Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth values of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely false.[1] By contrast, in Boolean logic, the truth values of variables may only be the integer values 0 or 1.
The term fuzzy logic was introduced with the 1965 proposal of fuzzy set theory by Lotfi Zadeh.[2][3] Fuzzy logic had however been studied since the 1920s, as infinite-valued logic—notably by Łukasiewicz and Tarski.[4]
Fuzzy logic has been applied to many fields, from control theory to artificial intelligence.
Overview
Classical logic only permits conclusions which are either true or false. However, there are also propositions with variable answers, such as one might find when asking a group of people to identify a color. In such instances, the truth appears as the result of reasoning from inexact or partial knowledge in which the sampled answers are mapped on a spectrum.[citation needed]Both degrees of truth and probabilities range between 0 and 1 and hence may seem similar at first, but fuzzy logic uses degrees of truth as a mathematical model of vagueness, while probability is a mathematical model of ignorance.[citation needed]
Applying truth values
A basic application might characterize various sub-ranges of a continuous variable. For instance, a temperature measurement for anti-lock brakes might have several separate membership functions defining particular temperature ranges needed to control the brakes properly. Each function maps the same temperature value to a truth value in the 0 to 1 range. These truth values can then be used to determine how the brakes should be controlled.[citation needed]Linguistic variables
While variables in mathematics usually take numerical values, in fuzzy logic applications, non-numeric values are often used to facilitate the expression of rules and facts.[5]A linguistic variable such as age may accept values such as young and its antonym old. Because natural languages do not always contain enough value terms to express a fuzzy value scale, it is common practice to modify linguistic values with adjectives or adverbs. For example, we can use the hedges rather and somewhat to construct the additional values rather old or somewhat young.
Fuzzification operations can map mathematical input values into fuzzy membership functions. And the opposite de-fuzzifying operations can be used to map a fuzzy output membership functions into a "crisp" output value that can be then used for decision or control purposes.
Process
- Fuzzify all input values into fuzzy membership functions.
- Execute all applicable rules in the rulebase to compute the fuzzy output functions.
- De-fuzzify the fuzzy output functions to get "crisp" output values.
Fuzzification
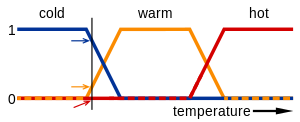
Fuzzy logic temperature
In this image, the meanings of the expressions cold, warm, and hot are represented by functions mapping a temperature scale. A point on that scale has three "truth values"—one for each of the three functions. The vertical line in the image represents a particular temperature that the three arrows (truth values) gauge. Since the red arrow points to zero, this temperature may be interpreted as "not hot". The orange arrow (pointing at 0.2) may describe it as "slightly warm" and the blue arrow (pointing at 0.8) "fairly cold".
Fuzzy sets are often defined as triangle or trapezoid-shaped curves, as each value will have a slope where the value is increasing, a peak where the value is equal to 1 (which can have a length of 0 or greater) and a slope where the value is decreasing.[citation needed] They can also be defined using a sigmoid function.[6] One common case is the standard logistic function defined as

Fuzzy logic operators
Fuzzy logic works with membership values in a way that mimics Boolean logic.[citation needed]To this end, replacements for basic operators AND, OR, NOT must be available. There are several ways to this. A common replacement is called the Zadeh operators:
| Boolean | Fuzzy |
|---|---|
| AND(x,y) | MIN(x,y) |
| OR(x,y) | MAX(x,y) |
| NOT(x) | 1 – x |
For TRUE/1 and FALSE/0, the fuzzy expressions produce the same result as the Boolean expressions.
There are also other operators, more linguistic in nature, called hedges that can be applied. These are generally adverbs such as very, or somewhat, which modify the meaning of a set using a mathematical formula.
However, an arbitrary choice table does not always define a fuzzy logic function. In the paper,[7] a criterion has been formulated to recognize whether a given choice table defines a fuzzy logic function and a simple algorithm of fuzzy logic function synthesis has been proposed based on introduced concepts of constituents of minimum and maximum. A fuzzy logic function represents a disjunction of constituents of minimum, where a constituent of minimum is a conjunction of variables of the current area greater than or equal to the function value in this area (to the right of the function value in the inequality, including the function value).
Another set of AND/OR operators is based on multiplication
x AND y = x*y
x OR y = 1-(1-x)*(1-y) = x+y-x*y
x OR y = NOT( AND( NOT(x), NOT(y) ) )
x OR y = NOT( AND(1-x, 1-y) )
x OR y = NOT( (1-x)*(1-y) )
x OR y = 1-(1-x)*(1-y)
IF-THEN rules
IF-THEN rules map input or computed truth values to desired output truth values. Example:IF temperature IS very cold THEN fan_speed is stopped
IF temperature IS cold THEN fan_speed is slow
IF temperature IS warm THEN fan_speed is moderate
IF temperature IS hot THEN fan_speed is high
Given a certain temperature, the fuzzy variable hot has a certain truth value, which is copied to the high variable.
Should an output variable occur in several THEN parts, then the values from the respective IF parts are combined using the OR operator.
Defuzzification
The goal is to get a continuous variable from fuzzy truth values.[citation needed]This would be easy if the output truth values were exactly those obtained from fuzzification of a given number. Since, however, all output truth values are computed independently, in most cases they do not represent such a set of numbers.[citation needed] One has then to decide for a number that matches best the "intention" encoded in the truth value. For example, for several truth values of fan_speed, an actual speed must be found that best fits the computed truth values of the variables 'slow', 'medium' and so on.[citation needed]
There is no single algorithm for this purpose.
A common algorithm is
- For each truth value, cut the membership function at this value
- Combine the resulting curves using the OR operator
- Find the center-of-weight of the area under the curve
- The x position of this center is then the final output.
Forming a consensus of inputs and fuzzy rules
Since the fuzzy system output is a consensus of all of the inputs and all of the rules, fuzzy logic systems can be well behaved when input values are not available or are not trustworthy. Weightings can be optionally added to each rule in the rulebase and weightings can be used to regulate the degree to which a rule affects the output values. These rule weightings can be based upon the priority, reliability or consistency of each rule. These rule weightings may be static or can be changed dynamically, even based upon the output from other rules.Early applications
Many of the early successful applications of fuzzy logic were implemented in Japan. The first notable application was on the subway train in Sendai, in which fuzzy logic was able to improve the economy, comfort, and precision of the ride.[8] It has also been used in recognition of hand written symbols in Sony pocket computers, flight aid for helicopters, controlling of subway systems in order to improve driving comfort, precision of halting, and power economy, improved fuel consumption for automobiles, single-button control for washing machines, automatic motor control for vacuum cleaners with recognition of surface condition and degree of soiling, and prediction systems for early recognition of earthquakes through the Institute of Seismology Bureau of Meteorology, Japan.[9]Logical analysis
In mathematical logic, there are several formal systems of "fuzzy logic", most of which are in the family of t-norm fuzzy logics.Propositional fuzzy logics
The most important propositional fuzzy logics are:- Monoidal t-norm-based propositional fuzzy logic MTL is an axiomatization of logic where conjunction is defined by a left continuous t-norm and implication is defined as the residuum of the t-norm. Its models correspond to MTL-algebras that are pre-linear commutative bounded integral residuated lattices.
- Basic propositional fuzzy logic BL is an extension of MTL logic where conjunction is defined by a continuous t-norm, and implication is also defined as the residuum of the t-norm. Its models correspond to BL-algebras.
- Łukasiewicz fuzzy logic is the extension of basic fuzzy logic BL where standard conjunction is the Łukasiewicz t-norm. It has the axioms of basic fuzzy logic plus an axiom of double negation, and its models correspond to MV-algebras.
- Gödel fuzzy logic is the extension of basic fuzzy logic BL where conjunction is Gödel t-norm. It has the axioms of BL plus an axiom of idempotence of conjunction, and its models are called G-algebras.
- Product fuzzy logic is the extension of basic fuzzy logic BL where conjunction is product t-norm. It has the axioms of BL plus another axiom for cancellativity of conjunction, and its models are called product algebras.
- Fuzzy logic with evaluated syntax (sometimes also called Pavelka's logic), denoted by EVŁ, is a further generalization of mathematical fuzzy logic. While the above kinds of fuzzy logic have traditional syntax and many-valued semantics, in EVŁ is evaluated also syntax. This means that each formula has an evaluation. Axiomatization of EVŁ stems from Łukasziewicz fuzzy logic. A generalization of classical Gödel completeness theorem is provable in EVŁ.
Predicate fuzzy logics
These extend the above-mentioned fuzzy logics by adding universal and existential quantifiers in a manner similar to the way that predicate logic is created from propositional logic. The semantics of the universal (resp. existential) quantifier in t-norm fuzzy logics is the infimum (resp. supremum) of the truth degrees of the instances of the quantified subformula.Decidability issues for fuzzy logic
The notions of a "decidable subset" and "recursively enumerable subset" are basic ones for classical mathematics and classical logic. Thus the question of a suitable extension of them to fuzzy set theory is a crucial one. A first proposal in such a direction was made by E.S. Santos by the notions of fuzzy Turing machine, Markov normal fuzzy algorithm and fuzzy program (see Santos 1970). Successively, L. Biacino and G. Gerla argued that the proposed definitions are rather questionable. For example, in [10] one shows that the fuzzy Turing machines are not adequate for fuzzy language theory since there are natural fuzzy languages intuitively computable that cannot be recognized by a fuzzy Turing Machine. Then, they proposed the following definitions. Denote by Ü the set of rational numbers in [0,1]. Then a fuzzy subset s : S [0,1] of a set S is recursively enumerable if a recursive map h : S×N
[0,1] of a set S is recursively enumerable if a recursive map h : S×N  Ü exists such that, for every x in S, the function h(x,n) is increasing with respect to n and s(x) = lim h(x,n). We say that s is decidable if both s and its complement –s
are recursively enumerable. An extension of such a theory to the
general case of the L-subsets is possible (see Gerla 2006). The proposed
definitions are well related with fuzzy logic. Indeed, the following
theorem holds true (provided that the deduction apparatus of the
considered fuzzy logic satisfies some obvious effectiveness property).
Ü exists such that, for every x in S, the function h(x,n) is increasing with respect to n and s(x) = lim h(x,n). We say that s is decidable if both s and its complement –s
are recursively enumerable. An extension of such a theory to the
general case of the L-subsets is possible (see Gerla 2006). The proposed
definitions are well related with fuzzy logic. Indeed, the following
theorem holds true (provided that the deduction apparatus of the
considered fuzzy logic satisfies some obvious effectiveness property).Any "axiomatizable" fuzzy theory is recursively enumerable. In particular, the fuzzy set of logically true formulas is recursively enumerable in spite of the fact that the crisp set of valid formulas is not recursively enumerable, in general. Moreover, any axiomatizable and complete theory is decidable.
It is an open question to give supports for a "Church thesis" for fuzzy mathematics, the proposed notion of recursive enumerability for fuzzy subsets is the adequate one. In order to solve this, an extension of the notions of fuzzy grammar and fuzzy Turing machine are necessary. Another open question is to start from this notion to find an extension of Gödel's theorems to fuzzy logic.
Fuzzy databases
Once fuzzy relations are defined, it is possible to develop fuzzy relational databases. The first fuzzy relational database, FRDB, appeared in Maria Zemankova's dissertation (1983). Later, some other models arose like the Buckles-Petry model, the Prade-Testemale Model, the Umano-Fukami model or the GEFRED model by J.M. Medina, M.A. Vila et al.Fuzzy querying languages have been defined, such as the SQLf by P. Bosc et al. and the FSQL by J. Galindo et al. These languages define some structures in order to include fuzzy aspects in the SQL statements, like fuzzy conditions, fuzzy comparators, fuzzy constants, fuzzy constraints, fuzzy thresholds, linguistic labels etc.
Comparison to probability
Fuzzy logic and probability address different forms of uncertainty. While both fuzzy logic and probability theory can represent degrees of certain kinds of subjective belief, fuzzy set theory uses the concept of fuzzy set membership, i.e., how much an observation is within a vaguely defined set, and probability theory uses the concept of subjective probability, i.e., likelihood of some event or condition. The concept of fuzzy sets was developed in the mid-twentieth century at Berkeley [11] as a response to the lacking of probability theory for jointly modelling uncertainty and vagueness.[12]Bart Kosko claims in Fuzziness vs. Probability that probability theory is a subtheory of fuzzy logic, as questions of degrees of belief in mutually-exclusive set membership in probability theory can be represented as certain cases of non-mutually-exclusive graded membership in fuzzy theory. In that context, he also derives Bayes' theorem from the concept of fuzzy subsethood. Lotfi A. Zadeh argues that fuzzy logic is different in character from probability, and is not a replacement for it. He fuzzified probability to fuzzy probability and also generalized it to possibility theory.
More generally, fuzzy logic is one of many different extensions to classical logic intended to deal with issues of uncertainty outside of the scope of classical logic, the inapplicability of probability theory in many domains, and the paradoxes of Dempster-Shafer theory.
Relation to ecorithms
Computational theorist Leslie Valiant uses the term ecorithms to describe how many less exact systems and techniques like fuzzy logic (and "less robust" logic) can be applied to learning algorithms. Valiant essentially redefines machine learning as evolutionary. In general use, ecorithms are algorithms that learn from their more complex environments (hence eco-) to generalize, approximate and simplify solution logic. Like fuzzy logic, they are methods used to overcome continuous variables or systems too complex to completely enumerate or understand discretely or exactly. [14] Ecorithms and fuzzy logic also have the common property of dealing with possibilities more than probabilities, although feedback and feed forward, basically stochastic weights, are a feature of both when dealing with, for example, dynamical systems.Compensatory fuzzy logic
Compensatory fuzzy logic (CFL) is a branch of fuzzy logic with modified rules for conjunction and disjunction. When the truth value of one component of a conjunction or disjunction is increased or decreased, the other component is decreased or increased to compensate. This increase or decrease in truth value may be offset by the increase or decrease in another component. An offset may be blocked when certain thresholds are met. Proponents claim that CFL allows for better computational semantic behaviors and mimic natural language.Compensatory Fuzzy Logic consists of four continuous operators: conjunction (c); disjunction (d); fuzzy strict order (or); and negation (n). The conjunction is the geometric mean and its dual as conjunctive and disjunctive operators.[17]
IEEE STANDARD 1855–2016 – IEEE Standard for Fuzzy Markup Language
The IEEE 1855, the IEEE STANDARD 1855–2016, is about a specification language named Fuzzy Markup Language (FML)[18] developed by the IEEE Standards Association. FML allows modelling a fuzzy logic system in a human-readable and hardware independent way. FML is based on eXtensible Markup Language (XML). The designers of fuzzy systems with FML have a unified and high-level methodology for describing interoperable fuzzy systems. IEEE STANDARD 1855–2016 uses the W3C XML Schema definition language to define the syntax and semantics of the FML programs.Prior to the introduction of FML, fuzzy logic practitioners could exchange information about their fuzzy algorithms by adding to their software functions the ability to read, correctly parse, and store the results of their work in a form compatible with the Fuzzy Control Language (FCL) described and specified by Part 7 of IEC 61131.[19][20]