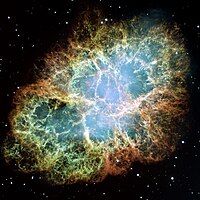
The Crab Nebula is a pulsar wind nebula associated with the 1054 supernova.
The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 AD, when supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.
Since the development of the telescope,
the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These
occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies.
Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and
the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly
understood.
Early history
The guest star reported by Chinese astronomers in 1054 is identified as SN 1054. The highlighted passages refer to the supernova.
The supernova explosion that formed the Vela Supernova Remnant most likely occurred 10,000–20,000 years ago. In 1976, NASA astronomers suggested that inhabitants of the southern hemisphere may have witnessed this explosion and recorded it symbolically. A year later, archaeologist George Michanowsky recalled some incomprehensible ancient markings in Bolivia that were left by Native Americans.
The carvings showed four small circles flanked by two larger circles.
The smaller circles resemble stellar groupings in the constellations Vela and Carina. One of the larger circles may represent the star Capella.
Another circle is located near the position of the supernova remnant,
George Michanowsky suggested this may represent the supernova explosion
as witnessed by the indigenous residents.
In 185 CE, Chinese astronomers
recorded the appearance of a bright star in the sky, and observed that
it took about eight months to fade from the sky. It was observed to
sparkle like a star and did not move across the heavens like a comet.
These observations are consistent with the appearance of a supernova,
and this is believed to be the oldest confirmed record of a supernova
event by humankind. SN 185 may have also possibly been recorded in Roman literature, though no records have survived.
The gaseous shell RCW 86 is suspected as being the remnant of this
event, and recent X-ray studies show a good match for the expected age.
In 393 CE, the Chinese recorded the appearance of another "guest star", SN 393, in the modern constellation of Scorpius. Additional unconfirmed supernovae events may have been observed in 369 CE, 386 CE,
437 CE, 827 CE and 902 CE.
However these have not yet been associated with a supernova remnant,
and so they remain only candidates. Over a span of about 2,000 years,
Chinese astronomers recorded a total of twenty such candidate events,
including later explosions noted by Islamic, European, and possibly
Indian and other observers.
The supernova SN 1006 appeared in the southern constellation of Lupus
during the year 1006 CE. This was the brightest recorded star ever to
appear in the night sky, and its presence was noted in China, Egypt, Iraq, Italy, Japan and Switzerland. It may also have been noted in France, Syria, and North America. Egyptian physician, astronomer and astrologer Ali ibn Ridwan
gave the brightness of this star as one-quarter the brightness of the
Moon. Modern astronomers have discovered the faint remnant of this
explosion and determined that it was only 7,100 light-years from the Earth.
Supernova SN 1054 was another widely observed event, with Arab, Chinese, and Japanese astronomers recording the star's appearance in 1054 CE. It may also have been recorded by the Anasazi as a petroglyph. This explosion appeared in the constellation of Taurus, where it produced the Crab Nebula remnant. At its peak, the luminosity of SN 1054 may have been four times as bright as Venus, and it remained visible in daylight for 23 days and was visible in the night sky for 653 days.
There are fewer records of supernova SN 1181, which occurred in the constellation Cassiopeia just over a century after SN 1054. It was noted by Chinese and Japanese astronomers, however. The pulsar 3C58 may be the stellar relic from this event.
The Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe was noted for his careful observations of the night sky from his observatory on the island of Hven. In 1572 he noted the appearance of a new star, also in the constellation Cassiopeia. Later called SN 1572, this
supernova was associated with a remnant during the 1960s.
A common belief in Europe during this period was the Aristotelian idea that the world beyond the Moon and planets was immutable.
So observers argued that the phenomenon was something in the Earth's
atmosphere. However Tycho noted that the object remained stationary from
night to night—never changing its parallax—so it must lie far away. He published his observations in the small book De nova et nullius aevi memoria prius visa stella (Latin for "Concerning the new and previously unseen star") in 1573. It is from the title of this book that the modern word nova for cataclysmic variable stars is derived.
Multiwavelength X-ray image of the remnant of Kepler's Supernova, SN 1604. (Chandra X-ray Observatory)
The most recent supernova to be seen in the Milky Way galaxy was SN 1604, which was observed October 9, 1604. Several people, including Johannes van Heeck, noted the sudden appearance of this star, but it was Johannes Kepler who became noted for his systematic study of the object. He published his observations in the work De Stella nova in pede Serpentarii.
Galileo,
like Tycho before him, tried in vain to measure the parallax of this
new star, and then argued against the Aristotelian view of an immutable
heavens. The remnant of this supernova was identified in 1941 at the Mount Wilson Observatory.
Telescope observation
The
true nature of the supernova remained obscure for some time. Observers
slowly came to recognize a class of stars that undergo long-term
periodic fluctuations in luminosity. Both John Russell Hind in 1848 and Norman Pogson
in 1863 had charted stars that underwent sudden changes in brightness.
However, these received little attention from the astronomical
community. Finally, in 1866, English astronomer William Huggins
made the first spectroscopic observations of a nova, discovering lines
of hydrogen in the unusual spectrum of the recurrent nova T Coronae Borealis. Huggins proposed a cataclysmic explosion as the underlying mechanism, and his efforts drew interest from other astronomers.
Animation
showing the sky position of supernovae discovered since 1885. Some
recent survey contributions are highlighted in color.
In 1885, a nova-like outburst was observed in the direction of the Andromeda Galaxy by Ernst Hartwig in Estonia. S Andromedae increased to 6th magnitude, outshining the entire nucleus of the galaxy, then faded in a manner much like a nova. In 1917, George W. Ritchey
measured the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy and discovered it lay
much farther than had previously been thought. This meant that S
Andromedae, which did not just lie along the line of sight to the galaxy
but had actually resided in the nucleus, released a much greater amount
of energy than was typical for a nova.
Early work on this new category of nova was performed during the 1930s by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky at Mount Wilson Observatory.
They identified S Andromedae, what they considered a typical supernova,
as an explosive event that released radiation approximately equal to
the Sun's total energy output for 107 years. They decided to
call this new class of cataclysmic variables super-novae, and postulated
that the energy was generated by the gravitational collapse of ordinary
stars into neutron stars. The name super-novae was first used in a 1931 lecture at Caltech by Zwicky, then used publicly in 1933 at a meeting of the American Physical Society. By 1938, the hyphen had been lost and the modern name was in use.
Although supernovae are relatively rare events, occurring on average about once every 50 years in the Milky Way,
observations of distant galaxies allowed supernovae to be discovered
and examined more frequently. The first supernova detection patrol was
begun by Zwicky in 1933. He was joined by Josef J. Johnson from Caltech in 1936. Using a 45-cm Schmidt telescope at Palomar observatory,
they discovered twelve new supernovae within three years by comparing
new photographic plates to reference images of extragalactic regions.
In 1938, Walter Baade became the first astronomer to identify a nebula as a supernova remnant when he suggested that the Crab Nebula was the remains of SN 1054. He noted that, while it had the appearance of a planetary nebula, the measured velocity of expansion was much too large to belong to that classification.
During the same year, Baade first proposed the use of the Type Ia
supernova as a secondary distance indicator. Later, the work of Allan Sandage and Gustav Tammann helped refine the process so that Type Ia supernovae became a type of standard candle for measuring large distances across the cosmos.
The first spectral classification of these distant supernovae was performed by Rudolph Minkowski
in 1941. He categorized them into two types, based on whether or not
lines of the element hydrogen appeared in the supernova spectrum.
Zwicky later proposed additional types III, IV, and V, although these
are no longer used and now appear to be associated with single peculiar
supernova types. Further sub-division of the spectra categories resulted
in the modern supernova classification scheme.
In the aftermath of the Second World War, Fred Hoyle
worked on the problem of how the various observed elements in the
universe were produced. In 1946 he proposed that a massive star could
generate the necessary thermonuclear reactions, and the nuclear
reactions of heavy elements were responsible for the removal of energy
necessary for a gravitational collapse to occur. The collapsing star
became rotationally unstable, and produced an explosive expulsion of
elements that were distributed into interstellar space. The concept that rapid nuclear fusion was the source of energy for a supernova explosion was developed by Hoyle and William Fowler during the 1960s.
The first computer-controlled search for supernovae was begun in the 1960s at Northwestern University. They built a 24-inch telescope at Corralitos Observatory in New Mexico
that could be repositioned under computer control. The telescope
displayed a new galaxy each minute, with observers checking the view on a
television screen. By this means, they discovered 14 supernovae over a
period of two years.
1970–1999
The modern standard model for Type Ia supernovae
explosions is founded on a proposal by Whelan and Iben in 1973, and is
based upon a mass-transfer scenario to a degenerate companion star. In particular, the light curve of SN1972e in NGC 5253,
which was observed for more than a year, was followed long enough to
discover that after its broad "hump" in brightness, the supernova faded
at a nearly constant rate of about 0.01 magnitudes per day. Translated to another system of units, this is nearly the same as the decay rate of cobalt-56 (56Co), whose half-life is 77 days. The degenerate explosion model predicts the production of about a solar mass of nickel-56 (56Ni) by the exploding star. The 56Ni decays with a half-life of 6.8 days to 56Co,
and the decay of the nickel and cobalt provides the energy radiated
away by the supernova late in its history. The agreement in both total
energy production and the fade rate between the theoretical models and
the observations of 1972e led to rapid acceptance of the
degenerate-explosion model.
Through observation of the light curves of many Type Ia
supernovae, it was discovered that they appear to have a common peak
luminosity.
By measuring the luminosity of these events, the distance to their host
galaxy can be estimated with good accuracy. Thus this category of
supernovae has become highly useful as a standard candle
for measuring cosmic distances. In 1998, the High-Z Supernova Search
and the Supernova Cosmology Project discovered that the most distant
Type Ia supernovae appeared dimmer than expected. This has provided
evidence that the expansion of the universe may be accelerating.
Although no supernova has been observed in the Milky Way since
1604, it appears that a supernova exploded in the constellation
Cassiopeia about 300 years ago, around the year 1667 or 1680. The
remnant of this explosion, Cassiopeia A—is
heavily obscured by interstellar dust, which is possibly why it did not
make a notable appearance. However it can be observed in other parts of
the spectrum, and it is currently the brightest radio source beyond our
solar system.
Supernova 1987A remnant near the center
In 1987, Supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud was observed within hours of its start. It was the first supernova to be detected through its neutrino emission and the first to be observed across every band of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The relative proximity of this supernova has allowed detailed
observation, and it provided the first opportunity for modern theories
of supernova formation to be tested against observations.
The rate of supernova discovery steadily increased throughout the twentieth century.
In the 1990s, several automated supernova search programs were
initiated. The Leuschner Observatory Supernova Search program was begun
in 1992 at Leuschner Observatory. It was joined the same year by the Berkeley Automated Imaging Telescope program. These were succeeded in 1996 by the Katzman Automatic Imaging Telescope at Lick Observatory,
which was primarily used for the Lick Observatory Supernova Search
(LOSS). By 2000, the Lick program resulted in the discovery of 96
supernovae, making it the world's most successful Supernova search
program.
In the late 1990s it was proposed that recent supernova remnants could be found by looking for gamma rays from the decay of titanium-44.
This has a half-life of 90 years and the gamma rays can traverse the
galaxy easily, so it permits us to see any remnants from the last
millennium or so. Two sources were found, the previously discovered Cassiopeia A remnant, and the RX J0852.0-4622 remnant, which had just been discovered overlapping the Vela Supernova Remnant
In 1999 a star within IC 755 was seen to explode as a supernova and named SN 1999an.
This remnant (RX J0852.0-4622) had been found in front (apparently) of the larger Vela Supernova Remnant.
The gamma rays from the decay of titanium-44 showed that it must have
exploded fairly recently (perhaps around 1200 AD), but there is no
historical record of it. The flux of gamma rays and x-rays indicates
that the supernova was relatively close to us (perhaps 200 parsecs or
600 ly). If so, this is a surprising event because supernovae less than
200 parsecs away are estimated to occur less than once per 100,000
years.
2000 to present
Cosmic lens MACS J1720+35 helps Hubble to find a distant supernova.
The "SN 2003fg"
was discovered in a forming galaxy in 2003. The appearance of this
supernova was studied in "real-time", and it has posed several major
physical questions as it seems more massive than the Chandrasekhar limit would allow.
First observed in September 2006, the supernova SN 2006gy, which occurred in a galaxy called NGC 1260 (240 million light-years away), is the largest and, until confirmation of luminosity of SN 2005ap
in October 2007, the most luminous supernova ever observed. The
explosion was at least 100 times more luminous than any previously
observed supernova, with the progenitor star being estimated 150 times more massive than the Sun. Although this had some characteristics of a Type Ia supernova, Hydrogen was found in the spectrum. It is thought that SN 2006gy is a likely candidate for a pair-instability supernova. SN 2005ap, which was discovered by Robert Quimby
who also discovered SN 2006gy, was about twice as bright as SN 2006gy
and about 300 times as bright as a normal type II supernova.
Host Galaxies of Calcium-Rich Supernovae.
On May 21, 2008, astronomers announced that they had for the first
time caught a supernova on camera just as it was exploding. By chance, a
burst of X-rays was noticed while looking at galaxy NGC 2770,
88 million light-years from Earth, and a variety of telescopes were
aimed in that direction just in time to capture what has been named SN 2008D. "This eventually confirmed that the big X-ray blast marked the birth of a supernova," said Alicia Soderberg of Princeton University.
One of the many amateur astronomers looking for supernovae, Caroline Moore, a member of the Puckett Observatory Supernova Search Team, found supernova SN 2008ha late November 2008. At the age of 14 she had been declared the youngest person ever to find a supernova.
However, in January 2011, 10-year-old Kathryn Aurora Gray from Canada
was reported to have discovered a supernova, making her the youngest
ever to find a supernova. Mr. Gray, her father, and a friend spotted SN 2010lt, a magnitude 17 supernova in galaxy UGC 3378 in the constellation Camelopardalis, about 240 million light years away.
Supernova SN 2012cg in spiral galaxy NGC 4424.
In 2009, researchers have found nitrates in ice cores
from Antarctica at depths corresponding to the known supernovae of 1006
and 1054 AD, as well as from around 1060 AD. The nitrates were
apparently formed from nitrogen oxides
created by gamma rays from the supernovae. This technique should be
able to detect supernovae going back several thousand years.
On November 15, 2010, astronomers using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory announced that, while viewing the remnant of SN 1979C in the galaxy Messier 100, they have discovered an object which could be a young, 30-year-old black hole. NASA also noted the possibility this object could be a spinning neutron star producing a wind of high energy particles.
On August 24, 2011, the Palomar Transient Factory automated survey discovered a new Type Ia supernova (SN 2011fe)
in the Pinwheel Galaxy (M101) shortly after it burst into existence.
Being only 21 million lightyears away and detected so early after the
event started, it will allow scientists to learn more about the early
developments of these types of supernovae.
On 16 March 2012, a Type II supernova, designated as SN 2012aw, was discovered in M95.
On January 22, 2014, students at the University of London Observatory spotted an exploding star SN 2014J
in the nearby galaxy M82 (the Cigar Galaxy). At a distance of around
12 million light years, the supernova is one of the nearest to be
observed in recent decades.
Future
The
estimated rate of supernova production in a galaxy the size of the Milky
Way is about twice per century. This is much higher than the actual
observed rate, implying that a portion of these events have been
obscured from the Earth by interstellar dust. The deployment of new
instruments that can observe across a wide range of the electromagnetic spectrum, along with neutrino detectors, means that the next such event will almost certainly be detected.
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) is predicted to discover three to four million supernovae during its ten-year survey, over a broad range of distances.