| |
| Developer(s) | IBM |
|---|---|
| Initial release | November 16, 2004 |
| Stable release | 7.14.3 |
| Development status | Active |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows, Linux, Android, macOS |
| Platform | BOINC |
| Type | Volunteer computing |
| Average performance | 566 TFLOPS |
| Active users | 42,152 |
| Total users | 132,187 |
| Active hosts | 147,993 |
| Total hosts | 363,385 |
| Website | worldcommunitygrid.org |
World Community Grid (WCG) is an effort to create the world's largest public computing grid to tackle scientific research projects that benefit humanity. Launched on November 16, 2004, it is co-ordinated by IBM with client software currently available for Windows, Linux, macOS, and Android operating systems.
Using the idle time of computers around the world, World Community Grid's research projects have analyzed aspects of the human genome, HIV, dengue, muscular dystrophy, cancer, influenza, Ebola, Zika virus, virtual screening, rice crop yields, clean energy and COVID-19.
The Research Projects have yielded numerous scientific papers. For example, in 2019 and with the help of WCG, the OpenZika project scientists published a paper on the discovery of a compound (FAM 3) that inhibits the NS3 Helicase protein of the Zika virus, thus reducing viral replication by up to 86%.
As of March 2020, the organization has partnered with 452 other companies and organizations to assist in its work, has over 40,000 active registered users, and a combined total run time of over 2 million years.
History
In 2003, IBM and other research participants sponsored the Smallpox Research Grid Project to accelerate the discovery of a cure for smallpox. The smallpox study used a massive distributed computing grid to analyze compounds' effectiveness against smallpox.
The project allowed scientists to screen 35 million potential drug
molecules against several smallpox proteins to identify good candidates
for developing into smallpox treatments. In the first 72 hours, 100,000
results were returned. By the end of the project, 44 strong treatment
candidates had been identified.
Based on the success of the Smallpox study, IBM announced the creation
of World Community Grid on November 16, 2004, with the goal of creating a
technical environment where other humanitarian research could be
processed.
World Community Grid initially only supported Windows, using the proprietary Grid MP software from United Devices which powered the grid.org
distributed computing projects. Demand for Linux support led to the
addition in November 2005 of open source Berkeley Open Infrastructure
for Network Computing (BOINC) grid technology which powers projects such as SETI@home and Climateprediction, and Mac OS X and Linux support was added since the introduction of BOINC. In 2007, the World Community Grid migrated from Grid MP to BOINC for all of its supported platforms.
Scale of the project
As of May 1 of 2019, World Community Grid had over 42,000 active user accounts, with over 147,000 active devices.
Over the course of the project, more than 2,000,000 cumulative years of
computing time have been donated, and over 5.3 billion workunits have
been completed.
Operation
The World Community Grid client software works in the background, showing itself as a small icon in the computer's system tray. When the BOINC client is used, as in this example, the icon is a small "B."
The
client software's status window, displaying information about the work
currently being done in the background. This particular computer is
60.3% complete with its current workunit. When it reaches 100%, it will
start on a new workunit and the results of the previous workunit will be
transmitted back to WCG.
The World Community Grid software uses the idle time of Internet-connected computers to perform research calculations.
Users install WCG client software onto their computers. This software
works in the background, using spare system resources to process work
for WCG. When a piece of work or workunit is completed, the client software sends it back to WCG over the Internet and downloads a new workunit. To ensure accuracy, the WCG servers send out multiple copies of each workunit. Then, when the results are received, they are collected and validated against each other.
While many public computing grids such as SETI@home and Folding@home are devoted to a single project, World Community Grid offers multiple humanitarian projects under a single umbrella.
Users are included in a subset of projects by default, but may opt out of projects as they choose.
When World Community Grid launched, they used the proprietary Grid MP client from United Devices. After adding support for the open source BOINC client in 2005, World Community Grid eventually discontinued the Grid MP client and consolidated on the BOINC platform in 2008.
Even though WCG makes use of open source client software, the
actual applications that perform the scientific calculations may not be.
However, several of the science applications are available under a free
license, although the source is not available directly from WCG.
Potential problems
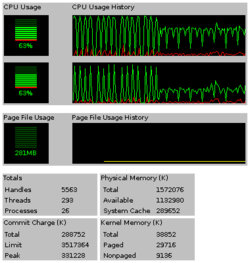
The picture shows particular two CPU usage history (under Hyper-threading) when BOINC client software is processing two tasks on each CPU under Microsoft Windows XP SP2. CPU usage history indicates almost 0% to 100% swing with peak to peak of 3 seconds interval,
when view +update speed set to high, at first half recording period.
The rest of half period of history is set to update speed normal, and
upper CPU usage history indicates slightly more than 60% and lower CPU
usage history show 35% approx. in average.
The World Community Grid software increases CPU
usage by consuming unused processing time; in the late 1990s and early
2000s, such calculations were meant to reduce "wasted" CPU cycles. With modern CPUs, where dynamic frequency scaling is prevalent, increased usage makes the processor run at higher frequency, increasing power usage and heating counter to power management. Additionally, because of an increasing focus on power performance, or performance per watt,
connecting old/inefficient computers to the grid will increase the
total/average power required to complete the same calculations.
The BOINC
client avoids slowing the computer by using a variety of limits that
suspend computation when there are insufficient free resources. Unlike
other BOINC projects, World Community Grid set the BOINC defaults
conservatively, making the chances of computer damage extremely small.
The default CPU throttle is 60%. The throttle is coarse-grained; for
example, if usage is set to 60% it will work at 100% for 3 seconds, then
at 0% for 2 seconds, resulting in an average decrease of processor use.
An add-on program for Windows computers – TThrottle
– can solve the problem of overheating by directly limiting the BOINC
project's use of the host computer. It does this by measuring the CPU
and/or the GPU temperature and adjusts the run time accordingly. It also
uses a shorter switching time of less than one second, resulting in
less temperature change during switching.
Statistics and competition
The contributions of each user are recorded and user contribution statistics are publicly available.
Due to the fact that the processing time of each workunit varies from
computer to computer, depending on the difficulty of the workunit, the
speed of the computer, and the amount of idle resources available,
contributions are usually measured in terms of points. Points are awarded for each workunit depending on the effort required to process it.
Upon completing a workunit, the BOINC client will request the number of points it thinks it deserves based on software benchmarks (see BOINC Credit System#Cobblestones).
Since multiple computers process the same workunit to ensure accuracy,
the World Community Grid servers can look at the points claimed by each
of those computers. The WCG servers disregard statistical outliers,
average the remaining values and award the resulting number of points to
each computer.
Within the grid, users may join teams that have been created by
organizations, groups, or individuals. Teams allow for a heightened
sense of community identity and can also inspire competition. As teams
compete against each other, more work is done for the grid overall.
Outreach
World Community Grid recognizes companies and organizations as partners if they promote WCG within their company or organization. As of March 2020, WCG had 452 partners.
Also, as part of its commitment to improving human health and
welfare, the results of all computations completed on World Community
Grid are released into the public domain and made available to the
scientific community.
Scientific results
Since its launch, more than thirty projects have run in the World Community Grid. Some of the results include:
- In February 2014, the Help Fight Childhood Cancer project scientists announced the discovery of 7 compounds that destroy neuroblastoma cancer cells without any apparent side effects. This discovery, made with the support of the WCG volunteers, is a positive step towards a new treatment. The project has announced that it is seeking a collaboration with a pharmaceutical company in order to develop the compounds into treatments. Given the success of the project, the scientists have stated that they are already planning a follow-up project which will focus on other pediatric cancers, possibly in collaboration with a newly-formed Pan-Asian oncology group, of which they are a founding member.
- The GO Fight Against Malaria project reported the discovery of several molecules that are effective against Malaria and Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (including TDR-TB, for which there is no treatment available). The project also tested for new molecules against MRSA, Filariasis and Bubonic Plague. Laboratory testing continues in order to turn those molecules into possible treatments. GFAM was also the first project ever to perform a billion different docking calculations. A paper was published in January 2015, with two more pending submission. In June 2015, the project reported that of the two "hits" discovered against a drug-resistant tuberculosis strain, several "analogs" have been synthesized, the best one of which inhibits the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is relatively non-toxic to mammalian cells.
- The Discovering Dengue Drugs - Together project scientists reported the discovery of several new Dengue protease inhibitors, most of which also inhibit the West Nile virus protease. A handful of these have already entered "crucial pre-clinical pharmacokinetic and efficacy studies". In November 2014, an update reported that the scientists have a drug lead that disables a key enzyme that allows the Dengue virus to replicate. It has also shown the same behaviour in other flaviviruses, such as the West Nile virus. No negative side effects such as toxicity, carcinogenicity or mutagenicity have been observed, making this drug lead a very strong antiviral drug candidate for these viruses. The scientists are now working to synthesize variants of the molecule to improve its activity and enter planned pre-clinical and clinical trials.
- In June 2013, the Clean Energy Project published a database of over 2.3 million organic molecules which have had their properties characterized. Of these, 35,000 molecules have shown the potential to double the efficiency over organic solar cells currently being produced. Before this initiative, scientists knew of just a handful of carbon-based materials that were able to convert sunlight into electricity efficiently.
- In February 2010, the FightAIDS@Home project scientists announced that they have found two compounds which make a potentially new class of AIDS-fighting drugs possible. The compounds attach to the virus at newly-discovered binding sites, and thus can be used to "enhance existing therapies, treat drug-resistant strains of the disease, and slow the evolution of drug resistance in the virus."
- In July 2015, the Drug Search for Leishmaniasis project announced it had tested the top 10 compounds with highest predicted efficiency out of over 100 identified via WCG workunits. Of those 10, 4 showed "positive results" in in vitro testing, with one showing "an exceptionally promising result". In August 2017, in vivo testing of the 4 compounds on hamsters showed favorable results, with one compound inducing "an almost complete curing of the lesions in two out of five hamsters."
- In July 2015, the Computing for Clean Water project announced that a paper had been published in the Nature Nanotechnology journal describing a new type of water filter efficiently utilising nanotubes. "[The] nanotubes are made of single-atom-thick sheets of carbon atoms, called graphene, rolled up into tiny tubes, with diameters of just a few nanometers - one ten-thousandth the diameter of a human hair. The size of the tubes allows water molecules to pass through, but blocks larger pathogens and contaminants, purifying the water." By running simulations on WCG, the scientists discovered that certain kinds of natural vibrations called phonons, under specific conditions, can lead to more than 300% increased flow of water through the nanotubes, compared to previous theoretical predictions.
- In April 2015, the Say No To Schistosoma project scientists reported that subsequent analysis had been performed, and the three most promising candidate substances had been identified for in vitro testing.
Active projects
OpenPandemics - COVID-19
On April 1st, 2020, IBM announced OpenPandemics - COVID-19. The project aims to identify possible treatments for the Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) which is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. WCG will partner with Scripps Research, with whom it has partnered in the past, notably in FightAIDS@Home
projects. The project will run on CPUs and eventually GPUs and will
also serve to create a "fast-response, open source tool that will help
all scientists quickly search for treatments for future pandemics."
The project launched on May 14, 2020.
Mapping Cancer Markers
Mapping Cancer Markers
(launched November 8, 2013). The project aims to identify the markers
associated with various types of cancer, and is analyzing millions of
data points collected from thousands of healthy and cancerous patient
tissue samples. These include tissues with lung, ovarian, prostate,
pancreatic and breast cancers. By comparing these different data points,
researchers aim to identify patterns of markers for different cancers
and correlate them with different outcomes, including responsiveness to
various treatment options. The project is focusing on 4 types of cancer,
with the first focus being on lung cancer, and will move on to ovarian
cancer, prostate cancer and sarcoma.
FightAIDS@Home Phase 2
FightAIDS@Home Phase 2 (launched September 30, 2015)
is looking more closely at the results of Phase 1. The project has two
goals in the early experiments; the simulation architecture is
functioning correctly and giving reliable results, and using BEDAM and AutoDock together provides better results than using just BEDAM or AutoDock.
Help Stop TB
Help Stop TB was launched in March 2016 to help combat tuberculosis, a disease caused by a bacterium that is evolving resistance to currently available treatments. The computations of this project target mycolic acids
in the bacterium's protective coat, simulating the behavior of these
molecules to better understand how they offer protection to the
bacteria.
Smash Childhood Cancer
Starting January 2017, the Smash Childhood Cancer
project builds on the work from the Help Fight Childhood Cancer project
by looking for drug candidates targeting additional childhood cancers.
Upon Dr. Akira Nakagawara's retirement in March 2020, the principal
investigator changed to Dr. Godfrey Chan, who was one of the original
members of the Smash Childhood Cancer team. Additionally, PRDM14 and
Fox01 have been added as new targets for investigation.
Microbiome Immunity Project
Microbiome Immunity Project (launched August 2017) is a study of proteins in bacteria located in and on the human body; the human microbiome,
which is made of around 3 million separate bacterial genes. By learning
bacteria genes, their individual shapes can be known, and each physical
shape determines the function of bacteria. Collaborative institutions includes the University of California San Diego, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and the Simons Foundation's Flatiron Institute.
Africa Rainfall Project
The Africa Rainfall Project
(launched October 2019) will use the computing power of World Community
Grid, data from The Weather Company, and other data to improve rainfall
modelling, which can help farmers in sub-Saharan Africa successfully
raise their crops.
Completed projects
Human Proteome Folding – Phase 1
The first project launched on World Community Grid was the Human
Proteome Folding Project, or HPF1, which aims to predict the structure
of human proteins. The project was launched on November 16, 2004, and completed on July 18, 2006. This project was unique in that computation was done in tandem with the grid.org distributed computing project. Devised by Richard Bonneau at the Institute for Systems Biology,
the project used grid computing to produce the likely structures for
each of the proteins using a Rosetta Score. From these predictions,
researchers hope to predict the function of the myriad proteins. This
increased understanding of the human proteins could prove vital in the
search for cures to human diseases. Computing for this project was officially completed on July 18, 2006. Research results for the yeast portion of HPF1 have been published.
Human Proteome Folding – Phase 2
Human Proteome Folding - Phase 2 (HPF2) (launched June 23, 2006)
was the third project to run on World Community Grid, and completed in
2013. This project, following on from HPF1, focused on human-secreted proteins, with special focus on biomarkers and the proteins on the surface of cells as well as Plasmodium,
the organism that causes malaria. HPF2 generates higher-resolution
protein models than HPF1. Though these higher-resolution models are more
useful, they also require more processing power to generate.
In a July 2012 status report, the project scientists reported
that the results generated by the WCG calculations are being used by Dr.
Markus Landthaler of the Max Delbruch Center for Molecular Medicine
(MDC) in Berlin. The HPF2 results helped Dr. Markus Landthaler and his
collaborators in writing up a new paper on "The mRNA-Bound Proteome and
Its Global Occupancy Profile on Protein-Coding Transcripts"
Help Defeat Cancer
The Help Defeat Cancer project seeks to improve the ability of
medical professionals to determine the best treatment options for
patients with breast, head, or neck cancer. The project was launched on
July 20, 2006, and completed in April 2007. The project worked by identifying visual patterns in large numbers of tissue microarrays
taken from archived tissue samples. By correlating the pattern data
with information about treatment and patient outcome, the results of
this project could help provide better targeted treatment options.
Genome Comparison
The Genome Comparison project is sponsored by the Brazilian research institution Fiocruz. The project was launched on November 21, 2006, and completed on July 21, 2007.
The project seeks to compare gene sequences of different organisms
against each other in order to find similarities between them.
Scientists hope to discover what purpose a particular gene sequence
serves in a particular function of one organism, via comparing it to a
similar gene sequence of known function in another organism.
Help Cure Muscular Dystrophy – Phase 1
Help Cure Muscular Dystrophy is run by Décrypthon, a collaboration between French Muscular Dystrophy Association, French National Center for Scientific Research and IBM. Phase 1 was launched on December 19, 2006, and completed on June 11, 2007. The project investigated protein–protein interactions for 40,000 proteins whose structures are known, with particular focus on those proteins that play a role in neuromuscular diseases. The database of information produced will help researchers design molecules to inhibit or enhance binding of particular macromolecules, hopefully leading to better treatments for muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular diseases. This project was available only to agents running the Grid MP client, making it unavailable to users running BOINC.
Discovering Dengue Drugs – Together
Discovering Dengue Drugs – Together was sponsored by scientists at the University of Texas and the University of Chicago and will run in two phases. Phase 1, launched August 21, 2007, used AutoDock 2007 (the same software used for FightAIDS@Home) to test potential antiviral drugs (through NS3 protease inhibition) against viruses from the family flaviviridae and completed on August 11, 2009. Phase 2 "[uses] a more computationally intensive program to screen the candidates that make it through Phase 1." The drug candidates that make it through Phase 2 will then be lab-tested.
AfricanClimate@Home
The
mission of AfricanClimate@Home was to develop more accurate climate
models of specific regions in Africa. It was intended to serve as a
basis for understanding how the climate will change in the future so
that measures designed to alleviate the adverse effects of climate
change could be implemented. World Community Grid's tremendous computing
power was used to understand and reduce the uncertainty with which
climate processes were simulated over Africa. Phase 1 of African
Climate@Home launched on September 3, 2007, and ended in July 2008.
Help Conquer Cancer
Help Conquer Cancer project (launched November 1, 2007) is sponsored by the Ontario Cancer Institute (OCI), Princess Margaret Hospital and University Health Network of Toronto, Canada. The project involves X-ray crystallography.
The mission of Help Conquer Cancer is to improve the results of protein
X-ray crystallography, which helps researchers not only annotate
unknown parts of the human proteome, but importantly improves their
understanding of cancer initiation, progression and treatment.
The HCC project was the first WCG project benefiting from graphics processing units
(GPU)s which helped finish it a lot earlier than initially projected
due to the massive power of GPUs. In the April 2013 status report
the scientists report there is still a lot of data to analyze but that
they are preparing a new project that will search for prognostic and
predictive signatures (sets of genes, proteins, microRNAs, etc.) that
help predict patient survival and response to treatment.
The project finished in May 2013.
Nutritious Rice for the World
The Nutritious Rice for the World project is carried out by Ram Samudrala's Computational Biology Research Group at the University of Washington. The project was launched on May 12, 2008, and completed on April 6, 2010. The purpose of this project is to predict the structure of proteins of major strains of rice, in order to help farmers breed better rice strains with higher crop yields, promote greater disease and pest resistance, and utilize a full range of bioavailable nutrients that can benefit people around the world, especially in regions where malnutrition is a critical concern. The project has been covered by more than 200 media outlets since its inception.
On April 13, 2010, World Community Grid officially announced that the
Nutritious Rice for the World project finished on April 6, 2010.
In April 2014, an update was posted stating that the research
team was able to publish structural information about thousands of
proteins, and advance the field of computational protein modeling. These
results – which were only possible because of the massive amount of
donated computing power they had available – are expected to guide
future research and plant science efforts.
The Clean Energy Project
The Clean Energy project is sponsored by the scientists of Harvard University's Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology. The mission of the Clean Energy Project is to find new materials for the next generation of solar cells and later, energy storage devices. Researchers are employing molecular mechanics and electronic structure
calculations to predict the optical and transport properties of
molecules that could become the next generation of solar cell materials.
Phase 1 was launched on December 5, 2008, and completed on October 13, 2009.
By harnessing the computing power of the World Community Grid,
researchers were able to calculate the electronic properties of tens of
thousands of organic materials – many more than could ever be tested in a
lab – and determine which candidates are most promising for developing
affordable solar energy technology.
Phase 2 was launched June 28, 2010, sponsored by the scientists of Harvard University's Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology.
Further calculations about optical, electronic and other physical
properties of the candidate materials are being conducted with the Q-Chem quantum chemistry software. Their findings have been submitted to the Energy & Environmental Science journal.
Help Fight Childhood Cancer
Help Fight Childhood Cancer project (launched March 13, 2009) is sponsored by the scientists at Chiba Cancer Center Research Institute and Chiba University.
The mission of the Help Fight Childhood Cancer project is to find drugs
that can disable three particular proteins associated with neuroblastoma, one of the most frequently occurring solid tumors in children. Identifying these drugs could potentially make the disease much more curable when combined with chemotherapy treatment.
Influenza Antiviral Drug Search
Influenza Antiviral Drug Search project is sponsored by Dr. Stan Watowich and his research team at The University of Texas Medical Branch (Galveston, Texas, USA). The project was launched on May 5, 2009, and completed on October 22, 2009. The mission of the Influenza Antiviral Drug Search project is to find new drugs that can stop the spread of an influenza
infection in the body. The research will specifically address the
influenza strains that have become drug resistant as well as new strains
that are appearing. Identifying the chemical compounds that are the
best candidates will accelerate the efforts to develop treatments that
would be useful in managing seasonal influenza outbreaks, and future
influenza epidemics and even pandemics.
Phase 1 of The Influenza Antiviral Drug Search project has already
finished on October 22, 2009. Now the researchers are performing
post-processing on the results from Phase 1 and are preparing for Phase
2.
In November 2012, the project's scientists stated that, given the
fact that there is no immediate danger of an influenza outbreak, all of
the project's results would be posted online and their resources would
be refocused on the Dengue Project.
Help Cure Muscular Dystrophy – Phase 2
World Community Grid and researchers supported by Decrypthon, a
partnership between AFM (French Muscular Dystrophy Association), CNRS
(French National Center for Scientific Research), Universite Pierre et
Marie Curie, and IBM were investigating protein–protein interactions for
more than 2,200 proteins whose structures are known, with particular
focus on those proteins that play a role in neuromuscular diseases. Phase 2 was launched on May 12, 2009,
and completed on September 26, 2012. The database of information
produced will help researchers design molecules to inhibit or enhance
binding of particular macromolecules, hopefully leading to better treatments for muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular diseases.
Phase 2 of the Help Cure Muscular Dystrophy project began once
the results from the first phase had been analyzed. Phase 2 ran on the BOINC platform.
Discovering Dengue Drugs – Together – Phase 2
Discovering Dengue Drugs – Together – Phase 2 (launched February 17, 2010) is sponsored by The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) in Galveston, Texas, United States and the University of Chicago in Illinois, USA. The mission is to identify promising drug candidates to combat the Dengue, Hepatitis C, West Nile, Yellow Fever,
and other related viruses. The extensive computing power of World
Community Grid will be used to complete the structure-based drug
discovery calculations required to identify these drug candidates.
Computing for Clean Water
Computing for Clean Water (launched September 20, 2010) is sponsored by the Center for Nano and Micro Mechanics of Tsinghua University in Beijing.
The project's mission is to provide deeper insight on the molecular
scale into the origins of the efficient flow of water through a novel
class of filter materials. This insight will in turn guide future
development of low-cost and more efficient water filters. It is
estimated that 1.2 billion people lack access to safe drinking water,
and 2.6 billion have little or no sanitation. As a result, millions of
people die annually – an estimated 3,900 children a day due to a lack of
clean water.
On April 25, 2014, the project scientists released an update stating
that they had exciting results to report when the paper is submitted and
that the project on WCG was finished.
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis
Drug Search for Leishmaniasis (launched September 7, 2011) is spearheaded by the University of Antioquia in Medellín, Colombia,
with assistance from researchers at the University of Texas Medical
Branch in Galveston, Texas. The mission is to identify potential
molecule candidates that could possibly be developed into treatments for
Leishmaniasis.
The extensive computing power of World Community Grid will be used to
perform computer simulations of the interactions between millions of
chemical compounds and certain target proteins. This will help find the
most promising compounds that may lead to effective treatments for the
disease.
GO Fight Against Malaria Project
The mission of the GO Fight Against Malaria project (launched November 16, 2011) is to discover promising drug candidates that could be developed into new drugs that cure drug resistant forms of malaria.
The computing power of World Community Grid will be used to perform
computer simulations of the interactions between millions of chemical
compounds and certain target proteins, to predict their ability to
eliminate malaria. The best compounds will be tested by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute of La Jolla, California, U.S.A. and further developed into possible treatments for the disease.
Say No to Schistosoma
Say No to Schistosoma (launched February 22, 2012) was the 20th research project to be launched on World Community Grid. The researchers at Infórium University in Belo Horizonte and FIOCRUZ-Minas, Brazil,
ran this project on World Community Grid to perform computer
simulations of the interactions between millions of chemical compounds
and certain target proteins in the hope of finding effective treatments
for schistosomiasis.
As of April 2015, subsequent analysis had been performed, and the three
most promising candidate substances had been identified for in-vitro
testing.
Computing for Sustainable Water
Computing for Sustainable Water was the 21st research project to be launched on World Community Grid. The researchers at the University of Virginia
were running this project on World Community Grid to study the effects
of human activity on a large watershed and gain deeper insights into
what actions can support the restoration, health and sustainability of
this important water resource. The project was launched on April 17, 2012 and completed on October 17, 2012.
Uncovering Genome Mysteries
Uncovering Genome Mysteries
project launched on October 16, 2014 and is a joint collaboration
between Australian and Brazilian scientists. The project aims to examine
close to 200 million genes from many life forms and compare them with
known genes in order to find out what their function is. The results
could have an effect in fields such as medicine and environmental
research.
Outsmart Ebola Together
Outsmart Ebola Together was a collaboration with the Scripps Research Institute to help find chemical compounds to fight Ebola virus disease. It was launched on 3 December 2014. The aim is to block crucial steps in the life cycle of the virus, by finding drugs with high binding affinity
with certain of its proteins. There are two targets: a surface protein
used by the virus to infect human cells, and "transformer" proteins
which change shape to carry out different functions. The project officially completed December 6, 2018.
OpenZika
OpenZika was launched on May 18, 2016 to help combat the Zika virus.
The project targets proteins that are believed to be used by the Zika
virus to survive and spread in the body, based on known results from
similar diseases like dengue fever and yellow fever. These results will help researchers develop an anti-Zika drug. The project officially completed December 13, 2019.
FightAIDS@Home
FightAIDS@Home (launched November 19, 2005)
was World Community Grid's second project and its first to target a
single disease. Each individual computer processes one potential drug
molecule and tests how well it would dock with HIV protease, acting as a protease inhibitor.
Scripps Research Institute published its first peer-reviewed scientific
paper about the results of FightAIDS@Home on April 21, 2007.
This paper explains that the results up to that point will primarily be
used to improve the efficiency of future FightAIDS@Home calculations.
FightAIDS@Home project is still ongoing, but there is no computation
necessity for the next few months, so tech at WCG changed the project
status to completed. According to the tech's words, "If and when more work becomes available, we can quickly open the project again."