Global mean surface temperature change since 1880. Source: NASA GISS
The global temperature record shows the fluctuations of the temperature
of the atmosphere and the oceans through various spans of time. The
most detailed information exists since 1850, when methodical
thermometer-based records began. There are numerous estimates of
temperatures since the end of the Pleistocene glaciation, particularly during the current Holocene epoch. Older time periods are studied by paleoclimatology.
Satellite and balloon (1950s-present)
Weather balloon radiosonde
measurements of atmospheric temperature at various altitudes begin to
show an approximation of global coverage in the 1950s. Since December
1978, microwave sounding units on satellites have produced data which can be used to infer temperatures in the troposphere.
Several groups have analyzed the satellite data to calculate temperature trends in the troposphere. Both the University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH) and the private, NASA funded, corporation Remote Sensing Systems RSS (RSS) find an upward trend.
For the lower troposphere, UAH found a global average trend between 1978 and 2019 of 0.130 degrees Celsius per decade.
RSS found a trend of 0.148 degrees Celsius per decade, to January 2011.
In 2004 Fu et al. found trends of +0.19 degrees Celsius per decade when applied to the RSS dataset.
Vinnikov and Grody found 0.20 degrees Celsius per decade up between
1978 and 2005, since which the dataset has not been updated.
Thermometers (1850-present)
Detailed information exists since 1850, when methodical thermometer-based records began.
Tree rings and ice cores (from 1,000-2,000 years before present)
This image compares ten reconstructed proxy temperature studies covering the last 2,000 years.
Proxy measurements can be used to reconstruct the temperature record before the historical period. Quantities such as tree ring widths, coral growth, isotope variations in ice cores, ocean and lake sediments, cave deposits, fossils, ice cores, borehole temperatures, and glacier
length records are correlated with climatic fluctuations. From these,
proxy temperature reconstructions of the last 2000 years have been
performed for the northern hemisphere, and over shorter time scales for
the southern hemisphere and tropics.
Geographic coverage by these proxies is necessarily sparse, and
various proxies are more sensitive to faster fluctuations. For example,
tree rings, ice cores, and corals generally show variation on an annual
time scale, but borehole reconstructions rely on rates of thermal diffusion,
and small scale fluctuations are washed out. Even the best proxy
records contain far fewer observations than the worst periods of the
observational record, and the spatial and temporal resolution of the
resulting reconstructions is correspondingly coarse. Connecting the
measured proxies to the variable of interest, such as temperature or
rainfall, is highly non-trivial. Data sets from multiple complementary
proxies covering overlapping time periods and areas are reconciled to
produce the final reconstructions.
Proxy reconstructions extending back 2,000 years have been
performed, but reconstructions for the last 1,000 years are supported by
more and higher quality independent data sets. These reconstructions
indicate:
- global mean surface temperatures over the last 25 years have been higher than any comparable period since AD 1600, and probably since AD 900
- there was a Little Ice Age centered on AD 1700
- there was a Medieval Warm Period centered on AD 1000, though the exact timing and magnitude are uncertain and may have shown regional variation.
Indirect historical proxies
As well as natural, numerical proxies (tree-ring widths, for example)
there exist records from the human historical period that can be used
to infer climate variations, including: reports of frost fairs on the Thames;
records of good and bad harvests; dates of spring blossom or lambing;
extraordinary falls of rain and snow; and unusual floods or droughts. Such records can be used to infer historical temperatures, but generally in a more qualitative manner than natural proxies.
Recent evidence suggests that a sudden and short-lived climatic shift between 2200 and 2100 BCE occurred in the region between Tibet and Iceland,
with some evidence suggesting a global change. The result was a
cooling and reduction in precipitation. This is believed to be a
primary cause of the collapse of the Old Kingdom of Egypt.
Paleoclimate (from 12,000 years before present)
Plot showing the variations, and relative stability, of climate during the last 12000 years.
Many estimates of past temperatures have been made over Earth's history.
The field of paleoclimatology includes ancient temperature records.
As the present article is oriented toward recent temperatures, there is a
focus here on events since the retreat of the Pleistocene glaciers. The 10,000 years of the Holocene epoch covers most of this period, since the end of the Northern Hemisphere's Younger Dryas millennium-long cooling. The Holocene Climatic Optimum
was generally warmer than the 20th century, but numerous regional
variations have been noted since the start of the Younger Dryas.
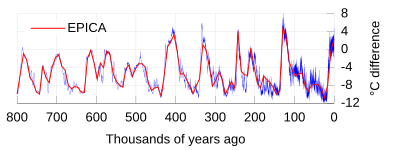
Ice cores (from 800,000 years before present)
Temperature
estimates relative to today from over 800,000 years of the EPICA ice
cores in Antarctica. Today's date is on the right side of the graph.
Even longer term records exist for few sites: the recent Antarctic EPICA core reaches 800 kyr; many others reach more than 100,000 years. The EPICA core covers eight glacial/interglacial cycles. The NGRIP core from Greenland stretches back more than 100 kyr, with 5 kyr in the Eemian interglacial.
Whilst the large-scale signals from the cores are clear, there are
problems interpreting the detail, and connecting the isotopic variation
to the temperature signal.
Geologic evidence (millions of years)
Reconstruction of the past 5 million years of climate history, based on oxygen isotope fractionation in deep sea sediment cores (serving as a proxy for the total global mass of glacial ice sheets), fitted to a model of orbital forcing (Lisiecki and Raymo 2005) and to the temperature scale derived from Vostok ice cores following Petit et al. (1999).
On longer time scales, sediment cores show that the cycles of
glacials and interglacials are part of a deepening phase within a
prolonged ice age that began with the glaciation of Antarctica
approximately 40 million years ago. This deepening phase, and the
accompanying cycles, largely began approximately 3 million years ago
with the growth of continental ice sheets in the Northern Hemisphere.
Gradual changes in Earth's climate of this kind have been frequent
during the Earth's 4500 million year existence and most often are
attributed to changes in the configuration of continents and ocean sea
ways.