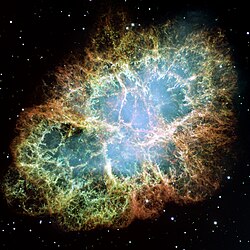
Giant picture mosaic of the Crab Nebula, remnant of SN 1054, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in visible light. Credit: NASA/ESA.
| |
| Other designations | SN 1054, SN 1054A, CSI+21-05315, PLX 1266, V* CM Tau |
|---|---|
| Event type | Supernova, star |
| Spectral class | Type II |
| Date | 4 July 1054 |
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 5h 34.5m |
| Declination | +22° 01' |
| Epoch | ? |
| Galactic coordinates | G.184.6–5.8 |
| Distance | 6.5 kly (2.0 kpc) |
| Remnant | Nebula |
| Host | Milky Way |
| Progenitor | Unknown |
| Progenitor type | Unknown |
| Colour (B-V) | Unknown |
| Peak apparent magnitude | −6 |
| Preceded by | SN 1006 |
| Followed by | SN 1181 |
SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 4 July 1054, and remained visible for around two years. The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a document from the Arab world. Furthermore, there are a number of proposed, but doubtful, references from European sources recorded in the 15th century, and perhaps a pictograph associated with the Ancestral Puebloan culture found near the Peñasco Blanco site in New Mexico.
The remnant of SN 1054, which consists of debris ejected during the explosion, is known as the Crab Nebula. It is located in the sky near the star Zeta Tauri (ζ Tauri). The core of the exploding star formed a pulsar, called the Crab Pulsar (or PSR B0531+21). The nebula and the pulsar that it contains are some of the most studied astronomical objects outside the Solar System. It is one of the few Galactic supernovae where the date of the explosion is well known. The two objects are the most luminous in their respective categories. For these reasons, and because of the important role it has repeatedly played in the modern era, SN 1054 is the best known supernova in the history of astronomy.
The Crab Nebula is easily observed by amateur astronomers thanks to its brightness, and was also catalogued early on by professional astronomers, long before its true nature was understood and identified. When the French astronomer Charles Messier watched for the return of Halley's Comet in 1758, he confused the nebula for the comet, as he was unaware of the former's existence. Motivated by this error, he created his catalogue of non-cometary nebulous objects, the Messier Catalogue, to avoid such mistakes in the future. The nebula is catalogued as the first Messier object, or M1.
Identification of the supernova
The Crab Nebula was identified as the supernova remnant
of SN 1054 between 1921 and 1942, at first speculatively (1920s), with
some plausibility by 1939, and beyond reasonable doubt by Jan Oort in 1942.
In 1921, Carl Otto Lampland was the first to announce that he had seen changes in the structure of the Crab Nebula.
This announcement occurred at a time when the nature of the nebulas in
the sky was completely unknown. Their nature, size and distance were
subject to debate. Observing changes in such objects allows astronomers
to determine whether their spatial extension is "small" or "large", in
the sense that notable fluctuations to an object as vast as our Milky Way
cannot be seen over a small time period, such as a few years, whereas
such substantial changes are possible if the size of the object does not
exceed a diameter of a few light-years. Lampland's comments were
confirmed some weeks later by John Charles Duncan, an astronomer at the Mount Wilson Observatory.
He benefited from photographic material obtained with equipment and
emulsions that had not changed since 1909; as a result the comparison
with older snapshots was easy and emphasized a general expansion of the
cloud. The points were moving away from the centre, and did so faster as
they got further from it.
Also in 1921, Knut Lundmark compiled the data for the "guest stars" mentioned in the Chinese chronicles known in the West. He based this on older works, having analysed various sources such as the Wenxian Tongkao, studied for the first time from an astronomical perspective by Jean-Baptiste Biot in the middle of the 19th century. Lundmark gives a list of 60 suspected novae, then the generic term for a stellar explosion, in fact covering what is now understood as two distinct phenomena, novae and supernovae. The nova of 1054, already mentioned by the Biots in 1843,
is part of the list. It stipulates the location of this guest star in a
note at the bottom of the page as being "close to NGC 1952", one of the
names for the Crab Nebula, but it does not seem to create an explicit
link between them.
In 1928, Edwin Hubble
was the first to note that the changing aspect of the Crab Nebula,
which was growing bigger in size, suggests that it is the remains of a
stellar explosion. He realised that the apparent speed of change in its
size signifies that the explosion which it comes from occurred only nine
centuries ago, which puts the date of the explosion in the period
covered by Lundmark's compilation. He also noted that the only possible
nova in the region of the Taurus constellation (where the cloud is
located) is that of 1054, whose age is estimated to correspond to an
explosion dating from the start of the second millennium.
Hubble therefore deduced, correctly, that this cloud was the remains of the explosion which was observed by Chinese astronomers.
Hubble's comment remained relatively unknown as the physical
phenomenon of the explosion was not known at the time. Eleven years
later, when the fact that supernovae are very bright phenomena was
highlighted by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky and when their nature was suggested by Zwicky, Nicholas Mayall proposed that the star of 1054 was actually a supernova,
based on the speed of expansion of the cloud, measured by spectroscopy,
which allows astronomers to determine its physical size and distance,
which he estimated at 5000 light-years.
This was under the assumption that the velocities of expansion along
the line of sight and perpendicularly to it were identical.
Based on the reference to the brightness of the star which featured in
the first documents discovered in 1934, he deduced that it was a
supernova rather than a nova.
This deduction was subsequently refined, which pushed Mayall and Jan Oort in 1942 to analyse historic accounts relating to the guest star more closely. These new accounts, globally and mutually concordant, confirm
the initial conclusions by Mayall and Oort in 1939 and the
identification of the guest star of 1054 is established beyond all
reasonable doubt.
Most other historical supernovas are not confirmed so conclusively:
supernovas of the first millennium (SN 185, SN 386 and SN 393)
are established on the basis of a single document each, and so they
cannot be confirmed; in relation to the supposed historical supernova
which followed the one in 1054, SN 1181, there are legitimate doubts concerning the proposed remnant (3C58)
and an object of less than 1000 years of age. Other historical
supernovae of which there are written accounts which precede the
invention of the telescope (SN 1006, SN 1572 and SN 1604)
are however established with certitude. Telescope-era supernovae are of
course associated with their remnant, when one is observed, with full
certitude, but none is known within the Milky Way.
Historical records
The Crab Nebula
is a remnant of an exploded star. This is the Crab Nebula in various
energy bands, including a hard X-ray image from the HEFT data taken
during its 2005 observation run. Each image is 6′ wide.
The guest star reported by Chinese astronomers in 1054 is identified as SN 1054. The highlighted passages refer to the supernova.
SN 1054 is one of eight supernovae in the Milky Way
that can be identified because written testimony describing the
explosion has survived. In the nineteenth century, astronomers began to
take an interest in the historic records. They compiled and examined the
records as part of their research on recent novae, comets, and later, the supernovae.
The first people to attempt a systematic compilation of records from China were the father and son Biot. In 1843, the sinologist Édouard Biot translated for his father, the astronomer Jean-Baptiste Biot, passages from the astronomical treatise of the 348-volume Chinese encyclopaedia, the Wenxian Tongkao.
Almost 80 years later, in 1921, Knut Lundmark undertook a similar effort based on a greater number of sources. In 1942, Jan Oort, convinced that the Crab Nebula was the "guest star" of 1054 described by the Chinese, asked sinologist J.J.L. Duyvendak to help him compile new evidence on the observation of the event.
Chinese astronomy
Simulated
image of supernova SN 1054 at the position of modern Crab Nebula, as
presumably would have been observed from capital of Song Dynasty at Kaifeng, China during the morning of July 4th, 1054.
Stars that appeared temporarily in the sky were generically called "guest stars" (kè xīng 客星) by Chinese astronomers. The guest star of 1054 occurred during the reign of the Emperor Renzong of the Song dynasty (960–1279). The relevant year is recorded in Chinese documents as "the first year of the Zhihe era". Zhihe was an era name
used during the reign of Emperor Renzong, and corresponds to the years
1054–1056 C.E., so the first year of the Zhihe era corresponds to the
year 1054 C.E.
Some of the Chinese accounts are well preserved and detailed. The oldest and most detailed accounts are from Song Huiyao and Song Shi,
historiographical works of which the extant text was redacted perhaps
within a few decades of the event. There are also some later records,
redacted in the 13th century, which are not necessarily independent of
the older ones.
Three accounts are apparently related because they describe the angular
distance from the guest star to Zeta Tauri as "perhaps several inches
away", but they are in apparent disagreement about the date of
appearance of the star. The older two mention the day jichou 己丑, but the third, the Xu Zizhi Tongjian Changbian, the day yichou 乙丑. These terms refer to the Chinese sexagenary cycle,
corresponding to numbers 26 and 2 of the cycle, which corresponds, in
the context where they are cited, respectively, to 4 July and 10 June.
As the redaction of the third source is of considerably later date
(1280) and the two characters are similar, this is easily explained as a
transcription error, the historical date being jichou 己丑, 4 July.
The description of the guest star's location as "to the
south-east of Tianguan, perhaps several inches away" has perplexed
modern astronomers, because the Crab Nebula is not situated in the
south-east, but to the north-west of Zeta Tauri.
The duration of visibility is explicitly mentioned in chapter 12 of Song Shi, and slightly less accurately, in the Song Huiyao. The last sighting was on 6 April 1056, after a total period of visibility of 642 days.
This duration is supported by the Song Shi. According to the Song Huiyao
the visibility of the guest star was for only 23 days, but this is
after mentioning visibility during daylight. This period of 23 days
applies in all likelihood solely to visibility during the day.
Sources
The Song Huiyao (literally "Collected important documents of the Song dynasty") covers the period 960–1220. Huiyao is a traditional form of history books in China which aimed mainly to preserve primary sources, and as such are important sources supplementing the official Twenty-Four Histories. The Song dynasty had a specific government department dedicated to compiling the Huiyao,
and some 2,200 volumes were published in ten batches during the Song
dynasty. However, most of these documents were lost by the time of the Qing Dynasty except for the synopsis and a relatively small portion preserved as part of the imperial Yongle Encyclopedia. In 1809, the portion preserved in the Yongle Encyclopedia was extracted and re-published as the Song Huiyao Jigao (the "draft extract of the Song Huiyao"). Subsequent scholars have worked on the project further and the current edition dates from 1936.
This document recounts the observation of the guest star,
focusing on the astrological aspect but also giving important
information on the visibility of the star, by day and by night.
Zhihe era, first year, seventh lunar month, 22nd day. [...] Yang Weide declared: "I humbly observe that a guest star has appeared; above the star there is a feeble yellow glimmer. If one examines the divination regarding the Emperor, the interpretation [of the presence of this guest star] is the following: The fact that the star has not overrun Bi and that its brightness must represent a person of great value. I demand that the Office of Historiography is informed of this." All officials congratulated the Emperor, who ordered his congratulations be [back] forwarded to the Office of Historiography. First year of the era of Jiayou, third lunar month, the director of the Astronomical Office said "The guest star has disappeared, which means the departure of the host [that it represents]." Previously, during the first year of the Zhihe era, during the fifth lunar month, it had appeared at dawn, in the direction of the east, under the watch of Tiānguān (天關, Zeta Tauri). It had been seen in daylight, like Venus. It had rays stemming in all directions, and its colour was reddish white. Altogether visible for 23 days.
The Song Shi is the official annals of the Song dynasty.
Chapter 12 mentions the guest star, not its appearance but rather the
moment of its disappearance. The corresponding entry dated 6 April 1056
indicates:
Jiayou era, first year, third lunar month, xinwei day, the director of the Office of Astronomy reported during the fifth lunar month of the first year of the Zhihe era, a guest star had appeared at dawn, in the direction of the east, under the watch of Tianguan. Now it has disappeared.
In chapter 56 ("Astronomical treaty") of the same document, the guest
star is again mentioned in a chapter dedicated to this type of
phenomenon, this time focusing on its appearance,
Zhihe era of the reign, first year, fifth lunar month, jichou day. A guest star has appeared to the south-east of Tianguan, perhaps several inches away. After a year or more, it gradually disappeared.
The Xu Zizhi Tongjian Changbian ("Long compilation of the continuation of the Zizhi Tongjian"), a book covering the period of 960–1126 and written 40 years or so later by Li Tao
(1114–1183), contains the oldest Chinese testimonies relating to the
observation of the star. It was rediscovered in 1970 by the specialist
in Chinese civilisations Ho Peng Yoke and collaborators.
It is relatively imprecise in the case of the explosion of SN 1054. A loose translation of what was stated:
First year of the Zhihe era, fifth lunar month, ji-chou day. A guest star has appeared to the south-east of Tianguan, perhaps several inches away [of this star]. (The star disappeared in the third lunar month of the first year of the Jiayou era.)
There is an account of the star from the Liao Dynasty, which ruled in the area around northeast China from 907–1125. The book in question, the Qidan Guo Zhi, was compiled by Ye Longli in 1247. It includes various astronomical notes, some of which are clearly copied from the Song Shi. This entry referring to the star of 1054 seems unique:
Chongxi era of the reign of [King Xingzong], twenty-third year eighth lunar moon, the ruler of the realm is dead. It happened before a solar eclipse at noon, and a guest star appeared. The highest office at the Office of History, Liu Yishou had said "These are omens of the death of the King." This prediction has been realised.
The account of Qidan Guo Zhi alluded to the notable
astronomical events that preceded the death of King Xingzong. Various
historical documents allow us to establish the date of death of the
Emperor Xingzong
as 28 August 1055, during the eighth lunar month of the twenty-fourth
(and not twenty-third) year of his reign. The dates of the two
astronomical events mentioned (the eclipse and the appearance of the
guest star) are not specified, but were probably before the obituary (2
or 3 years at most). Two solar eclipses were visible shortly before that
date in the Khitan kingdom, on 13 November 1053 and 10 May 1054. Of
these, only one occurred around noon, that of 13 November; it seems
likely that this is what the document mentions. As for the guest star,
only a rough estimate of location is given, corresponding to the moon
mansion Mao. This mansion is situated just east of where the star
appeared, as mentioned in the other testimonies. Since no other known
significant astronomical event occurred in this region of the sky during
the two years that preceded the death of Xingzong, it seems likely that
the text is actually referring to the star of 1054.
The Wenxian Tongkao is the first East Asian source that
came to the attention of Western astronomers; it was translated by
Édouard Biot in 1843. This source, compiled by Ma Duanlin in 1280, is relatively brief. The text is very close to that of the Song Shi:
Zhihe era of the reign, first year, fifth lunar month, ji-chou day. A guest star has appeared to the south-east of Tiānguān, perhaps several inches away. After a year or more, it gradually disappeared.
Identity of Tianguan
The asterisms
(or "constellations") of Chinese astronomy were catalogued around the
2nd century BC. The asterisms with the brightest stars in the sky were
compiled in a work called Shi Shi, which also includes Tianguan.
Identification of Tianguan is comparatively easy, as it is indicated that it is located at the foot of the Five Chariots
asterism, the nature of which is left in hardly any doubt by
representation on maps of the Chinese sky: it consists of a large
pentagon containing the bright stars of the Auriga. As Tianguan is also represented to the north of the Three Stars asterism, the composition of which is well known, corresponding to the bright stars of Orion, its possible localisation is strongly restricted to the immediate proximity of the star ζ Tauri, located between "Five Chariots" and "Three Stars". This star, of medium brightness (apparent magnitude
of 3.3), is the only star of its level of brightness in this area of
the sky (there is no other star that is brighter than an apparent
magnitude of 4.5 within 7 degrees of ζ Tauri), and therefore the only
one likely to figure among the asterisms of "Shi Shi". All of these
elements, along with some others, allow "Tianguan" to be confirmed
beyond reasonable doubt as corresponding to the star ζ Tauri.
Northeast
region of the Taurus constellation, with ζ and β Tauri stars and the
location of the supernova of 1054 between them (M1).
Position relative to Tianguan
Three Chinese documents indicate that the guest star was located "perhaps a few inches" South-East of Tianguan. Song Shi and Song Huiyao
stipulate that it "was standing guard" for the asterism, corresponding
to the star ζ Tauri. The "South-East" orientation has a simple
astronomical meaning, the celestial sphere having, like the Earth's
globe, both north and south celestial poles,
the "South-East" direction thus corresponding to a "bottom-left"
location in relation to the reference object (in this case, the star
ζ Tauri) when it appears at the South. However, this "South-East"
direction has long left modern astronomers perplexed in the context of this event: the logical remnant of the supernova corresponding to the guest star is the Crab Nebula, but it is not situated to the southeast of ζ Tauri, rather in the opposite direction, to the northwest.
The term "perhaps a few inches" (ke shu cun in the Latin transliteration) is relatively uncommon in Chinese astronomical documents. The first term, ke, is translated as "approximately" or "perhaps", the latter being currently preferred. The second term, shu, means "several", and more specifically any number between 3 and 9 (limits included). Finally, cun resembles a unit of measurement for angles translated by the term "inch".
It is part of a group of three angular units, zhang (also written chang), chi ("foot") and cun ("inch"). Different astronomical documents indicate without much possible discussion that a zhang corresponds to ten chi, and that one chi corresponds to ten cun. The angular units are not the ones used to determine stars' coordinates, which are given in terms of du,
an angular unit corresponding to the average angular distance travelled
by the sun per day, which corresponds to around 360/365.25 degrees, in
other words almost one degree. The use of different angular units can be
surprising, but it is similar to the current situation in modern
astronomy, where the angular unit used to measure angular distances
between two points is certainly the same as for declination (the degree), but is different for right ascension
(which is expressed in angular hours; an angular hour corresponds to
exactly 15 degrees. In Chinese astronomy, right ascension and
declination have the same unit, which is not the one used for other
angular distances. The reason for this choice to use different units in
the Chinese world is not well known.
Meaning of units
However, the exact value of these new units (zhang, chi and cun) was never stipulated, but can be deduced by the context in which they are used. For example, the spectacular passing of Halley's comet in 837 indicates that the tail of the comet measured 8 zhang. Even if it is not possible to know the angular size of the comet at the time it passed, it is certain that 8 zhang correspond to 180 degrees at the most (maximum visible angle on the celestial sphere), which means that one zhang can hardly exceed 20 degrees, and therefore one cun
cannot exceed 0.2 degrees. A more rigorous estimation was made from
1972 on the basis of references of minimal separations expressed in chi or cun between two stars in the case of various conjunctions.
The results suggest that one cun is between 0.1 and 0.2 degrees and that one chi is between 0.44 and 2.8 degrees, a range which is compatible with the estimations for one cun. A more solid estimation error is that it is generally accepted that one chi is in the order of one degree (or one du), and that one cun
is in the order of one tenth of a degree. The expression “perhaps a few
inches” therefore suggests an angular distance in the order of one
degree or less.
Problems with description
If
all the available elements strongly suggest that the star of 1054 was a
supernova, and that in the area next to where the star was seen, there
is a remnant of a supernova which has all of the characteristics
expected of an object that is around 1000 years old, a major problem
arises: the new star is described as being to the South-East of Tianguan,
while the Crab Nebula is to the North-East. This problem has been known
since the 1940s and has long been unsolved. In 1972 for example, Ho
Peng Yoke and his colleagues suggested that the Crab Nebula was not the
product of the explosion of 1054, but that the true remnant was to the
South-East, as indicated in several Chinese sources. For this, they
envisaged that the angular unit cun corresponds to a considerable
angle of 1 or 2 degrees, meaning that the distance from the remnant to
ζ Tauri was therefore considerable. Aside from the fact that this theory
does not account for the large angular sizes of certain comets,
expressed in zhang, it comes up against the fact that there it
does not make sense to measure the gap between a guest star and a star
located so far away from it, when there are closer asterisms that could
be used.
In their controversial article (see above) Collins and his colleagues make another suggestion:
on the morning of 4 July, the star ζ Tauri was not bright enough and
too low on the horizon to be visible. If the guest star, which was
located close to it, was visible, it is only because its brightness was
comparable to Venus. However, there was another star, brighter and
higher on the horizon, which was possibly visible, for reference: Beta Tauri
(β Tauri). This star is located at around 8 degrees north-north-west of
ζ Tauri. The Crab Nebula is south-south-east of β Tauri. Collins et al.
suggest therefore that at the time of its discovery, the star was seen
to the south-east of β Tauri, and that as the days passed and visibility
improved, astronomers were able to see that it was in fact a lot closer
to ζ Tauri, but that the direction "south-east" used for the first star
was kept in error.
The solution to this problem was suggested (without proof) by A. Breen and D. McCarthy in 1995.
and proved very convincingly by D. A. Green et F. R. Stephenson (2003)
The term "stand on guard" obviously signifies a proximity between the
two stars, but also means a general orientation: a guest star "standing
on guard" for a fixed star is systematically located below it. In order
to support this theory, Green and Stephenson investigated other entries
in Song Shi, which also includes reference to "standing on
guard". They selected entries relating to conjunctions betweens the
stars identified and planets, of which the trajectory can be calculated
without difficulty and with great precision on the indicated dates. Of
the 18 conjunctions analysed, spreading from 1172 (the Jupiter–Regulus conjunction on 5 December) to 1245 (the Saturn–Gamma Virginis
conjunction on 17 May), the planet was more to the north (in the sense
of a lower declination) in 15 cases, and in the three remaining cases,
it was never in the south quadrant of the star.
In addition, Stephenson and Clark (1977) had already highlighted
such an inversion of direction in a planetary conjunction: on 13
September 1253, an entry in the astronomical report Koryo-sa indicated that Mars had hidden the star to the south-east of the twenty-eight mansions sign Ghost (Chinese constellation) (Delta Cancri), while in reality, it approached the star north-west of the asterism (Eta Cancri).
Meigetsuki (Japan)
The oldest and most detailed record from Japan is in the Meigetsuki, the diary of Fujiwara no Teika (1162–1241), a poet and courtier.
There are two other Japanese documents, presumably dependent on the Meigetsuki:
- The 14th century Ichidai Yoki: The description is very similar to the Meigetsuki, omitting several details (hour of apparition, and possibly erroneous parts of the lunar month). The short text also contains many typographical errors.
- The 17th-century Dainihonshi, containing very little information. The brevity contrasts with the more detailed descriptions of "guest stars" (supernovas) of 1006 and 1181.
The Meigetsuki places the event in the fourth lunar moon, one month
earlier than the Chinese texts.
Whatever the exact date during this month, there seems to be a
contradiction between this period and the observation of the guest star:
the star was close to the sun, making daytime and nighttime observation
impossible.
The visibility in daylight as described by the Chinese texts is thus
validated by the Japanese documents, and is consistent with a period of
moderate visibility, which implies that the star's period of diurnal
visibility was very short.
In contrast, the day of the cycle given in the Chinese documents is
compatible with the months that they state, reinforcing the idea that
the month on the Japanese document is incorrect.
The study of other medieval supernovas (SN 1006 and SN 1181) reveals a proximity in the dates of discovery of a guest star in China and Japan, although clearly based on different sources.
Fujiwara no Teika's interest in the guest star seems to have come
accidentally whilst observing a comet in December 1230, which prompted
him to search for evidence of past guest stars, among those SN 1054 (as
well as SN 1006 and SN 1181, the two other historic supernovas from the early second millennium). The entry relating to SN 1054 can be translated as:
Tengi era of the emperor Go-Reizei, second year, fourth lunar month, after the middle period of ten days. At chou [a Chinese term for 1–3am], a guest star appeared in the degrees of the moon mansions of Zuixi and Shen. It has been viewed in the direction of the East and has emerged from the Tianguan star. It was as big as Jupiter.
The source used by Fujiwara no Teika is the records of Yasutoshi Abe
(Onmyōdō doctor), but it seems to have been based, for all the
astronomical events he has recorded, on documents of Japanese origin.
The date he gives is prior to the third part of ten days of the lunar
month mentioned, which corresponds to the period of between 30 May and 8
June 1054 of the Julian calendar, which is around one month earlier
than Chinese documentation. This difference is usually attributed to an
error in the lunar months (fourth place and fifth place).
The location of the guest star, clearly straddling the moon mansions
Shen and Zuixi, corresponds to what would be expected of a star
appearing in the immediate vicinity of Tianguan.
Ibn Butlan (Iraq)
While SN 1006,
which was significantly brighter than SN 1054, was mentioned by several
Arab chroniclers, there exist no Arabic reports relating to the rather
faint SN 1181.
Only one Arabic account has been found concerning SN 1054, whose
brightness is between those of the last two stars mentioned. This
account, discovered in 1978, is that of a Nestorian Christian doctor, Ibn Butlan, transcribed in the Uyun al-Anba, a book on detailed biographies of physicians in the Islamic World compiled by Ibn Abi Usaybi'a (1194–1270) in the mid-thirteenth century. This is a translation of the passage in question:
I copied the following hand written testimony [that of Ibn Butlan]. He stated: "One of the famous epidemics of our time has occurred when a spectacular star appeared in [the zodiac star] Gemini, of the year 446 [of the Muslim calendar]. In the autumn of that year, fourteen thousand people were buried in Constantinople. Thereafter, in the middle of the summer of 447, the majority of the Fostat people [Le Caire] and all foreigners died". He [Ibn Butlan] continues: "While this spectacular star appeared in the sign of Gemini [...] it caused the epidemic of the Fostat by the Nile being low when it appeared in 445 [sic]."
The three years cited (AH
445, 446, 447) refer, respectively, to: 23 April 1053 – 11 April 1054,
12 April 1054 – 1 April 1055, and 2 April 1055 – 20 March 1056. There is
an apparent inconsistency in the year of occurrence of the star, first
announced as 446, then 445. This problem is solved by reading other
entries in the book, which quite explicitly specify that the Nile was
low at 446.
This year of the Muslim calendar ran from 12 April 1054 to 1 April 1055,
which is compatible with the appearance of the star in July 1054, as
its location (admittedly rather vague), is in the astrological sign of
Gemini (which, due to axial precession,
covers the eastern part of the Constellation Taurus). The date of the
event in 446 is harder to determine, but the reference to the level of
the Nile refers to the period preceding its annual flood, which happens
during the summer.
Suggested European sightings
Since 1980, several European documents have been identified as possible observations of the supernova.
The first such suggestion was made in 1980 by Umberto Dall'Olmo (1925–1980). The following passage which reports an astronomical sighting is taken from an account compiled by Jacobus Malvecius in the 15th century:
And in those days a star of immense brightness appeared within the circle of the Moon a few days after its separation from the Sun.
The date this passage refers to is not explicit, however, and by means of a reference to an earthquake in Brescia 11 April 1064, it would seem ten years too late, attributed by Dall'Olmo to a transcription error.
Another candidate is the Cronaca Rampona, proposed in 1981, which however also indicates a date several years after the event, in 1058 instead of 1054.
The European candidate documents are all very imprecise, and
remain unconvincing from an astronomical perspective even when collated;
they would be impossible to interpret in the sense of an observation of
a supernova if no information had been preserved from the Chinese
accounts.
Conversely, the lack of accounts from European chroniclers has long raised questions. In fact, it is known that the supernova of 1006
was recorded in a large number of European documents, albeit not in
astronomical terms. Among the proposed explanations for the lack of
European accounts of SN 1054, its concurrence with the East-West Schism is prominent.
In fact, the date of the excommunication of the Patriarch of Constantinople Michael I Cerularius
(16 July) corresponds to the star reaching its maximum brightness and
being visible in the daytime.
Among the six proposed European documents, one does not seem to
correspond to the year of the supernova (the chronicle of Jacobus
Malvecius). Another (the Cronaca Rampona) has large dating and internal
coherence problems.
The four others are relatively precisely dated, but contradict the
Chinese documents: they date from Spring and not Summer 1054, that is to
say before the conjunction between the supernova and the sun. Three of
the documents (the chronicle of Jacobus Malvecius, the Cronaca Rampona
and the Armenian chronicle) make reference relatively explicitly to
conjunctions between the moon and stars, of which one is identified
(Jupiter, in the Armenian chronicle).
The three other documents are very unclear and have almost unusable
astronomical content.
In 1999, George W. Collins and his colleagues
defended the plausibility of European sighting of SN 1054. They argue
that the records suggest that European sightings even predate Chinese
and Japanese reports by more than two months (April 1054). These authors
emphasize the problems associated with the Chinese reports, especially
the position of the supernova relative to Zeta Tauri. They also adduce a
Khitan
document which they suggest might establish observation of the
supernova at the time of the solar eclipse of 10 May 1054 (which would
corrobate the "late" date of Chinese observation of the event).
Conversely, they interpret the European documents, taken in conjunction,
as plausibly establishing that an unusual astronomical phenomenon was
visible in Europe in the spring of 1054, i.e. even before the Sun's
conjunction with Zeta Tauri.
They also surmise that the correct year in the report by Ibn Butlan is
AH 445 (23 April 1053 – 11 April 1054) rather than AH 446 (12 April 1054
– 1 April 1055).
The publication by Collins et al. was criticised by Stephenson
and Green (2003). These authors insist that the problems with the
Chinese and Japanese documents can easily be resolved philologically (as
common copyists' mistakes) and need not indicate unreliability of the
Chinese observations. Stephenson and Green condemn attempts at
uncovering European sightings of the supernova as it were at any cost as
suffering from confirmation bias, "anxious to ensure that this event
was recorded by Europeans".
They also reject the idea of the Khitan document referring to the
supernova as a mistake based in a translation of the document, and as
inconsistent with astronomical reality. Green and Stephenson (2003) thus
argue for the standing majority consensus established by 1995, to the
effect that the European documents do not offer themselves to an
interpretation as sightings of SN 1054.
The thesis of Collins et al. upon publication was reviewed in the magazine Ciel & Espace with some enthusiasm but it has not received much attention since its rejection by Stephenson and Green (2003).
The Cronaca Rampona
The account of a supernova sighting which is considered the most feasible comes from a medieval chronicle from the region of Bologna, the Cronaca Rampona. This text, a subject of astronomers' attention since 1972, was interpreted as a possible sighting of the supernova in 1981, and again in 1999. The part of the chronicle that was highlighted translates to:
In AD 1058, Pope Stephen IX has come to the throne [...] Also in this year of Christ 1058, Henry III reigned [or "lived"] for 49 years. He went to Rome for the first time in the month of May. At this time, famine and death was upon the whole world. He stayed in the province of Tibur for three days in the month of June [...] At that time, a very brightly-shining star (stella clarissima) entered into the circle [or the circuit] of the new moon, in the thirteenth calends at the beginning of the night.
Without even discussing the last, astronomical part of the passage,
skeptics point out at least two discrepancies in the following: Pope Stephen IX became Pope in 1057, not 1058, and Emperor Henry III who is mentioned, actually Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor, was born in 1017, 39 and not 49 years before 1058, his reign having started in 1039 (King of the Romans, then as emperor of the Romans from 1046 after being consecrated by Pope Clement II
during the course of his brief pontificate). Henry III, therefore, was
dead in 1056, and his reign could not have coincided with that of
Stephen IX. It seems more likely that the text was the subject of
various alterations, as the date format (for example, the number 1058 is
written as Ml8, with a mix of Roman and Arab characters, common
in the period when the Cronaca Rampona was written (15th century) but
not in the 11th century.
Furthermore, associating the event described with the sighting of a
supernova in 1054 would require the supposition that the Cronaca Rampona
entry was in the wrong place in relation to the rest of the document,
as the different entries are in chronological order and several previous
entries are later than 1054 (in order, the previous entries refer to
1046, 1049, 1051, 1055, 1056, written in a mix of Arab and Roman
characters, namely Mxl6, Mxl9, Mli, Mlv and Ml6). Additionally, there is
a discrepancy with the date of the new moon. The term calends, which refers to the Roman calendar, can be written in the ordinary form of the Gregorian calendar,
and the phase of the moon can be calculated from it.
It is clear that the new moon did not occur on the thirteenth day of the
Calends in any month in 1054. All of this is in strong opposition to
the precision of the dates of references to eclipses in medieval European chronicles: a study of 48 partial or total solar eclipses
from 733 to 1544, reveals that 42 dates out of 48 are correct, and of
the six remaining, three are incorrect by one of two days and the three
others give the correct day and month, but not the year.
Finally, even considering that the stated event corresponds to
May or June 1054 nevertheless, and describes a conjunction between the
already visible supernova and the moon, another problem arises: during
those months, the moon did not pass very close to the location of the
supernova.
Therefore, it is possible that the account describes an approach or a
concealment of a planet by the moon, contemporary to the suggested date
(1058). This scenario is corroborated by two contemporary documents
which are perfectly dated and describe a conjunction and a planetary
concealment by the moon in relatively similar terms. These two
documents, unearthed by Robert Russell Newton, are taken from the Annales Cavenses, Latin chronicles from la Trinità della Cava (Province of Salerno). They mention
"a bright star that entered into the circle of the (new) moon"
for both 17 February 1086 ([Martii incipiente nocte] stella clarissima in circulum lunae primae ingressa est) and for 6 August 1096 (stella clarissima venit in circulum lunae).
The first event can be verified as Venus being eclipsed by the moon,
the second as the Moon passing Jupiter at a distance of less than one
degree after a lunar eclipse which was also mentioned in the chronicle.
Hayton of Corycus
The Cronaca Rampona account is apparently also reflected in the Armenian chronicle of Hayton of Corycus (written before 1307).
The relevant passage translated from the Armenian manuscript reads:
AD 1048. There was the 5th year, 2nd month, 6th day of Pope Leo in Rome. Robert Kijart arrived in Rome and sieged the Tiburtina town. There was starvation over the whole world. That year a bright star appeared within the circle of the Moon, the Moon was new, on May 14th, in the first part of the night.
Vahe Gurzadyan's proposal connecting the Hayton of Corycus's chronicle with Cronaca Rampona and SN 1054 dates to 2012.
Other
View
of the sky at dusk on the day of the death of Pope Leo IX. The three
planets Mercury, Mars, and Venus are seen together on the
West-South-West horizon (at the bottom-right of the image), with Jupiter
the furthest away (top right), all next to the constellation of Orion
(centre-bottom) and its bright peripheral stars (notably Sirius,
bottom-left, and Capella, top right). They could be "countless lamps"
caused by Albertus cited in De Obitus Leonis, that the supernova had been present or not.
In a work entitled De Obitus Leonis ("On the Death of [Pope] Leo") by one subdeacon Libuinus, there is a report of an unusual celestial phenomenon. A certain Albertus, leading a group of pilgrims in the region of Todi, Umbria, reportedly confirmed having seen, on the day that Pope Leo IX died, a phenomenon described as
quasi stratam palliis fulgentibus adornatam at innumeris coruscantem lampadibus.
[Translation:] like a road decorated with wonderful adornments and shining with innumerable lamps
Guidoboni et al. (1994), proposed that this may relate to SN 1054, and was endorsed by Collins et al. (1999).
Guidoboni et al. (1994) also proposed a Flemish text as an account of a sighting of the supernova. The text, from Saint Paul's church—no longer extant—in the Flemish town of Oudenburg, describes the death of Pope Leo IX in Spring 1054 (the date described corresponds to 14 April 1054).
On the eighteenth calends of May, on the second day of the week at around midday, the soul [of Pope Leo IX] departed. At the moment it left his body, in Rome, where he rests, but "also everywhere on earth, a circle of extraordinary brightness appeared in the sky for half an hour."
McCarthy and Breen (1997) proposed an extract from an Irish chronicle as a possible European sighting of the supernova. This chronicle indicates the following for 1054:
A round circle of fire was seen at Ros Ela on the Sunday of the feast day of Saint George over five hours during the day, and countless black birds passed before it, in the centre of which there was a larger bird [...]
The date of the event corresponds to 24 April: (Saint George's Day
is 23 April and fell on a Saturday in 1054. Thus the mention of the
"Sunday of Saint George's Day" corresponds to the next day, 24 April)
long before the sighting noted by the Chinese. The astronomical nature
of the account remains very uncertain, and interpretation as a solar halo or aurora seems at least as probable.
Suggested records in North American petroglyphs
The
sky on the morning of 5 July, showing the conjunction between the
supernova (blue square) and the moon. If the orientation of the
phenomenon does not correspond to the petroglyph, the relative
orientation of the crescent moon in relation to the star corresponds,
along with the order of size of the angular distance between the two
stars.
Two Native American paintings in Arizona show a crescent moon located next to a circle that could represent a star. It has been proposed that this represents a conjunction between the moon and the supernova, made possible by the fact that, seen from the Earth, the supernova occurred in the path of the Ecliptic.
This theory is compatible with the datings in these paintings. In fact,
on the morning of 5 July, the moon was located in the immediate
proximity of the supernova, which could reinforce the idea that it was
this proximity that had been represented in these paintings. This
interpretation cannot be confirmed. The dating of the paintings is
extremely imprecise (between the 10th and 12th century), and only one of
them shows the crescent moon with the correct orientation in relation
to the supernova. Moreover, this type of drawing could well represent a
proximity of the moon with Venus or Jupiter.
Another, better known document was updated during the 1970s at the Chaco Canyon site (New Mexico), occupied around 1000 AD by the Ancestral Pueblo Peoples.
On the flat underside of an overhang, it represents a hand, below which
there is a crescent moon facing a star at the bottom-left. On the wall
underneath the petroglyph there is a drawing which could be the core and
tail of a comet. Apart from the petroglyph, which could represent the
configuration of the moon and supernova on the morning of 5 July 1054,
this period corresponds to the apogee of the Anasazi civilisation. It
seems possible to propose an interpretation of the other petroglyph,
which, if it is more recent than the other one, could possibly
correspond to the passing of Halley's Comet
in 1066. Although plausible, this interpretation is impossible to
confirm and does not explain why it was the supernova of 1054 that was
represented, rather than the supernova of 1006, which was brighter and also visible to this civilisation.
Suggested records in Aboriginal oral tradition
The Aboriginal people of the region around Ooldea have passed in oral tradition a detailed account of their mythology of the constellation Orion and the Pleiades. The anthropologist Daisy Bates was the first to attempt to compile records of this story. Work done by her and others has shown that all of the protagonists of the story of Nyeeruna and the Yugarilya correspond to individual stars covering the region around Orion and the Pleiades, with the exception of Baba, the father dingo, which is a major protagonist of the story and of the yearly re-enactments of the myth by the local people:
Again Nyeeruna's magic comes back in great force and brightness, and when Kambugudha sees the strong magic in arm and body, she calls to a father dingo (horn of the Bull) to come and humiliate Nyeeruna and Babba the Dingo rushes over to Nyeeruna and shakes and swings him east and west by his middle and Kambugudha points at him and laughs but her frightened little sisters hide their heads under their little mountain devil neck humps until Babba loosens his hold and returns to his place again.
It has been suggested by Leaman and Hamacher that the location usually assigned to Baba
by the locals (recorded by Bates as being at the "horn of the bull") is
more likely to correspond to SN 1054 than to a faint star of that
region such as β or ζ Tauri. This is motivated by the reference to Babba "returning to his place again" after attacking Nyeeruna
which could refer to a transient star, as well as the fact that
important characters of the myth are associated with bright stars.
However, Leaman and Hamacher clarify there is no solid evidence to
support this interpretation, which remains speculative. Hamacher demonstrates the extreme difficulty in identifying supernovae in indigenous oral traditions.
Other elements of the story which have been found to correspond
to astronomical elements by these authors include: awareness by the
Aboriginal people of the different colors of the stars, possible
awareness of the variability of Betelgeuse, observations of meteors in the Orionid meteor shower
and the possibility that the rite associated with the myth is held at a
time of astronomical significance, corresponding to the few days in the
year when due to the Sun’s proximity to Orion, it is unseen throughout
the night, but is always in the sky during the daytime.
Media references
The supernova is mentioned in Ayreon's song To the Quasar, from the album Universal Migrator Part 2: Flight of the Migrator, and is also the subject of Elen Cora's song Astronomers in China.







