A rotavirus
A virus is a biological agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts.
When infected by a virus, a host cell is forced to produce thousands of
identical copies of the original virus at an extraordinary rate. Unlike
most living things, viruses do not have cells that divide; new viruses
are assembled in the infected host cell. But unlike still simpler infectious agents, viruses contain genes, which gives them the ability to mutate and evolve. Over 5,000 species of viruses have been discovered.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids—pieces
of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from
bacteria. A virus consists of two or three parts: genes, made from either DNA or RNA, long molecules that carry genetic information; a protein coat that protects the genes; and in some viruses, an envelope
of fat that surrounds the protein coat and is used, in combination with
specific receptors, to enter a new host cell. Viruses vary in shape
from the simple helical and icosahedral to more complex structures. Viruses range in size from 20 to 300 nanometres; it would take 33,000 to 500,000 of them, side by side, to stretch to 1 centimetre (0.39 in).
Viruses spread in many ways. Just as many viruses are very specific as to which host species or tissue they attack, each species
of virus relies on a particular method for propagation. Plant viruses
are often spread from plant to plant by insects and other organisms, known as vectors. Some viruses of animals, including humans, are spread by exposure to infected bodily fluids. Viruses such as influenza are spread through the air by droplets of moisture when people cough or sneeze. Viruses such as norovirus are transmitted by the faecal–oral route, which involves the contamination of hands, food and water. Rotavirus is often spread by direct contact with infected children. The human immunodeficiency virus, HIV, is transmitted by bodily fluids transferred during sex. Others, such as the Dengue virus, are spread by blood-sucking insects.
Viral infections can cause disease in humans, animals and even plants. However, they are usually eliminated by the immune system, conferring lifetime immunity to the host for that virus. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses, but antiviral drugs have been developed to treat life-threatening infections. Vaccines that produce lifelong immunity can prevent some viral infections.
Discovery
Scanning electron micrograph of HIV-1 viruses, coloured green, budding from a lymphocyte
In 1884 the French microbiologist Charles Chamberland invented a filter, known today as the Chamberland filter
or Chamberland–Pasteur filter, that has pores smaller than bacteria.
Thus he could pass a solution containing bacteria through the filter and
completely remove them from the solution. In the early 1890s the Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky used this filter to study what became known as the tobacco mosaic virus. His experiments showed that extracts from the crushed leaves of infected tobacco plants remain infectious after filtration.
At the same time several other scientists proved that, although these agents (later called viruses)
were different from bacteria, they could still cause disease, and they
were about one hundredth the size of bacteria. In 1899 the Dutch
microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck
observed that the agent multiplied only in dividing cells. Having
failed to demonstrate its particulate nature, he called it a "contagium vivum fluidum", a "soluble living germ". In the early 20th century the English bacteriologist Frederick Twort discovered viruses that infect bacteria, and the French-Canadian microbiologist Félix d'Herelle described viruses that, when added to bacteria growing on agar,
would lead to the formation of whole areas of dead bacteria. Counting
these dead areas allowed him to calculate the number of viruses in the
suspension.
With the invention of the electron microscope in 1931 by the German engineers Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll came the first images of viruses. In 1935 American biochemist and virologist Wendell Meredith Stanley examined the tobacco mosaic virus and found it to be mostly made from protein. A short time later, this virus was separated into protein and RNA parts.
A problem for early scientists was that they did not know how to grow
viruses without using live animals. The breakthrough came in 1931, when
the American pathologist Ernest William Goodpasture and Alice Miles Woodruff grew influenza and several other viruses in fertilised chickens' eggs. Some viruses could not be grown in chickens' eggs, but this problem was solved in 1949 when John Franklin Enders, Thomas Huckle Weller and Frederick Chapman Robbins grew polio virus in cultures of living animal cells. Over 5,000 species of virus have been discovered.
Origins
Viruses co-exist with life wherever it occurs. They have probably
existed since living cells first evolved. The origin of viruses remains
unclear because they do not form fossils, so molecular techniques
have been the most useful means of hypothesising how they arose.
However, these techniques rely on the availability of ancient viral DNA
or RNA but most of the viruses that have been preserved and stored in
laboratories are less than 90 years old. Molecular methods have only been successful in tracing the ancestry of viruses that evolved in the 20th century. Three main theories speculate on the origins of viruses:
- Regressive theory
- Viruses may have once been small cells that parasitised larger cells. Over time, genes not required by their parasitism were lost. The bacteria rickettsia and chlamydia are living cells that, like viruses, can reproduce only inside host cells. They lend credence to this theory, as their dependence on parasitism is likely to have caused the loss of genes that enabled them to survive outside a cell.
- Cellular origin theory
- Some viruses may have evolved from bits of DNA or RNA that "escaped" from the genes of a larger organism. The escaped DNA could have come from plasmids—pieces of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from bacteria.
- Coevolution theory
- Viruses may have evolved from complex molecules of protein and DNA at the same time as cells first appeared on earth and would have depended on cellular life for many millions of years.
There are problems with all of these hypotheses: the regressive
hypothesis does not explain why even the smallest of cellular parasites
do not resemble viruses in any way. The escape hypothesis does not
explain the structures of virus particles. The coevolution, or
virus-first hypothesis, contravenes the definition of viruses, in that
they are dependent on host cells. But viruses are recognised as ancient and to have origins that pre-date the divergence of life into the three domains. This discovery has led modern virologists to reconsider and re-evaluate these three classical hypotheses.
Structure
A simplified diagram of the structure of a virus
A virus particle, also known as a virion, consists of genes made from DNA or RNA which are surrounded by a protective coat of protein called a capsid.
The capsid is made of many smaller, identical protein molecules which
are called capsomers. The arrangement of the capsomers can either be icosahedral (20-sided), helical or more complex. There is an inner shell around the DNA or RNA called the nucleocapsid, which is formed by proteins. Some viruses are surrounded by a bubble of lipid (fat) called an envelope.
Size
Viruses are among the smallest infectious agents, and most of them can only be seen by electron microscopy. Most viruses cannot be seen by light microscopy (in other words, they are sub-microscopic); their sizes range from 20 to 300 nm. They are so small that it would take 30,000 to 750,000 of them, side by side, to stretch to one cm. By contrast bacterial sizes are typically around 1 micrometre (1000 nm) in diameter, and the cells of higher organisms a few tens of micrometres. Some viruses such as megaviruses and pandoraviruses are relatively large. At around 1 micrometer, these viruses, which infect amoebae, were discovered in 2003 and 2013. They are around a thousand times larger than influenza viruses and the discovery of these "giant" viruses astonished scientists.
Genes
Genes are made from DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and, in many viruses,
RNA (ribonucleic acid). The biological information contained in an
organism is encoded in its DNA or RNA. Most organisms use DNA, but many viruses have RNA as their genetic material. The DNA or RNA of viruses consists of either a single strand or a double helix.
Viruses reproduce rapidly because they have only a few genes compared to humans who have 20,000–25,000. For example, influenza virus has only eight genes and rotavirus
has eleven. These genes encode structural proteins that form the virus
particle, or non-structural proteins, that are only found in cells
infected by the virus.
All cells, and many viruses, produce proteins that are enzymes called DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase
which make new copies of DNA and RNA. A virus's polymerase enzymes are
often much more efficient at making DNA and RNA than the host cell's.
However, RNA polymerase enzymes often make mistakes, and this is one of
the reasons why RNA viruses often mutate to form new strains.
In some species of RNA virus, the genes are not on a continuous
molecule of RNA, but are separated. The influenza virus, for example,
has eight separate genes made of RNA. When two different strains of
influenza virus infect the same cell, these genes can mix and produce
new strains of the virus in a process called reassortment.
Protein synthesis
Diagram of a typical eukaryotic cell, showing subcellular components. Organelles: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (6) Golgi apparatus (7) cytoskeleton (8) smooth ER (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytoplasm (12) lysosome (13) centrioles within centrosome (14) virus particle shown to approximate scale
Proteins are essential to life. Cells produce new protein molecules from amino acid
building blocks based on information coded in DNA. Each type of protein
is a specialist that usually only performs one function, so if a cell
needs to do something new, it must make a new protein. Viruses force the
cell to make new proteins that the cell does not need, but are needed
for the virus to reproduce. Protein synthesis consists of two major steps: transcription and translation.
Transcription is the process where information in DNA, called the genetic code, is used to produce RNA copies called messenger RNA (mRNA). These migrate through the cell and carry the code to ribosomes where it is used to make proteins. This is called translation because the protein's amino acid
structure is determined by the mRNA's code. Information is hence
translated from the language of nucleic acids to the language of amino
acids.
Some nucleic acids of RNA viruses function directly as mRNA
without further modification. For this reason, these viruses are called
positive-sense RNA viruses.
In other RNA viruses, the RNA is a complementary copy of mRNA and these
viruses rely on the cell's or their own enzyme to make mRNA. These are
called negative-sense
RNA viruses. In viruses made from DNA, the method of mRNA production is
similar to that of the cell. The species of viruses called retroviruses
behave completely differently: they have RNA, but inside the host cell a
DNA copy of their RNA is made with the help of the enzyme reverse
transcriptase. This DNA is then incorporated into the host's own DNA,
and copied into mRNA by the cell's normal pathways.
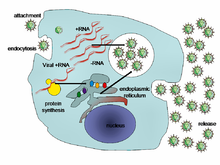
Life-cycle
Life-cycle
of a typical virus (left to right); following infection of a cell by a
single virus, hundreds of offspring are released.
When a virus infects a cell, the virus forces it to make thousands
more viruses. It does this by making the cell copy the virus's DNA or
RNA, making viral proteins, which all assemble to form new virus
particles.
There are six basic, overlapping stages in the life cycle of viruses in living cells:
- Attachment is the binding of the virus to specific molecules on the surface of the cell. This specificity restricts the virus to a very limited type of cell. For example, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects only human T cells, because its surface protein, gp120, can only react with CD4 and other molecules on the T cell's surface. Plant viruses can only attach to plant cells and cannot infect animals. This mechanism has evolved to favour those viruses that only infect cells in which they are capable of reproducing.
- Penetration follows attachment; viruses penetrate the host cell by endocytosis or by fusion with the cell.
- Uncoating happens inside the cell when the viral capsid is removed and destroyed by viral enzymes or host enzymes, thereby exposing the viral nucleic acid.
- Replication of virus particles is the stage where a cell uses viral messenger RNA in its protein synthesis systems to produce viral proteins. The RNA or DNA synthesis abilities of the cell produce the virus's DNA or RNA.
- Assembly takes place in the cell when the newly created viral proteins and nucleic acid combine to form hundreds of new virus particles.
- Release occurs when the new viruses escape or are released from the cell. Most viruses achieve this by making the cells burst, a process called lysis. Other viruses such as HIV are released more gently by a process called budding.
Effects on the host cell
The range of structural and biochemical effects that viruses have on the host cell is extensive. These are called cytopathic effects.
Most virus infections eventually result in the death of the host cell.
The causes of death include cell lysis (bursting), alterations to the
cell's surface membrane and apoptosis (cell "suicide").
Often cell death is caused by cessation of its normal activity due to
proteins produced by the virus, not all of which are components of the
virus particle.
Some viruses cause no apparent changes to the infected cell. Cells in which the virus is latent and inactive show few signs of infection and often function normally. This causes persistent infections and the virus is often dormant for many months or years. This is often the case with herpes viruses.
Some viruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus, often cause cells to proliferate without causing malignancy; but some other viruses, such as papillomavirus, are an established cause of cancer.
When a cell's DNA is damaged by a virus, and if the cell cannot repair
itself, this often triggers apoptosis. One of the results of apoptosis
is destruction of the damaged DNA by the cell itself. Some viruses have
mechanisms to limit apoptosis so that the host cell does not die before
progeny viruses have been produced; HIV, for example, does this.
Viruses and diseases
Norovirus.
Ten Norovirus particles; this RNA virus causes winter vomiting disease.
It is often in the news as a cause of gastro-enteritis on cruise ships
and in hospitals.
Common human diseases caused by viruses include the common cold, the flu, chickenpox and cold sores. Serious diseases such as Ebola and AIDS
are also caused by viruses. Many viruses cause little or no disease and
are said to be "benign". The more harmful viruses are described as virulent.
Viruses cause different diseases depending on the types of cell that they infect.
Some viruses can cause lifelong or chronic infections where the viruses continue to reproduce in the body despite the host's defence mechanisms. This is common in hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus
infections. People chronically infected with a virus are known as
carriers. They serve as important reservoirs of the virus. If there is a
high proportion of carriers in a given population, a disease is said to
be endemic.
There are many ways in which viruses spread from host to host but
each species of virus uses only one or two. Many viruses that infect
plants are carried by organisms; such organisms are called vectors.
Some viruses that infect animals, including humans, are also spread by
vectors, usually blood-sucking insects. However, direct transmission is
more common. Some virus infections, such as norovirus and rotavirus, are spread by contaminated food and water, hands and communal objects
and by intimate contact with another infected person, while others are
airborne (influenza virus). Viruses such as HIV, hepatitis B and
hepatitis C are often transmitted by unprotected sex or contaminated hypodermic needles. It is important to know how each different kind of virus is spread to prevent infections and epidemics.
Diseases of plants
Peppers infected by mild mottle virus
There are many types of plant virus, but often they only cause a loss of yield, and it is not economically viable to try to control them. Plant viruses are often spread from plant to plant by organisms (vectors). These are normally insects, but some fungi, nematode worms and single-celled organisms
have been shown to be vectors. When control of plant virus infections
is considered economical (perennial fruits, for example) efforts are
concentrated on killing the vectors and removing alternate hosts such as
weeds. Plant viruses are harmless to humans and other animals because they can only reproduce in living plant cells.
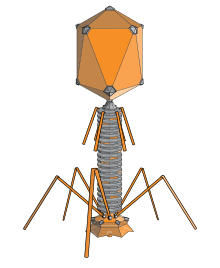
Bacteriophages
The structure of a typical bacteriophage
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria and archaea. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses officially recognises 28 genera of bacteriophages that belong to 11 families. They are important in marine ecology:
as the infected bacteria burst, carbon compounds are released back into
the environment, which stimulates fresh organic growth. Bacteriophages
are useful in scientific research because they are harmless to humans
and can be studied easily. These viruses can be a problem in industries
that produce food and drugs by fermentation
and depend on healthy bacteria. Some bacterial infections are becoming
difficult to control with antibiotics, so there is a growing interest in
the use of bacteriophages to treat infections in humans.
Host resistance
Innate immunity of animals
Animals, including humans, have many natural defences against
viruses. Some are non-specific and protect against many viruses
regardless of the type. This innate
immunity is not improved by repeated exposure to viruses and does not
retain a "memory" of the infection. The skin of animals, particularly
its surface, which is made from dead cells, prevents many types of
viruses from infecting the host. The acidity of the contents of the
stomach destroys many viruses that have been swallowed. When a virus
overcomes these barriers and enters the host, other innate defences
prevent the spread of infection in the body. A special hormone called interferon
is produced by the body when viruses are present, and this stops the
viruses from reproducing by killing the infected cell and its close
neighbours. Inside cells, there are enzymes that destroy the RNA of
viruses. This is called RNA interference. Some blood cells engulf and destroy other virus infected cells.
Adaptive immunity of animals
Two rotavirus particles: the one on the right is coated with antibodies which stop its attaching to cells and infecting them
Specific immunity to viruses develops over time and white blood cells called lymphocytes play a central role. Lymphocytes retain a "memory" of virus infections and produce many special molecules called antibodies.
These antibodies attach to viruses and stop the virus from infecting
cells. Antibodies are highly selective and attack only one type of
virus. The body makes many different antibodies, especially during the
initial infection; however, after the infection subsides, some
antibodies remain and continue to be produced, often giving the host
lifelong immunity to the virus.
Plant resistance
Plants have elaborate and effective defence mechanisms against viruses. One of the most effective is the presence of so-called resistance (R) genes.
Each R gene confers resistance to a particular virus by triggering
localised areas of cell death around the infected cell, which can often
be seen with the unaided eye as large spots. This stops the infection
from spreading. RNA interference is also an effective defence in plants. When they are infected, plants often produce natural disinfectants which destroy viruses, such as salicylic acid, nitric oxide and reactive oxygen molecules.
Resistance to bacteriophages
The
major way bacteria defend themselves from bacteriophages is by
producing enzymes which destroy foreign DNA. These enzymes, called restriction endonucleases, cut up the viral DNA that bacteriophages inject into bacterial cells.
Prevention and treatment of viral disease in humans and other animals
Vaccines
The structure of DNA showing the position of the nucleosides and the phosphorus atoms that form the "backbone" of the molecule
Vaccination is a way of preventing diseases caused by viruses.
Vaccines simulate a natural infection and its associated immune
response, but do not cause the disease. Their use has resulted in the
eradication of smallpox and a dramatic decline in illness and death caused by infections such as polio, measles, mumps and rubella. Vaccines are available to prevent over fourteen viral infections of humans and more are used to prevent viral infections of animals. Vaccines may consist of either live or killed viruses. Live vaccines contain weakened forms of the virus, but these vaccines can be dangerous when given to people with weak immunity. In these people, the weakened virus can cause the original disease.
Biotechnology and genetic engineering techniques are used to produce
"designer" vaccines that only have the capsid proteins of the virus.
Hepatitis B vaccine is an example of this type of vaccine. These vaccines are safer because they can never cause the disease.
Antiviral drugs
Since the mid 1980s, the development of antiviral drugs has increased rapidly, mainly driven by the AIDS pandemic. Antiviral drugs are often nucleoside analogues,
which are molecules very similar, but not identical to DNA building
blocks. When the replication of virus DNA begins, some of these fake
building blocks are incorporated. As soon as that happens, replication
stops prematurely—the fake building blocks lack the essential features
that allow the addition of further building blocks. Thus, DNA production
is halted, and the virus can no longer reproduce. Examples of nucleoside analogues are aciclovir for herpes virus infections and lamivudine for HIV and hepatitis B virus infections. Aciclovir is one of the oldest and most frequently prescribed antiviral drugs.
Other antiviral drugs target different stages of the viral life cycle. HIV is dependent on an enzyme called the HIV-1 protease for the virus to become infectious. There is a class of drugs called protease inhibitors, which bind to this enzyme and stop it from functioning.
Hepatitis C is caused by an RNA virus. In 80% of people infected, the disease becomes chronic,
and they remain infectious for the rest of their lives unless they are
treated. There is an effective treatment that uses the nucleoside
analogue drug ribavirin combined with interferon. Treatments for chronic carriers of the hepatitis B virus by a similar strategy using lamivudine and other anti-viral drugs have been developed. In both diseases, the drugs stop the virus from reproducing and the interferon kills any remaining infected cells.
HIV infections are usually treated with a combination of
antiviral drugs, each targeting a different stage in the virus's
life-cycle. There are drugs that prevent the virus from attaching to
cells, others that are nucleoside analogues and some poison the virus's
enzymes that it needs to reproduce. The success of these drugs is proof of the importance of knowing how viruses reproduce.
Role in ecology
Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in aquatic environments—there are about one million of them in a teaspoon of seawater—and they are essential to the regulation of saltwater and freshwater ecosystems.
Most of these viruses are bacteriophages, which are harmless to plants
and animals. They infect and destroy the bacteria in aquatic microbial
communities and this is the most important mechanism of recycling carbon
in the marine environment. The organic molecules released from the
bacterial cells by the viruses stimulate fresh bacterial and algal
growth.
Microorganisms constitute more than 90% of the biomass in the
sea. It is estimated that viruses kill approximately 20% of this biomass
each day and that there are fifteen times as many viruses in the oceans
as there are bacteria and archaea. Viruses are mainly responsible for
the rapid destruction of harmful algal blooms, which often kill other marine life.
The number of viruses in the oceans decreases further offshore and deeper into the water, where there are fewer host organisms.
Their effects are far-reaching; by increasing the amount of
respiration in the oceans, viruses are indirectly responsible for
reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by approximately
3 gigatonnes of carbon per year.
Marine mammals are also susceptible to viral infections. In 1988 and 2002, thousands of harbour seals were killed in E.