| Orthocoronavirinae | |
|---|---|
| |
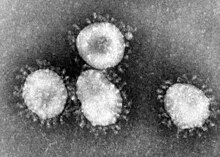
| Electron micrograph of avian infectious bronchitis virus | |

| |
| Illustration of the morphology of coronaviruses; the club-shaped viral spike peplomers, coloured red, create the look of a corona surrounding the virion, when viewed electron microscopically | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Order: | Nidovirales |
| Family: | Coronaviridae |
| Subfamily: | Orthocoronavirinae |
| Genera | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans, coronaviruses cause respiratory tract infections that are typically mild, such as some cases of the common cold (among other possible causes, predominantly rhinoviruses), though rarer forms can be lethal, such as SARS, MERS, and COVID-19. Symptoms vary in other species: in chickens, they cause an upper respiratory tract disease, while in cows and pigs they cause diarrhea. There are yet to be vaccines or antiviral drugs to prevent or treat human coronavirus infections.
Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae, in the family Coronaviridae, order Nidovirales, and realm Riboviria. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 27 to 34 kilobases, the largest among known RNA viruses. The name coronavirus is derived from the Latin corona, meaning "crown" or "halo", which refers to the characteristic appearance reminiscent of a crown or a solar corona around the virions (virus particles) when viewed under two-dimensional transmission electron microscopy, due to the surface covering in club-shaped protein spikes.
Discovery
Coronaviruses were first discovered in the 1960s. The earliest ones discovered were infectious bronchitis virus in chickens and two viruses from the nasal cavities of human patients with the common cold that were subsequently named human coronavirus 229E and human coronavirus OC43. Other members of this family have since been identified, including SARS-CoV in 2003, HCoV NL63 in 2004, HKU1 in 2005, MERS-CoV in 2012, and SARS-CoV-2 (formerly known as 2019-nCoV) in 2019. Most of these have involved serious respiratory tract infections.Name and morphology
The name "coronavirus" is derived from Latin corona, meaning "crown" or "wreath", itself a borrowing from Greek κορώνη korṓnē, "garland, wreath". The name refers to the characteristic appearance of virions (the infective form of the virus) by electron microscopy, which have a fringe of large, bulbous surface projections creating an image reminiscent of a crown or of a solar corona. This morphology is created by the viral spike (S) peplomers, which are proteins on the surface of the virus that determines host tropism.Proteins that contribute to the overall structure of all coronaviruses are the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N). In the specific case of the SARS coronavirus (see below), a defined receptor-binding domain on S mediates the attachment of the virus to its cellular receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Some coronaviruses (specifically the members of Betacoronavirus subgroup A) also have a shorter spike-like protein called hemagglutinin esterase (HE).
Replication
The infection cycle of a coronavirus
After entry into the host cell, the virus particle is uncoated, and its genome enters the cell cytoplasm.
The coronavirus RNA genome has a 5′ methylated cap and a 3′ polyadenylated tail, which allows the RNA to attach to the host cell's ribosome for translation. The host ribosome translates the initial overlapping open reading frame of the virus genome and forms a long polyprotein. The polyprotein has its own proteases which cleave the polyprotein into multiple nonstructural proteins.
A number of the nonstructural proteins coalesce to form a multi-protein replicase-transcriptase complex (RTC). The main replicase-transcriptase protein is the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). It is directly involved in the replication and transcription
of RNA from an RNA strand. The other nonstructural proteins in the
complex assist in the replication and transcription process. The exoribonuclease non-structural protein for instance provides extra fidelity to replication by providing a proofreading function which the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase lacks.
One of the main functions of the complex is to replicate the viral genome. RdRp directly mediates the synthesis
of negative-sense genomic RNA from the positive-sense genomic RNA. This
is followed by the replication of positive-sense genomic RNA from the
negative-sense genomic RNA. The other important function of the complex is to transcribe the viral genome. RdRp directly mediates the synthesis
of negative-sense subgenomic RNA molecules from the positive-sense
genomic RNA. This is followed by the transcription of these
negative-sense subgenomic RNA molecules to their corresponding
positive-sense mRNAs.
The replicated positive-sense genomic RNA becomes the genome of the progeny viruses.
The mRNAs are gene transcripts of the last third of the virus genome
after the initial overlapping reading frame. These mRNAs are translated
by the host's ribosomes into the structural proteins and a number of
accessory proteins. RNA translation occurs inside the endoplasmic reticulum. The viral structural proteins S, E, and M move along the secretory pathway into the Golgi intermediate compartment. There, the M proteins direct most protein-protein interactions required for assembly of viruses following its binding to the nucleocapsid. Progeny viruses are then released from the host cell by exocytosis through secretory vesicles.
Transmission
Human to human transmission of coronaviruses is primarily thought to occur among close contacts via respiratory droplets generated by sneezing and coughing.
Taxonomy
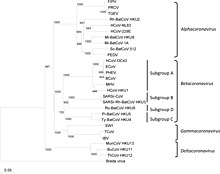
Phylogenetic tree of coronaviruses
The scientific name for coronavirus is Orthocoronavirinae or Coronavirinae. Coronavirus belongs to the family of Coronaviridae.
- Genus: Alphacoronavirus
- Genus Betacoronavirus; type species: Murine coronavirus
- Species: Betacoronavirus 1, Human coronavirus HKU1, Murine coronavirus, Pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5, Rousettus bat coronavirus HKU9, Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Tylonycteris bat coronavirus HKU4, Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, Human coronavirus OC43, Hedgehog coronavirus 1 (EriCoV)
- Genus Gammacoronavirus; type species: Infectious bronchitis virus
- Genus Deltacoronavirus; type species: Bulbul coronavirus HKU11
Evolution
The most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all coronaviruses has been placed at around 8000 BCE.
The MRCAs of the Alphacoronavirus line has been placed at about 2400
BCE, the Betacoronavirus line at 3300 BCE, the Gammacoronavirus line at
2800 BCE, and the Deltacoronavirus line at about 3000 BCE. It appears
that bats and birds, as warm-blooded flying vertebrates, are ideal hosts
for the coronavirus gene source (with bats for Alphacoronavirus and
Betacoronavirus, and birds for Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus) to
fuel coronavirus evolution and dissemination.
Bovine coronavirus and canine respiratory coronaviruses diverged from a common ancestor in 1951.
Bovine coronavirus and human coronavirus OC43 diverged around the
1890s. Bovine coronavirus diverged from the equine coronavirus species
at the end of the 18th century.
The MRCA of human coronavirus OC43 has been dated to the 1950s.
MERS-CoV, although related to several bat coronavirus species, appears to have diverged from these several centuries ago. The human coronavirus NL63 and a bat coronavirus shared an MRCA 563–822 years ago.
The most closely related bat coronavirus and SARS-CoV diverged in 1986.
A path of evolution of the SARS virus and keen relationship with bats
have been proposed. The authors suggest that the coronaviruses have been
coevolved with bats for a long time and the ancestors of SARS-CoV first
infected the species of the genus Hipposideridae, subsequently spread to species of the Rhinolophidae and then to civets, and finally to humans.
Alpaca coronavirus and human coronavirus 229E diverged before 1960.
Cross-sectional model of a coronavirus
Coronaviruses vary significantly in risk factor. Some can kill more than 30% of those infected (such as MERS-CoV), and some are relatively harmless, such as the common cold. Coronaviruses cause colds with major symptoms, such as fever and sore throat from swollen adenoids, primarily in the winter and early spring seasons. Coronaviruses can cause pneumonia – either direct viral pneumonia or a secondary bacterial pneumonia – and may cause bronchitis – either direct viral bronchitis or a secondary bacterial bronchitis. The much publicized human coronavirus discovered in 2003, SARS-CoV, which causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), has a unique pathogenesis because it causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections.
Seven strains of human coronaviruses are known:
- Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E)
- Human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43)
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV)
- Human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63, New Haven coronavirus)
- Human coronavirus HKU1
- Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), previously known as novel coronavirus 2012 and HCoV-EMC
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), previously known as 2019-nCoV or "novel coronavirus 2019"
The coronaviruses HCoV-229E, -NL63, -OC43, and -HKU1 continually
circulate in the human population and cause respiratory infections in
adults and children world-wide.
Outbreaks of coronavirus types of relatively high mortality are as follows:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
In 2003, following the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome
(SARS) which had begun the prior year in Asia, and secondary cases
elsewhere in the world, the World Health Organization
(WHO) issued a press release stating that a novel coronavirus
identified by a number of laboratories was the causative agent for SARS.
The virus was officially named the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV). Over
8,000 people were infected, about 10% of whom died.
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)
In September 2012, a new type of coronavirus was identified,
initially called Novel Coronavirus 2012, and now officially named Middle
East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). The World Health Organization issued a global alert soon after. The WHO update on 28 September 2012 stated that the virus did not seem to pass easily from person to person.
However, on 12 May 2013, a case of human-to-human transmission in
France was confirmed by the French Ministry of Social Affairs and
Health. In addition, cases of human-to-human transmission were reported by the Ministry of Health in Tunisia.
Two confirmed cases involved people who seemed to have caught the
disease from their late father, who became ill after a visit to Qatar
and Saudi Arabia. Despite this, it appears that the virus had trouble
spreading from human to human, as most individuals who are infected do
not transmit the virus. By 30 October 2013, there were 124 cases and 52 deaths in Saudi Arabia.
After the Dutch Erasmus Medical Centre
sequenced the virus, the virus was given a new name, Human
Coronavirus–Erasmus Medical Centre (HCoV-EMC). The final name for the
virus is Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). In May
2014, the only two United States cases of MERS-CoV infection were
recorded, both occurring in healthcare workers who worked in Saudi
Arabia and then travelled to the U.S. One was treated in Indiana and one
in Florida. Both of these individuals were hospitalized temporarily and
then discharged.
In May 2015, an outbreak of MERS-CoV occurred in the Republic of Korea,
when a man who had traveled to the Middle East, visited 4 hospitals in
the Seoul area to treat his illness. This caused one of the largest
outbreaks of MERS-CoV outside the Middle East.
As of December 2019, 2,468 cases of MERS-CoV infection had been
confirmed by laboratory tests, 851 of which were fatal, a mortality rate
of approximately 34.5%.
In December 2019, a pneumonia outbreak was reported in Wuhan, China. On 31 December 2019, the outbreak was traced to a novel strain of coronavirus, which was given the interim name 2019-nCoV by the World Health Organization (WHO), later renamed SARS-CoV-2 by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Some researchers have suggested that the Huanan Seafood Market may not be the original source of viral transmission to humans.
As of 9 March 2020, there have been at least 3,996 confirmed deaths and more than 113,584 confirmed cases in the coronavirus pneumonia outbreak. The Wuhan strain has been identified as a new strain of Betacoronavirus from group 2B with approximately 70% genetic similarity to the SARS-CoV. The virus has a 96% similarity to a bat coronavirus, so it is widely suspected to originate from bats as well.
The pandemic has resulted in serious restrictions over travel.
Other animals
Coronaviruses have been recognized as causing pathological conditions in veterinary medicine since the early 1970s. Except for avian infectious bronchitis, the major related diseases have mainly an intestinal location.
Diseases caused
Coronaviruses primarily infect the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tract
of mammals and birds. They also cause a range of diseases in farm
animals and domesticated pets, some of which can be serious and are a
threat to the farming industry. In chickens, the infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), a coronavirus, targets not only the respiratory tract but also the urogenital tract. The virus can spread to different organs throughout the chicken. Economically significant coronaviruses of farm animals include porcine coronavirus (transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus, TGE) and bovine coronavirus, which both result in diarrhea in young animals. Feline coronavirus: two forms, feline enteric coronavirus is a pathogen of minor clinical significance, but spontaneous mutation of this virus can result in feline infectious peritonitis
(FIP), a disease associated with high mortality. Similarly, there are
two types of coronavirus that infect ferrets: Ferret enteric coronavirus
causes a gastrointestinal syndrome known as epizootic catarrhal
enteritis (ECE), and a more lethal systemic version of the virus (like
FIP in cats) known as ferret systemic coronavirus (FSC). There are two types of canine coronavirus (CCoV), one that causes mild gastrointestinal disease and one that has been found to cause respiratory disease. Mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) is a coronavirus that causes an epidemic murine illness with high mortality, especially among colonies of laboratory mice.
Sialodacryoadenitis virus (SDAV) is highly infectious coronavirus of
laboratory rats, which can be transmitted between individuals by direct
contact and indirectly by aerosol. Acute infections have high morbidity and tropism for the salivary, lachrymal and harderian glands.
A HKU2-related bat coronavirus called swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV) causes diarrhea in pigs.
Prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV, MHV had been the best-studied coronavirus both in vivo and in vitro
as well as at the molecular level. Some strains of MHV cause a
progressive demyelinating encephalitis in mice which has been used as a
murine model for multiple sclerosis. Significant research efforts have been focused on elucidating the viral pathogenesis of these animal coronaviruses, especially by virologists interested in veterinary and zoonotic diseases.
In domestic animals
- Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) causes avian infectious bronchitis.
- Porcine coronavirus (transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus of pigs, TGEV).
- Bovine coronavirus (BCV), responsible for severe profuse enteritis in of young calves.
- Feline coronavirus (FCoV) causes mild enteritis in cats as well as severe Feline infectious peritonitis (other variants of the same virus).
- the two types of canine coronavirus (CCoV) (one causing enteritis, the other found in respiratory diseases).
- Turkey coronavirus (TCV) causes enteritis in turkeys.
- Ferret enteric coronavirus causes epizootic catarrhal enteritis in ferrets.
- Ferret systemic coronavirus causes FIP-like systemic syndrome in ferrets.
- Pantropic canine coronavirus.
- Rabbit enteric coronavirus causes acute gastrointestinal disease and diarrhea in young European rabbits. Mortality rates are high.
- Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PED or PEDV), has emerged around the world.
Genomic cis-acting elements
In common with the genomes of all other RNA viruses, coronavirus genomes contain cis-acting
RNA elements that ensure the specific replication of viral RNA by a
virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. The embedded cis-acting
elements devoted to coronavirus replication constitute a small fraction
of the total genome, but this is presumed to be a reflection of the fact
that coronaviruses have the largest genomes of all RNA viruses. The
boundaries of cis-acting elements essential to replication are fairly
well-defined, and the RNA secondary structures
of these regions are understood. However, how these cis-acting
structures and sequences interact with the viral replicase and host cell
components to allow RNA synthesis is not well understood.
Genome packaging
The assembly of infectious coronavirus particles requires the
selection of viral genomic RNA from a cellular pool that contains an
abundant excess of non-viral and viral RNAs. Among the seven to ten
specific viral mRNAs synthesized in virus-infected cells, only the
full-length genomic RNA is packaged efficiently into coronavirus
particles. Studies have revealed cis-acting elements and trans-acting
viral factors involved in the coronavirus genome encapsidation
and packaging. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of genome
selection and packaging is critical for developing antiviral strategies
and viral expression vectors based on the coronavirus genome.