Network computer devices that originate, route and terminate the data are called network nodes. Nodes are identified by network addresses, and can include hosts such as personal computers, phones, and servers, as well as networking hardware
such as routers and switches. Two such devices can be said to be
networked together when one device is able to exchange information with
the other device, whether or not they have a direct connection to each
other. In most cases, application-specific communications protocols are layered (i.e. carried as payload) over other more general communications protocols. This formidable collection of information technology requires skilled network management to keep it all running reliably.
Computer networks support an enormous number of applications and services such as access to the World Wide Web, digital video, digital audio, shared use of application and storage servers, printers, and fax machines, and use of email and instant messaging applications as well as many others. Computer networks differ in the transmission medium used to carry their signals, communications protocols to organize network traffic, the network's size, topology, traffic control mechanism and organizational intent. The best-known computer network is the Internet.
History
The chronology of significant computer-network developments includes:
- In the late 1950s, early networks of computers included the U.S. military radar system Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE).
- In 1959, Anatolii Ivanovich Kitov proposed to the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union a detailed plan for the re-organisation of the control of the Soviet armed forces and of the Soviet economy on the basis of a network of computing centres, the OGAS.
- In 1960, the commercial airline reservation system semi-automatic business research environment (SABRE) went online with two connected mainframes.
- In 1963, J. C. R. Licklider sent a memorandum to office colleagues discussing the concept of the "Intergalactic Computer Network", a computer network intended to allow general communications among computer users.
- In 1964, researchers at Dartmouth College developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System for distributed users of large computer systems. The same year, at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, a research group supported by General Electric and Bell Labs used a computer to route and manage telephone connections.
- Throughout the 1960s, Paul Baran, and Donald Davies independently developed the concept of packet switching to transfer information between computers over a network. Davies pioneered the implementation of the concept with the NPL network, a local area network at the National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom) using a line speed of 768 kbit/s.
- In 1965, Western Electric introduced the first widely used telephone switch that implemented true computer control.
- In 1966, Thomas Marill and Lawrence G. Roberts published a paper on an experimental wide area network (WAN) for computer time sharing.
- In 1969, the first four nodes of the ARPANET were connected using 50 kbit/s circuits between the University of California at Los Angeles, the Stanford Research Institute, the University of California at Santa Barbara, and the University of Utah. Leonard Kleinrock carried out theoretical work to model the performance of packet-switched networks, which underpinned the development of the ARPANET. His theoretical work on hierarchical routing in the late 1970s with student Farouk Kamoun remains critical to the operation of the Internet today.
- In 1972, commercial services using X.25 were deployed, and later used as an underlying infrastructure for expanding TCP/IP networks.
- In 1973, the French CYCLADES network was the first to make the hosts responsible for the reliable delivery of data, rather than this being a centralized service of the network itself.
- In 1973, Robert Metcalfe wrote a formal memo at Xerox PARC describing Ethernet, a networking system that was based on the Aloha network, developed in the 1960s by Norman Abramson and colleagues at the University of Hawaii. In July 1976, Robert Metcalfe and David Boggs published their paper "Ethernet: Distributed Packet Switching for Local Computer Networks" and collaborated on several patents received in 1977 and 1978. In 1979, Robert Metcalfe pursued making Ethernet an open standard.
- In 1976, John Murphy of Datapoint Corporation created ARCNET, a token-passing network first used to share storage devices.
- In 1995, the transmission speed capacity for Ethernet increased from 10 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s. By 1998, Ethernet supported transmission speeds of a Gigabit. Subsequently, higher speeds of up to 400 Gbit/s were added (as of 2018). The ability of Ethernet to scale easily (such as quickly adapting to support new fiber optic cable speeds) is a contributing factor to its continued use.
Properties
Computer networking may be considered a branch of electrical engineering, electronics engineering, telecommunications, computer science, information technology or computer engineering, since it relies upon the theoretical and practical application of the related disciplines.
A computer network facilitates interpersonal communications
allowing users to communicate efficiently and easily via various means:
email, instant messaging, online chat,
telephone, video telephone calls, and video conferencing. A network
allows sharing of network and computing resources. Users may access and
use resources provided by devices on the network, such as printing a
document on a shared network printer or use of a shared storage device. A
network allows sharing of files, data, and other types of information
giving authorized users the ability to access information stored on
other computers on the network. Distributed computing uses computing resources across a network to accomplish tasks.
A computer network may be used by security hackers to deploy computer viruses or computer worms on devices connected to the network, or to prevent these devices from accessing the network via a denial-of-service attack.
Network packet
Computer communication links that do not support packets, such as traditional point-to-point telecommunication links, simply transmit data as a bit stream. However, the overwhelming majority of computer networks carry their data in packets. A network packet is a formatted unit of data (a list of bits or bytes, usually a few tens of bytes to a few kilobytes long) carried by a packet-switched network.
Packets are sent through the network to their destination. Once the
packets arrive they are reassembled into their original message.
Packets consist of two kinds of data: control information, and
user data (payload). The control information provides data the network
needs to deliver the user data, for example: source and destination network addresses, error detection codes, and sequencing information. Typically, control information is found in packet headers and trailers, with payload data in between.
With packets, the bandwidth of the transmission medium can be better shared among users than if the network were circuit switched.
When one user is not sending packets, the link can be filled with
packets from other users, and so the cost can be shared, with relatively
little interference, provided the link isn't overused. Often the route a
packet needs to take through a network is not immediately available. In
that case the packet is queued and waits until a link is free.
Network topology
The physical layout of a network is usually less important than the
topology that connects network nodes. Most diagrams that describe a
physical network are therefore topological, rather than geographic. The
symbols on these diagrams usually denote network links and network
nodes.
Network links
The transmission media (often referred to in the literature as the physical media) used to link devices to form a computer network include electrical cable, optical fiber, and radio waves. In the OSI model, these are defined at layers 1 and 2 — the physical layer and the data link layer.
A widely adopted family of transmission media used in local area network (LAN) technology is collectively known as Ethernet. The media and protocol standards that enable communication between networked devices over Ethernet are defined by IEEE 802.3. Ethernet transmits data over both copper and fiber cables. Wireless LAN standards use radio waves, others use infrared signals as a transmission medium. Power line communication uses a building's power cabling to transmit data.
Wired technologies
Fiber optic cables are used to transmit light from one computer/network node to another
The following classes of wired technologies are used in computer networking.
- Coaxial cable is widely used for cable television systems, office buildings, and other work-sites for local area networks. Transmission speed ranges from 200 million bits per second to more than 500 million bits per second.
- ITU-T G.hn technology uses existing home wiring (coaxial cable, phone lines and power lines) to create a high-speed local area network.
- Twisted pair cabling is used for wired Ethernet and other standards. It typically consists of 4 pairs of copper cabling that can be utilized for both voice and data transmission. The use of two wires twisted together helps to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic induction. The transmission speed ranges from 2 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s. Twisted pair cabling comes in two forms: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted-pair (STP). Each form comes in several category ratings, designed for use in various scenarios.
2007 map showing submarine optical fiber telecommunication cables around the world.
- An optical fiber is a glass fiber. It carries pulses of light that represent data. Some advantages of optical fibers over metal wires are very low transmission loss and immunity to electrical interference. Optical fibers can simultaneously carry multiple streams of data on different wavelengths of light, which greatly increases the rate that data can be sent to up to trillions of bits per second. Optic fibers can be used for long runs of cable carrying very high data rates, and are used for undersea cables to interconnect continents. There are two basic types of fiber optics, single-mode optical fiber (SMF) and multi-mode optical fiber (MMF). Single-mode fiber has the advantage of being able to sustain a coherent signal for dozens or even a hundred kilometers. Multimode fiber is cheaper to terminate but is limited to a few hundred or even only a few dozens of meters, depending on the data rate and cable grade.
Price is a main factor distinguishing wired- and wireless-technology
options in a business. Wireless options command a price premium that can
make purchasing wired computers, printers and other devices a financial
benefit. Before making the decision to purchase hard-wired technology
products, a review of the restrictions and limitations of the selections
is necessary. Business and employee needs may override any cost
considerations.
Wireless technologies
Computers are very often connected to networks using wireless links
- Terrestrial microwave – Terrestrial microwave communication uses Earth-based transmitters and receivers resembling satellite dishes. Terrestrial microwaves are in the low gigahertz range, which limits all communications to line-of-sight. Relay stations are spaced approximately 48 km (30 mi) apart.
- Communications satellites – Satellites communicate via microwave radio waves, which are not deflected by the Earth's atmosphere. The satellites are stationed in space, typically in geosynchronous orbit 35,400 km (22,000 mi) above the equator. These Earth-orbiting systems are capable of receiving and relaying voice, data, and TV signals.
- Cellular and PCS systems use several radio communications technologies. The systems divide the region covered into multiple geographic areas. Each area has a low-power transmitter or radio relay antenna device to relay calls from one area to the next area.
- Radio and spread spectrum technologies – Wireless local area networks use a high-frequency radio technology similar to digital cellular and a low-frequency radio technology. Wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology to enable communication between multiple devices in a limited area. IEEE 802.11 defines a common flavor of open-standards wireless radio-wave technology known as Wi-Fi.
- Free-space optical communication uses visible or invisible light for communications. In most cases, line-of-sight propagation is used, which limits the physical positioning of communicating devices.
Exotic technologies
There have been various attempts at transporting data over exotic media:
- IP over Avian Carriers was a humorous April fool's Request for Comments, issued as RFC 1149. It was implemented in real life in 2001.
- Extending the Internet to interplanetary dimensions via radio waves, the Interplanetary Internet.
Both cases have a large round-trip delay time, which gives slow two-way communication, but doesn't prevent sending large amounts of information.
Network nodes
Apart from any physical transmission media there may be, networks comprise additional basic system building blocks, such as network interface controllers (NICs), repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, routers, modems, and firewalls. Any particular piece of equipment will frequently contain multiple building blocks and perform multiple functions.
Network interfaces
An ATM network interface in the form of an accessory card. A lot of network interfaces are built-in.
A network interface controller (NIC) is computer hardware
that provides a computer with the ability to access the transmission
media, and has the ability to process low-level network information. For
example, the NIC may have a connector for accepting a cable, or an
aerial for wireless transmission and reception, and the associated
circuitry.
The NIC responds to traffic addressed to a network address for either the NIC or the computer as a whole.
In Ethernet networks, each network interface controller has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address—usually stored in the controller's permanent memory. To avoid address conflicts between network devices, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) maintains and administers MAC address uniqueness. The size of an Ethernet MAC address is six octets.
The three most significant octets are reserved to identify NIC
manufacturers. These manufacturers, using only their assigned prefixes,
uniquely assign the three least-significant octets of every Ethernet
interface they produce.
Repeaters and hubs
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a network signal, cleans it of unnecessary noise and regenerates it. The signal is retransmitted
at a higher power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so
that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation. In most
twisted pair Ethernet configurations, repeaters are required for cable
that runs longer than 100 meters. With fiber optics, repeaters can be
tens or even hundreds of kilometers apart.
A repeater with multiple ports is known as an Ethernet hub.
Repeaters work on the physical layer of the OSI model. Repeaters
require a small amount of time to regenerate the signal. This can cause a
propagation delay
that affects network performance and may affect proper function. As a
result, many network architectures limit the number of repeaters that
can be used in a row, e.g., the Ethernet 5-4-3 rule.
Hubs and repeaters in LANs have been mostly obsoleted by modern switches.
Bridges
A network bridge connects and filters traffic between two network segments at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model
to form a single network. This breaks the network's collision domain
but maintains a unified broadcast domain. Network segmentation breaks
down a large, congested network into an aggregation of smaller, more
efficient networks.
Bridges come in three basic types:
- Local bridges: Directly connect LANs
- Remote bridges: Can be used to create a wide area network (WAN) link between LANs. Remote bridges, where the connecting link is slower than the end networks, largely have been replaced with routers.
- Wireless bridges: Can be used to join LANs or connect remote devices to LANs.
Switches
A network switch is a device that forwards and filters OSI layer 2 datagrams (frames) between ports based on the destination MAC address in each frame.
A switch is distinct from a hub in that it only forwards the frames to
the physical ports involved in the communication rather than all ports
connected. It can be thought of as a multi-port bridge.
It learns to associate physical ports to MAC addresses by examining the
source addresses of received frames. If an unknown destination is
targeted, the switch broadcasts to all ports but the source. Switches
normally have numerous ports, facilitating a star topology for devices,
and cascading additional switches.
Routers
A router is an internetworking device that forwards packets
between networks by processing the routing information included in the
packet or datagram (Internet protocol information from layer 3). The
routing information is often processed in conjunction with the routing
table (or forwarding table). A router uses its routing table to
determine where to forward packets. A destination in a routing table can
include a "null" interface, also known as the "black hole" interface
because data can go into it, however, no further processing is done for
said data, i.e. the packets are dropped.
Modems
Modems
(MOdulator-DEModulator) are used to connect network nodes via wire not
originally designed for digital network traffic, or for wireless. To do
this one or more carrier signals are modulated by the digital signal to produce an analog signal that can be tailored to give the required properties for transmission. Modems are commonly used for telephone lines, using a Digital Subscriber Line technology.
Firewalls
A firewall
is a network device for controlling network security and access rules.
Firewalls are typically configured to reject access requests from
unrecognized sources while allowing actions from recognized ones. The
vital role firewalls play in network security grows in parallel with the
constant increase in cyber attacks.
Network structure
Network topology
is the layout or organizational hierarchy of interconnected nodes of a
computer network. Different network topologies can affect throughput,
but reliability is often more critical. With many technologies, such as
bus networks, a single failure can cause the network to fail entirely.
In general the more interconnections there are, the more robust the
network is; but the more expensive it is to install.
Common layouts
Common network topologies
Common layouts are:
- A bus network: all nodes are connected to a common medium along this medium. This was the layout used in the original Ethernet, called 10BASE5 and 10BASE2. This is still a common topology on the data link layer, although modern physical layer variants use point-to-point links instead.
- A star network: all nodes are connected to a special central node. This is the typical layout found in a Wireless LAN, where each wireless client connects to the central Wireless access point.
- A ring network: each node is connected to its left and right neighbour node, such that all nodes are connected and that each node can reach each other node by traversing nodes left- or rightwards. The Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) made use of such a topology.
- A mesh network: each node is connected to an arbitrary number of neighbours in such a way that there is at least one traversal from any node to any other.
- A fully connected network: each node is connected to every other node in the network.
- A tree network: nodes are arranged hierarchically.
Note that the physical layout of the nodes in a network may not necessarily reflect the network topology. As an example, with FDDI,
the network topology is a ring (actually two counter-rotating rings),
but the physical topology is often a star, because all neighboring
connections can be routed via a central physical location.
Overlay network
A sample overlay network
An overlay network
is a virtual computer network that is built on top of another network.
Nodes in the overlay network are connected by virtual or logical links.
Each link corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links,
in the underlying network. The topology of the overlay network may (and
often does) differ from that of the underlying one. For example, many peer-to-peer networks are overlay networks. They are organized as nodes of a virtual system of links that run on top of the Internet.
Overlay networks have been around since the invention of
networking when computer systems were connected over telephone lines
using modems, before any data network existed.
The most striking example of an overlay network is the Internet
itself. The Internet itself was initially built as an overlay on the telephone network.
Even today, each Internet node can communicate with virtually any other
through an underlying mesh of sub-networks of wildly different
topologies and technologies. Address resolution and routing are the means that allow mapping of a fully connected IP overlay network to its underlying network.
Another example of an overlay network is a distributed hash table,
which maps keys to nodes in the network. In this case, the underlying
network is an IP network, and the overlay network is a table (actually a
map) indexed by keys.
Overlay networks have also been proposed as a way to improve Internet routing, such as through quality of service guarantees to achieve higher-quality streaming media. Previous proposals such as IntServ, DiffServ, and IP Multicast have not seen wide acceptance largely because they require modification of all routers in the network.
On the other hand, an overlay network can be incrementally deployed on
end-hosts running the overlay protocol software, without cooperation
from Internet service providers.
The overlay network has no control over how packets are routed in the
underlying network between two overlay nodes, but it can control, for
example, the sequence of overlay nodes that a message traverses before
it reaches its destination.
For example, Akamai Technologies manages an overlay network that provides reliable, efficient content delivery (a kind of multicast). Academic research includes end system multicast, resilient routing and quality of service studies, among others.
Communication protocols
The TCP/IP model or Internet layering scheme and its relation to common protocols often layered on top of it.
Message
flows (A-B) in the presence of a router (R), red flows are effective
communication paths, black paths are across the actual network links.
A communication protocol is a set of rules for exchanging information over a network. In a protocol stack (also see the OSI model),
each protocol leverages the services of the protocol layer below it,
until the lowest layer controls the hardware which sends information
across the media. The use of protocol layering is today ubiquitous
across the field of computer networking. An important example of a
protocol stack is HTTP (the World Wide Web protocol) running over TCP over IP (the Internet protocols) over IEEE 802.11 (the Wi-Fi protocol). This stack is used between the wireless router and the home user's personal computer when the user is surfing the web.
Communication protocols have various characteristics. They may be connection-oriented or connectionless, they may use circuit mode or packet switching, and they may use hierarchical addressing or flat addressing.
There are many communication protocols, a few of which are described below.
IEEE 802
IEEE 802
is a family of IEEE standards dealing with local area networks and
metropolitan area networks. The complete IEEE 802 protocol suite
provides a diverse set of networking capabilities. The protocols have a
flat addressing scheme. They operate mostly at levels 1 and 2 of the OSI model.
For example, MAC bridging (IEEE 802.1D) deals with the routing of Ethernet packets using a Spanning Tree Protocol. IEEE 802.1Q describes VLANs, and IEEE 802.1X defines a port-based Network Access Control
protocol, which forms the basis for the authentication mechanisms used
in VLANs (but it is also found in WLANs) – it is what the home user sees
when the user has to enter a "wireless access key".
Ethernet
Ethernet, sometimes simply called LAN, is a family of protocols used in wired LANs, described by a set of standards together called IEEE 802.3 published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
Wireless LAN
Wireless LAN, also widely known as WLAN or WiFi, is probably the most well-known member of the IEEE 802 protocol family for home users today. It is standardized by IEEE 802.11 and shares many properties with wired Ethernet.
Internet Protocol Suite
The Internet Protocol Suite,
also called TCP/IP, is the foundation of all modern networking. It
offers connection-less as well as connection-oriented services over an
inherently unreliable network traversed by data-gram transmission at the
Internet protocol (IP) level. At its core, the protocol suite defines the addressing, identification, and routing specifications for Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) and for IPv6, the next generation of the protocol with a much enlarged addressing capability.
SONET/SDH
Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) are standardized multiplexing
protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams over optical fiber
using lasers. They were originally designed to transport circuit mode
communications from a variety of different sources, primarily to support
real-time, uncompressed, circuit-switched voice encoded in PCM
(Pulse-Code Modulation) format. However, due to its protocol neutrality
and transport-oriented features, SONET/SDH also was the obvious choice
for transporting Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) frames.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a switching technique for telecommunication networks. It uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing and encodes data into small, fixed-sized cells. This differs from other protocols such as the Internet Protocol Suite or Ethernet that use variable sized packets or frames. ATM has similarity with both circuit and packet
switched networking. This makes it a good choice for a network that
must handle both traditional high-throughput data traffic, and
real-time, low-latency content such as voice and video. ATM uses a connection-oriented model in which a virtual circuit must be established between two endpoints before the actual data exchange begins.
While the role of ATM is diminishing in favor of next-generation networks, it still plays a role in the last mile, which is the connection between an Internet service provider and the home user.
Cellular standards
There are a number of different digital cellular standards, including: Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), cdmaOne, CDMA2000, Evolution-Data Optimized (EV-DO), Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT), Digital AMPS (IS-136/TDMA), and Integrated Digital Enhanced Network (iDEN).
Geographic scale
A network can be characterized by its physical capacity or its
organizational purpose. Use of the network, including user authorization
and access rights, differ accordingly.
- Nanoscale network
A nanoscale communication
network has key components implemented at the nanoscale including
message carriers and leverages physical principles that differ from
macroscale communication mechanisms. Nanoscale communication extends
communication to very small sensors and actuators such as those found in
biological systems and also tends to operate in environments that would
be too harsh for classical communication.
- Personal area network
A personal area network
(PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer and
different information technological devices close to one person. Some
examples of devices that are used in a PAN are personal computers,
printers, fax machines, telephones, PDAs, scanners, and even video game
consoles. A PAN may include wired and wireless devices. The reach of a
PAN typically extends to 10 meters.
A wired PAN is usually constructed with USB and FireWire connections
while technologies such as Bluetooth and infrared communication
typically form a wireless PAN.
- Local area network
A local area network
(LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited
geographical area such as a home, school, office building, or closely
positioned group of buildings. Each computer or device on the network is
a node. Wired LANs are most likely based on Ethernet technology. Newer standards such as ITU-T G.hn also provide a way to create a wired LAN using existing wiring, such as coaxial cables, telephone lines, and power lines.
The defining characteristics of a LAN, in contrast to a wide area network (WAN), include higher data transfer rates, limited geographic range, and lack of reliance on leased lines to provide connectivity. Current Ethernet or other IEEE 802.3 LAN technologies operate at data transfer rates up to 100 Gbit/s, standardized by IEEE in 2010. Currently, 400 Gbit/s Ethernet is being developed.
A LAN can be connected to a WAN using a router.
- Home area network
A home area network
(HAN) is a residential LAN used for communication between digital
devices typically deployed in the home, usually a small number of
personal computers and accessories, such as printers and mobile
computing devices. An important function is the sharing of Internet
access, often a broadband service through a cable TV or digital subscriber line (DSL) provider.
- Storage area network
A storage area network
(SAN) is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated,
block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to make storage
devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes,
accessible to servers so that the devices appear like locally attached
devices to the operating system. A SAN typically has its own network of
storage devices that are generally not accessible through the local area
network by other devices. The cost and complexity of SANs dropped in
the early 2000s to levels allowing wider adoption across both enterprise
and small to medium-sized business environments.
- Campus area network
A campus area network
(CAN) is made up of an interconnection of LANs within a limited
geographical area. The networking equipment (switches, routers) and
transmission media (optical fiber, copper plant, Cat5 cabling, etc.) are almost entirely owned by the campus tenant / owner (an enterprise, university, government, etc.).
For example, a university campus network is likely to link a
variety of campus buildings to connect academic colleges or departments,
the library, and student residence halls.
- Backbone network
A backbone network
is part of a computer network infrastructure that provides a path for
the exchange of information between different LANs or sub-networks. A
backbone can tie together diverse networks within the same building,
across different buildings, or over a wide area.
For example, a large company might implement a backbone network
to connect departments that are located around the world. The equipment
that ties together the departmental networks constitutes the network
backbone. When designing a network backbone, network performance and network congestion
are critical factors to take into account. Normally, the backbone
network's capacity is greater than that of the individual networks
connected to it.
Another example of a backbone network is the Internet backbone, which is the set of wide area networks (WANs) and core routers that tie together all networks connected to the Internet.
- Metropolitan area network
A Metropolitan area network (MAN) is a large computer network that usually spans a city or a large campus.
- Wide area network
A wide area network
(WAN) is a computer network that covers a large geographic area such as
a city, country, or spans even intercontinental distances. A WAN uses a
communications channel that combines many types of media such as
telephone lines, cables, and air waves. A WAN often makes use of
transmission facilities provided by common carriers, such as telephone
companies. WAN technologies generally function at the lower three layers
of the OSI reference model: the physical layer, the data link layer, and the network layer.
- Enterprise private network
An enterprise private network
is a network that a single organization builds to interconnect its
office locations (e.g., production sites, head offices, remote offices,
shops) so they can share computer resources.
- Virtual private network
A virtual private network
(VPN) is an overlay network in which some of the links between nodes
are carried by open connections or virtual circuits in some larger
network (e.g., the Internet) instead of by physical wires. The data link
layer protocols of the virtual network are said to be tunneled through
the larger network when this is the case. One common application is
secure communications through the public Internet, but a VPN need not
have explicit security features, such as authentication or content
encryption. VPNs, for example, can be used to separate the traffic of
different user communities over an underlying network with strong
security features.
VPN may have best-effort performance, or may have a defined
service level agreement (SLA) between the VPN customer and the VPN
service provider. Generally, a VPN has a topology more complex than
point-to-point.
- Global area network
A global area network
(GAN) is a network used for supporting mobile across an arbitrary
number of wireless LANs, satellite coverage areas, etc. The key
challenge in mobile communications is handing off user communications
from one local coverage area to the next. In IEEE Project 802, this
involves a succession of terrestrial wireless LANs.
Organizational scope
Networks
are typically managed by the organizations that own them. Private
enterprise networks may use a combination of intranets and extranets.
They may also provide network access to the Internet, which has no single owner and permits virtually unlimited global connectivity.
Intranet
An intranet is a set of networks that are under the control of a single administrative entity. The intranet uses the IP
protocol and IP-based tools such as web browsers and file transfer
applications. The administrative entity limits use of the intranet to
its authorized users. Most commonly, an intranet is the internal LAN of
an organization. A large intranet typically has at least one web server
to provide users with organizational information. An intranet is also
anything behind the router on a local area network.
Extranet
An extranet
is a network that is also under the administrative control of a single
organization, but supports a limited connection to a specific external
network. For example, an organization may provide access to some
aspects of its intranet to share data with its business partners or
customers. These other entities are not necessarily trusted from a
security standpoint. Network connection to an extranet is often, but
not always, implemented via WAN technology.
Internetwork
An internetwork is the connection of multiple computer networks via a common routing technology using routers.
Internet
Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable.
The Internet
is the largest example of an internetwork. It is a global system of
interconnected governmental, academic, corporate, public, and private
computer networks. It is based on the networking technologies of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is the successor of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) developed by DARPA of the United States Department of Defense. The Internet is also the communications backbone underlying the World Wide Web (WWW).
Participants in the Internet use a diverse array of methods of
several hundred documented, and often standardized, protocols compatible
with the Internet Protocol Suite and an addressing system (IP addresses) administered by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority and address registries. Service providers and large enterprises exchange information about the reachability of their address spaces through the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), forming a redundant worldwide mesh of transmission paths.
Darknet
A darknet
is an overlay network, typically running on the Internet, that is only
accessible through specialized software. A darknet is an anonymizing
network where connections are made only between trusted peers —
sometimes called "friends" (F2F) — using non-standard protocols and ports.
Darknets are distinct from other distributed peer-to-peer networks as sharing is anonymous (that is, IP addresses are not publicly shared), and therefore users can communicate with little fear of governmental or corporate interference.
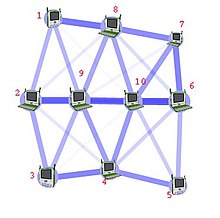
Routing
Routing
calculates good paths through a network for information to take. For
example, from node 1 to node 6 the best routes are likely to be 1-8-7-6
or 1-8-10-6, as this has the thickest routes.
Routing is the process of selecting network paths to carry network traffic. Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including circuit switching networks and packet switched networks.
In packet switched networks, routing directs packet forwarding (the transit of logically addressed network packets from their source toward their ultimate destination) through intermediate nodes. Intermediate nodes are typically network hardware devices such as routers, bridges, gateways, firewalls, or switches. General-purpose computers
can also forward packets and perform routing, though they are not
specialized hardware and may suffer from limited performance. The
routing process usually directs forwarding on the basis of routing tables,
which maintain a record of the routes to various network destinations.
Thus, constructing routing tables, which are held in the router's memory, is very important for efficient routing.
There are usually multiple routes that can be taken, and to
choose between them, different elements can be considered to decide
which routes get installed into the routing table, such as (sorted by
priority):
- Prefix-Length: where longer subnet masks are preferred (independent if it is within a routing protocol or over different routing protocol)
- Metric: where a lower metric/cost is preferred (only valid within one and the same routing protocol)
- Administrative distance: where a lower distance is preferred (only valid between different routing protocols)
Most routing algorithms use only one network path at a time. Multipath routing techniques enable the use of multiple alternative paths.
Routing, in a more narrow sense of the term, is often contrasted with bridging in its assumption that network addresses
are structured and that similar addresses imply proximity within the
network. Structured addresses allow a single routing table entry to
represent the route to a group of devices. In large networks,
structured addressing (routing, in the narrow sense) outperforms
unstructured addressing (bridging). Routing has become the dominant form
of addressing on the Internet. Bridging is still widely used within
localized environments.
Network service
Network services are applications hosted by servers on a computer network, to provide some functionality for members or users of the network, or to help the network itself to operate.
The World Wide Web, E-mail, printing and network file sharing are examples of well-known network services. Network services such as DNS (Domain Name System) give names for IP and MAC addresses (people remember names like “nm.lan” better than numbers like “210.121.67.18”), and DHCP to ensure that the equipment on the network has a valid IP address.
Services are usually based on a service protocol that defines the format and sequencing of messages between clients and servers of that network service.
Network performance
Quality of service
Depending on the installation requirements, network performance is usually measured by the quality of service of a telecommunications product. The parameters that affect this typically can include throughput, jitter, bit error rate and latency.
The following list gives examples of network performance measures for a circuit-switched network and one type of packet-switched network, viz. ATM:
- Circuit-switched networks: In circuit switched networks, network performance is synonymous with the grade of service. The number of rejected calls is a measure of how well the network is performing under heavy traffic loads. Other types of performance measures can include the level of noise and echo.
- ATM: In an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network, performance can be measured by line rate, quality of service (QoS), data throughput, connect time, stability, technology, modulation technique and modem enhancements.
There are many ways to measure the performance of a network, as each
network is different in nature and design. Performance can also be
modeled instead of measured. For example, state transition diagrams
are often used to model queuing performance in a circuit-switched
network. The network planner uses these diagrams to analyze how the
network performs in each state, ensuring that the network is optimally
designed.
Network congestion
Network congestion occurs when a link or node is carrying so much data that its quality of service deteriorates. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A consequence of these latter two is that incremental increases in offered load lead either only to small increase in network throughput, or to an actual reduction in network throughput.
Network protocols that use aggressive retransmissions
to compensate for packet loss tend to keep systems in a state of
network congestion—even after the initial load is reduced to a level
that would not normally induce network congestion. Thus, networks using
these protocols can exhibit two stable states under the same level of
load. The stable state with low throughput is known as congestive collapse.
Modern networks use congestion control, congestion avoidance and traffic control techniques to try to avoid congestion collapse. These include: exponential backoff in protocols such as 802.11's CSMA/CA and the original Ethernet, window reduction in TCP, and fair queueing in devices such as routers.
Another method to avoid the negative effects of network congestion is
implementing priority schemes, so that some packets are transmitted with
higher priority than others. Priority schemes do not solve network
congestion by themselves, but they help to alleviate the effects of
congestion for some services. An example of this is 802.1p.
A third method to avoid network congestion is the explicit allocation
of network resources to specific flows. One example of this is the use
of Contention-Free Transmission Opportunities (CFTXOPs) in the ITU-T G.hn standard, which provides high-speed (up to 1 Gbit/s) Local area networking over existing home wires (power lines, phone lines and coaxial cables).
Network resilience
Network resilience is "the ability to provide and maintain an acceptable level of service in the face of faults and challenges to normal operation.”
Security
Network security
Network security consists of provisions and policies adopted by the network administrator to prevent and monitor unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of the computer network and its network-accessible resources.
Network security is the authorization of access to data in a network,
which is controlled by the network administrator. Users are assigned an
ID and password that allows them access to information and programs
within their authority. Network security is used on a variety of
computer networks, both public and private, to secure daily transactions
and communications among businesses, government agencies and
individuals.
Network surveillance
Network surveillance is the monitoring of data being transferred over computer networks such as the Internet.
The monitoring is often done surreptitiously and may be done by or at
the behest of governments, by corporations, criminal organizations, or
individuals. It may or may not be legal and may or may not require
authorization from a court or other independent agency.
Computer and network surveillance programs are widespread today,
and almost all Internet traffic is or could potentially be monitored for
clues to illegal activity.
Surveillance is very useful to governments and law enforcement to maintain social control, recognize and monitor threats, and prevent/investigate criminal activity. With the advent of programs such as the Total Information Awareness program, technologies such as high speed surveillance computers and biometrics software, and laws such as the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act, governments now possess an unprecedented ability to monitor the activities of citizens.
However, many civil rights and privacy groups—such as Reporters Without Borders, the Electronic Frontier Foundation, and the American Civil Liberties Union—have expressed concern that increasing surveillance of citizens may lead to a mass surveillance society, with limited political and personal freedoms. Fears such as this have led to numerous lawsuits such as Hepting v. AT&T. The hacktivist group Anonymous has hacked into government websites in protest of what it considers "draconian surveillance".
End to end encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a digital communications paradigm of uninterrupted protection of data traveling between two communicating parties. It involves the originating party encrypting
data so only the intended recipient can decrypt it, with no dependency
on third parties. End-to-end encryption prevents intermediaries, such as
Internet providers or application service providers, from discovering or tampering with communications. End-to-end encryption generally protects both confidentiality and integrity.
Examples of end-to-end encryption include HTTPS for web traffic, PGP for email, OTR for instant messaging, ZRTP for telephony, and TETRA for radio.
Typical server-based
communications systems do not include end-to-end encryption. These
systems can only guarantee protection of communications between clients and servers, not between the communicating parties themselves. Examples of non-E2EE systems are Google Talk, Yahoo Messenger, Facebook, and Dropbox.
Some such systems, for example LavaBit and SecretInk, have even
described themselves as offering "end-to-end" encryption when they do
not. Some systems that normally offer end-to-end encryption have turned
out to contain a back door that subverts negotiation of the encryption key between the communicating parties, for example Skype or Hushmail.
The end-to-end encryption paradigm does not directly address risks at the communications endpoints themselves, such as the technical exploitation of clients, poor quality random number generators, or key escrow. E2EE also does not address traffic analysis, which relates to things such as the identities of the end points and the times and quantities of messages that are sent.
SSL/TLS
The
introduction and rapid growth of e-commerce on the world wide web in
the mid-1990s made it obvious that some form of authentication and
encryption was needed. Netscape took the first shot at a new standard. At the time, the dominant web browser was Netscape Navigator.
Netscape created a standard called secure socket layer (SSL). SSL
requires a server with a certificate. When a client requests access to
an SSL-secured server, the server sends a copy of the certificate to the
client. The SSL client checks this certificate (all web browsers come
with an exhaustive list of CA root certificates preloaded), and if the
certificate checks out, the server is authenticated and the client
negotiates a symmetric-key cipher for use in the session. The session is
now in a very secure encrypted tunnel between the SSL server and the
SSL client.
Views of networks
Users
and network administrators typically have different views of their
networks. Users can share printers and some servers from a workgroup,
which usually means they are in the same geographic location and are on
the same LAN, whereas a Network Administrator is responsible to keep
that network up and running. A community of interest
has less of a connection of being in a local area, and should be
thought of as a set of arbitrarily located users who share a set of
servers, and possibly also communicate via peer-to-peer technologies.
Network administrators can see networks from both physical and
logical perspectives. The physical perspective involves geographic
locations, physical cabling, and the network elements (e.g., routers, bridges and application layer gateways) that interconnect via the transmission media. Logical networks, called, in the TCP/IP architecture, subnets,
map onto one or more transmission media. For example, a common practice
in a campus of buildings is to make a set of LAN cables in each
building appear to be a common subnet, using virtual LAN (VLAN) technology.
Both users and administrators are aware, to varying extents, of
the trust and scope characteristics of a network. Again using TCP/IP
architectural terminology, an intranet
is a community of interest under private administration usually by an
enterprise, and is only accessible by authorized users (e.g. employees). Intranets do not have to be connected to the Internet, but generally have a limited connection. An extranet
is an extension of an intranet that allows secure communications to
users outside of the intranet (e.g. business partners, customers).
Unofficially, the Internet is the set of users, enterprises, and content providers that are interconnected by Internet Service Providers (ISP). From an engineering viewpoint, the Internet is the set of subnets, and aggregates of subnets, which share the registered IP address space and exchange information about the reachability of those IP addresses using the Border Gateway Protocol. Typically, the human-readable names of servers are translated to IP addresses, transparently to users, via the directory function of the Domain Name System (DNS).
Over the Internet, there can be business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C) and consumer-to-consumer (C2C) communications. When money or sensitive information is exchanged, the communications are apt to be protected by some form of communications security
mechanism. Intranets and extranets can be securely superimposed onto
the Internet, without any access by general Internet users and
administrators, using secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology.