In the United States, the relationship between race and crime has been a topic of public controversy and scholarly debate for more than a century. Crime rates vary significantly between racial groups. Most homicide victims in the United States are of the same race as the perpetrator.
Academic research indicates that the over-representation of some racial minorities in the criminal justice system can in part be explained by socioeconomic factors, such as poverty, exposure to poor neighborhoods, poor access to public education, poor access to early childhood education, and exposure to harmful chemicals (such as lead) and pollution. Racial housing segregation has also been linked to racial disparities in crime rates, as blacks have historically and to the present been prevented from moving into prosperous low-crime areas through actions of the government (such as redlining) and private actors. Various explanations within criminology have been proposed for racial disparities in crime rates, including conflict theory, strain theory, general strain theory, social disorganization theory, macrostructural opportunity theory, social control theory, and subcultural theory.
Research also indicates that there is extensive racial and ethnic discrimination by police and the judicial system. A substantial academic literature has compared police searches (showing that contraband is found at higher rates in whites who are stopped), bail decisions (showing that whites with the same bail decision as blacks commit more pre-trial violations), and sentencing (showing that blacks are more harshly sentenced by juries and judges than whites when the underlying facts and circumstances of the cases are similar), providing valid causal inferences of racial discrimination. Studies have documented patterns of racial discrimination, as well as patterns of police brutality and disregard for the constitutional rights of African-Americans, by police departments in various American cities, including Los Angeles, New York, Chicago and Philadelphia.
Terminology
The term "black-on-black" violence has been criticized for being misleading and racially charged. One columnist writing in the wake of the murder of George Floyd has accused opponents of the Black Lives Matter movement of using "blacks killing blacks" rhetoric to avoid discussions about police brutality.
Researchers note that there are socioeconomic factors underlying these crime statistics, and that crime is often higher in low-income neighborhoods. Media coverage of "black on black" violence has been criticized for perpetuating racial stereotypes of violent black people. Researchers have highlighted media language drawing connections between intracommunity violence in black neighborhoods and supposed "moral bankruptcy" in black family structures and communities. Edward A. Flynn has noted that African-Americans are disproportionately murdered, accounting for 80% of murder victims in Milwaukee. Researchers have noted these arguments but say that the term black-on-black crime is "inaccurate and vague" and "generally offensive to black Americans".
Crime data sources
In the United States, crime data are collected from three major sources:
- Law enforcement agency crime reports, collected monthly by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and processed annually as Uniform Crime Reports (UCR)
- victimization surveys, collected biannually by the Bureau of Justice Statistics and processed annually in the National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS)
- self-report surveys
The Uniform Crime Reports represent the primary source of data used in the calculation of official statistics regarding serious crimes such as murder and homicide, which is supplemented by the information provided through the NCVS and self-report studies, the latter being the best indicator of actual crime rates for minor offenses such as illegal substance abuse and petty theft. These crime data collection programs provide most of the statistical information utilized by criminologists and sociologists in their analysis of crime and the extent of its relationship to race. Another form of data is that regarding the prison population.
Uniform Crime Reports (UCR)
Established in 1927, the Uniform Crime Reports (UCR) program is a summary-based reporting system that collects data on crime reported to local and state law enforcement agencies across the US. The UCR system indexes crimes under two headings: Part I and Part II offenses. Part I offenses include: murder and non-negligent homicide; non-lethal violent crimes comprising robbery, forcible rape and aggravated assault; and property crimes comprising burglary, larceny/theft, motor vehicle theft and arson. Part II offenses include fraud, forgery/counterfeiting, embezzlement, simple assault, sex offenses, offenses against the family, drug and liquor offenses, weapons offenses and other non-violent offenses excluding traffic violations.
There are fundamental limitations of the UCR system, including:
- Inaccuracy: UCR statistics do not represent the actual amount of criminal activity occurring in the United States. As it relies upon local law enforcement agency crime reports, the UCR program can only measure crime known to police and cannot provide an accurate representation of actual crime rates.
- Misrepresentation: The UCR program is focused upon street crime, and does not record information on many other types of crime, such as organized crime, corporate crime or federal crime. Further, law enforcement agencies can provide inadvertently misleading data as a result of local policing practices. These factors can lead to misrepresentations regarding the nature and extent of criminal activity in the United States.
- Manipulation: UCR data are capable of being manipulated by local law enforcement agencies. Information is supplied voluntarily to the UCR program, and manipulation of data can occur at the local level.
- Race and ethnicity: The UCR tracks crime for the racial category of "White" to include both Hispanic and non-Hispanic ethnicities. According to the ACLU, with over 50 million Latinos residing in the United States, this hides the incarceration rates for Latinos vis-à-vis marijuana-related offenses, as they are considered "White" with respect to the UCR.
As a response to these and other limitations, a new system of crime data collection was established in 1988 as an outgrowth of the UCR system. The National Incident-Based Reporting System (NIBRS) is an incident-based reporting system that will collect more comprehensive and detailed data on crime from local, state and federal law enforcement agencies. As it is still under development, NIBRS coverage is not yet nationwide.
National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS)
The National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS) program, established in 1972, is a national survey of a representative sample of households in the United States which covers the frequency of crime victimization and the characteristics and consequences of victimization. The primary purpose behind the NCVS program is to gather information on crimes that were not reported to police, though information is also collected on reported crimes. The survey collects data on rape, assault, robbery, burglary, personal and household larceny and motor vehicle theft. The NCVS also includes supplemental questions which allow information to be gathered on tangentially relevant issues such as school violence, attitudes towards law enforcement or perceptions regarding crime.
There are fundamental limitations to the NCVS program, including:
- Reliability: NCVS statistics do not represent verified or evidenced instances of victimization. As it depends upon the recollection of the individuals surveyed, the NCVS cannot distinguish between true and fabricated claims of victimization, nor can it verify the truth of the severity of the reported incidents. Further, the NCVS cannot detect cases of victimization where the victim is too traumatized to report. These factors can contribute to deficits in the reliability of NCVS statistics.
- Misrepresentation: The NCVS program is focused upon metropolitan and urban areas, and does not adequately cover suburban and rural regions. This can lead to misrepresentations regarding the nature and extent of victimization in the United States.
Comparison of UCR and NCVS data
According to the NCVS for 1992–2000, 43% of violent criminal acts, and 53% of serious violent crime (not verbal threats, or cuts and bruises) were reported to the police. Overall, black (49%) and indigenous Americans (48%) victims reported most often, higher than whites (42%) and Asians (40%). Serious violent crime and aggravated assault against blacks (58% and 61%) and indigenous Americans (55% and 59%) was reported more often than against whites (51% and 54%) or Asians (50% and 51%). indigenous Americans were unusually unlikely to report a robbery (45%), as with Asians and a simple assault (31%).
Despite the differences in the amount of crime reported, comparisons of the UCR and NCVS data sets show there to be a high degree of correspondence between the two systems. This correspondence extends to the racial demography of both perpetrators and victims of violent crime reported in both systems.
Classification of Hispanics
The UCR classifies most Hispanics into the "white" category. The NCVS classifies some Hispanic criminals as "white" and some as "other race". The victim categories for the NCVS are more distinct.
According to a report by the National Council of La Raza, research obstacles undermine the census of Latinos in prison, and "Latinos in the criminal justice system are seriously undercounted. The true extent of the overrepresentation of Latinos in the system probably is significantly greater than researchers have been able to document. Lack of empirical data on Latinos is partially due to prisons' failures to document ethnic details at intake, or recording practices that historically have classified Latinos as white.
The FBI did not include a "Latino" or "Hispanic" category until recently, and 93% of Hispanics are classified as "white" by law enforcement officers (irrespective of their ancestry), often inflating the amount of crimes attributed to whites.
Crime statistics
Scholars have found that some racial and ethnic minorities, particularly African-Americans, are disproportionately represented in the arrest and victimization reports which are used to compile crime rate statistics in the United States. The data from 2008 reveals that black Americans are over-represented in terms of arrests made in virtually all types of crime, with the exceptions of "driving under the influence," "liquor laws," and hate crime. Overall, black Americans are arrested at 2.6 times the per-capita rate of all other Americans, and this ratio is even higher for murder (6.3 times) and robbery (8.1 times).
Homicide
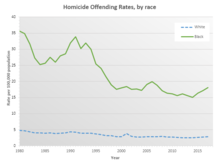
According to the FBI, African-Americans accounted for 55.9% of all homicide offenders in 2019, with whites 41.1%, and "Other"/Unknown 3.0% in cases where the race was known. Among homicide victims in 2019 where the race was known, 54.7% were black or African-American, 42.3% were white, and 3.1% were of other races. The per-capita offending rate for African-Americans was roughly six times higher than that of whites, and the victim rate is a similar figure. Most homicides were intraracial; where the perpetrator's race was known, 81% of white victims were killed by whites and 91% of black or African-American victims were killed by African-Americans.
Assault
The CDC keeps data on non-fatal injury emergency department visits and the race of victims. While non-Hispanic white victims account for approximately half of total non-fatal assault injuries, most of which did not involve any weapon, black and Hispanic victims account for the vast majority of non-fatal firearm injuries. There was a total of 17.3 million emergency department visits or hospitalizations for non-fatal assaults in the United States in the 10-year period between 2007–2016. For non-fatal assaults with recorded race, 6.5 million victims were white non-Hispanic, 4.3 million black, 2.3 million Hispanic and 0.4 million other (non-Hispanic) and for 3.8 million, the race was not recorded. There were a total of 603,000 emergency department visits in the US for non-fatal firearm assaults in the 10-year period between 2007–2016. For non-fatal firearm assaults with recorded race, 77,000 victims were white non-Hispanic, 261,000 were black and 94,000 were Hispanic, 8,500 were other non-Hispanic and for 162,000 the race was not recorded. Despite gun injuries only accounting for about 3.5% of serious assault injuries between 2007 and 2016, they accounted for nearly 70% of overall homicides.
While African Americans are highly overrepresented in murders and gun assaults, the disparity in arrests is small for the most common form of assault not involving any weapon or serious injury (non-aggravated assault). Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites are arrested for non-aggravated assault in a similar ratio to their share of the US population. Of the 9,468 murder arrests in the US in 2017, 53.5% were black and 20.8% Hispanic. Of the 822,671 arrests for non-aggravated assault, 31.4% were black and 18.4% Hispanic.
According to the FBI Uniform Crime Reports, in 2008, black youths, who make up 16% of the youth population, accounted for 52% of juvenile violent crime arrests, including 58.5% of youth arrests for homicide and 67% for robbery. Black youths were overrepresented in all offense categories except DUI, liquor laws, and drunkenness. Racial disparities in arrest have consistently been far less among older population groups.
Robbery
According to the National Crime Victimization Survey in 2002, robberies with white victims and black offenders were more than 12 times more common than the opposite.
Victim surveys
In 1978, Michael Hindelang compared data from the National Crime Victimization Survey (then known as the National Crime Survey, or NCS) to data from the Uniform Crime Reports, both from 1974. He found that NCS data generally agreed with UCR data in regards to the percent of perpetrators of rape, robbery, and assault who were black. For instance, Hindelang's analysis found that both the NCS and UCR estimated that 62% of robbery offenders were black in the United States in 1974. A 2004 National Crime Victimization Survey report which analyzed carjacking over 10 years found that carjacking victims identified 56% of offenders as black, 21% as white, and 16% as indigenous American or Asian.
Youth crime
The "National Youth Gang Survey Analysis" (2011) state that of gang members, 46% are Hispanic/Latino, 35% are black, 11.5% are white, and 7% are other races/ethnicities.
Hispanics
According to a 2009 report by the Pew Hispanic Center, in 2007 Latinos "accounted for 40% of all sentenced federal offenders ‒ more than triple their share (13%) of the total U.S. adult population". This was an increase from 24% in 1991. Between 1991 and 2007, enforcement of federal immigration laws became a growing priority in response to undocumented immigration. By 2007, among Hispanic offenders sentenced in federal courts, 48% were immigration offenses, 37% drug offenses, and 15% for other offenses. One reason for the large increase in immigration offenses is that they exclusively fall under federal jurisdiction.
Racially motivated hate crime
The federal government publishes a list annually of Hate Crime Statistics, 2009. Also published by the federal government is the Known Offender's Race by Bias Motivation, 2009. According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation Uniform Crime Report database, in 2010 of 3,949 victims of racial hate crimes, 58.6% of reported hate crime offenders were white or hispanic-white, 18.4% of offenders were black, 8.9% were of individuals of multiple races and 1% of offenders were indigenous Americans. The report also reveals that 48% of all hate crime offenders were motivated by the victim's race, while 18% were based on the victim's religion, and another 18% were based on the victim's sexual orientation. The report states that among hate crime offenses motivated by race, 70% were composed of anti-black bias, while 17.7% were of anti-white bias, and 5% were of anti-Asian or Pacific Islander bias.
Racial composition of geographic areas
Studies have examined that ethnic/racially heterogeneous areas, most often neighborhoods in large cities, have higher crime rates than more homogeneous areas. Most studies find that the more ethnically/racially heterogeneous an area is, the higher its crime rates tend to be.
Studies examining the relationship between percentages of different races in an area and crime rates have generally either found similar relationships as for nationwide crime rates or no significant relationships. Most often studied are correlations between black and Hispanic populations in a given area and crime. According to a study in the American Journal of Sociology, a positive correlation exists between the percentage of black males in a neighborhood and perceptions of neighborhood crime rates, even after controlling other correlating factors and neighborhood characteristics. The study was conducted amongst the perceptions of residents in neighborhoods in Chicago, Seattle, and Baltimore in comparison with census data and police department crime statistics. Survey respondents consistently rated African Americans as more prone to violence than the data and statistics stated leading to the conclusion that the stereotype of blacks as more likely criminals is deeply embedded in the collective consciousness and societal norms of Americans. Such data may reveal a possible connection, but is functionally inconclusive due to a variety of other correlating factors which overlap with race and ethnicity.
Trends
Some studies have argued for smaller racial disparities in violent crime in recent times. However, a study of government data from 1980–2008 found that the reduction in black violent crime relative to white violent crime may have been an artifact of those previous studies, which was due to Hispanic offenders being counted as White in the comparison. The Hispanic population has been increasing rapidly and Hispanics have violence rates higher than that of whites but lower than that of blacks.
Other data suggests a genuine decline in racial disparities in recent years. In the 1980s and early 1990s black/white (including Hispanics) imprisonment disparities increased peaking in the early 1990s when a slim majority of new admissions were blacks. Relative to 2000, disparities in prisons and jails have since declined modestly in recent decades between both blacks and whites and Hispanics and whites. Between 2000 and 2019, the ratio of disparity amongst male state and federal prisoners per capita declined between blacks and non-Hispanic whites from 7.7 to 5.7 and between Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites from 2.7 to 2.5. Declines in disparities were more pronounced when considering jail inmates of both sexes between 2005 and 2018 with the ratio of disparity per capita declining from 4.8 to 3.2 between blacks and non-Hispanic whites and 1.6 to 1.0 between Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites.
Similarly, declines in the racial disparity of homicide victimization can be seen although to a much greater extent between Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites. Using CDC data between 1990 and 2019, the ratio of the murder rate between Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites declined from 4.5 to 2.0 and between blacks and non-Hispanic whites from 9.9 to 8.3. When considering non-firearm homicide victimization rates racial disparities the ratio of decline is very significant between 1990 and 2019, falling between blacks and non-Hispanic whites from 7.0 to 3.3 and between Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites from 3.4 to 1.3.
Explanations for racial discrepancies
Discrimination by law enforcement
Research suggests that police practices, such as racial profiling, over-policing in areas populated by minorities and in-group bias may result in disproportionately high numbers of racial minorities among crime suspects.
In-group bias has been observed when it comes to traffic citations, as black and white cops are more likely to cite out-groups. A 2013 report by the American Civil Liberties Union found that blacks were "3.73 times more likely than whites to be arrested for marijuana possession," even though "blacks and whites use drugs, including marijuana, at similar rates." A 2020 study in the journal Nature found that black drivers were stopped more often than white drivers, and that the threshold by which police decided to search black and Hispanic drivers was lower than that for whites (judging by the rate at which contraband was found in searches). Analysis of more than 20 million traffic stops in North Carolina showed that blacks were more than twice as likely as whites to be pulled over by police for traffic stops, and that blacks were more likely to be searched following the stop. There were no significant difference in the likelihood that Hispanics would be pulled over, but Hispanics were much more likely to be searched following a traffic stop than whites. When the study controlled for searches in high-crime areas, it still found that police disproportionately targeted black individuals. These racial disparities were particularly pronounced for young men. The study found that whites who were searched were more likely to carry contraband than blacks and Hispanics. In-group bias by voters has also been suggested as possibly causing disparities, as voters discount criminal acts done by their in-group and thus will vote for higher enforcement in areas where the minority population is higher due to the lack of in-group leniency, allowing for racial disparities in the justice system even if the authorities are unbiased.
A 2018 study in the Journal of Empirical Legal Studies found that law enforcement officers in Texas who could charge shoplifters with two types of crimes (one more serious, one less so) due to a vaguely worded statute were more likely to charge blacks and Hispanics with the more serious crime.
A 2019 study, which made use of a dataset of the racial makeup of every U.S. sheriff over a 25-year period, found that "ratio of Black‐to‐White arrests is significantly higher under White sheriffs" and that the effects appear to be "driven by arrests for less‐serious offenses and by targeting Black crime types."
A 2019 study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology found that facial-recognition systems were substantially more likely to misidentify the faces of racial minorities. Some ethnic groups, such as Asian-Americans and African-American, were up to 100 times more likely to be misidentified than white men.
A 2018 study in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that tall young black men are especially likely to receive unjustified attention by law enforcement. The authors furthermore found a "causal link between perceptions of height and perceptions of threat for Black men, particularly for perceivers who endorse stereotypes that Black people are more threatening than White people."
Childhood exposure to violence
Research shows that childhood exposure to violence significantly increases the likelihood to engage in violent behavior. When studies control for childhood exposure to violence, black and white males are equally likely to engage in violent behavior. White and black families have no major difference in child abuse except in the $6,000-$11,999 income range (which falls under the Poverty Threshold in the United States). A study in Australia showed a direct correlation to poverty in later life from childhood abuse. While poverty in the United States and Australia are not the same, a general understanding of the negative effects of childhood abuse later in life has been found, many of these effects being contributing factors to poverty.
A paper written by Anna Aizer, analyzes the disadvantages children face when they are exposed to frequent neighborhood violence. In a survey of 2248 6th, 8th, and 10th graders in an urban public school system, “Schwab-Stone et al (1995) found that 40% of youth reported exposure to a shooting or a stabbing in the past year. Children exposed to high levels of violence were more likely to be black and/or Latino…”. Using ANOVA to observe differences in child outcomes, they found that exposure to violence is associated with willingness to use physical aggression, diminished perception of risk, lowered expectations of the future, substance use, and low academic achievement. The Los Angeles Family and Neighborhood Study (LA FANS) studied a representative sample of all neighborhoods in LA and evaluated the conditions and circumstances in which each family was living under. Families were randomly selected within each neighborhood and interviews were conducted with adults, caregivers, and children. 21% of children reported having violent peers that were a part of gangs, 11% reported being robbed, 8% reported witnessing a shooting within the past year.
Inability to post bail
According to a 2017 study in the Journal of Law and Economics, "Higher pretrial detention rates among minority defendants explain 40 percent of the black-white gap in rates of being sentenced to prison and 28 percent of the Hispanic-white gap." The majority of individuals held in pretrial detention are being held because they cannot afford to post bail. The individuals in pretrial detention face higher incentives to plead guilty (even if they are innocent) for a number of reasons, which leads to a higher sentencing rates for these individuals.
Socioeconomic factors
Evidence supporting the role of structural factors in high black crime rates comes from multiple studies. For example, Robert J. Sampson has reported that most of the reason violent crime rates are so high among blacks originates mainly from unemployment, economic deprivation, and family disorganization. Specifically, he found that "the scarcity of employed black men increases the prevalence of families headed by females in black communities" and that the increased prevalence of such families in turn results in family disruption that significantly increases black murder and robbery rates. Sampson, et al. and Phillips have reported that at least half of the black-white homicide offending differential is attributable to structural neighborhood factors like parents' marital status and social context. Multiple other studies have found a link between black crime rates and structural factors, such as single-parent families and structural inequality.
While there is a correlation between blacks and Hispanics and crime, the data imply a much stronger tie between poverty and crime than crime and any racial group, when gender is taken into consideration. The direct correlation between crime and class, when factoring for race alone, is relatively weak. When gender, and familial history are factored, class correlates more strongly with crime than race or ethnicity. Studies indicate that areas with low socioeconomic status may have the greatest correlation of crime with young and adult males, regardless of racial composition, though its effect on females is negligible. A 1996 study looking at data from Columbus, Ohio found that differences in disadvantage in city neighborhoods explained the vast majority of the difference in crime rates between blacks and whites, and two 2003 studies looking at violent offending among juveniles reached similar conclusions.
Housing segregation
A 1996 study found a strong association between black-white spatial isolation and rates of black violence, consistent with the hypothesis that segregation is responsible for higher rates of black crime. Multiple other studies have reached similar conclusions. However, correlation does not equal causation, and the disproportionately higher crime rates seen in black communities—as well as the reason for their segregation—can be attributed to a number of underlying symptoms.
Additionally, "Hagan and Peterson (1995) further propose that the segregation of racial minorities in sections of concentrated poverty contributes to inferior educational and employment opportunities, which, in turn, enhance the likelihood of crime and delinquency."
Theories of causation
Historically, crime statistics have played a central role in the discussion of the relationship between race and crime in the United States. As they have been designed to record information not only on the kinds of crimes committed, but also on the individuals involved in crime, criminologists and sociologists have and continue to use crime rate statistics to make general statements regarding the racial demographics of crime-related phenomena such as victimization, arrests, prosecutions, convictions, and incarceration. Regardless of their views regarding causation, scholars acknowledge that some racial and ethnic minorities are disproportionately represented in the arrest and victimization reports which are used to compile crime rate statistics. There is, however, a great deal of debate regarding the causes of that disproportionality. Sociologist Orlando Patterson has explained these controversies as disputes between liberal and conservative criminologists in which each camp focuses on mutually exclusive aspects of the causal net, with liberals focusing on factors external to the groups in question and conservatives focusing on internal cultural and behavioral factors.
History
The relationship between race and crime has been an area of study for criminologists since the emergence of anthropological criminology in the late 19th century. Cesare Lombroso, founder of the Italian school of criminology, argued that criminal behavior was the product of biological factors, including race. He was among the first criminologists to claim a direct link between race and crime. This biological perspective, sometimes seen as racist and increasingly unpopular, was criticized by early 20th century scholars, including Frances Kellor, Johan Thorsten Sellin and William Du Bois, who argued that other circumstances, such as social and economic conditions, were the central factors which led to criminal behavior, regardless of race. Du Bois traced the causes of the disproportional representation of blacks in the criminal justice system back to the improperly handled emancipation of black slaves in general and the convict leasing program in particular. In 1901, he wrote:
There are no reliable statistics to which one can safely appeal to measure exactly the growth of crime among the emancipated slaves. About seventy per cent of all prisoners in the South are black; this, however, is in part explained by the fact that accused Negroes are still easily convicted and get long sentences, while whites still continue to escape the penalty of many crimes even among themselves. And yet allowing for all this, there can be no reasonable doubt but that there has arisen in the South since the [civil] war a class of black criminals, loafers, and ne'er-do-wells who are a menace to their fellows, both black and white.
The debate that ensued remained largely academic until the late 20th century, when the relationship between race and crime became a recognized field of specialized study in criminology. Helen T. Greene, professor of justice administration at Texas Southern University, and Shaun L. Gabbidon, professor of criminal justice at Pennsylvania State University, note that many criminology and criminal justice programs now either require or offer elective courses on the topic of the relationship between race and crime.
Modern theories of causation
Conflict theory
Conflict theory is considered "one of the most popular theoretical frameworks among race and crime scholars". Rather than one monolithic theory, conflict theory represents a group of closely related theories which operate on a common set of fundamental assumptions. As a general theory of criminal behavior, conflict theory proposes that crime is an inevitable consequence of the conflict which arises between competing groups within society. Such groups can be defined through a number of factors, including class, economic status, religion, language, ethnicity, race or any combination thereof. Further, conflict theory proposes that crime could be largely eliminated if the structure of society were to be changed.
The form of conflict theory which emphasizes the role of economics, being heavily influenced by the work of Karl Marx and sometimes referred to as Marxist criminology, views crime as a natural response to the inequality arising from the competition inherent in capitalist society. Sociologists and criminologists emphasizing this aspect of social conflict argue that, in a competitive society in which there is an inequality in the distribution of goods, those groups with limited or restricted access to goods will be more likely to turn to crime. Dutch criminologist Willem Adriaan Bonger, one of the first scholars to apply the principles of economic determinism to the issue of crime, argued that such inequality as found in capitalism was ultimately responsible for the manifestation of crime at all levels of society, particularly among the poor. Though this line of thinking has been criticized for requiring the establishment of a utopian socialist society, the notion that the disproportionality observed in minority representation in crime rate statistics could be understood as the result of systematic economic disadvantage found its way into many of the theories developed in subsequent generations.
Culture conflict theory, derived from the pioneering work of sociologist Thorsten Sellin, emphasizes the role of culturally accepted norms of conduct in the formation of cultural groups and the conflicts which arise through their interaction. Culture conflict theory argues that the group with the most power in any society ensures that their values, traditions and behaviors, which Sellin referred to as "conduct norms", are those to which all other members of society are forced to conform, and any actions which conflict with the interests of the dominant group are identified as deviant and/or criminal in nature. Sellin's original ideas continued to be developed throughout the 20th century, most notably by George Vold in the 1950s and Austin Turk in the 1960s, and continue to influence the contemporary debate. The recent work of Gregory J. Howard, Joshua D. Freilich and Graeme R. Newman applies culture conflict theory to the issue of immigrant and minority crime around the world. According to their research, while culturally homogeneous groups experience little to no cultural conflict, as all the members share the same set of "conduct norms", culturally heterogeneous groups, such as modern industrial nations with large immigrant populations, display heightened competition between sets of cultural norms which, in turn, leads to an increase in violence and crime. Societies which have high levels of cultural diversity in their population, it is claimed, are more likely to have higher rates of violent crime.
According to conflict theorists such as Marvin Wolfgang, Hubert Blalock and William Chambliss, the disproportionate representation of racial minorities in crime statistics and in the prison population is the result of race- and class-motivated disparities in arrests, prosecutions and sentencing rather than differences in actual participation in criminal activity, an approach which has also been taken by proponents of critical race theory. This line of argumentation is generally seen as part of a wider approach to race-related issues referred to as the Discrimination Thesis, which assumes that differences in the treatment received by people of minority racial background in a number of public institutions, including the criminal justice, education and health care systems, is the result of overt racial discrimination. Opposed to this view is the Non-Discrimination Thesis, which seeks to defend these institutions from such accusations.
At the time it was first proposed, conflict theory was considered outside the mainstream of more established criminological theories, such as strain theory, social disorganization theory and differential association theory. Barbara D. Warner, associate professor of criminal justice and police studies at Eastern Kentucky University, notes that conflict theory has been the subject of increasing criticism in recent years. Recent studies claim that, while there may have been real sentencing differences related to non-legal characteristics such as race in the 1960s, sentencing discrimination as described by the conflict theorists at that time no longer exists. Criticism has also pointed to the lack of testability of the general theory. While much research has been done to correlate race, income level and crime frequency, typically of less serious criminal behavior such as theft or larceny, research has shown there to be no significant correlation between race, income level and crime seriousness. Thus, conflict theory encounters difficulties in attempting to account for the high levels of violent crime such as murder, homicide and rape, in minority populations.
Strain (anomie) theory
Strain theory, which is largely derived from the work of Robert K. Merton in the 1930s and 1940s, argues that social structures within society which lead to inequality and deprivation in segments of its population indirectly encourage those segments to commit crime. According to strain theory, differences in crime rates between races are the result of real differences in behavior, but to be understood as an attempt to alleviate either absolute or relative deprivation and adapt to the existing opportunity structure.
A more recent approach to strain theory was proposed by Steven F. Messner and Richard Rosenfeld in the 1990s. In their version of the theory, which they refer to as institutional anomie theory, Messner and Rosenfeld argue that the dominance of materialistic concerns and measurements of success manifested in the American Dream weakens the effectiveness of informal social control mechanisms and support processes, which encourages economic gain by any means, legal or illegal. In those segments of the population which experience the greatest relative deprivation, therefore, there is readiness to turn to crime to overcome inequality and eliminate relative deprivation.
Critics of strain theory point to its weaknesses when compared with actual criminal behavior patterns. Michael R. Gottfredson and Travis Hirschi argue that strain theory "misconstrue(s) the nature of the criminal act, supplying it with virtues it does not possess." They further point out that, while strain theory suggests that criminals should tend to target people in a more advantageous economic situation than themselves, they more often victimize individuals who live in the same economic circumstances.
General strain theory
Multiple studies have found evidence that Agnew's general strain theory explains much of the difference in crime between blacks and whites.
Social disorganization theory
Social disorganization theory proposes that high rates of crime are largely the result of a heterogeneous and impoverished social ecology. Proponents of the theory point to the process of urban decay as a major contributing factor to the breakdown of healthy urban communities which would normally curb the spread of many forms of criminal behavior. The diversity of minority cultures present in poverty-stricken neighborhoods prevents the formation of strong social bonds and leaves inhabitants uninterested in maintaining positive community relationships. This has been observed to increase the likelihood of crime in certain urban areas, which can lead to increased policing and a further breakdown of familial structures as a result of arrests, which, in turn, precipitates more crime. Social disorganization theory has been instrumental in establishing the notion that stable, culturally homogeneous communities have lower rates of delinquency and crime regardless of race.
Macrostructural opportunity theory
Phillippia Simmons reports that many of the studies which have investigated intra- and interracial crime seek to explain this through a theory of macrostructural opportunity which states that interracial violence is primarily a function of opportunity and access. According to this theory, intraracial crime rates remain relatively high due to the fact that much of the US remains residentially segregated. She notes that this theory predicts that, if residential areas were more racially integrated, intraracial crime would decrease and interracial crime would increase correspondingly. However, she also notes that not all researchers on the topic of intraracial crime agree with this result, with some pointing to other macrostructural factors, such as income and education, which may negate the effect of race on inter- and intraracial crime.
Anthony Walsh criticizes the attempt to use the macrostructural opportunity model to explain interracial rape as has been done in studies conducted in the past few decades, pointing out that such a defense is directly contradicted by the data related to homicide. Walsh argues that the macrostructural opportunity model helps explain why black murderers almost always choose black victims. There are disparities in rates of reporting rape where victims of some races are statistically less likely or more likely to report their rape, especially depending on the race of the offender. Black women in America are more likely to report sexual assault that has been perpetrated by a stranger. Black women are more likely to under-report rapes overall as they are more likely to blame themselves, feel they will be blamed or feel they won't be believed.
Social control theory
Social control theory, which is among the most popular theories in criminology, proposes that crime is most commonly perpetrated by individuals who lack strong bonds or connections with their social environment. Based upon Travis Hirschi's Causes of Delinquency (1969), social bonding theory pioneered the notion that criminologists can gain useful insight into the motives behind criminal behavior by examining what normally motivates individuals to refrain from crime. From this it is argued that, in those segments of the population where such motivation is lacking, crime will be more prevalent. Hirschi was explicit in mentioning that he believed his theory held true across all racial boundaries, and subsequent research—both in the US and abroad—seems to confirm this belief. The core idea of social control theory is elaborated upon in several other theories of causation, particularly social disorganization theory.
Subculture of violence theory
As a theory of criminal behavior, subculture of violence theory claims that certain groups or subcultures exist in society in which violence is viewed as an appropriate response to what, in the context of that subculture, are perceived as threatening situations. Building upon the work of cultural anthropologist Walter B. Miller's focal concerns theory, which focused on the social mechanisms behind delinquency in adolescents, sociologists Marvin Wolfgang and Franco Ferracuti proposed that the disproportionally high rate of crime among African Americans could be explained by their possessing a unique racial subculture in which violence is experienced and perceived in a manner different from that commonly observed in mainstream American culture.
As to the origins of this subculture of violence among African Americans, sociologists promoting the theory have pointed towards their Southern heritage. As noted in several studies conducted throughout the 1960s and 1970s, there is a traditional north–south discrepancy in the distribution of homicide in the US, regardless of race, and this, it was argued, indicates that lower-class Southern blacks and Whites share the same subculture of violence.
The empirical basis for the subculture of violence theory, however, has been described as "extremely limited and unpersuasive". Very little has been done to attempt an adequate assessment of supposedly criminogenic subcultural values, and several studies conducted in the late 1970s claimed to falsify the assumptions upon which the subculture of violence theory depends. More recently, scholars have criticized the theory as potentially racist in nature in its implication of one given ethnicity or culture supposedly being less fit for or less worthy of being qualified as "civilized", the built-in implication of which in turn would denote stereotypically "white" behavior as an objective norm for all societies to follow. The hypothesis was reconsidered recently by Barry Latzer, who suggested that black Americans had inherited a subculture of violence from white Southern American honor culture (who themselves had developed that culture from the brutal and lawless border region of northern Britain) and that difference in crime rates could be partially explained by this contemporary manifestation of Southern honor culture. Latzer's argument was criticized by German Lopez for not adequately demonstrating the alleged causality between culture and crime, and for not accounting for the decrease in crime rates in the 20th century or clearly defining the limits of what would constitute "culture" for the purposes of Latzer's argument.