Protester holding Adbusters Corporate American Flag at Bush's 2nd inauguration, Washington DC.
Corporatocracy (/ˌkɔːrpərəˈtɒkrəsi/, from corporate and Greek: -κρατία, romanized: -kratía, lit. 'domination by'; short form corpocracy) is a recent term used to refer to an economic and political system controlled by corporations or corporate interests. It is a form of Plutocracy.
The concept has been used in explanations of bank bailouts, excessive pay for CEOs as well as complaints such as the exploitation of national treasuries, people and natural resources. It has been used by critics of globalization, sometimes in conjunction with criticism of the World Bank or unfair lending practices as well as criticism of "free trade agreements".
Use of "corporatocracy" and similar ideas
Historian Howard Zinn argues that during the Gilded Age in the United States, the U.S. government was acting exactly as Karl Marx described capitalist states: "pretending neutrality to maintain order, but serving the interests of the rich".
According to economist Joseph Stiglitz, there has been a severe increase in market power of corporations, largely due to U.S. antitrust laws being weakened by neoliberal reforms, leading to growing income inequality and a generally underperforming economy. He states that to improve the economy, it is necessary to decrease the influence of money on U.S. politics.
In his 1956 book The power elite, sociologist C Wright Mills states that together with the military and political establishment, leaders of the biggest corporations form a "power elite" that is in control of the U.S.
Economist Jeffrey Sachs described the United States as a corporatocracy in The Price of Civilization (2011). He suggested that it arose from four trends: weak national parties and strong political representation of individual districts, the large U.S. military establishment after World War II, large corporations using money to finance election campaigns, and globalization tilting the balance of power away from workers.
In 2013, economist Edmund Phelps criticised the economic system of the U.S. and other western countries in recent decades as being what he calls "the new corporatism",
which he characterises as a system in which the state is far too
involved in the economy, tasked with "protecting everyone against
everyone else", but in which at the same time big companies have a great
deal of influence on the government, with lobbyists' suggestions being
"welcome, especially if they come with bribes".
Corporate influence on politics in the United States
Corruption
During the Gilded Age
in the United States, corruption was rampant as business leaders spent
significant amounts of money ensuring that government did not regulate
their activities.
Corporate influence on legislation
Corporations have significant influence on the regulations and regulators that monitor them. For example, Senator Elizabeth Warren
explained in December 2014 how an omnibus spending bill required to
fund the government was modified late in the process to weaken banking
regulations. The modification made it easier to allow taxpayer-funded
bailouts of banking "swaps entities", which the Dodd-Frank banking regulations prohibited. She singled out Citigroup,
one of the largest banks, which had a role in modifying the
legislation. She also explained how both Wall Street bankers and members
of the government that formerly had worked on Wall Street stopped
bi-partisan legislation that would have broken up the largest banks. She
repeated President Theodore Roosevelt's warnings regarding powerful
corporate entities that threatened the "very foundations of Democracy."
Perceived symptoms of corporatocracy in the United States
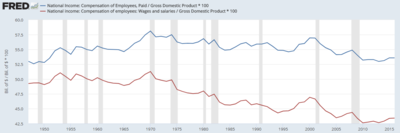
Labor's
share of GDP has declined 1970 to 2013, measured based on total
compensation as well as salaries and wages. This implies capital's share
is increasing.
With regard to income inequality, the 2014 income analysis of University of California, Berkeley economist Emmanuel Saez
confirms that relative growth of income and wealth is not occurring
among small and mid-sized entrepreneurs and business owners (who
generally populate the lower half of top one per-centers in income), but instead only among the top .1 percent of income distribution, who earn $2,000,000 or more every year.
Corporate power can also increase income inequality. Nobel Prize winner of economics Joseph Stiglitz
wrote in May 2011: "Much of today’s inequality is due to manipulation
of the financial system, enabled by changes in the rules that have been
bought and paid for by the financial industry itself—one of its best
investments ever. The government lent money to financial institutions at
close to zero percent interest and provided generous bailouts on
favorable terms when all else failed. Regulators turned a blind eye to a
lack of transparency and to conflicts of interest." Stiglitz explained
that the top 1% got nearly "one-quarter" of the income and own
approximately 40% of the wealth.
Measured relative to GDP, total compensation and its component
wages and salaries have been declining since 1970. This indicates a
shift in income from labor (persons who derive income from hourly wages
and salaries) to capital (persons who derive income via ownership of
businesses, land and assets).
Larry Summers
estimated in 2007 that the lower 80% of families were receiving $664
billion less income than they would be with a 1979 income distribution,
or approximately $7,000 per family. Not receiving this income may have led many families to increase their debt burden, a significant factor in the 2007–2009 subprime mortgage crisis,
as highly leveraged homeowners suffered a much larger reduction in
their net worth during the crisis. Further, since lower income families
tend to spend relatively more of their income than higher income
families, shifting more of the income to wealthier families may slow
economic growth.
Effective corporate tax rates
U.S. corporate effective tax rates have fallen significantly since the year 2000.
Some large U.S. corporations have used a strategy called tax inversion
to change their headquarters to a non-U.S. country to reduce their tax
liability. About 46 companies have reincorporated in low-tax countries
since 1982, including 15 since 2012. Six more also planned to do so in
2015.
Stock buybacks versus wage increases
One
indication of increasing corporate power was the removal of
restrictions on their ability to buy back stock, contributing to
increased income inequality. Writing in the Harvard Business Review in September 2014, William Lazonick blamed record corporate stock buybacks
for reduced investment in the economy and a corresponding impact on
prosperity and income inequality. Between 2003 and 2012, the 449
companies in the S&P 500 used 54% of their earnings ($2.4 trillion)
to buy back their own stock. An additional 37% was paid to stockholders
as dividends. Together, these were 91% of profits. This left little for
investment in productive capabilities or higher income for employees,
shifting more income to capital rather than labor. He blamed executive
compensation arrangements, which are heavily based on stock options,
stock awards and bonuses for meeting earnings per share (EPS) targets.
EPS increases as the number of outstanding shares decreases. Legal
restrictions on buybacks were greatly eased in the early 1980s. He
advocates changing these incentives to limit buybacks.
In the 12 months to March 31, 2014, S&P 500 companies
increased their stock buyback payouts by 29% year on year, to $534.9
billion.
U.S. companies are projected to increase buybacks to $701 billion in
2015 according to Goldman Sachs, an 18% increase over 2014. For scale,
annual non-residential fixed investment (a proxy for business investment
and a major GDP component) was estimated to be about $2.1 trillion for
2014.
Industry concentration
Percentage of banking assets held by largest five U.S. banks from 1997–2011.
Brid Brennan of the Transnational Institute explained how
concentration of corporations increases their influence over government:
"It’s not just their size, their enormous wealth and assets that make
the TNCs [transnational corporations] dangerous to democracy. It’s also
their concentration, their capacity to influence, and often infiltrate,
governments and their ability to act as a genuine international social
class in order to defend their commercial interests against the common
good. It is such decision making power as well as the power to impose
deregulation over the past 30 years, resulting in changes to national
constitutions, and to national and international legislation which has
created the environment for corporate crime and impunity." Brennan
concludes that this concentration in power leads to again more
concentration of income and wealth.
An example of such industry concentration is in banking. The top 5
U.S. banks had approximately 30% of the U.S. banking assets in 1998;
this rose to 45% by 2008 and to 48% by 2010, before falling to 47% in
2011.
The Economist
also explained how an increasingly profitable corporate financial and
banking sector caused Gini coefficients to rise in the U.S. since 1980:
"Financial services' share of GDP in America doubled to 8% between 1980
and 2000; over the same period their profits rose from about 10% to 35%
of total corporate profits, before collapsing in 2007–09. Bankers are
being paid more, too. In America the compensation of workers in
financial services was similar to average compensation until 1980. Now
it is twice that average."