| Wernicke's area | |
|---|---|
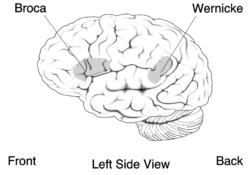
Wernicke's area is located in the temporal lobe, shown here in grey
| |
| Details | |
| Location | Temporal lobe of the dominant cerebral hemisphere. |
| Artery | Branches from the middle cerebral artery |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D065813 |
| NeuroNames | 1233 |
| NeuroLex ID | nlx_144087 |
| FMA | 242178 |
Wernicke's area (/ˈvɛərnɪkə/ or /ˈvɛərnɪki/; German: [ˈvɛʁnɪkə]), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech (the other is Broca's area). It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language (in contrast to Broca's area that is involved in the production of language). It is traditionally thought to be in Brodmann area 39,40, which is located in the superior temporal lobe in the dominant cerebral hemisphere (which is the left hemisphere in about 95% of right handed individuals and 60% of left handed individuals).
Damage caused to Wernicke's area results in receptive, fluent aphasia. This means that the person with aphasia will be able to fluently connect words, but the phrases will lack meaning. This is unlike non-fluent aphasia, in which the person will use meaningful words, but in a non-fluent, telegraphic manner.
Structure
Wernicke's area is classically located in the posterior section of the superior temporal gyrus (STG) in the (most commonly) left cerebral hemisphere. This area encircles the auditory cortex on the lateral sulcus (the part of the brain where the temporal lobe and parietal lobe meet). This area is neuroanatomically described as the posterior part of Brodmann area 22.
However, there is an absence of consistent definitions as to the location.
Some identify it with the unimodal auditory association in the superior
temporal gyrus anterior to the primary auditory cortex (the anterior
part of BA 22). This is the site most consistently implicated in auditory word recognition by functional brain imaging experiments. Others include also adjacent parts of the heteromodal cortex in BA 39 and BA40 in the parietal lobe.
While previously thought to connect Wernicke's area and Broca's area, new research demonstrates that the arcuate fasciculus instead connects to posterior receptive areas with premotor/motor areas, and not to Broca's area. Consistent with the word recognition site identified in brain imaging, the uncinate fasciculus connects anterior superior temporal regions with Broca's area.
Function
Right homologous area
Research using Transcranial magnetic stimulation
suggests that the area corresponding to the Wernicke’s area in the
non-dominant cerebral hemisphere has a role in processing and resolution
of subordinate meanings of ambiguous words—such as ‘‘river’’ when given
the ambiguous word "bank." In contrast, the Wernicke's area in the
dominant hemisphere processes dominant word meanings (‘‘teller’’ given
‘‘bank’’).
Modern views
Neuroimaging suggests the functions earlier attributed to Wernicke's area occur more broadly in the temporal lobe and indeed happen also in Broca's area.
| “ |
There
are some suggestions that middle and inferior temporal gyri and basal
temporal cortex reflect lexical processing ... there is consensus that
the STG from rostral to caudal fields and the STS
constitute the neural tissue in which many of the critical computations
for speech recognition are executed ... aspects of Broca’s area
(Brodmann areas 44 and 45) are also regularly implicated in speech
processing.
... the range of areas implicated in speech processing go well beyond
the classical language areas typically mentioned for speech; the vast
majority of textbooks still state that this aspect of perception and
language processing occurs in Wernicke’s area (the posterior third of
the STG).
|
” |
Support for a broad range of speech processing areas was furthered by a recent study caried out at the University of Rochester in which American Sign Language native speakers were subject to MRI
while interpreting sentences that identified a relationship using
either syntax (relationship is determined by the word order) or
inflection (relationship is determined by physical motion of "moving
hands through space or signing on one side of the body"). Distinct
areas of the brain were activated with the frontal cortex (associated
with ability to put information into sequences) being more active in the
syntax condition and the temporal lobes (associated with dividing
information into its constituent parts) being more active in the
inflection condition. However, these areas are not mutually exclusive
and show a large amount of overlap. These findings imply that while
speech processing is a very complex process, the brain may be using
fairly basic, preexisting computational methods.
Clinical significance
Human brain with Wernicke's area highlighted in red
Aphasia
Wernicke's area is named after Carl Wernicke, a German neurologist and psychiatrist
who, in 1874, hypothesized a link between the left posterior section of
the superior temporal gyrus and the reflexive mimicking of words and
their syllables that associated the sensory and motor images of spoken
words. He did this on the basis of the location of brain injuries that caused aphasia. Receptive aphasia in which such abilities are preserved is also known as Wernicke's aphasia.
In this condition there is a major impairment of language
comprehension, while speech retains a natural-sounding rhythm and a
relatively normal syntax. Language as a result is largely meaningless (a condition sometimes called fluent or jargon aphasia).
While neuroimaging and lesion evidence generally support the idea
that malfunction of or damage to Wernicke's area is common in people
with receptive aphasia, this is not always so. Some people may use the
right hemisphere for language, and isolated damage of Wernicke's area
cortex (sparing white matter and other areas) may not cause severe
receptive aphasia. Even when patients with Wernicke's area lesions have comprehension deficits, these are usually not restricted to language processing
alone. For example, one study found that patients with posterior
lesions also had trouble understanding nonverbal sounds like animal and
machine noises. In fact, for Wernicke's area, the impairments in nonverbal sounds were statistically stronger than for verbal sounds.

