Virome refers to the collection of nucleic acids, both RNA and DNA, that make up the viral community associated with a particular ecosystem or holobiont. The word is derived from virus and genome and first used by Forest Rohwer and colleagues to describe viral shotgun metagenomes. All macro-organisms have viromes that include bacteriophage and viruses. Viromes are important in the nutrient and energy cycling, development of immunity, and a major source of genes through lysogenic conversion.
History
Viromes were the first examples of shotgun community sequence, which is now known as metagenomics. In the 2000s, the Rohwer lab sequenced viromes from seawater, marine sediments, adult human stool, infant human stool, soil, and blood. This group also performed the first RNA virome with collaborators from the Genomic Institute of Singapore.
From these early works, it was concluded that most of the genomic
diversity is contained in the global virome and that most of this
diversity remains uncharacterized. This view was supported by individual genomic sequencing project, particularly the mycobacterium phage.
Methods of study
In
order to study the virome, virus-like particles are separated from
cellular components, usually using a combination of filtration, density
centrifugation, and enzymatic treatments to get rid of free nucleic
acids. The nucleic acids are then sequenced and analyzed using metagenomic
methods. Alternatively, there are recent computational methods that use
directly metagenomic assembled sequences to discover viruses.
The Global Ocean Viromes (GOV) is a dataset consisting of deep sequencing from over 150 samples collected across the world's oceans in two survey periods by an international team.
Virus hosts
We can determine the metagenome host from prophage identity sequence.
Viruses are the most abundant biological entities on Earth, but
challenges in detecting, isolating, and classifying unknown viruses have
prevented exhaustive surveys of the global virome. Over 5 Tb of metagenomic
sequence data were used from 3,042 geographically diverse samples to
assess the global distribution, phylogenetic diversity, and host
specificity of viruses.
Proportion of 18,470 viral connected with predicted hosts at various taxonomic levels.
In August 2016, over 125,000 partial DNA viral genomes, including the
largest phage yet identified, increased the number of known viral genes
by 16-fold. A suite of computational methods was used to identify putative host virus connections. The isolate viral host information was projected onto a group, resulting in host assignments for 2.4% of viral groups.
Then the CRISPR–Cas
prokaryotic immune system which holds a "library" of genome fragments
from phages (proto-spacers) that have previously infected the host. Spacers from isolate microbial genomes with matches to metagenomic viral contigs (mVCs) were identified for 4.4% of the viral groups and 1.7% of singletons. The hypothesis was explored that viral transfer RNA (tRNA) genes originate from their host.
Viral tRNAs identified in 7.6% of the mVCs were matched to isolate genomes from a single species or genus.
The specificity of tRNA-based host viral assignment was confirmed by
CRISPR–Cas spacer matches showing a 94% agreement at the genus level.
These approaches identified 9,992 putative host–virus associations
enabling host assignment to 7.7% of mVCs.
The majority of these connections were previously unknown, and include
hosts from 16 prokaryotic phyla for which no viruses have previously
been identified.
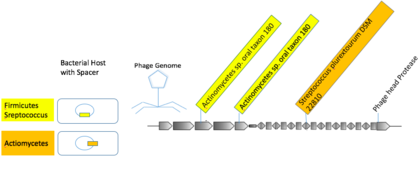
Three
proto-spacers encoded on mVCs identified in human oral metagenomic
samples that were linked to CRISPR spacers from hosts from distinct
phyla, Actinomycetes sp. oral taxon 180 (Actinobacteria) and
Streptococcus plurextorum DSM 22810 (Firmicutes).
Many viruses specialize in infecting related hosts. Viral generalists that infect hosts across taxonomic orders may exist. Most CRISPR spacer matches were from viral sequences to hosts within one species or genus.
Some mVCs were linked to multiple hosts from higher taxa. A viral
group composed of macs from human oral samples contained three distinct
photo-spacers with nearly exact matches to spacers in Actionbacteria and Firmicutes.
In January 2017, the IMG/VR system -- the largest interactive public virus database contained 265,000
metagenomic viral sequences and isolate viruses. This number scaled up
to over 760,000 in November 2018 (IMG/VR v.2.0). The IMG/VR systems serve as a starting point for the sequence analysis of viral fragments derived from metagenomic samples.