A neutron bomb, officially defined as a type of enhanced radiation weapon (ERW), is a low yield thermonuclear weapon designed to maximize lethal neutron radiation
in the immediate vicinity of the blast while minimizing the physical
power of the blast itself. The neutron release generated by a nuclear fusion reaction is intentionally allowed to escape the weapon, rather than being absorbed by its other components. The neutron burst,
which is used as the primary destructive action of the warhead, is able
to penetrate enemy armor more effectively than a conventional warhead,
thus making it more lethal as a tactical weapon.
The concept was originally developed by the US in the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was seen as a "cleaner" bomb for use against massed Soviet armored divisions. As these would be used over allied nations, notably West Germany, the reduced blast damage was seen as an important advantage.
ERWs were first operationally deployed for anti-ballistic missiles (ABM). In this role the burst of neutrons would cause nearby warheads to undergo partial fission, preventing them from exploding properly. For this to work, the ABM would have to explode within ca. 100 metres (300 ft) of its target. The first example of such a system was the W66, used on the Sprint missile used in the US's Nike-X system. It is believed the Soviet equivalent, the A-135's 53T6 missile, uses a similar design.
The weapon was once again proposed for tactical use by the US in the 1970s and 1980s, and production of the W70 began for the MGM-52 Lance in 1981. This time it experienced a firestorm of protest as the growing anti-nuclear movement gained strength through this period. Opposition was so intense that European leaders refused to accept it on their territory. President Ronald Reagan bowed to pressure and the built examples of the W70-3 remained stockpiled in the US until they were retired in 1992. The last W70 was dismantled in 2011.
The concept was originally developed by the US in the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was seen as a "cleaner" bomb for use against massed Soviet armored divisions. As these would be used over allied nations, notably West Germany, the reduced blast damage was seen as an important advantage.
ERWs were first operationally deployed for anti-ballistic missiles (ABM). In this role the burst of neutrons would cause nearby warheads to undergo partial fission, preventing them from exploding properly. For this to work, the ABM would have to explode within ca. 100 metres (300 ft) of its target. The first example of such a system was the W66, used on the Sprint missile used in the US's Nike-X system. It is believed the Soviet equivalent, the A-135's 53T6 missile, uses a similar design.
The weapon was once again proposed for tactical use by the US in the 1970s and 1980s, and production of the W70 began for the MGM-52 Lance in 1981. This time it experienced a firestorm of protest as the growing anti-nuclear movement gained strength through this period. Opposition was so intense that European leaders refused to accept it on their territory. President Ronald Reagan bowed to pressure and the built examples of the W70-3 remained stockpiled in the US until they were retired in 1992. The last W70 was dismantled in 2011.
Basic concept
In a standard thermonuclear design, a small fission bomb is placed close to a larger mass of thermonuclear fuel. The two components are then placed within a thick radiation case, usually made from uranium, lead
or steel. The case traps the energy from the fission bomb for a brief
period, allowing it to heat and compress the main thermonuclear fuel.
The case is normally made of depleted uranium or natural uranium metal, because the thermonuclear reactions give off massive numbers of high-energy neutrons
that can cause fission reactions in the casing material. These can add
considerable energy to the reaction; in a typical design as much as 50%
of the total energy comes from fission events in the casing. For this
reason, these weapons are technically known as fission-fusion-fission
designs.
In a neutron bomb, the casing material is selected either to be
transparent to neutrons or to actively enhance their production. The
burst of neutrons created in the thermonuclear reaction is then free to
escape the bomb, outpacing the physical explosion. By designing the
thermonuclear stage of the weapon carefully, the neutron burst can be
maximized while minimizing the blast itself. This makes the lethal
radius of the neutron burst greater than that of the explosion itself.
Since the neutrons disappear from the environment rapidly, such a burst
over an enemy column would kill the crews and leave the area able to be
quickly reoccupied.
Compared to a pure fission bomb with an identical explosive yield, a neutron bomb would emit about ten times the amount of neutron radiation. In a fission bomb, at sea level, the total radiation pulse energy which is composed of both gamma rays
and neutrons is approximately 5% of the entire energy released; in
neutron bombs it would be closer to 40%, with the percentage increase
coming from the higher production of neutrons. Furthermore, the neutrons
emitted by a neutron bomb have a much higher average energy level
(close to 14 MeV) than those released during a fission reaction (1–2 MeV).
Technically speaking, every low yield nuclear weapon is a
radiation weapon, including non-enhanced variants. Up to about 10
kilotons in yield, all nuclear weapons have prompt neutron radiation
as their furthest-reaching lethal component, after which yield in
regular nuclear weapons, the lethal blast and thermal effects radius
begins to out-range the lethal ionizing radiation radius.
Enhanced radiation weapons also fall into this same yield range and
simply enhance the intensity and range of the neutron dose for a given
yield.
History and deployment to present
The conception of neutron bombs is generally credited to Samuel T. Cohen of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, who developed the concept in 1958.
Initial development was carried out as part of projects Dove and
Starling, and an early device was tested underground in early 1962.
Designs of a "weaponized" version were carried out in 1963.
Development of two production designs for the army's MGM-52 Lance short-range missile began in July 1964, the W63 at Livermore and the W64 at Los Alamos.
Both entered phase three testing in July 1964, and the W64 was
cancelled in favor of the W63 in September 1964. The W63 was in turn
cancelled in November 1965 in favor of the W70 (Mod 0), a conventional design. By this time, the same concepts were being used to develop warheads for the Sprint missile, an anti-ballistic missile (ABM), with Livermore designing the W65 and Los Alamos the W66.
Both entered phase three testing in October 1965, but the W65 was
cancelled in favor of the W66 in November 1968. Testing of the W66 was
carried out in the late 1960s, and entered production in June 1974,
the first neutron bomb to do so. Approximately 120 were built, with
about 70 of these being on active duty during 1975 and 1976 as part of
the Safeguard Program. When that program was shut down they were placed in storage, and eventually decommissioned in the early 1980s.
Development of ER warheads for Lance continued, but in the early
1970s attention had turned to using modified versions of the W70, the
W70 Mod 3. Development was subsequently postponed by President Jimmy Carter in 1978 following protests against his administration's plans to deploy neutron warheads to ground forces in Europe. On November 17, 1978, in a test the USSR detonated its first similar-type bomb. President Ronald Reagan restarted production in 1981. The Soviet Union renewed a propaganda campaign against the US's neutron bomb in 1981 following Reagan's announcement. In 1983 Reagan then announced the Strategic Defense Initiative,
which surpassed neutron bomb production in ambition and vision and with
that, neutron bombs quickly faded from the center of the public's
attention.
Three types of enhanced radiation weapons (ERW) were deployed by the United States.
The W66 warhead, for the anti-ICBM Sprint missile system, was deployed
in 1975 and retired the next year, along with the missile system. The
W70 Mod 3 warhead was developed for the short-range, tactical MGM-52
Lance missile, and the W79 Mod 0 was developed for nuclear artillery shells. The latter two types were retired by President George H. W. Bush in 1992, following the end of the Cold War. The last W70 Mod 3 warhead was dismantled in 1996, and the last W79 Mod 0 was dismantled by 2003, when the dismantling of all W79 variants was completed.
According to the Cox Report,
as of 1999 the United States had never deployed a neutron weapon. The
nature of this statement is not clear; it reads "The stolen information
also includes classified design information for an enhanced radiation
weapon (commonly known as the "neutron bomb"), which neither the United
States, nor any other nation, has ever deployed."
However, the fact that neutron bombs had been produced by the US was
well known at this time and part of the public record. Cohen suggests
the report is playing with the definitions; while the US bombs were
never deployed to Europe, they remained stockpiled in the US.
In addition to the two superpowers, France and China are known to
have tested neutron or enhanced radiation bombs. France conducted an
early test of the technology in 1967 and tested an "actual" neutron bomb in 1980.
China conducted a successful test of neutron bomb principles in 1984
and a successful test of a neutron bomb in 1988. However, neither of
those countries chose to deploy neutron bombs. Chinese nuclear
scientists stated before the 1988 test that China had no need for
neutron bombs, but it was developed to serve as a "technology reserve",
in case the need arose in the future.
In August, 1999, the Indian government disclosed that India was capable of producing a neutron bomb.
Although no country is currently known to deploy them in an offensive manner, all thermonuclear dial-a-yield
warheads that have about 10 kiloton and lower as one dial option, with a
considerable fraction of that yield derived from fusion reactions, can
be considered able to be neutron bombs in use, if not in name. The only
country definitely known to deploy dedicated (that is, not dial-a-yield)
neutron warheads for any length of time is the Soviet Union/Russia, which inherited the USSR's neutron warhead equipped ABM-3 Gazelle
missile program. This ABM system contains at least 68 neutron warheads
with a 10 kiloton yield each and it has been in service since 1995, with
inert missile testing approximately every other year since then (2014).
The system is designed to destroy incoming endoatmospheric level nuclear warheads aimed at Moscow and other targets and is the lower-tier/last umbrella of the A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (NATO reporting name: ABM-3).
By 1984, according to Mordechai Vanunu, Israel was mass-producing neutron bombs.
Considerable controversy arose in the US and Western Europe following a June 1977 Washington Post
exposé describing US government plans to purchase the bomb. The article
focused on the fact that it was the first weapon specifically intended
to kill humans with radiation. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory director Harold Brown and Soviet General Secretary Leonid Brezhnev both described neutron bombs as a "capitalist bomb", because it was designed to destroy people while preserving property.
Use
The 1979 Soviet/Warsaw Pact invasion plan, "Seven Days to the River Rhine" to seize West Germany. Soviet analysts had correctly assumed that the NATO response would be to use regular tactical nuclear weapons to stop such a massive Warsaw Pact invasion.
According to proponents, neutron bombs would blunt an invasion by
Soviet tanks and armored vehicles without causing as much damage or
civilian deaths as the older nuclear weapons would. Neutron bombs would have been used if the REFORGER conventional response of NATO to the invasion was too slow or ineffective.
Neutron bombs are purposely designed with explosive yields lower than
other nuclear weapons. Since neutrons are scattered and absorbed by
air,
neutron radiation effects drop off rapidly with distance in air. As
such, there is a sharper distinction, relative to thermal effects,
between areas of high lethality and areas with minimal radiation doses. All high yield (more than c. 10 kiloton) nuclear bombs, such as the extreme example of a device that derived 97% of its energy from fusion, the 50 megaton Tsar Bomba, are not able to radiate sufficient neutrons beyond their lethal blast range when detonated as a surface burst or low altitude air burst
and so are no longer classified as neutron bombs, thus limiting the
yield of neutron bombs to a maximum of about 10 kilotons. The intense pulse of high-energy neutrons generated by a neutron bomb is the principal killing mechanism, not the fallout, heat or blast.
The inventor of the neutron bomb, Sam Cohen, criticized the
description of the W70 as a neutron bomb since it could be configured to
yield 100 kilotons:
the W-70 ... is not even remotely a "neutron bomb." Instead of being the type of weapon that, in the popular mind, "kills people and spares buildings" it is one that both kills and physically destroys on a massive scale. The W-70 is not a discriminate weapon, like the neutron bomb—which, incidentally, should be considered a weapon that "kills enemy personnel while sparing the physical fabric of the attacked populace, and even the populace too."
Although neutron bombs are commonly believed to "leave the
infrastructure intact", with current designs that have explosive yields
in the low kiloton range,
detonation in (or above) a built-up area would still cause a sizable
degree of building destruction, through blast and heat effects out to a
moderate radius, albeit considerably less destruction, than when
compared to a standard nuclear bomb of the exact same total energy release or "yield".
U.S. Army M110 howitzers in a 1984 REFORGER staging area before transport. Variants of this "dual capable" nuclear artillery howitzer would launch the W79 neutron bomb.
The Warsaw Pact tank strength was over twice that of NATO, and Soviet deep battle doctrine
was likely to be to use this numerical advantage to rapidly sweep
across continental Europe if the Cold War ever turned hot. Any weapon
that could break up their intended mass tank formation deployments and
force them to deploy their tanks in a thinner, more easily dividable manner, would aid ground forces in the task of hunting down solitary tanks and using anti-tank missiles against them, such as the contemporary M47 Dragon and BGM-71 TOW missiles, of which NATO had hundreds of thousands.
Rather than making extensive preparations for battlefield nuclear
combat in Central Europe, "The Soviet military leadership believed that
conventional superiority provided the Warsaw Pact with the means to
approximate the effects of nuclear weapons and achieve victory in Europe
without resort to those weapons."
Neutron bombs, or more precisely, enhanced [neutron] radiation
weapons were also to find use as strategic anti-ballistic missile
weapons, and in this role they are believed to remain in active service within Russia's Gazelle missile.
Effects
Wood frame house in 1953 nuclear test, 5 pounds per square inch (psi) overpressure, full collapse.
Upon detonation, a near-ground airburst of a 1 kiloton neutron bomb would produce a large blast wave and a powerful pulse of both thermal radiation and ionizing radiation, and non-ionizing radiation in the form of fast (14.1 MeV) neutrons. The thermal pulse would cause third degree burns
to unprotected skin out to approximately 500 meters. The blast would
create pressures of at least 4.6 psi out to a radius of 600 meters,
which would severely damage all non-reinforced concrete structures. At
the conventional effective combat range against modern main battle tanks and armored personnel carriers
(< 690–900 m), the blast from a 1 kt neutron bomb would destroy or
damage to the point of nonusability almost all un-reinforced civilian
buildings.
Using neutron bombs to stop an enemy armored attack by rapidly incapacitating crews with a dose of 8000+ rads of radiation
would require exploding large numbers of them to blanket the enemy
forces, destroying all normal civilian buildings within c. 600 meters of
the immediate area. Neutron activation from the explosions could make many building materials in the city radioactive, such as zinc coated steel/galvanized steel (see area denial use below).
Because liquid-filled objects like the human body are resistant to gross overpressure, the 4–5 psi blast overpressure
would cause very few direct casualties at a range of c. 600 m. The
powerful winds produced by this overpressure, however, could throw
bodies into objects or throw debris at high velocity, including window
glass, both with potentially lethal results. Casualties would be highly
variable depending on surroundings, including potential building
collapses.
The pulse of neutron radiation would cause immediate and
permanent incapacitation to unprotected outdoor humans in the open out
to 900 meters, with death occurring in one or two days. The median lethal dose (LD50) of 600 rads would extend to between 1350 and 1400 meters for those unprotected and outdoors, where approximately half of those exposed would die of radiation sickness after several weeks.
A human residing within, or simply shielded by, at least one
concrete building with walls and ceilings 30 cm (12 in) thick, or
alternatively of damp soil 24 inches thick, would receive a neutron radiation exposure reduced by a factor of 10.
Even near ground zero, basement sheltering or buildings with similar
radiation shielding characteristics would drastically reduce the
radiation dose.
Furthermore, the neutron absorption spectrum of air is disputed by some authorities, and depends in part on absorption by hydrogen from water vapor. Thus, absorption might vary exponentially with humidity, making neutron bombs far more deadly in desert climates than in humid ones.
Effectiveness in modern anti-tank role
The neutron cross section and absorption probability in barns of the two natural boron
isotopes found in nature (top curve is for 10 B and bottom curve for
11 B. As neutron energy increases to 14 MeV, the absorption
effectiveness, in general, decreases. Thus, for boron-containing armor
to be effective, fast neutrons must first be slowed by another element
by neutron scattering.
The questionable effectiveness of ER weapons against modern tanks is
cited as one of the main reasons that these weapons are no longer
fielded or stockpiled.
With the increase in average tank armor thickness since the first ER
weapons were fielded, it was argued in the March 13, 1986 New Scientist
magazine that tank armor protection was approaching the level where
tank crews would be almost fully protected from radiation effects. Thus,
for an ER weapon to incapacitate a modern tank crew through
irradiation, the weapon must be detonated at such proximity to the tank
that the nuclear explosion's blast would now be equally effective at incapacitating it and its crew. However this assertion was regarded as dubious in the 12 June, 1986 New Scientist reply by C.S. Grace, a member of the Royal Military College of Science, as neutron radiation from a 1 kiloton neutron bomb would incapacitate the crew of a tank with a protection factor
of 35 out to a range of 280 meters, but the incapacitating blast range,
depending on the exact weight of the tank, is much less, from 70 to 130
meters. However although the author did note that effective neutron absorbers and neutron poisons such as boron carbide can be incorporated into conventional armor and strap-on neutron moderating hydrogenous material (substances containing hydrogen atoms), such as explosive reactive armor, can both increase the protection factor, the author holds that in practice combined with neutron scattering, the actual average total tank area protection factor is rarely higher than 15.5 to 35. According to the Federation of American Scientists, the neutron protection factor of a "tank" can be as low as 2, without qualifying whether the statement implies a light tank, medium tank, or main battle tank.
A composite high density concrete, or alternatively, a laminated graded-Z shield, 24 units thick of which 16 units are iron and 8 units are polyethylene
containing boron (BPE), and additional mass behind it to attenuate
neutron capture gamma rays, is more effective than just 24 units of pure
iron or BPE alone, due to the advantages of both iron and BPE in
combination. During Neutron transport
Iron is effective in slowing down/scattering high-energy neutrons in
the 14-MeV energy range and attenuating gamma rays, while the hydrogen
in polyethylene is effective in slowing down these now slower fast neutrons in the few MeV range, and boron 10 has a high absorption cross section for thermal neutrons and a low production yield of gamma rays when it absorbs a neutron. The Soviet T72 tank, in response to the neutron bomb threat, is cited as having fitted a boronated polyethylene liner, which has had its neutron shielding properties simulated.
The radiation weighting factor
for neutrons of various energy has been revised over time and certain
agencies have different weighting factors, however despite the variation
amongst the agencies, from the graph, for a given energy, A fusion neutron (14.1 MeV) although more energetic, is less biologically harmful as rated in Sieverts, than a fission generated thermal neutron or a fusion neutron slowed to that energy, c. 0.8 MeV.
However, some tank armor material contains depleted uranium (DU), common in the US's M1A1 Abrams tank, which incorporates steel-encased depleted uranium armor, a substance that will fast fission when it captures a fast, fusion-generated neutron, and thus on fissioning will produce fission neutrons and fission products
embedded within the armor, products which emit among other things,
penetrating gamma rays. Although the neutrons emitted by the neutron
bomb may not penetrate to the tank crew in lethal quantities, the fast
fission of DU within the armor could still ensure a lethal environment
for the crew and maintenance personnel by fission neutron and gamma ray
exposure,
largely depending on the exact thickness and elemental composition of
the armor—information usually hard to attain. Despite this, Ducrete—which has an elemental composition similar (but not identical) to the ceramic second generation heavy metal Chobham armor of the Abrams tank—is an effective radiation shield, to both fission neutrons and gamma rays due to it being a graded Z material.
Uranium, being about twice as dense as lead, is thus nearly twice as
effective at shielding gamma ray radiation per unit thickness.
Use against ballistic missiles
As
an anti-ballistic missile weapon, the first fielded ER warhead, the
W66, was developed for the Sprint missile system as part of the
Safeguard Program to protect United States cities and missile silos from incoming Soviet warheads.
A problem faced by Sprint and similar ABMs was that the blast
effects of their warheads change greatly as they climb and the
atmosphere thins out. At higher altitudes, starting around 60,000 feet
(18,000 m) and above, the blast effects begin to drop off rapidly as the
air density becomes very low. This can be countered by using a larger
warhead, but then it becomes too powerful when used at lower altitudes.
An ideal system would use a mechanism that was less sensitive to changes
in air density.
Neutron-based attacks offer one solution to this problem. The
burst of neutrons released by an ER weapon can induce fission in the
fissile materials of primary in the target warhead. The energy released
by these reactions may be enough to melt the warhead, but even at lower
fission rates the "burning up" of some of the fuel in the primary can
cause it to fail to explode properly, or "fizzle".
Thus a small ER warhead can be effective across a wide altitude band,
using blast effects at lower altitudes and the increasingly long-ranged
neutrons as the engagement rises.
The use of neutron-based attacks was discussed as early as the 1950s, with the US Atomic Energy Commission mentioning weapons with a "clean, enhanced neutron output" for use as "antimissile defensive warheads."
Studying, improving and defending against such attacks was a major area
of research during the 1950s and 60s. A particular example of this is
the US Polaris A-3
missile, which delivered three warheads travelling on roughly the same
trajectory, and thus with a short distance between them. A single ABM
could conceivably destroy all three through neutron flux. Developing
warheads that were less sensitive to these attacks was a major area of
research in the US and UK during the 1960s.
Some sources claim that the neutron flux attack was also the main
design goal of the various nuclear-tipped anti-aircraft weapons like
the AIM-26 Falcon and CIM-10 Bomarc. One F-102 pilot noted:
GAR-11/AIM-26 was primarily a weapon-killer. The bomber(s, if any) was collateral damage. The weapon was proximity-fused to ensure detonation close enough so an intense flood of neutrons would result in an instantaneous nuclear reaction (NOT full-scale) in the enemy weapon’s pit; rendering it incapable of functioning as designed...[O]ur first “neutron bombs” were the GAR-11 and MB-1 Genie.
It has also been suggested that neutron flux's effects on the warhead
electronics are another attack vector for ER warheads in the ABM role. Ionization greater than 5,000 rads in silicon chips delivered over seconds to minutes will degrade the function of semiconductors for long periods.
However, while such attacks might be useful against guidance systems
which used relatively advanced electronics, in the ABM role these
components have long ago separated from the warheads by the time they
come within range of the interceptors. The electronics in the warheads
themselves tend to be very simple, and hardening them was one of the
many issues studied in the 1960s.
Lithium-6 hydride
(Li6H) is cited as being used as a countermeasure to reduce the
vulnerability and "harden" nuclear warheads from the effects of
externally generated neutrons.
Radiation hardening
of the warhead's electronic components as a countermeasure to high
altitude neutron warheads somewhat reduces the range that a neutron
warhead could successfully cause an unrecoverable glitch by the transient radiation effects on electronics (TREE) effects.
At very high altitudes, at the edge of the atmosphere and above it, another effect comes into play. At lower altitudes, the x-rays generated by the bomb are absorbed by the air and have mean free paths
on the order of meters. But as the air thins out, the x-rays can travel
further, eventually outpacing the area of effect of the neutrons. In
exoatmospheric explosions, this can be on the order of 10 kilometres
(6.2 mi) in radius. In this sort of attack, it is the x-rays promptly
delivering energy on the warhead surface that is the active mechanism;
the rapid ablation (or "blow off") of the surface creates shock waves
that can break up the warhead.
Use as an area denial weapon
In November 2012, during the planning stages of Operation Hammer of God, British Labour peer Lord Gilbert
suggested that multiple enhanced radiation reduced blast (ERRB)
warheads could be detonated in the mountain region of the
Afghanistan-Pakistan border to prevent infiltration. He proposed to warn the inhabitants to evacuate, then irradiate the area, making it unusable and impassable. Used in this manner, the neutron bomb(s), regardless of burst height, would release neutron activated casing materials used in the bomb, and depending on burst height, create radioactive soil activation products.
In much the same fashion as the area denial effect resulting from fission product (the substances that make up most fallout) contamination in an area following a conventional surface burst nuclear explosion, as considered in the Korean War by Douglas MacArthur, it would thus be a form of radiological warfare—with
the difference that neutron bombs produce half, or less, of the
quantity of fission products relative to the same-yield pure fission bomb. Radiological warfare with neutron bombs that rely on fission primaries would thus still produce fission fallout, albeit a comparatively cleaner
and shorter lasting version of it in the area than if air bursts were
used, as little to no fission products would be deposited on the direct
immediate area, instead becoming diluted global fallout.
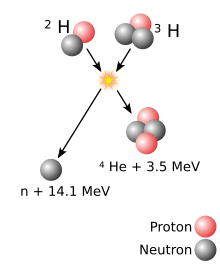
The easiest to achieve fusion reaction, of deuterium ("D) with tritium (T") creating helium-4, freeing a neutron, and releasing only 3.5 MeV in the form of kinetic energy as the charged alpha particle that will inherently generate heat(which
manifests as blast and thermal effects), while the majority of the
energy of the reaction(14.1 MeV) is carried away by the uncharged fast neutron. Devices with a higher proportion of yield derived from this reaction would be more efficient in the stand-off asteroid impact avoidance role, due to the penetrative depth of fast-neutrons and the resulting higher momentum transfer
that is produced in this "scabbing" of a much larger mass of material
free from the main body, as opposed to the shallower surface penetration
and ablation of regolith, that is produced by thermal/soft X-rays.
However the most effective use of a neutron bomb with respect to area
denial would be to encase it in a thick shell of material that could be
neutron activated, and use a surface burst. In this manner the neutron
bomb would be turned into a salted bomb; a case of zinc-64, produced as a byproduct of depleted zinc oxide
enrichment, would for example probably be the most attractive for
military use, as when activated, the zinc-65 so formed is a gamma
emitter, with a half life of 244 days.
Hypothetical effects of a pure fusion bomb
With considerable overlap between the two devices, the prompt radiation effects of a pure fusion weapon
would similarly be much higher than that of a pure-fission device:
approximately twice the initial radiation output of current standard
fission-fusion-based weapons. In common with all neutron bombs that must
presently derive a small percentage of trigger energy from fission, in
any given yield a 100% pure fusion bomb would likewise generate a more
diminutive atmospheric blast wave than a pure-fission bomb. The
latter fission device has a higher kinetic energy-ratio per unit of
reaction energy released, which is most notable in the comparison with
the D-T fusion reaction. A larger percentage of the energy from a D-T
fusion reaction, is inherently put into uncharged neutron generation as
opposed to charged particles, such as the alpha particle of the D-T reaction, the primary species, that is most responsible for the coulomb explosion/fireball.