| Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Korsakoff's psychosis, alcoholic encephalopathy |
 | |
| Thiamine | |
| Specialty | Psychiatry, neurology |
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome (WKS) is the combined presence of Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) and alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. Due to the close relationship between these two disorders, people with either are usually diagnosed with WKS as a single syndrome. It mainly causes vision changes, ataxia and impaired memory.
The cause of the disorder is thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. This can occur due to beriberi, Wernicke encephalopathy, and alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. These disorders may manifest together or separately. WKS is usually secondary to alcohol abuse.
Wernicke encephalopathy and WKS are most commonly seen in people with an alcohol use disorder. Failure in diagnosis of WE and thus treatment of the disease leads to death in approximately 20% of cases, while 75% are left with permanent brain damage associated with WKS. Of those affected, 25% require long-term institutionalization in order to receive effective care.
Signs and symptoms
The syndrome is a combined manifestation of two namesake disorders, Wernicke encephalopathy and alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome.
It involves an acute Wernicke-encephalopathy phase, followed by the
development of a chronic alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome phase.
Wernicke encephalopathy
WE is characterized by the presence of a triad of symptoms:
- Ocular disturbances (ophthalmoplegia)
- Changes in mental state (confusion)
- Unsteady stance and gait (ataxia)
This triad of symptoms results from a deficiency in vitamin B1 which is an essential coenzyme. The aforementioned changes in mental state occur in approximately 82% of patients' symptoms of which range from confusion, apathy,
inability to concentrate, and a decrease in awareness of the immediate
situation they are in. If left untreated, WE can lead to coma or death.
In about 29% of patients, ocular disturbances consist of nystagmus and paralysis of the lateral rectus muscles
or other muscles in the eye. A smaller percentage of patients
experience a decrease in reaction time of the pupils to light stimuli
and swelling of the optic disc which may be accompanied by retinal hemorrhage. Finally, the symptoms involving stance and gait occur in about 23% of patients and result from dysfunction in the cerebellum and vestibular system. Other symptoms that have been present in cases of WE are stupor, low blood pressure (hypotension), elevated heart rate (tachycardia), as well as hypothermia, epileptic seizures and a progressive loss of hearing.
About 19% of patients have none of the symptoms in the classic
triad at first diagnosis of WE; however, usually one or more of the
symptoms develops later as the disease progresses.
Alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome
The
DSM-V classifies Korsakoff syndrome under Substance/Medication-Induced
Major or Mild Neurocognitive Disorders, specifically alcohol-induced
amnestic confabulatory.[6]
The diagnostic criteria defined as necessary for diagnosis includes,
prominent amnesia, forgetting quickly, and difficulty learning. Presence
of thiamine deficient encephalopathy can occur in conjunction with
these symptoms.
Despite the assertion that alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome must be
caused by the use of alcohol, there have been several cases where it has
developed from other instances of thiamine deficiency resulting from
gross malnutrition due to conditions such as; stomach cancer, anorexia nervosa, and gastrectomy.
Cognitive effects
Several
cases have been documented where Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome has been
seen on a large scale. In 1947, 52 cases of WKS were documented in a
prisoner of war hospital in Singapore where the prisoners' diets
included less than 1 mg of thiamine per day. Such cases provide an
opportunity to gain an understanding of what effects this syndrome has
on cognition. In this particular case, cognitive symptoms included insomnia, anxiety,
difficulties in concentration, loss of memory for the immediate past,
and gradual degeneration of mental state; consisting of confusion, confabulation, and hallucinations.
In other cases of WKS, cognitive effects such as severely disrupted
speech, giddiness, and heavy headedness have been documented. In
addition to this, it has been noted that some patients displayed an
inability to focus, and the inability of others to catch patients'
attention.
In a study conducted in 2003 by Brand et al. on the cognitive effects of WKS, the researchers used a neuropsychological test battery which included tests of intelligence, speed of information processing,
memory, executive function and cognitive estimation. They found that
patients suffering from WKS showed impairments in all aspects of this
test battery but most noticeably, on the cognitive estimation tasks.
This task required subjects to estimate a physical quality such as size,
weight, quantity or time (i.e. What is the average length of a
shower?), of a particular item. Patients with WKS performed worse than
normal control participants on all of the tasks in this category. The
patients found estimations involving time to be the most difficult,
whereas quantity was the easiest estimation to make. Additionally, the
study included a category for classifying "bizarre" answers, which
included any answer that was far outside of the normal range of expected
responses. WKS patients did give answers that could fall into such a
category and these included answers such as 15s or 1 hour for the
estimated length of a shower, or 4 kg or 15 tonnes as the weight of a
car.
Memory deficits
As mentioned previously, the amnesic symptoms of WKS include both retrograde and anterograde amnesia.
The retrograde deficit has been demonstrated through an inability of
WKS patients to recall or recognize information for recent public
events. The anterograde memory loss is demonstrated through deficits in
tasks that involve encoding and then recalling lists of words and faces, as well as semantic
learning tasks. WKS patients have also demonstrated difficulties in
perseveration as evidenced by a deficit in performance on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test.
The retrograde amnesia that accompanies WKS can extend as far back as
twenty to thirty years, and there is generally a temporal gradient seen,
where earlier memories are recalled better than more recent memories.
It has been widely accepted that the critical structures that lead to
the memory impairment in WKS are the mammillary bodies, and the thalamic
regions. Despite the aforementioned memory deficits, non-declarative memory functions appear to be intact in WKS patients. This has been demonstrated through measures that assess perceptual priming.
Other studies have shown deficits in recognition memory and stimulus-reward associative functions in patients with WKS.
The deficit in stimulus-reward functions was demonstrated by
Oscar-Berman and Pulaski who presented patients with reinforcements for
certain stimuli but not others, and then required the patients to
distinguish the rewarded stimuli from the non-rewarded stimuli. WKS
patients displayed significant deficits in this task. The researchers
were also successful in displaying a deficit in recognition memory by
having patients make a yes/no decision as to whether a stimulus was
familiar (previously seen) or novel (not previously seen). The patients
in this study also showed a significant deficit in their ability to
perform this task.
Confabulation
People with WKS often show confabulation, spontaneous confabulation being seen more frequently than provoked confabulation.
Spontaneous confabulations refer to incorrect memories that the patient
holds to be true, and may act on, arising spontaneously without any
provocation. Provoked confabulations can occur when a patient is cued to
give a response, this may occur in test settings. The spontaneous
confabulations viewed in WKS are thought to be produced by an impairment
in source memory, where they are unable to remember the spatial and
contextual information for an event, and thus may use irrelevant or old
memory traces to fill in for the information that they cannot access. It
has also been suggested that this behaviour may be due to executive
dysfunction where they are unable to inhibit incorrect memories or
because they are unable to shift their attention away from an incorrect
response.
Causes
WKS is
usually found in people who have used alcohol chronically.
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome results from thiamine deficiency. It is
generally agreed that Wernicke encephalopathy results from severe acute
deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1), whilst Korsakoff's psychosis is a chronic neurologic sequela of Wernicke encephalopathy. The metabolically active form of thiamine is thiamine pyrophosphate, which plays a major role as a cofactor or coenzyme in glucose metabolism. The enzymes that are dependent on thiamine pyrophosphate are associated with the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and catalyze the oxidation of pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate and branched chain amino acids. Thus, anything that encourages glucose metabolism will exacerbate an existing clinical or sub-clinical thiamine deficiency.
As stated above, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome in the United States is usually found in malnourished chronic alcoholics, though it is also found in patients who undergo prolonged intravenous (IV) therapy without vitamin B1 supplementation, gastric stapling, intensive care unit (ICU) stays, hunger strikes,
or people with eating disorders. In some regions, physicians have
observed thiamine deficiency brought about by severe malnutrition,
particularly in diets consisting mainly of polished rice, which is thiamine-deficient. The resulting nervous system ailment is called beriberi.
In individuals with sub-clinical thiamine deficiency, a large dose of
glucose (either as sweet food, etc. or glucose infusion) can precipitate
the onset of overt encephalopathy.
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome in people with chronic alcohol use particularly is associated with atrophy/infarction of specific regions of the brain, especially the mammillary bodies. Other regions include the anterior region of the thalamus (accounting for amnesic symptoms), the medial dorsal thalamus, the basal forebrain, the median and dorsal raphe nuclei, and the cerebellum.
One as-yet-unreplicated study has associated susceptibility to this syndrome with a hereditary deficiency of transketolase, an enzyme that requires thiamine as a coenzyme.
Post-gastrectomy
The
fact that gastrointestinal surgery can lead to the development of WKS
was demonstrated in a study that was completed on three patients who
recently undergone a gastrectomy.
These patients had developed WKS but were not alcoholics and had never
suffered from dietary deprivation. WKS developed between 2 and 20 years
after the surgery.
There were small dietary changes that contributed to the development of
WKS but overall the lack of absorption of thiamine from the
gastrointestinal tract was the cause. Therefore, it must be ensured that
patients who have undergone gastrectomy have a proper education on
dietary habits, and carefully monitor their thiamine intake.
Additionally, an early diagnosis of WKS, should it develop, is very
important.
Alcohol–thiamine interactions
Strong
evidence suggests that ethanol interferes directly with thiamine uptake
in the gastrointestinal tract. Ethanol also disrupts thiamine storage
in the liver and the transformation of thiamine into its active form.
The role of alcohol consumption in the development of WKS has been
experimentally confirmed through studies in which rats were subjected to
alcohol exposure and lower levels of thiamine through a low-thiamine
diet.
In particular, studies have demonstrated that clinical signs of the
neurological problems that result from thiamine deficiency develop
faster in rats that have received alcohol and were also deficient in
thiamine than rats who did not receive alcohol.
In another study, it was found that rats that were chronically fed
alcohol had significantly lower liver thiamine stores than control rats.
This provides an explanation for why alcoholics with liver cirrhosis have a higher incidence of both thiamine deficiency and WKS.
Pathophysiology
The
vitamin thiamine also referred to as Vitamin B1, is required by three
different enzymes to allow for conversion of ingested nutrients into
energy. Thiamine can not be produced in the body and must be obtained through diet and supplementation. The duodenum is responsible for absorbing thiamine. The liver can store thiamine for 18 days.
Prolonged and frequent consumption of alcohol causes a decreased
ability to absorb thiamine in the duodenum. Thiamine deficiency is also
related to malnutrition from poor diet, impaired use of thiamine by the
cells and impaired storage in the liver. Without thiamine the Kreb's Cycle enzymes pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH) and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (alpha-KGDH) are impaired.
The impaired functioning of the Kreb's Cycle results in inadequate
production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or energy for the cells
functioning.
Energy is required by the brain for proper functioning and use of its
neurotransmitters. Injury to the brain occurs when neurons that require
high amounts of energy from thiamine dependent enzymes are not supplied
with enough energy and die.
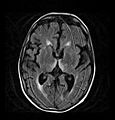
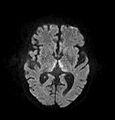
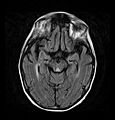
Brain atrophy associated with WKS occurs in the following regions of the brain: the mammillary bodies, the thalamus, the periaqueductal grey, the walls of the 3rd ventricle, the floor of the 4th ventricle, the cerebellum, and the frontal lobe. In addition to the damage seen in these areas there have been reports of damage to cortex,
although it was noted that this may be due to the direct toxic effects
of alcohol as opposed to thiamine deficiency that has been attributed as
the underlying cause of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome.
The amnesia that is associated with this syndrome is a result of the atrophy in the structures of the diencephalon (the thalamus, hypothalamus and mammillary bodies), and is similar to amnesia that is presented as a result of other cases of damage to the medial temporal lobe. It has been argued that the memory impairments can occur as a result of damage along any part of the mammillo-thalamic tract, which explains how WKS can develop in patients with damage exclusively to either the thalamus or the mammillary bodies.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
of Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome is by clinical impression and can
sometimes be confirmed by a formal neuropsychological assessment.
Wernicke encephalopathy typically presents with ataxia and nystagmus, and Korsakoff's psychosis with anterograde and retrograde amnesia and confabulation upon relevant lines of questioning.
Frequently, secondary to thiamine deficiency and subsequent
cytotoxic edema in Wernicke encephalopathy, patients will have marked
degeneration of the mammillary bodies. Thiamine (vitamin B1)
is an essential coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism and is also a
regulator of osmotic gradient. Its deficiency may cause swelling of the
intracellular space and local disruption of the blood-brain barrier.
Brain tissue is very sensitive to changes in electrolytes and pressure
and edema can be cytotoxic. In Wernicke this occurs specifically in the
mammillary bodies, medial thalami, tectal plate, and periaqueductal
areas. Sufferers may also exhibit a dislike for sunlight and so may
wish to stay indoors with the lights off. The mechanism of this
degeneration is unknown, but it supports the current neurological theory
that the mammillary bodies play a role in various "memory circuits"
within the brain. An example of a memory circuit is the Papez circuit.
Prevention
As
described, alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome usually follows or accompanies
Wernicke encephalopathy. If treated quickly, it may be possible to
prevent the development of AKS with thiamine treatments. This treatment
is not guaranteed to be effective and the thiamine needs to be
administered adequately in both dose and duration. A study on
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome showed that with consistent thiamine
treatment there were noticeable improvements in mental status after only
2–3 weeks of therapy. Thus, there is hope that with treatment Wernicke encephalopathy will not necessarily progress to WKS.
In order to reduce the risk of developing WKS it is important to
limit the intake of alcohol in order to ensure that proper nutrition
needs are met. A healthy diet
is imperative for proper nutrition which, in combination with thiamine
supplements, may reduce the chance of developing WKS. This prevention
method may specifically help heavy drinkers who refuse to or are unable
to quit.
A number of proposals have been put forth to fortify
alcoholic beverages with thiamine to reduce the incidence of WKS among
those heavily abusing alcohol. To date, no such proposals have been
enacted.
Daily recommendations of thiamine requirements are
0.66 mg/2,000kcal daily or 1.2 mg for adult men and 1.1 mg for adult
women per day.
Treatment
The
onset of Wernicke encephalopathy is considered a medical emergency, and
thus thiamine administration should be initiated immediately when the
disease is suspected.
Prompt administration of thiamine to patients with Wernicke
encephalopathy can prevent the disorder from developing into
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome, or reduce its severity. Treatment can also
reduce the progression of the deficits caused by WKS, but will not
completely reverse existing deficits. WKS will continue to be present,
at least partially, in 80% of patients. Patients suffering from WE should be given a minimum dose of 500 mg of thiamine hydrochloride, delivered by infusion
over a 30-minute period for two to three days. If no response is seen
then treatment should be discontinued but for those patients that do
respond, treatment should be continued with a 250 mg dose delivered intravenously or intramuscularly for three to five days unless the patient stops improving. Such prompt administration of thiamine may be a life-saving measure. Banana bags, a bag of intravenous fluids containing vitamins and minerals, is one means of treatment.
Epidemiology
WKS occurs more frequently in men than women and has the highest prevalence in the ages 55–65 approximately 71% are unmarried.
Internationally, the prevalence rates of WKS are relatively
standard, being anywhere between zero and two percent. Despite this,
specific sub-populations seem to have higher prevalence rates including
people who are homeless, older individuals (especially those living
alone or in isolation), and psychiatric inpatients. Additionally, studies show that prevalence is not connected to alcohol consumption per capita.
For example, in France, a country that is well known for its
consumption and production of wine, prevalence was only 0.4% in 1994,
while Australia had a prevalence of 2.8%.
History
Wernicke encephalopathy
Carl Wernicke discovered Wernicke encephalopathy in 1881. His first diagnosis noted symptoms including paralyzed eye movements, ataxia, and mental confusion. Also noticed were hemorrhages in the gray matter around the third and fourth ventricles and the cerebral aqueduct.
Brain atrophy was only found upon post-mortem autopsy. Wernicke
believed these hemorrhages were due to inflammation and thus the disease
was named polioencephalitis haemorrhagica superior. Later, it was found
that Wernicke encephalopathy and alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome are
products of the same cause.
Alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome
Sergei Korsakoff
was a Russian physician after whom the disease "Korsakoff's syndrome"
was named. In the late 1800s Korsakoff was studying long-term alcoholic
patients and began to notice a decline in their memory function. At the 13th International Medical Congress in Moscow in 1897, Korsakoff presented a report called: "On a special form of mental illness combined with degenerative polyneuritis". After the presentation of this report the term "Korsakoff's syndrome" was coined.
Although WE and AKS were discovered separately, these two
syndromes are usually referred to under one name, Wernicke–Korsakoff
syndrome, due to the fact that they are part of the same cause and
because the onset of AKS usually follows WE if left untreated.
Society and culture
The British neurologist Oliver Sacks describes case histories of some of his patients with the syndrome in the book The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat (1985).