 3s, 3p, and 3d; the fourth shell has 4s, 4p, 4d and 4f; the fifth shell has 5s, 5p, 5d, and 5f and can theoretically hold more in the 5g subshell that is not occupied in the ground-state electron configuration of any known element. The various possible subshells are shown in the following table:| Subshell label | ℓ | Max electrons | Shells containing it | Historical name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | 0 | 2 | Every shell | sharp |
| p | 1 | 6 | 2nd shell and higher | principal |
| d | 2 | 10 | 3rd shell and higher | diffuse |
| f | 3 | 14 | 4th shell and higher | fundamental |
| g | 4 | 18 | 5th shell and higher (theoretically) | (next in alphabet after f, excluding j) |
- The first column is the "subshell label", a lowercase-letter label for the type of subshell. For example, the "4s subshell" is a subshell of the fourth (N) shell, with the type (s) described in the first row.
- The second column is the azimuthal quantum number (ℓ) of the subshell. The precise definition involves quantum mechanics, but it is a number that characterizes the subshell.
- The third column is the maximum number of electrons that can be put into a subshell of that type. For example, the top row says that each s-type subshell (1s, 2s, etc.) can have at most two electrons in it. In each case the figure is 4 greater than the one above it.
- The fourth column says which shells have a subshell of that type. For example, looking at the top two rows, every shell has an s subshell, while only the second shell and higher have a p subshell (i.e., there is no "1p" subshell).
- The final column gives the historical origin of the labels s, p, d, and f. They come from early studies of atomic spectral lines. The other labels, namely g, h and i, are an alphabetic continuation following the last historically originated label of f.
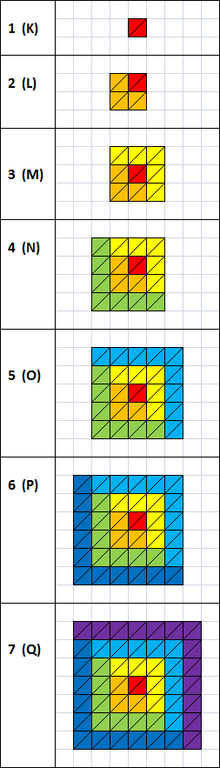
Number of electrons in each shell
Shells
and subshells. 1 rectangular triangle (1/2 of a cell) = 1 electron on
the level. Red color indicates sublevel s; orange - p; yellow - d; green
- f; blue - g; indigo - h; violet - i
| Shell name |
Subshell name |
Subshell max electrons |
Shell max electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | 1s | 2 | 2 |
| L | 2s | 2 | 2 + 6 = 8 |
| 2p | 6 | ||
| M | 3s | 2 | 2 + 6 + 10 = 18 |
| 3p | 6 | ||
| 3d | 10 | ||
| N | 4s | 2 | 2 + 6 + 10 + 14 = 32 |
| 4p | 6 | ||
| 4d | 10 | ||
| 4f | 14 | ||
| O | 5s | 2 | 2 + 6 + 10 + 14 + 18 = 50 |
| 5p | 6 | ||
| 5d | 10 | ||
| 5f | 14 | ||
| 5g | 18 |
Each subshell is constrained to hold 4ℓ + 2 electrons at most, namely:
- Each s subshell holds at most 2 electrons
- Each p subshell holds at most 6 electrons
- Each d subshell holds at most 10 electrons
- Each f subshell holds at most 14 electrons
- Each g subshell holds at most 18 electrons
Therefore, the K shell, which contains only an s subshell, can hold up to 2 electrons; the L shell, which contains an s and a p, can hold up to 2 + 6 = 8 electrons, and so forth; in general, the nth shell can hold up to 2n2 electrons.
Although that formula gives the maximum in principle, in fact that maximum is only achieved (by known elements) for the first four shells (K, L, M, N). No known element has more than 32 electrons in any one shell. This is because the subshells are filled according to the Aufbau principle. The first elements to have more than 32 electrons in one shell would belong to the g-block of period 8 of the periodic table. These elements would have some electrons in their 5g subshell and thus have more than 32 electrons in the O shell (fifth principal shell).
Valence shell
The valence shell is the outermost shell of an atom. Valence electrons in non-transition metal elements reside in this shell. Such elements with complete valence shells (noble gases) are the most chemically non-reactive, while those with only one electron in their valence shells (alkali metals) or just missing one electron from having a complete shell (halogens) are the most reactive.
However, this terminology is somewhat misleading in the case of
transition metals. In these elements, a valence electron can also be in
an inner shell. Thus, the electrons that determine how an atom reacts
chemically are those that travel farthest from the nucleus, that is,
those with the highest energy, and not necessarily in the valence shell.