

The Soviet Union introduced forced collectivization (Russian: Коллективизация) of its agricultural sector between 1928 and 1940 during the ascension of Joseph Stalin. It began during and was part of the first five-year plan. The policy aimed to integrate individual landholdings and labour into nominally collectively-controlled and openly or directly state-controlled farms: Kolkhozes and Sovkhozes accordingly. The Soviet leadership confidently expected that the replacement of individual peasant farms by collective ones would immediately increase the food supply for the urban population, the supply of raw materials for the processing industry, and agricultural exports via state-imposed quotas on individuals working on collective farms. Planners regarded collectivization as the solution to the crisis of agricultural distribution (mainly in grain deliveries) that had developed from 1927. This problem became more acute as the Soviet Union pressed ahead with its ambitious industrialization program, meaning that more food would be needed to keep up with urban demand.
In October 1929, approximately 7.5% of the peasant households were in collective farms, and by February 1930, 52.7% had been collectivised. The collectivization era saw several famines, as well as peasant resistance to collectivization.
Background

After the emancipation of the serfs in 1861, peasants gained control of about half of the land they had previously cultivated and began to ask for the redistribution of all land. The Stolypin agricultural reforms between 1905 and 1914 gave incentives for the creation of large farms, but these ended during World War I. The Russian Provisional Government accomplished little during the difficult World War I months, though Russian leaders continued to promise redistribution. Peasants began to turn against the Provisional Government and organized themselves into land committees, which together with the traditional peasant communes became a powerful force of opposition. When Vladimir Lenin returned to Russia on April 16, 1917, he promised the people "Peace, Land and Bread," the latter two appearing as a promise to the peasants for the redistribution of confiscated land and a fair share of food for every worker respectively.
During the period of war communism, however, the policy of Prodrazvyorstka meant that the peasantry was obligated to surrender the surpluses of agricultural produce for a fixed price. When the Russian Civil War ended, the economy changed with the New Economic Policy (NEP) and specifically, the policy of prodnalog or "food tax." This new policy was designed to re-build morale among embittered farmers and lead to increased production.
Leon Trotsky and the Opposition bloc had advocated a programme of industrialization which also proposed agricultural cooperatives and the formation of collective farms on a voluntary basis. According to Fitzpatrick, the scholarly consensus was that Stalin appropriated the position of the Left Opposition on such matters as industrialisation and collectivisation. Other scholars have argued that the economic programme of Trotsky differed from the forced policy of collectivisation implemented by Stalin after 1928 due to the levels of brutality associated with its enforcement.
The pre-existing communes, which periodically redistributed land, did little to encourage improvement in technique and formed a source of power beyond the control of the Soviet government. Although the income gap between wealthy and poor farmers did grow under the NEP, it remained quite small, but the Bolsheviks began to take aim at the kulaks, peasants with enough land and money to own several animals and hire a few labourers . Kulaks were blamed for withholding surpluses of agricultural produce. Clearly identifying this group was difficult, though, since only about 1% of the peasantry employed labourers (the basic Marxist definition of a capitalist), and 82% of the country's population were peasants. According to Robert Conquest, the definition of "kulak" also varied depending on who was using it; "peasants with a couple of cows or five or six acres [~2 ha] more than their neighbors" were labeled kulaks" in Stalin's first Five Year Plan.
The small shares of most of the peasants resulted in food shortages in the cities. Although grain had nearly returned to pre-war production levels, the large estates which had produced it for urban markets had been divided up. Not interested in acquiring money to purchase overpriced manufactured goods, the peasants chose to consume their produce rather than sell it. As a result, city dwellers only saw half the grain that had been available before the war. Before the revolution, peasants controlled only 2,100,000 km2 divided into 16 million holdings, producing 50% of the food grown in Russia and consuming 60% of total food production. After the revolution, the peasants controlled 3,140,000 km2 divided into 25 million holdings, producing 85% of the food, but consuming 80% of what they grew (meaning that they ate 68% of the total).
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union had never been happy with private agriculture and saw collectivization as the best remedy for the problem. Lenin claimed, "Small-scale production gives birth to capitalism and the bourgeoisie constantly, daily, hourly, with elemental force, and in vast proportions." Apart from ideological goals, Joseph Stalin also wished to embark on a program of rapid heavy industrialization which required larger surpluses to be extracted from the agricultural sector in order to feed a growing industrial workforce and to pay for imports of machinery (by exporting grain). Social and ideological goals would also be served through the mobilization of the peasants in a co-operative economic enterprise that would provide social services to the people and empower the state. Not only was collectivization meant to fund industrialization, but it was also a way for the Bolsheviks to systematically exterminate the Kulaks and peasants in general in a back-handed manner. Stalin was incredibly suspicious of the peasants, viewing them as a major threat to socialism. Stalin's use of the collectivization process served to not only address the grain shortages, but his greater concern over the peasants' willingness to conform to the collective farm system and state mandated grain acquisitions. He viewed this as an opportunity to punish the Kulaks as a class by means of collectivization.
Crisis of 1928
This demand for more grain resulted in the reintroduction of requisitioning which was resisted in rural areas. In 1928 there was a 2-million-ton shortfall in grains purchased by the Soviet Union from neighbouring markets. Stalin claimed the grain had been produced but was being hoarded by "kulaks." Stalin tried to appear as being on the side of the peasants, but it did not help, and the peasants as a whole resented the grain seizures. The peasants did everything they could to protest what they considered unfair seizures. Instead of raising the price, the Politburo adopted an emergency measure to requisition 2.5 million tons of grain.
The seizures of grain discouraged the peasants and less grain was produced during 1928, and again the government resorted to requisitions, much of the grain being requisitioned from middle peasants as sufficient quantities were not in the hands of the "kulaks." The impact that this had on poorer peasants forced them to move to the cities. The peasants moved in search of jobs in the rapidly expanding industry. This, however, had a fairly negative impact upon their arrival as the peasants brought with them their habits from the farms. They struggled with punctuality and demonstrated a rather poor work ethic, which hindered their ability to perform in the workplace. In 1929, especially after the introduction of the Ural-Siberian Method of grain procurement, resistance to grain seizures became widespread with some violent incidents of resistance. Also, massive hoarding (burial was the common method) and illegal transfers of grain took place.
Faced with the refusal to hand grain over, a decision was made at a plenary session of the Central Committee in November 1929 to embark on a nationwide program of collectivization.
Several forms of collective farming were suggested by the People's Commissariat for Agriculture (Narkomzem), distinguished according to the extent to which property was held in common:
- Association for Joint Cultivation of Land (Товарищество по совместной обработке земли, ТОЗ/TOZ), where only land was in common use;
- agricultural artel (initially in a loose meaning, later formalized to become an organizational basis of kolkhozes, via The Standard Statute of an Agricultural Artel adopted by Sovnarkom in March 1930);
- agricultural commune, with the highest level of common use of resources.
Also, various cooperatives for the processing of agricultural products were installed.
In November 1929, the Central Committee decided to implement accelerated collectivization in the form of kolkhozes and sovkhozes. This marked the end of the New Economic Policy (NEP), which had allowed peasants to sell their surpluses on the open market. Peasants that were willing to conform and join the kolkhozes were rewarded with higher quality land and tax breaks, whereas peasants were unwilling to join the kolkhozes were punished with being given lower quality land and increased taxes. The taxes imposed on the peasants was primarily to fund the industrial blitz that Stalin had made a priority. If these lesser forms of social coercion proved to be ineffective then the central government would resort to harsher forms of state coercion. Stalin had many kulaks transported to collective farms in distant places to work in agricultural labour camps. In response to this, many peasants began to resist, often began arming themselves against the activists sent from the towns. As a form of protest, many peasants preferred to slaughter their animals for food rather than give them over to collective farms, which produced a major reduction in livestock.
Collectivization had been encouraged since the revolution, but in 1928, only about 1% of farmland was collectivized, and despite efforts to encourage and coerce collectivization, the rather optimistic first five-year plan only forecast 15 per cent of farms to be run collectively.
All-out drive, winter 1929–30

The situation changed quickly in the autumn of 1929 and the winter of 1930. Between September and December 1929, collectivization increased from 7.4% to 15%, but in the first two months of 1930, 11 million households joined collectivized farms, pushing the total to nearly 60%.
To assist collectivization, the Party decided to send 25,000 "socially conscious" industry workers to the countryside. This was accomplished from 1929 to 1933, and these workers have become known as twenty-five-thousanders ("dvadtsat'pyat'tysyachniki"). Soviet officials had hoped that by sending the twenty-five thousanders to the countryside that they would be able to produce grain more rapidly. Their hopes were that key areas in the North Caucasus and Volga regions would be collectivized by 1931, and then the other regions by 1932. Shock brigades were used to force reluctant peasants into joining the collective farms and remove those who were declared kulaks and their "agents".
Collectivization sought to modernize Soviet agriculture, consolidating the land into parcels that could be farmed by modern equipment using the latest scientific methods of agriculture. It was often claimed that an American Fordson tractor (called "Фордзон" in Russian) was the best propaganda in favour of collectivization.
The means of production (land, equipment, livestock) were to be totally "socialized", i.e. removed from the control of individual peasant households.
"Dizzy with Success"
The zeal for collectivization was so high that the March 2, 1930, issue of Pravda contained Stalin's article Dizzy with Success (Russian: Головокружение от успехов, lit. 'Dizziness from success'), in which he called for a temporary halt to the process:
It is a fact that by February 20 of this year 50 percent of the peasant farms throughout the U.S.S.R. had been collectivized. That means that by February 20, 1930, we had overfulfilled the five-year plan of collectivization by more than 100 per cent.... some of our comrades have become dizzy with success and for the moment have lost clearness of mind and sobriety of vision.
After the publication of the article, the pressure for collectivization temporarily abated and peasants started leaving collective farms. According to Martin Kitchen, the number of members of collective farms dropped by 50% in 1930. But soon collectivization was intensified again, and by 1936, about 90% of Soviet agriculture was collectivized.
Peasant resistance

Stalin's efforts to implement agricultural collectivization played a significant role in the overall mortality figures attributed to his regime, notably evidenced by the Ukrainian famine, a single famine responsible for 3 to 5 million deaths. Some peasants viewed collectivization as the end of the world. By no means was joining the collective farm (also known as the kolkhoz) voluntary. The drive to collectivize understandably had little support from experienced farmers.
The oversimplified intent was to withhold grain from the market and increase the total crop and food supply via state collective farms, with the surplus funding future industrialization. The kulaks were coerced into giving up their land to make way for these collective farms or risk being killed, deported, or sent to labor camps. Inexperienced peasants from urban areas would then replace the missing workforce of the agriculture sector, which is now considered overstaffed, inefficient and import-dependent. Under Stalin's grossly inefficient system, agricultural yields declined rather than increased. The situation persisted into the 1980s, when Soviet farmers averaged about 10 percent of the output of their counterparts in the United States. To make matters worse, tractors promised to the peasants could not be produced due to the poor policies in the Industrial sector of the Soviet Union.
Peasants tried to protest through peaceful means by speaking out at collectivization meetings and writing letters to the central authorities, to no avail. The kulaks argued to the collectors that starvation was inevitable, but they still started to seize everything edible from the kulaks to meet quotas, regardless if the kulaks had anything for themselves. Stalin falsely denied there even was a famine and prohibited journalists from visiting the collective farms. In order to cover up for the poor harvests, the Soviet government created a fierce propaganda campaign blaming the kulaks for the famine. The propaganda said they were creating an artificial food shortage by hiding crops only to sell them when prices were high. The propaganda also claimed kulaks were committing crimes such as arson, lynching, and murder of local authorities, kolkhoz, and activists.
Collectivization as a "second serfdom"
Rumors circulated in the villages warning the rural residents that collectivization would bring disorder, hunger, famine, and the destruction of crops and livestock. Readings and reinterpretations of Soviet newspapers labelled collectivization as a second serfdom. Villagers were afraid the old landowners/serf owners were coming back and that the villagers joining the collective farm would face starvation and famine. More reason for peasants to believe collectivization was a second serfdom was that entry into the kolkhoz had been forced. Farmers did not have the right to leave the collective without permission. The level of state procurements and prices on crops also enforced the serfdom analogy. The government would take a majority of the crops and pay extremely low prices. The serfs during the 1860s were paid nothing but collectivization still reminded the peasants of serfdom. To them, this "second serfdom" became code for the Communist betrayal of the revolution. To the peasants, the revolution was about giving more freedom and land to the peasants, but instead, they had to give up themselves, with any land or livestock they had to the centrally controlled ‘collective farm’ in accordance with the state's policies.
Women's role in resistance
Women were the primary vehicle for rumours that touched upon issues of family and everyday life. Fears that collectivization would result in the socialization of children, the export of women's hair, communal wife-sharing, and the notorious common blanket affected many women, causing them to revolt. For example, when it was announced that a collective farm in Crimea would become a commune and that the children would be socialized, women killed their soon-to-be socialized livestock, which spared the children. Stories that the Communists believed short hair gave women a more urban and industrial look insulted peasant women. After local activists in a village in North Caucasus actually confiscated all blankets, more fear dispersed among villagers. The common blanket meant that all men and women would sleep on a seven-hundred meter long bed under a seven-hundred-meter long blanket. Historians argue that women took advantage of these rumours without actually believing them so they could attack the collective farm "under the guise of irrational, nonpolitical protest." Women were less vulnerable to retaliation than peasant men, and therefore able to get away with a lot more.
Peasant women were rarely held accountable for their actions because of the officials' perceptions of their protests. They "physically blocked the entrances to huts of peasants scheduled to be exiled as kulaks, forcibly took back socialized seed and livestock and led assaults on officials." Officials ran away and hid to let the riots run their course. When women came to trial, they were given less harsh punishments as the men because women, to officials, were seen as illiterate and the most backward part of the peasantry. One particular case of this was a riot in a Russian village of Belovka where protestors were beating members of the local soviet and setting fire to their homes. The men were held exclusively responsible as the main culprits. Women were given sentences to serve as a warning, not as a punishment. Because of how they were perceived, women were able to play an essential role in the resistance to collectivization.
Religious persecution

Collectivization did not just entail the acquisition of land from farmers but also the closing of churches, burning of icons, and the arrests of priests. Associating the church with the tsarist regime, the Soviet state continued to undermine the church through expropriations and repression. They cut off state financial support to the church and secularized church schools. Peasants began to associate Communists with atheists because the attack on the church was so devastating. The Communist assault on religion and the church angered many peasants, giving them more reason to revolt. Riots exploded after the closing of churches as early as 1929.
Identification of Soviet power with the Antichrist also decreased peasant support for the Soviet regime. Rumors about religious persecution spread mostly by word of mouth, but also through leaflets and proclamations. Priests preached that the Antichrist had come to place "the Devil's mark" on the peasants and that the Soviet state was promising the peasants a better life but was actually signing them up for Hell. Peasants feared that if they joined the collective farm they would be marked with the stamp of the Antichrist. They faced a choice between God and the Soviet collective farm. Choosing between salvation and damnation, peasants had no choice but to resist the policies of the state. These rumours of the Soviet state as the Antichrist functioned to keep peasants from succumbing to the government. The attacks on religion and the Church affected women the most because they were upholders of religion within the villages.
Dovzhenko's film Earth gives example of peasants' skepticism with collectivization on the basis that it was an attack on the church. Coiner of the term genocide, Raphael Lemkin, considered the repression of the Orthodox Church to be a prong of genocide against Ukrainians when seen in correlation to the Holodomor famine.
Results
Resistance to collectivization and consequences
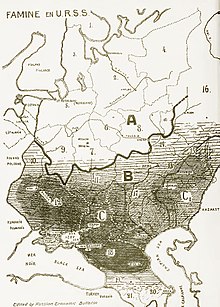


Due to the high government production quotas, peasants received, as a rule, less for their labour than they did before collectivization, and some refused to work. Merle Fainsod estimated that, in 1952, collective farm earnings were only one-fourth of the cash income from private plots on Soviet collective farms. In many cases, the immediate effect of collectivization was the reduction of output and the cutting of the number of livestock in half. The subsequent recovery of the agricultural production was also impeded by the losses suffered by the Soviet Union during World War II and the severe drought of 1946. However, the largest loss of livestock was caused by collectivization for all animals except pigs. The numbers of cows in the USSR fell from 33.2 million in 1928 to 27.8 million in 1941 and to 24.6 million in 1950. The number of pigs fell from 27.7 million in 1928 to 27.5 million in 1941 and then to 22.2 million in 1950. The number of sheep fell from 114.6 million in 1928 to 91.6 million in 1941 and to 93.6 million in 1950. The number of horses fell from 36.1 million in 1928 to 21.0 million in 1941 and to 12.7 million in 1950. Only by the late 1950s did Soviet farm animal stocks begin to approach 1928 levels. Peasant slaughter of livestock was significant, for instance in the Central Black Earth Region 25% of cattle, 55% of sheep, 53% of pigs and 40% of chickens were slaughtered within the first three months of 1930.
Despite the initial plans, collectivization, accompanied by the bad harvest of 1932–1933, did not live up to expectations. Between 1929 and 1932 there was a massive fall in agricultural production resulting in famine in the countryside. Stalin and the CPSU blamed the prosperous peasants, referred to as 'kulaks' (Russian: fist), who were organizing resistance to collectivization. Allegedly, many kulaks had been hoarding grain in order to speculate on higher prices, thereby sabotaging grain collection. Stalin resolved to eliminate them as a class. The methods Stalin used to eliminate the kulaks were dispossession, deportation, and execution. The term "Ural-Siberian Method" was coined by Stalin, the rest of the population referred to it as the "new method". Article 107 of the criminal code was the legal means by which the state acquired grain.
The Soviet government responded to these acts by cutting off food rations to peasants and areas where there was opposition to collectivization, especially in Ukraine. For peasants that were unable to meet the grain quota, they were fined five-times the quota. If the peasant continued to be defiant the peasants' property and equipment would be confiscated by the state. If none of the previous measures were effective the defiant peasant would be deported or exiled. The practice was made legal in 1929 under Article 61 of the criminal code. Many peasant families were forcibly resettled in Siberia and Kazakhstan into exile settlements, and some of them died on the way. Estimates suggest that about a million so-called 'kulak' families, or perhaps some 5 million people, were sent to forced labour camps.
On August 7, 1932, the Decree about the Protection of Socialist Property proclaimed that the punishment for theft of kolkhoz or cooperative property was the death sentence, which "under extenuating circumstances" could be replaced by at least ten years of incarceration. With what some called the Law of Spikelets ("Закон о колосках"), peasants (including children) who hand-collected or gleaned grain in the collective fields after the harvest were arrested for damaging the state grain production.
During the Famine of 1932–33 it's estimated that 5.7 to 8.7 million people died from starvation. The implication is that the total death toll (both direct and indirect) for Stalin's collectivization program was on the order of 12 million people. There is a popular story that at the 1945 Yalta Conference when Winston Churchill asked Joseph Stalin how many died in the famine, the Soviet leader responded with a shrug, a gesture that on account of Stalin's raised hands having 10 fingers, has been cited by historians as a direct admission that ten million people perished as a result of collectivization.
Siberia
Since the second half of the 19th century, Siberia had been a major agricultural region within Russia, espеcially its southern territories (nowadays Altai Krai, Omsk Oblast, Novosibirsk Oblast, Kemerovo Oblast, Khakassia, Buryatia, Irkutsk Oblast). Stolypin's program of resettlement granted a lot of land for immigrants from elsewhere in the empire, creating a large portion of well-off peasants and stimulating rapid agricultural development in the 1910s. Local merchants exported large quantities of labelled grain, flour, and butter into central Russia and Western Europe. In May 1931, a special resolution of the Western-Siberian Regional Executive Committee (classified "top secret") ordered the expropriation of property and the deportation of 40,000 kulaks to "sparsely populated and unpopulated" areas in Tomsk Oblast in the northern part of the Western-Siberian region. The expropriated property was to be transferred to kolkhozes as indivisible collective property and the kolkhoz shares representing this forced contribution of the deportees to kolkhoz equity were to be held in the "collectivization fund of poor and landless peasants" (фонд коллективизации бедноты и батрачества). A notable uprising against collectivisation in Siberia occurred in Buryatia, where a revolt was put down by the Red Army in 1929.
It has since been perceived by historians such as Lynne Viola as a Civil War of the peasants against the Bolshevik Government and the attempted colonization of the countryside.
Central Asia and Kazakhstan
In 1928 within Soviet Kazakhstan, authorities started a campaign to confiscate cattle from richer Kazakhs, who were called bai, known as Little October. The confiscation campaign was carried out by Kazakhs against other Kazakhs, and it was up to those Kazakhs to decide who was a bai and how much to confiscate from them. This engagement was intended to make Kazakhs active participants in the transformation of Kazakh society. More than 10,000 bais may have been deported due to the campaign against them. In areas where the major agricultural activity was nomadic herding, collectivization met with massive resistance and major losses and confiscation of livestock. Livestock in Kazakhstan fell from 7 million cattle to 1.6 million and from 22 million sheep to 1.7 million. Restrictions on migration proved ineffective and half a million migrated to other regions of Central Asia and 1.5 million to China. Of those who remained, as many as a million died in the resulting famine. In Mongolia, a so-called 'Soviet dependency', attempted collectivization was abandoned in 1932 after the loss of 8 million head of livestock.
Historian Sarah Cameron argues that while Stalin did not intend to starve Kazakhs, he saw some deaths as a necessary sacrifice to achieve the political and economic goals of the regime. Cameron believes that while the famine combined with a campaign against nomads was not genocide in the sense of the United Nations (UN) definition, it complies with Raphael Lemkin's original concept of genocide, which considered destruction of culture to be as genocidal as physical annihilation. Historian Stephen Wheatcroft criticized this view in regard to the Soviet famine because he believes that the nominally stated high expectations of central planners was sufficient to demonstrate their ignorance of the ultimate consequences of their actions and that the result of them would be famine. Niccolò Pianciola goes further than Cameron and argues that from Lemkin's point of view on genocide all nomads of the Soviet Union were victims of the crime, not just the Kazakhs.
Ukraine
Most historians agree that the disruption caused by collectivization and the resistance of the peasants significantly contributed to the Great Famine of 1932–1933, especially in Ukraine, a region famous for its rich soil (chernozem). This particular period is called "Holodomor" in Ukrainian. During the similar famines of 1921–1923, numerous campaigns – inside the country, as well as internationally – were held to raise money and food in support of the population of the affected regions. Nothing similar was done during the drought of 1932–1933, mainly because the information about the disaster was suppressed by Stalin. Stalin also undertook a purge of the Ukrainian communists and intelligentsia, with devastating long-term effects on the area. Many Ukrainian villages were blacklisted and penalized by government decree for perceived sabotage of food supplies. Moreover, migration of population from the affected areas was restricted. According to Stalin in his conversation with the prize-winning writer Mikhail Sholokhov, the famine was caused by the excesses of local party workers and sabotage,
I've thanked you for the letters, as they expose a sore in our Party-Soviet work and show how our workers, wishing to curb the enemy, sometimes unwittingly hit friends and descend to sadism. ... the esteemed grain-growers of your district (and not only of your district alone) carried on an 'Italian strike' (sabotage!) and were not loath to leave the workers and the Red Army without bread. That the sabotage was quiet and outwardly harmless (without blood) does not change the fact that the esteemed grain-growers waged what was in fact a 'quiet' war against Soviet power. A war of starvation, dear com[rade] Sholokhov. This, of course, can in no way justify the outrages, which, as you assure me, have been committed by our workers. ... And those guilty of those outrages must be duly punished.

About 40 million people were affected by the food shortages including areas near Moscow where mortality rates increased by 50%. The center of the famine, however, was Ukraine and surrounding regions, including the Don, the Kuban, the Northern Caucasus and Kazakhstan where the toll was one million dead. The countryside was affected more than cities, but 120,000 died in Kharkiv, 40,000 in Krasnodar and 20,000 in Stavropol.
Whilst there is no comprehensive official account of famine deaths known of, historians R. W. Davies and Stephen G. Wheatcroft used official archival soviet 'registered death' statistics of 2,577,065 deaths from all causes in Ukraine to extrapolate an 'excess registered mortality' of 1,544,840 from 1932 to 1933. Alec Nove claims that registration of deaths largely ceased in many areas during the famine. However, it's been pointed out that the registered deaths in the archives were substantially revised by the demographics officials. The older version of the data showed 600,000 fewer deaths in Ukraine than the current, revised statistics. In The Black Book of Communism, the authors claim that the number of deaths was at least 4 million, and they also characterize the Great Famine as "a genocide of the Ukrainian people".
Latvia
After the Soviet Occupation of Latvia in June 1940, the country's new rulers were faced with a problem: the agricultural reforms of the inter-war period had expanded individual holdings. The property of "enemies of the people" and refugees, as well as those above 30 hectares, was nationalized in 1940–44, but those who were still landless were then given plots of 15 hectares each. Thus, Latvian agriculture remained essentially dependent on personal smallholdings, making central planning difficult. In 1940–41 the Communist Party repeatedly said that collectivization would not occur forcibly, but rather voluntarily and by example. To encourage collectivization high taxes were enforced and new farms were given no government support. But after 1945 the Party dropped its restrained approach as the voluntary approach was not yielding results. Latvians were accustomed to individual holdings (viensētas), which had existed even during serfdom, and for many farmers, the plots awarded to them by the interwar reforms were the first their families had ever owned. Furthermore, the countryside was filled with rumours regarding the harshness of collective farm life.
Pressure from Moscow to collectivize continued and the authorities in Latvia sought to reduce the number of individual farmers (increasingly labelled kulaki or budži) through higher taxes and requisitioning of agricultural products for state use. The first kolkhoz was established only in November 1946 and by 1948, just 617 kolkhozes had been established, integrating 13,814 individual farmsteads (12.6% of the total). The process was still judged too slow, and in March 1949 just under 13,000 kulak families, as well as a large number of individuals, were identified. Between March 24 and March 30, 1949, about 40,000 people were deported and resettled at various points throughout the USSR.
After these deportations, the pace of collectivization increased as a flood of farmers rushed into kolkhozes. Within two weeks 1740 new kolkhozes were established and by the end of 1950, just 4.5% of Latvian farmsteads remained outside the collectivized units; about 226,900 farmsteads belonged to collectives, of which there were now around 14,700. Rural life changed as farmers' daily movements were governed by plans, decisions, and quotas formulated elsewhere and delivered through an intermediate non-farming hierarchy. The new kolkhozes, especially smaller ones, were ill-equipped and poor – at first farmers were paid once a year in kind and then in cash, but salaries were very small and at times farmers went unpaid or even ended up owing money to the kolkhoz.
Farmers still had small pieces of land (not larger than 0.5 ha) around their houses where they grew food for themselves. Along with collectivization, the government tried to uproot the custom of living in individual farmsteads by resettling people in villages. However this process failed due to lack of money since the Soviets planned to move houses as well.
Collectivization as a project of colonialism or imperialism
Due to factional struggles with Bukharin wing of the party, peasant resistance to the NEP under Lenin, and the need for industrialization, Joseph Stalin declared a need to extract a "tribute" or "tax" from the peasantry. This idea was supported by most of the party in the 1920s. The tribute collected by the party took on the form of a virtual war against the peasantry that would lead to its cultural destruction and the relegating of the countryside to essentially a colony homogenized to the urban culture of the Soviet elite. This campaign of "colonizing" the peasantry had its roots both in old Russian Imperialism and modern social engineering of the nation state yet with key differences to the latter, such as Soviet repression reflecting more the weakness of said state rather than its strength. There have also been more selective discussions of collectivization as a project of colonialism in regard to Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
Progress of collectivization, 1927–1940
| Year | Number of collective farms |
Percent of farmsteads in collective farms |
Percent of sown area in collective use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1927 | 14,800 | 0.8 | – |
| 1928 | 33,300 | 1.7 | 2.3 |
| 1929 | 57,000 | 3.9 | 4.9 |
| 1930 | 85,900 | 23.6 | 33.6 |
| 1931 | 211,100 | 52.7 | 67.8 |
| 1932 | 211,100 | 61.5 | 77.7 |
| 1933 | 224,500 | 65.6 | 83.1 |
| 1934 | 233,300 | 71.4 | 87.4 |
| 1935 | 249,400 | 83.2 | 94.1 |
| 1936 | – | 90.5 | 98.2 |
| 1937 | 243,700 | 93.0 | 99.1 |
| 1938 | 242,400 | 93.5 | 99.8 |
| 1939 | 235,300 | 95.6 | – |
| 1940 | 236,900 | 96.9 | 99.8 |
Sources: Sotsialisticheskoe sel'skoe khoziaistvo SSSR, Gosplanizdat, Moscow-Leningrad, 1939 (pp. 42, 43); supplementary numbers for 1927–1935 from Sel'skoe khoziaistvo SSSR 1935, Narkomzem SSSR, Moscow, 1936 (pp. 630, 634, 1347, 1369); 1937 from Great Soviet Encyclopedia, vol. 22, Moscow, 1953 (p. 81); 1939 from Narodnoe khoziaistvo SSSR 1917–1987, Moscow, 1987 (pp. 35); 1940 from Narodnoe khoziaistvo SSSR 1922–1972, Moscow, 1972 (pp. 215, 240).
The official numbers for the collectivized areas (the column with per cent of sown area in collective use in the table above) are biased upward by two technical factors. First, these official numbers are calculated as a per cent of sown area in peasant farmsteads, excluding the area cultivated by sovkhozes and other agricultural users. Estimates based on the total sown area (including state farms) reduce the share of collective farms between 1935 and 1940 to about 80%. Second, the household plots of kolkhoz members (i.e., collectivized farmsteads) are included in the land base of collective farms. Without the household plots, arable land in collective cultivation in 1940 was 96.4% of land in collective farms, and not 99.8% as shown by official statistics. Although there is no arguing with the fact that collectivization was sweeping and total between 1928 and 1940, the table below provides different (more realistic) numbers on the extent of collectivization of sown areas.
Distribution of sown area by land users, 1928 and 1940
| Land users | 1928 | 1940 |
|---|---|---|
| All farms, '000 hectares | 113,000 | 150,600 |
| State farms (sovkhozes) | 1.5% | 8.8% |
| Collective farms (kolkhozes) | 1.2% | 78.2% |
| Household plots (in collective and state farms) |
1.1% | 3.5% |
| Peasant farms and other users | 96.2% | 9.5% |
Source: Narodnoe khoziaistvo SSSR 1922–1972, Moscow, 1972 (p. 240).
Decollectivization under German occupation
During World War II, Alfred Rosenberg, in his capacity as the Reich Minister for the Occupied Eastern Territories, issued a series of posters announcing the end of the Soviet collective farms in areas of the USSR under German occupation. He also issued an Agrarian Law in February 1942, annulling all Soviet legislation on farming, restoring family farms for those willing to collaborate with the occupiers. But decollectivization conflicted with the wider demands of wartime food production, and Hermann Göring demanded that the kolkhoz be retained, save for a change of name. Hitler himself denounced the redistribution of land as 'stupid.' In the end, the German occupation authorities retained most of the kolkhozes and simply renamed them "community farms" (Russian: Общинные хозяйства, a throwback to the traditional Russian commune). German propaganda described this as a preparatory step toward the ultimate dissolution of the kolkhozes into private farms, which would be granted to peasants who had loyally delivered compulsory quotas of farm produce to the Germans. By 1943, the German occupation authorities had converted 30% of the kolkhozes into German-sponsored "agricultural cooperatives", but as yet had made no conversions to private farms.
