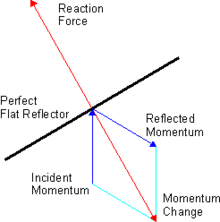
Force on a reflector results from reflecting the photon flux
Radiation pressure is the pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength which is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules).
The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too
small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are
important in some physical processes. This particularly includes objects
in outer space
where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity,
and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative
effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the
sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the Viking program been ignored, the spacecraft would have missed Mars orbit by about 15,000 km (9,300 mi). Radiation pressure from starlight is crucial in a number of astrophysical
processes as well. The significance of radiation pressure increases
rapidly at extremely high temperatures, and can sometimes dwarf the
usual gas pressure, for instance in stellar interiors and thermonuclear weapons.
The radiation pressure of sunlight on earth is equivalent to that
exerted by about a thousandth of a gram on an area of 1 square metre
(measured in units of force: approx. 10 μN/m2).
Radiation pressure can equally well be accounted for by
considering the momentum of a classical electromagnetic field or in
terms of the momenta of photons, particles of light. The interaction of electromagnetic waves or photons with matter may involve an exchange of momentum. Due to the law of conservation of momentum,
any change in the total momentum of the waves or photons must involve
an equal and opposite change in the momentum of the matter it interacted
with (Newton's third law of motion),
as is illustrated in the accompanying figure for the case of light
being perfectly reflected by a surface. This transfer of momentum is the
general explanation for what we term radiation pressure.
Discovery
Johannes Kepler put forward the concept of radiation pressure back in 1619 to explain the observation that a tail of a comet always points away from the Sun.
The assertion that light, as electromagnetic radiation, has the property of momentum and thus exerts a pressure upon any surface it is exposed to was published by James Clerk Maxwell in 1862, and proven experimentally by Russian physicist Pyotr Lebedev in 1900 and by Ernest Fox Nichols and Gordon Ferrie Hull in 1901.
The pressure is very feeble, but can be detected by allowing the
radiation to fall upon a delicately poised vane of reflective metal in a
Nichols radiometer (this should not be confused with the Crookes radiometer, whose characteristic motion is not caused by radiation pressure but by impacting gas molecules).
Theory
Radiation pressure can be viewed as a consequence of the conservation of momentum
given the momentum attributed to electromagnetic radiation. That
momentum can be equally well calculated on the basis of electromagnetic
theory or from the combined momenta of a stream of photons, giving
identical results as is shown below.
Radiation pressure from momentum of an electromagnetic wave
According to Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism, an electromagnetic
wave carries momentum, which will be transferred to an opaque surface
it strikes.
The energy flux (irradiance) of a plane wave is calculated using the Poynting vector , whose magnitude we denote by S. S divided by the speed of light
is the density of the linear momentum per unit area (pressure) of the
electromagnetic field. So, dimensionally, the Poynting vector is
S=(power/area)=(rate of doing work/area)=(ΔF/Δt)Δx/area, which is the
speed of light, c=Δx/Δt, times pressure, ΔF/area. That pressure is
experienced as radiation pressure on the surface:
where is pressure (usually in Pascals), is the incident irradiance (usually in W/m2) and is the speed of light in vacuum.
If the surface is planar at an angle α to the incident wave, the
intensity across the surface will be geometrically reduced by the cosine
of that angle and the component of the radiation force against the
surface will also be reduced by the cosine of α, resulting in a
pressure:
The momentum from the incident wave is in the same direction of that
wave. But only the component of that momentum normal to the surface
contributes to the pressure on the surface, as given above. The
component of that force tangent to the surface is not called pressure.
Radiation pressure from reflection
The
above treatment for an incident wave accounts for the radiation
pressure experienced by a black (totally absorbing) body. If the wave is
specularly reflected,
then the recoil due to the reflected wave will further contribute to
the radiation pressure. In the case of a perfect reflector, this
pressure will be identical to the pressure caused by the incident wave:
thus doubling the net radiation pressure on the surface:
For a partially reflective surface, the second term must be
multiplied by the reflectivity (also known as reflection coefficient of
intensity), so that the increase is less than double. For a diffusely reflective
surface, the details of the reflection and geometry must be taken into
account, again resulting in an increased net radiation pressure of less
than double.
Radiation pressure by emission
Just
as a wave reflected from a body contributes to the net radiation
pressure experienced, a body that emits radiation of its own (rather
than reflected) obtains a radiation pressure again given by the
irradiance of that emission in the direction normal to the surface Ie:
The emission can be from black-body radiation
or any other radiative mechanism. Since all materials emit black-body
radiation (unless they are totally reflective or at absolute zero), this
source for radiation pressure is ubiquitous but usually very tiny.
However, because black-body radiation increases rapidly with temperature
(according to the fourth power of temperature as given by the Stefan–Boltzmann law),
radiation pressure due to the temperature of a very hot object (or due
to incoming black-body radiation from similarly hot surroundings) can
become very significant. This becomes important in stellar interiors
which are at millions of degrees.
Radiation pressure in terms of photons
Electromagnetic radiation can be viewed in terms of particles rather than waves; these particles are known as photons.
Photons do not have a rest-mass; however, photons are never at rest
(they move at the speed of light) and acquire a momentum nonetheless
which is given by:
where p is momentum, h is Planck's constant, λ is wavelength, and c is speed of light in vacuum. And Ep is the energy of a single photon given by:
The radiation pressure again can be seen as the transfer of each
photon's momentum to the opaque surface, plus the momentum due to a
(possible) recoil photon for a (partially) reflecting surface. Since an
incident wave of irradiance If over an area A has a power of IfA, this implies a flux of If/Ep
photons per second per unit area striking the surface. Combining this
with the above expression for the momentum of a single photon, results
in the same relationships between irradiance and radiation pressure
described above using classical electromagnetics. And again, reflected
or otherwise emitted photons will contribute to the net radiation
pressure identically.
Compression in a uniform radiation field
In general, the pressure of electromagnetic waves can be obtained from the vanishing of the trace of the electromagnetic stress tensor: Since this trace equals 3P – u, we get
where u is the radiation density per unit volume.
This can also be shown in the specific case of the pressure exerted on surfaces of a body in thermal equilibrium with its surroundings, at a temperature T: The body will be surrounded by a uniform radiation field described by the Planck black-body radiation law,
and will experience a compressive pressure due to that impinging
radiation, its reflection, and its own black body emission. From that it
can be shown that the resulting pressure is equal to one third of the
total radiant energy per unit volume in the surrounding space.
By using Stefan–Boltzmann law, this can be expressed as
where is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
Solar radiation pressure
Solar radiation pressure is due to the sun's radiation at closer distances, thus especially within the Solar System.
While it acts on all objects, its net effect is generally greater on
smaller bodies since they have a larger ratio of surface area to mass.
All spacecraft experience such a pressure except when they are behind
the shadow of a larger orbiting body.
Solar radiation pressure on objects near the earth may be calculated using the sun's irradiance at 1 AU, known as the solar constant or GSC, whose value is set at 1361 W/m2 as of 2011.
All stars have a spectral energy distribution that depends on their surface temperature. The distribution is approximately that of black-body radiation.
This distribution must be taken into account when calculating the
radiation pressure or identifying reflector materials for optimizing a solar sail for instance.
Pressures of absorption and reflection
Solar radiation pressure at the earth's distance from the sun, may be calculated by dividing the solar constant GSC (above) by the speed of light c. For an absorbing sheet facing the sun, this is simply:
This result is in the S.I. unit Pascals, equivalent to N/m2 (newtons per square meter). For a sheet at an angle α to the sun, the effective area A of a sheet is reduced by a geometrical factor resulting in a force in the direction of the sunlight of:
To find the component of this force normal to the surface, another cosine factor must be applied resulting in a pressure P on the surface of:
Note, however, that in order to account for the net effect of solar
radiation on a spacecraft for instance, one would need to consider the total
force (in the direction away from the sun) given by the preceding
equation, rather than just the component normal to the surface that we
identify as "pressure".
The solar constant is defined for the sun's radiation at the distance to the earth, also known as one astronomical unit (AU). Consequently, at a distance of R astronomical units (R thus being dimensionless), applying the inverse-square law, we would find:
Finally, considering not an absorbing but a perfectly reflecting surface, the pressure is doubled due to the reflected wave, resulting in:
Note that unlike the case of an absorbing material, the resulting
force on a reflecting body is given exactly by this pressure acting
normal to the surface, with the tangential forces from the incident and
reflecting waves canceling each other. In practice, materials are
neither totally reflecting nor totally absorbing, so the resulting force
will be a weighted average of the forces calculated using these
formulae.
| Distance from sun | Radiation pressure in μPa (μN/m2) |
|---|---|
| 0.20 AU | 227 |
| 0.39 AU (Mercury) | 60.6 |
| 0.72 AU (Venus) | 17.4 |
| 1.00 AU (Earth) | 9.08 |
| 1.52 AU (Mars) | 3.91 |
| 3.00 AU (Typical asteroid) | 1.01 |
| 5.20 AU (Jupiter) | 0.34 |
Radiation pressure perturbations
Solar radiation pressure is a source of orbital perturbations. It significantly affects the orbits and trajectories of small bodies including all spacecraft.
Solar radiation pressure affects bodies throughout much of the
Solar System. Small bodies are more affected than large ones because of
their lower mass relative to their surface area. Spacecraft are
affected along with natural bodies (comets, asteroids, dust grains, gas
molecules).
The radiation pressure results in forces and torques on the
bodies that can change their translational and rotational motions.
Translational changes affect the orbits of the bodies. Rotational rates
may increase or decrease. Loosely aggregated bodies may break apart
under high rotation rates. Dust grains can either leave the Solar
System or spiral into the Sun.
A whole body is typically composed of numerous surfaces that have
different orientations on the body. The facets may be flat or curved.
They will have different areas. They may have optical properties
differing from other aspects.
At any particular time, some facets will be exposed to the Sun
and some will be in shadow. Each surface exposed to the Sun will be
reflecting, absorbing, and emitting radiation. Facets in shadow will be
emitting radiation. The summation of pressures across all of the
facets will define the net force and torque on the body. These can be
calculated using the equations in the preceding sections.
The Yarkovsky effect
affects the translation of a small body. It results from a face
leaving solar exposure being at a higher temperature than a face
approaching solar exposure. The radiation emitted from the warmer face
will be more intense than that of the opposite face, resulting in a net
force on the body that will affect its motion.
The YORP effect
is a collection of effects expanding upon the earlier concept of the
Yarkovsky effect, but of a similar nature. It affects the spin
properties of bodies.
The Poynting–Robertson effect
applies to grain-size particles. From the perspective of a grain of
dust circling the Sun, the Sun's radiation appears to be coming from a
slightly forward direction (aberration of light).
Therefore, the absorption of this radiation leads to a force with a
component against the direction of movement. (The angle of aberration is
tiny since the radiation is moving at the speed of light while the dust
grain is moving many orders of magnitude slower than that.) The result
is a gradual spiral of dust grains into the Sun. Over long periods of
time, this effect cleans out much of the dust in the Solar System.
While rather small in comparison to other forces, the radiation
pressure force is inexorable. Over long periods of time, the net effect
of the force is substantial. Such feeble pressures can produce marked
effects upon minute particles like gas ions and electrons, and are essential in the theory of electron emission from the Sun, of cometary material, and so on.
Because the ratio of surface area to volume (and thus mass) increases with decreasing particle size, dusty (micrometre-size) particles are susceptible to radiation pressure even in the outer solar system. For example, the evolution of the outer rings of Saturn is significantly influenced by radiation pressure.
As a consequence of light pressure, Einstein
in 1909 predicted the existence of "radiation friction" which would
oppose the movement of matter. He wrote, "radiation will exert pressure
on both sides of the plate. The forces of pressure exerted on the two
sides are equal if the plate is at rest. However, if it is in motion,
more radiation will be reflected on the surface that is ahead during the
motion (front surface) than on the back surface. The backward acting
force of pressure exerted on the front surface is thus larger than the
force of pressure acting on the back. Hence, as the resultant of the two
forces, there remains a force that counteracts the motion of the plate
and that increases with the velocity of the plate. We will call this
resultant 'radiation friction' in brief."
Solar sails
Solar sailing, an experimental method of spacecraft propulsion, uses radiation pressure from the Sun as a motive force. The idea of interplanetary travel by light was mentioned by Jules Verne in From the Earth to the Moon.
A sail reflects about 90% of the incident radiation. The 10%
that is absorbed is radiated away from both surfaces, with the
proportion emitted from the unlit surface depending on the thermal
conductivity of the sail. A sail has curvature, surface irregularities,
and other minor factors that affect its performance.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has successfully unfurled a solar sail in space which has already succeeded in propelling its payload with the IKAROS project.
Cosmic effects of radiation pressure
Radiation
pressure has had a major effect on the development of the cosmos, from
the birth of the universe to ongoing formation of stars and shaping of
clouds of dust and gasses on a wide range of scales.
The early universe
The photon epoch is a phase when the energy of the universe was dominated by photons, between 10 seconds and 380,000 years after the Big Bang.
Galaxy formation and evolution
The process of galaxy formation and evolution
began early in the history of the cosmos. Observations of the early
universe strongly suggest that objects grew from bottom-up (i.e.,
smaller objects merging to form larger ones). As stars are thereby
formed and become sources of electromagnetic radiation, radiation
pressure from the stars becomes a factor in the dynamics of remaining circumstellar material.
Clouds of dust and gases
The Pillars of Creation clouds within the Eagle Nebula shaped by radiation pressure and stellar winds.
The gravitational compression
of clouds of dust and gases is strongly influenced by radiation
pressure, especially when the condensations lead to star births. The
larger young stars forming within the compressed clouds emit intense
levels of radiation that shift the clouds, causing either dispersion or
condensations in nearby regions, which influences birth rates in those
nearby regions.
Clusters of stars
Stars predominantly form in regions of large clouds of dust and gases, giving rise to star clusters.
Radiation pressure from the member stars eventually disperses the
clouds, which can have a profound effect on the evolution of the
cluster.
Many open clusters are inherently unstable, with a small enough mass that the escape velocity of the system is lower than the average velocity
of the constituent stars. These clusters will rapidly disperse within a
few million years. In many cases, the stripping away of the gas from
which the cluster formed by the radiation pressure of the hot young
stars reduces the cluster mass enough to allow rapid dispersal.
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects
as its immediate products. Star formation theory, as well as
accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the
statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.
Stellar planetary systems
A protoplanetary disk with a cleared central region (artist's conception).
Planetary systems are generally believed to form as part of the same process that results in star formation. A protoplanetary disk forms by gravitational collapse of a molecular cloud, called a solar nebula,
and then evolves into a planetary system by collisions and
gravitational capture. Radiation pressure can clear a region in the
immediate vicinity of the star. As the formation process continues,
radiation pressure continues to play a role in affecting the
distribution of matter. In particular, dust and grains can spiral into
the star or escape the stellar system under the action of radiation
pressure.
Stellar interiors
In stellar interiors the temperatures are very high. Stellar models predict a temperature of 15 MK in the center of the Sun, and at the cores of supergiant
stars the temperature may exceed 1 GK. As the radiation pressure scales
as the fourth power of the temperature, it becomes important at these
high temperatures. In the Sun, radiation pressure is still quite small
when compared to the gas pressure. In the heaviest non-degenerate stars,
radiation pressure is the dominant pressure component.
Comets
Comet Hale–Bopp (C/1995 O1). Radiation pressure and solar wind effects on the dust and gas tails are clearly seen.
Solar radiation pressure strongly affects comet tails. Solar heating causes gases to be released from the comet nucleus, which also carry away dust grains. Radiation pressure and solar wind
then drive the dust and gases away from the Sun's direction. The gases
form a generally straight tail, while slower moving dust particles
create a broader, curving tail.
Laser applications of radiation pressure
Optical tweezers
Lasers can be used as a source of monochromatic light with wavelength . With a set of lenses, one can focus the laser beam to a point that is in diameter (or ).
The radiation pressure of a 30 mW laser of 1064 nm can therefore be computed as follows:
This is used in optical tweezers.
Other examples
Laser cooling is applied to cooling materials very close to absolute zero. Atoms traveling towards a laser light source perceive a doppler effect
tuned to the absorption frequency of the target element. The radiation
pressure on the atom slows movement in a particular direction until the
Doppler effect moves out of the frequency range of the element, causing
an overall cooling effect.
Large lasers operating in space have been suggested as a means of propelling sail craft in beam-powered propulsion.
The reflection of a laser pulse from the surface of an elastic
solid gives rise to various types of elastic waves that propagate inside
the solid. The weakest waves are generally those that are generated by
the radiation pressure acting during the reflection of the light.
Recently, such light-pressure-induced elastic waves were observed inside
an ultrahigh-reflectivity dielectric mirror. These waves are the most basic fingerprint of a light-solid matter interaction on the macroscopic scale.