History
Although fungi products have been used in traditional and folk medicines,
probably since pre-history, the ability to identify beneficial
properties and then extract the active ingredient started with the
discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming
in 1928. Since that time, many additional antibiotics have been
discovered and the potential for fungi to synthesize biologically active
molecules, useful in a wide range of clinical therapies, has been
extensively exploited.
Pharmacological research has now isolated antifungal, antiviral, and antiprotozoan, isolates from fungi.
The fungus with probably the longest record of medicinal use, Ganoderma lucidum, is known in Chinese as líng zhī ("spirit plant"), and in Japanese as mannentake ("10,000-year mushroom"). In ancient Japan, Grifola frondosa was worth its weight in silver, although no significant therapeutic benefits have been demonstrated in humans.
Studies have shown another species of genus Ganoderma, G. applanatum, contains compounds with anti-tumor and anti-fibrotic properties.
Inonotus obliquus was used in Russia as early as the 16th century, and it featured in Alexandr Solzhenitsyn's 1967 novel Cancer Ward.
Applications
Cancer
40x brightfield microscopy of Pestalotia/Pestalotiopsis spores. Note the appendages. Some strains (Pestalotiopsis pauciseta) produce taxol.
Paclitaxel is synthesised using Penicillium raistrickii and plant cell fermentation. Fungi can synthesize other mitotic inhibitors including vinblastine, vincristine, podophyllotoxin, griseofulvin, aurantiamine, oxaline, and neoxaline.
11,11'-Dideoxyverticillin A, an isolate of marine Penicillium, was used to create dozens of semi-synthetic anticancer compounds. 11,11'-Dideoxyverticillin A, andrastin A, barceloneic acid A, and barceloneic acid B, are farnesyl transferase inhibitors that can be made by Penicillium. 3-O-Methylfunicone, anicequol, duclauxin, and rubratoxin B, are anticancer/cytotoxic metabolites of Penicillium.
Penicillium is a potential source of the leukemia medicine asparaginase.
Some countries have approved Beta-glucan fungal extracts lentinan, polysaccharide-K, and polysaccharide peptide as immunologic adjuvants.
Evidence suggests this use as effective in prolonging and improving the
quality of life for patients with certain cancers, although the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
observes that "well designed, large scale studies are needed to
establish the role of lentinan as a useful adjunct to cancer treatment". According to Cancer Research UK, "there is currently no evidence that any type of mushroom or mushroom extract can prevent or cure cancer". Fungal metabolites such as ergosterol, clavilactones, and triterpenoids
are efficient Cdk inhibitors that lead to G1/S or G2/M arrest of cancer
cells. Other metabolites, such as panepoxydone, are inhibitors of
NF-κB. Fucose and mannose fragments of fungal cell wall are antagonists
of VEGF-receptors
Antibacterial agents (antibiotics)
Alexander Fleming led the way to the beta-lactam antibiotics with the Penicillium mold and penicillin. Subsequent discoveries included alamethicin, aphidicolin, brefeldin A, Cephalosporin, cerulenin, citromycin, eupenifeldin, fumagillin, fusafungine, fusidic acid, itaconic acid, MT81, nigrosporin B, usnic acid, verrucarin A, vermiculine and many others.
Ling Zhi-8, an immunomodulatory protein isolated from Ganoderma lucidum
Antibiotics retapamulin, tiamulin, and valnemulin are derivatives of the fungal metabolite pleuromutilin. Plectasin, austrocortilutein, austrocortirubin, coprinol, oudemansin A, strobilurin, illudin, pterulone, and sparassol are antibiotics isolated from basidiomycete species.
Cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors
The red yeast rice fungus, Monascus purpureus, can synthesize three statins.
Statins are an important class of cholesterol-lowering drugs; the first generation of statins were derived from fungi. Lovastatin, the first commercial statin, was extracted from a fermentation broth of Aspergillus terreus. Industrial production is now capable of producing 70 mg lovastatin per kilogram of substrate. The red yeast rice fungus, Monascus purpureus, can synthesize lovastatin, mevastatin, and the simvastatin precursor monacolin J. Nicotinamide riboside, a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, is made by Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Antifungals
Some antifungals are derived or extracted from other fungal species. Griseofulvin is derived from a number of Penicillium species, caspofungin is derived from Glarea lozoyensis. Strobilurin, azoxystrobin, micafungin, and echinocandins, are all extracted from fungi. Anidulafungin is a derivative of an Aspergillus metabolite.
Immunosuppressants
Ciclosporin, was discovered in Tolypocladium inflatum. Bredinin was discovered in Eupenicillium brefeldianum. Mycophenolic acid was discovered in Penicillium stoloniferum. Thermophilic fungi were the source of the fingolimod precursor myriocin. Aspergillus synthesizes immunosuppressants gliotoxin and endocrocin. Subglutinols are immunosuppressants isolated from Fusarium subglutinans.
Other compounds include mizoribine.
Malaria
Diabetes
Many fungal isolates act as DPP-4 inhibitors, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, and alpha amylase inhibitors in vitro. Ternatin is a fungal isolate that suppresses hyperglycemia.
Aspergillusol A is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor made by Aspergillus.
Sclerotiorin is an aldose reductase inhibitor made by Penicillium.
Psychotropic effects
A number of fungi have well documented psychotropic effects, some of
them severe and associated with sometimes acute and life-threatening
side-effects. Well known amongst these is Amanita muscaria, the fly agaric. More widely used informally are a range of fungi collectively known as "magic mushrooms", which contain psilocybin and psilocin.
The history of bread-making is also peppered with references to deadly ergotism caused by ergot, most commonly Claviceps purpurea, a parasite of cereal crops. A number of therapeutically useful drugs have subsequently been extracted from ergot including ergotamine, pergolide and cabergoline.
Psychotropic compounds created from ergot alkaloids also include dihydroergotamine, methysergide, methylergometrine, hydergine, nicergoline, lisuride, bromocriptine, cabergoline, pergolide. Polyozellus multiplex synthesizes prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors polyozellin, thelephoric acid, kynapcins. Neurotrophic fungal isolates include L-theanine, tricholomalides, scabronines, termitomycesphins. Many fungi synthesize the partial, non-selective, serotonin receptor agonist/analog psilocin.
A number of other fungal species, including species of Aspergillus and Penicillium, have been induced to produce ergot alkaloids.
Vitamins
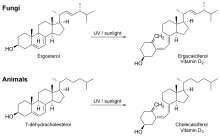
The photochemistry of vitamin D biosynthesis
Fungi are a source of ergosterol which can be converted to vitamin D upon exposure to ultraviolet light to synthesize vitamins D2 (ergocalciferol), D4 (22-dihydroergocalciferol), and D1 (Lumisterol+D2).
Phytase
Aspergillus niger is used to produce recombinant phytase, an enzyme added to animal feeds to improve absorption of phosphorus.
Edible species containing drugs
Edible species which contain drugs (biologically active constituents) include:
- Agaricus subrufescens (Agaricus blazei/brasiliensis, almond mushroom) is a fungus associated with Brazil and Japan. Blazein, a bioactive steroid, was isolated from A. subrufescens.
- The adenosine analog cordycepin was originally isolated from Cordyceps. Other Cordyceps isolates include, cordymin, cordycepsidone, and cordyheptapeptide. CS-4 is commercially sold as C. sinensis, but Cs-4 has recently been confirmed to be a different species from the Cordyceps species used in traditional Chinese medicine. CS-4 is properly known as Paecilomyces hepiali. Hirsutella sinensis is the accepted asexual form of C. sinensis.
- Ganoderma lucidum (Ling zhi, mannentake, reishi) contains p-hydroxybenzoic acid, cinnamic acid, and lanostane-type triterpenoids such as ganoderic acids.
- Hydnellum peckii has yielded atromentin, a compound isolated from the mycorrhiza, and subsequently its biosynthesis has been characterized.
- Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) has been used as a source of Lentinan, AHCC, and eritadenine.
- Schizophyllum commune (Split gill) has yielded schizophyllan (SPG, sizofiran, sonifilan). Hydrophobins were originally isolated from S. commune. A chemically analogous polysaccharide, scleroglucan, is an isolate of Sclerotium rolfsii.
- Tolypocladium inflatum Gams yields the immunosuppressant ciclosporin.
- Trametes versicolor (Coriolus versicolor, yun zhi, kawaratake, turkey tail) have produced protein-bound polysaccharides PSK and PSP (polysaccharopeptide) from different mycelia strains.
- Ustilago maydis (Mexican truffle, huitlacoche, corn fungus) synthesises ustilagine and ustilagic acid.
Yeasts
Saccharomyces is used industrially to produce the amino acid lysine, as well as recombinant proteinsinsulin and Hepatitis B surface antigen. Transgenic yeast are used to produce artemisinin, as well as a number of insulin analogs. Candida is used industrially to produce vitamins ascorbic acid and riboflavin. Pichia is used to produce the amino acid tryptophan and the vitamin pyridoxine. Rhodotorula is used to produce the amino acid phenylalanine. Moniliella is used industrially to produce the sugar alcoholerythritol.