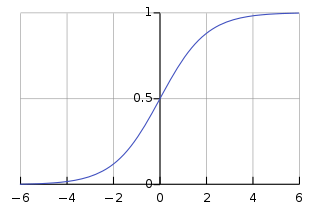
Standard logistic sigmoid function i.e.
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common "S" shape (sigmoid curve), with equation:
where
- e = the natural logarithm base (also known as Euler's number),
- x0 = the x-value of the sigmoid's midpoint,
- L = the curve's maximum value, and
- k = the logistic growth rate or steepness of the curve.
For values of x in the domain of real numbers from −∞ to +∞, the S-curve shown on the right is obtained, with the graph of f approaching L as x approaches +∞ and approaching zero as x approaches −∞.
The logistic function finds applications in a range of fields, including artificial neural networks, biology (especially ecology), biomathematics, chemistry, demography, economics, geoscience, mathematical psychology, probability, sociology, political science, linguistics, and statistics.
History
Original image of a logistic curve, contrasted with a logarithmic curve
The logistic function was introduced in a series of three papers by Pierre François Verhulst between 1838 and 1847, who devised it as a model of population growth by adjusting the exponential growth model, under the guidance of Adolphe Quetelet. Verhulst first devised the function in the mid 1830s, publishing a brief note in 1838, then presented an expanded analysis and named the function in 1844 (published 1845); the third paper adjusted the correction term in his model of Belgian population growth.
The initial stage of growth is approximately exponential
(geometric); then, as saturation begins, the growth slows to linear
(arithmetic), and at maturity, growth stops. Verhulst did not explain
the choice of the term "logistic" (French: logistique), but it is presumably in contrast to the logarithmic curve, and by analogy with arithmetic and geometric. His growth model is preceded by a discussion of arithmetic growth and geometric growth (whose curve he calls a logarithmic curve, instead of the modern term exponential curve), and thus "logistic growth" is presumably named by analogy, logistic being from Ancient Greek: λογῐστῐκός, romanized: logistikós, a traditional division of Greek mathematics. The term is unrelated to the military and management term logistics, which is instead from French: logis "lodgings", though some believe the Greek term also influenced logistics; see Logistics § Origin for details.
Mathematical properties
The standard logistic function is the logistic function with parameters (k = 1, x0 = 0, L = 1) which yields
In practice, due to the nature of the exponential function e−x, it is often sufficient to compute the standard logistic function for x
over a small range of real numbers such as a range contained in
[−6, +6] as it quickly converges very close to its saturation values of 0
and 1.
The logistic function has the symmetry property that:
Thus, is an odd function.
The logistic function is an offset and scaled hyperbolic tangent function
or
- .
This follows from
Derivative
The standard logistic function has an easily calculated derivative:
The derivative of the logistic function is an even function, that is,
Integral
Conversely, its antiderivative can be computed by the substitution , since , so (dropping the constant of integration):
In artificial neural networks, this is known as the softplus function, and (with scaling) is a smooth approximation of the ramp function, just as the logistic function (with scaling) is a smooth approximation of the Heaviside step function.
Logistic differential equation
The standard logistic function is the solution of the simple first-order non-linear ordinary differential equation
with boundary condition f(0) = 1/2. This equation is the continuous version of the logistic map.
The qualitative behavior is easily understood in terms of the phase line: the derivative is 0 when the function is 1; and the derivative is positive for f between 0 and 1, and negative for f
above 1 or less than 0 (though negative populations do not generally
accord with a physical model). This yields an unstable equilibrium at 0,
and a stable equilibrium at 1, and thus for any function value greater
than 0 and less than 1, it grows to 1.
The logistic equation is a special case of the Bernoulli differential equation and has the following solution:
Choosing the constant of integration gives the other well-known form of the definition of the logistic curve
More quantitatively, as can be seen from the analytical solution, the logistic curve shows early exponential growth
for negative argument, which slows to linear growth of slope 1/4 for an
argument near 0, then approaches 1 with an exponentially decaying gap.
The logistic function is the inverse of the natural logit function and so can be used to convert the logarithm of odds into a probability. In mathematical notation the logistic function is sometimes written as expit in the same form as logit. The conversion from the log-likelihood ratio of two alternatives also takes the form of a logistic curve.
The hyperbolic tangent relationship leads to another form for the logistic function's derivative:
which ties the logistic function into the logistic distribution.
Rotational symmetry about (0, ½)
The sum of the logistic function and its reflection about the vertical axis, f (−x) isApplications
In ecology: modeling population growth
Pierre-François Verhulst (1804–1849)
A typical application of the logistic equation is a common model of population growth (see also population dynamics), originally due to Pierre-François Verhulst
in 1838, where the rate of reproduction is proportional to both the
existing population and the amount of available resources, all else
being equal. The Verhulst equation was published after Verhulst had read
Thomas Malthus' An Essay on the Principle of Population. Verhulst derived his logistic equation to describe the self-limiting growth of a biological population. The equation was rediscovered in 1911 by A. G. McKendrick for the growth of bacteria in broth and experimentally tested using a technique for nonlinear parameter estimation. The equation is also sometimes called the Verhulst-Pearl equation following its rediscovery in 1920 by Raymond Pearl (1879–1940) and Lowell Reed (1888–1966) of the Johns Hopkins University. Another scientist, Alfred J. Lotka derived the equation again in 1925, calling it the law of population growth.
Letting P represent population size (N is often used in ecology instead) and t represent time, this model is formalized by the differential equation:
- ,
where the constant r defines the growth rate and K is the carrying capacity.
In the equation, the early, unimpeded growth rate is modeled by the first term +rP. The value of the rate r represents the proportional increase of the population P in one unit of time. Later, as the population grows, the modulus of the second term (which multiplied out is −rP2/K) becomes almost as large as the first, as some members of the population P
interfere with each other by competing for some critical resource, such
as food or living space. This antagonistic effect is called the bottleneck, and is modeled by the value of the parameter K. The competition diminishes the combined growth rate, until the value of P ceases to grow (this is called maturity of the population).
The solution to the equation (with being the initial population) is
- ,
where
- .
Which is to say that K is the limiting value of P: the
highest value that the population can reach given infinite time (or come
close to reaching in finite time). It is important to stress that the
carrying capacity is asymptotically reached independently of the initial
value P(0) > 0, and also in the case that P(0) > K.
In ecology, species are sometimes referred to as r-strategist or K-strategist depending upon the selective processes that have shaped their life history strategies.
Choosing the variable dimensions so that n measures the population in units of carrying capacity, and τ measures time in units of 1/r, gives the dimensionless
differential equation
- .
Time-varying carrying capacity
Since the environmental conditions influence the carrying capacity, as a consequence it can be time-varying: K(t) > 0, leading to the following mathematical model:
A particularly important case is that of carrying capacity that varies periodically with period T:
- .
It can be shown that in such a case, independently from the initial value P(0) > 0, P(t) will tend to a unique periodic solution P*(t), whose period is T.
A typical value of T is one year: In such case K(t) may reflect periodical variations of weather conditions.
Another interesting generalization is to consider that the carrying capacity K(t)
is a function of the population at an earlier time, capturing a delay
in the way population modifies its environment. This leads to a logistic
delay equation,
which has a very rich behavior, with bistability in some parameter
range, as well as a monotonic decay to zero, smooth exponential growth,
punctuated unlimited growth (i.e., multiple S-shapes), punctuated growth
or alternation to a stationary level, oscillatory approach to a
stationary level, sustainable oscillations, finite-time singularities as
well as finite-time death.
In statistics and machine learning
Logistic functions are used in several roles in statistics. For example, they are the cumulative distribution function of the logistic family of distributions, and they are, a bit simplified, used to model the chance a chess player has to beat his opponent in the Elo rating system. More specific examples now follow.
Logistic regression
Logistic functions are used in logistic regression to model how the probability p of an event may be affected by one or more explanatory variables: an example would be to have the model
where x is the explanatory variable and a and b are model parameters to be fitted and f is the standard logistic function.
Logistic regression and other log-linear models are also commonly used in machine learning. A generalisation of the logistic function to multiple inputs is the softmax activation function, used in multinomial logistic regression.
Another application of the logistic function is in the Rasch model, used in item response theory. In particular, the Rasch model forms a basis for maximum likelihood estimation of the locations of objects or persons on a continuum,
based on collections of categorical data, for example the abilities of
persons on a continuum based on responses that have been categorized as
correct and incorrect.
Neural networks
Logistic functions are often used in neural networks to introduce nonlinearity in the model or to clamp signals to within a specified range. A popular neural net element computes a linear combination
of its input signals, and applies a bounded logistic function to the
result; this model can be seen as a "smoothed" variant of the classical threshold neuron. A common choice for the activation or "squashing" functions, used
to clip for large magnitudes to keep the response of the neural network
bounded is
which is a logistic function.
These relationships result in simplified implementations of artificial neural networks with artificial neurons. Practitioners caution that sigmoidal functions which are antisymmetric about the origin (e.g. the hyperbolic tangent) lead to faster convergence when training networks with backpropagation.
The logistic function is itself the derivative of another proposed activation function, the softplus.
In medicine: modeling of growth of tumors
Another application of logistic curve is in medicine, where the
logistic differential equation is used to model the growth of tumors.
This application can be considered an extension of the above-mentioned
use in the framework of ecology (see also the Generalized logistic curve, allowing for more parameters). Denoting with X(t) the size of the tumor at time t, its dynamics are governed by:
which is of the type:
where F(X) is the proliferation rate of the tumor.
If a chemotherapy is started with a log-kill effect, the equation may be revised to be
where c(t) is the therapy-induced death rate. In the idealized case of very long therapy, c(t) can be modeled as a periodic function (of period T) or (in case of continuous infusion therapy) as a constant function, and one has that
i.e. if the average therapy-induced death rate is greater than the
baseline proliferation rate then there is the eradication of the
disease. Of course, this is an oversimplified model of both the growth
and the therapy (e.g. it does not take into account the phenomenon of
clonal resistance).
In chemistry: reaction models
The concentration of reactants and products in autocatalytic reactions follow the logistic function.
The degradation of platinum group metal-free (PGM-free) oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst in fuel cell cathodes follows the logistic decay function, suggesting an autocatalytic degradation mechanism.
In physics: Fermi distribution
The
logistic function determines the statistical distribution of fermions
over the energy states of a system in thermal equilibrium. In
particular, it is the distribution of the probabilities that each
possible energy level is occupied by a fermion, according to Fermi–Dirac statistics.
In linguistics: language change
In linguistics, the logistic function can be used to model language change:
an innovation that is at first marginal begins to spread more quickly
with time, and then more slowly as it becomes more universally adopted.
In agriculture: modeling crop response
The
logistic S-curve can be used for modeling the crop response to changes
in growth factors. There are two types of response functions: positive and negative growth curves. For example, the crop yield may increase with increasing value of the growth factor up to a certain level (positive function), or it may decrease with increasing growth factor values (negative function owing to a negative growth factor), which situation requires an inverted S-curve.
S-curve model for yield versus depth of watertable.
Inverted S-curve model for yield versus soil salinity.
|
In economics and sociology: diffusion of innovations
The logistic function can be used to illustrate the progress of the diffusion of an innovation through its life cycle.
In The Laws of Imitation (1890), Gabriel Tarde
describes the rise and spread of new ideas through imitative chains. In
particular, Tarde identifies three main stages through which
innovations spread: the first one corresponds to the difficult
beginnings, during which the idea has to struggle within a hostile
environment full of opposing habits and beliefs; the second one
corresponds to the properly exponential take-off of the idea, with ; finally, the third stage is logarithmic, with ,
and corresponds to the time when the impulse of the idea gradually
slows down while, simultaneously new opponent ideas appear. The ensuing
situation halts or stabilizes the progress of the innovation, which
approaches an asymptote.
In the history of economy, when new products are introduced there
is an intense amount of research and development which leads to
dramatic improvements in quality and reductions in cost. This leads to a
period of rapid industry growth. Some of the more famous examples are:
railroads, incandescent light bulbs, electrification, cars
and air travel. Eventually, dramatic improvement and cost reduction
opportunities are exhausted, the product or process are in widespread
use with few remaining potential new customers, and markets become
saturated.
Logistic analysis was used in papers by several researchers at the International Institute of Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA).
These papers deal with the diffusion of various innovations,
infrastructures and energy source substitutions and the role of work in
the economy as well as with the long economic cycle. Long economic
cycles were investigated by Robert Ayres (1989). Cesare Marchetti published on long economic cycles and on diffusion of innovations.
Arnulf Grübler's book (1990) gives a detailed account of the diffusion
of infrastructures including canals, railroads, highways and airlines,
showing that their diffusion followed logistic shaped curves.
Carlota Perez used a logistic curve to illustrate the long (Kondratiev) business cycle with the following labels: beginning of a technological era as irruption, the ascent as frenzy, the rapid build out as synergy and the completion as maturity.







![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\tanh(x)&={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{x}\cdot \left(1-e^{-2x}\right)}{e^{x}\cdot \left(1+e^{-2x}\right)}}\\[6pt]&=f(2x)-{\frac {e^{-2x}}{1+e^{-2x}}}=f(2x)-{\frac {e^{-2x}+1-1}{1+e^{-2x}}}=2f(2x)-1.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/164e1e9f671027b78d338827517d027d678864b3)




























