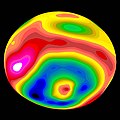
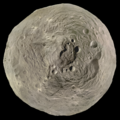
Color image of Vesta taken by Dawn
| |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers |
| Discovery date | 29 March 1807 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | (4) Vesta |
| Pronunciation | /ˈvɛstə/ |
Named after
| Vesta |
| Main belt (Vesta family) | |
| Adjectives | Vestan, Vestian |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 2014-Dec-09 (JD 2457000.5) | |
| Aphelion | 2.57138 AU |
| Perihelion | 2.15221 AU |
| 2.36179 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.08874 |
| 3.63 yr (1325.75 d) | |
Average orbital speed
| 19.34 km/s |
| 20.86384° | |
| Inclination | 7.14043° to ecliptic 5.56° to invariable plane |
| 103.85136° | |
| 151.19853° | |
| Satellites | None |
| Proper orbital elements | |
Proper semi-major axis
| 2.36151 AU |
Proper eccentricity
| 0.098758 |
Proper inclination
| 6.39234° |
Proper mean motion
| 99.1888 deg / yr |
Proper orbital period
| 3.62944 yr (1325.654 d) |
Precession of perihelion
| 36.8729 (2343 years) arcsec / yr |
Precession of the ascending node
| −39.5979 (2182 years) arcsec / yr |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 572.6 km × 557.2 km × 446.4 km |
Mean diameter
| 525.4±0.2 km |
| Flattening | 0.2204 |
| (8.66±0.2)×105 km2 | |
| Volume | (7.46±0.3)×107 km3 |
| Mass | (2.59076±0.00001)×1020 kg |
Mean density
| 3.456±0.035 g/cm3 |
Equatorial surface gravity
| 0.25 m/s2 0.025 g |
Equatorial escape velocity
| 0.36 km/s |
| 0.2226 d (5.342 h) | |
Equatorial rotation velocity
| 93.1 m/s |
North pole right ascension
| 20h 32m |
North pole declination
| 48° |
| 0.423 | |
| Temperature | min: 85 K (−188 °C) max: 270 K (−3 °C) |
| V | |
| 5.1 to 8.48 | |
| 3.20 | |
| 0.70″ to 0.22″ | |
Vesta (minor-planet designation: 4 Vesta) is one of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, with a mean diameter of 525 kilometres (326 mi). It was discovered by the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers on 29 March 1807 and is named after Vesta, the virgin goddess of home and hearth from Roman mythology.
Vesta is the second-most-massive and second-largest body in the asteroid belt, after the dwarf planet Ceres, and it contributes an estimated 9% of the mass of the asteroid belt. It is slightly larger than Pallas, though significantly more massive. Vesta is the only known remaining rocky protoplanet (with a differentiated interior) of the kind that formed the terrestrial planets. Numerous fragments of Vesta were ejected by collisions one and two billion years ago that left two enormous craters occupying much of Vesta's southern hemisphere. Debris from these events has fallen to Earth as howardite–eucrite–diogenite (HED) meteorites, which have been a rich source of information about Vesta.
Vesta is the brightest asteroid visible from Earth. Its maximum distance from the Sun is slightly greater than the minimum distance of Ceres from the Sun, though its orbit lies entirely within that of Ceres.
NASA's Dawn spacecraft entered orbit around Vesta on 16 July 2011 for a one-year exploration and left orbit on 5 September 2012 en route to its final destination, Ceres. Researchers continue to examine data collected by Dawn for additional insights into the formation and history of Vesta.
History
Discovery
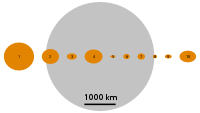
Size comparison: the first 10 asteroid-belt objects profiled against the Moon. Vesta is fourth from the left.
Heinrich Olbers discovered Pallas in 1802, the year after the discovery of Ceres. He proposed that the two objects were the remnants of a destroyed planet. He sent a letter with his proposal to the English astronomer William Herschel,
suggesting that a search near the locations where the orbits of Ceres
and Pallas intersected might reveal more fragments. These orbital
intersections were located in the constellations of Cetus and Virgo.
Olbers commenced his search in 1802, and on 29 March 1807 he discovered
Vesta in the constellation Virgo—a coincidence, because Ceres, Pallas,
and Vesta are not fragments of a larger body. Because the asteroid Juno had been discovered in 1804, this made Vesta the fourth object to be identified in the region that is now known as the asteroid belt. The discovery was announced in a letter addressed to German astronomer Johann H. Schröter dated 31 March.
Because Olbers already had credit for discovering a planet (Pallas; at
the time, the asteroids were considered to be planets), he gave the
honor of naming his new discovery to German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss,
whose orbital calculations had enabled astronomers to confirm the
existence of Ceres, the first asteroid, and who had computed the orbit
of the new planet in the remarkably short time of 10 hours. Gauss decided on the Roman virgin goddess of home and hearth, Vesta.
Name
Vesta was the fourth asteroid to be discovered, hence the number 4 in its formal designation. The name Vesta, or national variants thereof, is in international use with two exceptions: Greece and China. In Greek, the name adopted was the Hellenic equivalent of Vesta, Hestia (4 Εστία); in English, that name is used for 46 Hestia (Greeks use the name "Hestia" for both, with the minor-planet numbers used for disambiguation). In Chinese, Vesta is called the 'hearth-god(dess) star', 灶神星 zàoshénxīng,
naming the asteroid for Vesta's role rather than literally
transliterating her name into Chinese, as is done with other bodies
discovered in modern times, including Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto.
Upon its discovery, Vesta was, like Ceres, Pallas, and Juno before it, classified as a planet and given a planetary symbol. The symbol representing the altar of Vesta with its sacred fire and was designed by Gauss. In Gauss's conception, this was drawn  ; in its modern form, it is
; in its modern form, it is  .
.
After the discovery of Vesta, no further objects were discovered
for 38 years, and the Solar System was thought to have eleven planets.
However, in 1845, new asteroids started being discovered at a rapid
pace, and by 1851 there were fifteen, each with its own symbol, in
addition to the eight major planets (Neptune
had been discovered in 1846). It soon became clear that it would be
impractical to continue inventing new planetary symbols indefinitely,
and some of the existing ones proved difficult to draw quickly. That
year, the problem was addressed by Benjamin Apthorp Gould,
who suggested numbering asteroids in their order of discovery, and
placing this number in a disk (circle) as the generic symbol of an
asteroid. Thus, the fourth asteroid, Vesta, acquired the generic symbol
④. This was soon coupled with the name into an official number–name
designation, ④ Vesta, as the number of minor planets increased. By 1858, the circle had been simplified to parentheses, (4) Vesta, which were easier to typeset. Other punctuation, such as 4) Vesta and 4, Vesta, was also used, but had more or less completely died out by 1949. Today, either Vesta, or, more commonly, 4 Vesta, is used.
Early measurements
SPHERE image is shown on the left, with a synthetic view derived from space-based data shown on the right for comparison.
Photometric observations of Vesta were made at the Harvard College Observatory in 1880–1882 and at the Observatoire de Toulouse
in 1909. These and other observations allowed the rotation rate of
Vesta to be determined by the 1950s. However, the early estimates of the
rotation rate came into question because the light curve included variations in both shape and albedo.
Early estimates of the diameter of Vesta ranged from 383 (in 1825) to 444 km. E.C. Pickering produced an estimated diameter of 513±17 km in 1879, which is close to the modern value for the mean diameter, but the subsequent estimates ranged from a low of 390 km up to a high of 602 km during the next century. The measured estimates were based on photometry. In 1989, speckle interferometry was used to measure a dimension that varied between 498 and 548 km during the rotational period. In 1991, an occultation of the star SAO 93228
by Vesta was observed from multiple locations in the eastern United
States and Canada. Based on observations from 14 different sites, the
best fit to the data was an elliptical profile with dimensions of about 550 km × 462 km. Dawn confirmed this measurement.
Vesta became the first asteroid to have its mass determined. Every 18 years, the asteroid 197 Arete approaches within 0.04 AU of Vesta. In 1966, based upon observations of Vesta's gravitational perturbations of Arete, Hans G. Hertz estimated the mass of Vesta as (1.20±0.08)×10−10 solar masses. More refined estimates followed, and in 2001 the perturbations of 17 Thetis were used to estimate the mass of Vesta as (1.31±0.02)×10−10 solar masses.
Orbit
Vesta orbits the Sun between Mars and Jupiter, within the asteroid belt, with a period of 3.6 Earth years, specifically in the inner asteroid belt, interior to the Kirkwood gap at 2.50 AU. Its orbit is moderately inclined (i = 7.1°, compared to 7° for Mercury and 17° for Pluto) and moderately eccentric (e = 0.09, about the same as for Mars).
True orbital resonances
between asteroids are considered unlikely; due to their small masses
relative to their large separations, such relationships should be very
rare.
Nevertheless, Vesta is able to capture other asteroids into temporary
1:1 resonant orbital relationships (for periods up to 2 million years or
more); about forty such objects have been identified. Decameter-sized objects detected in the vicinity of Vesta by Dawn may be such quasi-satellites rather than proper satellites.
Rotation
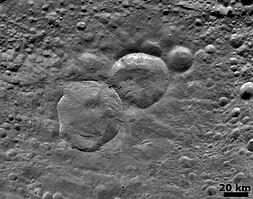
Olbers Regio (dark area) defines the prime meridian in the IAU coordinate system. It is shown here in a Hubble shot of Vesta, because it is not visible in the more detailed Dawn images.
Claudia crater (indicated by the arrow at the bottom of the closeup image at right) defines the prime meridian in the Dawn/NASA coordinate system.
Vesta's rotation is relatively fast for an asteroid (5.342 h) and prograde, with the north pole pointing in the direction of right ascension 20 h 32 min, declination +48° (in the constellation Cygnus) with an uncertainty of about 10°. This gives an axial tilt of 29°.
Coordinate systems
There are two longitudinal coordinate systems in use for Vesta, with prime meridians separated by 150°. The IAU established a coordinate system in 1997 based on Hubble photos, with the prime meridian running through the center of Olbers Regio, a dark feature 200 km across. When Dawn
arrived at Vesta, mission scientists found that the location of the
pole assumed by the IAU was off by 10°, so that the IAU coordinate
system drifted across the surface of Vesta at 0.06° per year, and also
that Olbers Regio was not discernible from up close, and so was not
adequate to define the prime meridian with the precision they needed.
They corrected the pole, but also established a new prime meridian 4°
from the center of Claudia, a sharply defined crater 700 meters across, which they say results in a more logical set of mapping quadrangles.
All NASA publications, including images and maps of Vesta, use the
Claudian meridian, which is unacceptable to the IAU. The IAU Working
Group on Cartographic Coordinates and Rotational Elements recommended a
coordinate system, correcting the pole but rotating the Claudian
longitude by 150° to coincide with Olbers Regio. It was accepted by the IAU, though it disrupts the maps prepared by the Dawn team, which had been positioned so they would not bisect any major surface features.
Physical characteristics
Composite greyscale image of Vesta taken by Dawn
The IAU 2006 draft proposal on the definition of a planet listed Vesta as a candidate. Vesta is shown fourth from the left along the bottom row.
Vesta is the second-most-massive body in the asteroid belt, though only 28% as massive as Ceres. Vesta's density is lower than those of the four terrestrial planets, but higher than that of most asteroids and all of the moons in the Solar System except Io. Vesta's surface area is about the same as that of Pakistan (about 800,000 square kilometers). It has a differentiated interior. Vesta is only slightly larger (525.4±0.2 km) than 2 Pallas (512±3 km) in volume, but is about 25% more massive.
Vesta's shape is close to a gravitationally relaxed oblate spheroid, but the large concavity and protrusion at the southern pole combined with a mass less than 5×1020 kg precluded Vesta from automatically being considered a dwarf planet under International Astronomical Union (IAU) Resolution XXVI 5. A 2012 analysis of Vesta's shape and gravity field using data gathered by the Dawn spacecraft has shown that Vesta is currently not in hydrostatic equilibrium.
Temperatures on the surface have been estimated to lie between about −20 °C with the Sun
overhead, dropping to about −190 °C at the winter pole. Typical daytime
and nighttime temperatures are −60 °C and −130 °C respectively. This
estimate is for 6 May 1996, very close to perihelion, although details vary somewhat with the seasons.
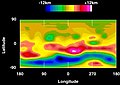
Geologic map of Vesta
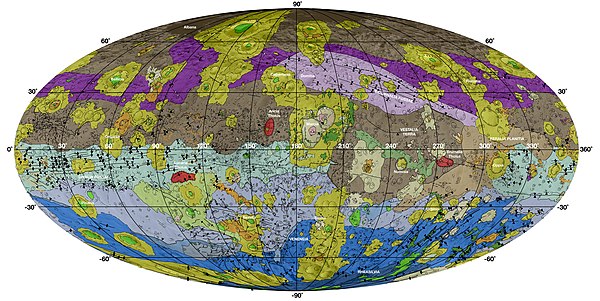
The most ancient and heavily cratered regions are brown; areas modified by the Veneneia and Rheasilvia impacts are purple (the Saturnalia Fossae Formation, in the north) and light cyan (the Divalia Fossae Formation, equatorial),
respectively; the Rheasilvia impact basin interior (in the south) is
dark blue, and neighboring areas of Rheasilvia ejecta (including an area
within Veneneia) are light purple-blue; areas modified by more recent impacts or mass wasting are yellow/orange or green, respectively.
|
Surface features
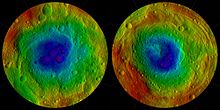
Northern
(left) and southern (right) hemispheres. The 'Snowman' craters are at
the top of the left image; Rheasilvia and Veneneia (green and blue)
dominate the right. Parallel troughs are seen in both. Colors of the two
hemispheres are not to scale, and the equatorial region is not shown.
South pole of Vesta, showing the extent of Rheasilvia crater.
Prior to the arrival of the Dawn spacecraft, some Vestan surface features had already been resolved using the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based telescopes (e.g. the Keck Observatory). The arrival of Dawn in July 2011 revealed the complex surface of Vesta in detail.
Rheasilvia and Veneneia craters
The most prominent of these surface features are two enormous
craters, the 500-kilometre (311 mi)-wide Rheasilvia crater, centered
near the south pole, and the 400 kilometres (249 mi) wide Veneneia
crater. The Rheasilvia crater is younger and overlies the Veneneia
crater. The Dawn science team named the younger, more prominent crater Rheasilvia, after the mother of Romulus and Remus and a mythical vestal virgin.
Its width is 95% of the mean diameter of Vesta. The crater is about 19
kilometres (12 mi) deep. A central peak rises 23 km above the lowest
measured part of the crater floor and the highest measured part of the
crater rim is 31 km above the crater floor low point. It is estimated
that the impact responsible excavated about 1% of the volume of Vesta,
and it is likely that the Vesta family and V-type asteroids
are the products of this collision. If this is the case, then the fact
that 10-km fragments have survived bombardment until the present
indicates that the crater is at most only about 1 billion years old. It would also be the site of origin of the HED meteorites.
All the known V-type asteroids taken together account for only about 6%
of the ejected volume, with the rest presumably either in small
fragments, ejected by approaching the 3:1 Kirkwood gap, or perturbed away by the Yarkovsky effect or radiation pressure. Spectroscopic
analyses of the Hubble images have shown that this crater has
penetrated deep through several distinct layers of the crust, and
possibly into the mantle, as indicated by spectral signatures of olivine.
The large peak at the center of Rheasilvia is 20 to 25 kilometres (12–16 mi) high and 180 kilometres (110 mi) wide, and is possibly a result of a planetary-scale impact.
Other craters
Aelia Crater
Feralia
Planitia, an old, degraded crater near Vesta's equator (green and
blue). It is 270 km across and predates Rheasilvia (green at bottom).
Several old, degraded craters rival Rheasilvia and Veneneia in size, though none are quite so large. They include Feralia Planitia, shown at right, which is 270 km across. More-recent, sharper craters range up to 158 kilometres (98 mi) Varronilla and 196 kilometres (122 mi) Postumia.
"Snowman craters"
The
"snowman craters" is an informal name given to a group of three
adjacent craters in Vesta's northern hemisphere. Their official names
from largest to smallest (west to east) are Marcia, Calpurnia, and
Minucia. Marcia is the youngest and cross-cuts Calpurnia. Minucia is the
oldest.
Troughs
The majority of the equatorial region of Vesta is sculpted by a series of concentric troughs. The largest is named Divalia Fossa (10–20 km wide, 465 km long). Despite the fact that Vesta is a one-seventh the size of the Moon, Divalia Fossa dwarfs the Grand Canyon. A second series, inclined to the equator, is found further north. The largest of the northern troughs is named Saturnalia Fossa (≈ 40 km wide, > 370 km long). These troughs are thought to be large-scale graben resulting from the impacts that created Rheasilvia and Veneneia craters, respectively. They are some of the longest chasms in the Solar System, nearly as long as Ithaca Chasma on Tethys.
The troughs may be graben that formed after another asteroid collided
with Vesta, a process that can happen only in a body that, like Vesta,
is differentiated. Vesta's differentiation is one of the reasons why scientists consider it a protoplanet.
Surface composition
Compositional
information from the visible and infrared spectrometer (VIR), gamma-ray
and neutron detector (GRaND), and framing camera (FC), all indicate
that the majority of the surface composition of Vesta is consistent with
the composition of the howardite, eucrite, and diogenite meteorites.
The Rheasilvia region is richest in diogenite, consistent with the
Rheasilvia-forming impact excavating material from deeper within Vesta.
The presence of olivine within the Rheasilvia region would also be
consistent with excavation of mantle material. However, olivine has only
been detected in localized regions of the northern hemisphere, not
within Rheasilvia. The origin of this olivine is currently uncertain.
Features associated with volatiles
Pitted terrain has been observed in four craters on Vesta: Marcia, Cornelia, Numisia and Licinia.
The formation of the pitted terrain is proposed to be degassing of
impact-heated volatile-bearing material. Along with the pitted terrain,
curvilinear gullies are found in Marcia and Cornelia craters. The
curvilinear gullies end in lobate deposits, which are sometimes covered
by pitted terrain, and are proposed to form by the transient flow of
liquid water after buried deposits of ice were melted by the heat of the
impacts. Hydrated materials have also been detected, many of which are associated with areas of dark material.
Consequently, dark material is thought to be largely composed of
carbonaceous chondrite, which was deposited on the surface by impacts.
Carbonaceous chondrites are comparatively rich in mineralogically bound
OH.
Geology
Cut-away schematic of Vestan core, mantle, and crust
Eucrite meteorite
There is a large collection of potential samples from Vesta accessible to scientists, in the form of over 1200 HED meteorites (Vestan achondrites), giving insight into Vesta's geologic history and structure. NASA Infrared Telescope Facility (NASA IRTF) studies of asteroid (237442) 1999 TA10 suggest that it originated from deeper within Vesta than the HED meteorites
Vesta is thought to consist of a metallic iron–nickel core 214–226 km in diameter, an overlying rocky olivine mantle, with a surface crust. From the first appearance of calcium–aluminium-rich inclusions (the first solid matter in the Solar System, forming about 4.567 billion years ago), a likely time line is as follows:
| 2–3 million years | Accretion completed |
|---|---|
| 4–5 million years | Complete or almost complete melting due to radioactive decay of 26Al, leading to separation of the metal core |
| 6–7 million years | Progressive crystallization of a convecting molten mantle. Convection stopped when about 80% of the material had crystallized |
| Extrusion of the remaining molten material to form the crust, either as basaltic lavas in progressive eruptions, or possibly forming a short-lived magma ocean. | |
| The deeper layers of the crust crystallize to form plutonic rocks, whereas older basalts are metamorphosed due to the pressure of newer surface layers. | |
| Slow cooling of the interior | |
Vesta is the only known intact asteroid that has been resurfaced in
this manner. Because of this, some scientists refer to Vesta as a
protoplanet. However, the presence of iron meteorites and achondritic meteorite classes without identified parent bodies indicates that there once were other differentiated planetesimals with igneous histories, which have since been shattered by impacts.
| A lithified regolith, the source of howardites and brecciated eucrites. |
| Basaltic lava flows, a source of non-cumulate eucrites. |
| Plutonic rocks consisting of pyroxene, pigeonite and plagioclase, the source of cumulate eucrites. |
| Plutonic rocks rich in orthopyroxene with large grain sizes, the source of diogenites. |
On the basis of the sizes of V-type asteroids
(thought to be pieces of Vesta's crust ejected during large impacts),
and the depth of Rheasilvia crater (see below), the crust is thought to
be roughly 10 kilometres (6 mi) thick.
Findings from the Dawn spacecraft have found evidence that the
troughs that wrap around Vesta could be graben formed by impact-induced
faulting (see Troughs section above), meaning that Vesta has more
complex geology than other asteroids. Vesta could have been classified
as a dwarf planet if it had retained a spherical shape, and it has other
qualities that lead to the thought it could be a protoplanet. The only
thing that knocked it out of the category of a dwarf planet was the
formation of two large impact basins at its southern pole. At the time of these impacts Vesta was not warm and plastic enough to return to a shape in hydrostatic equilibrium.
Regolith
Vesta's surface is covered by regolith distinct from that found on the Moon or asteroids such as Itokawa. This is because space weathering acts differently. Vesta's surface shows no significant trace of nanophase iron because the impact
speeds on Vesta are too low to make rock melting and vaporization an
appreciable process. Instead, regolith evolution is dominated by brecciation and subsequent mixing of bright and dark components. The dark component is probably due to the infall of carbonaceous material, whereas the bright component is the original Vesta basaltic soil.
Fragments
Some small Solar System bodies are suspected to be fragments of Vesta caused by impacts. The Vestian asteroids and HED meteorites are examples. The V-type asteroid 1929 Kollaa has been determined to have a composition akin to cumulate eucrite meteorites, indicating its origin deep within Vesta's crust.
Vesta is currently one of only six identified Solar System
bodies of which we have physical samples, coming from a number of
meteorites suspected to be Vestan fragments. It is estimated that 1 out
of 16 meteorites originated from Vesta. The other identified Solar System samples are from Earth itself, meteorites from Mars, meteorites from the Moon, and samples returned from the Moon, the comet Wild 2, and the asteroid 25143 Itokawa.
Exploration
Artist's conception of Dawn orbiting Vesta
In 1981, a proposal for an asteroid mission was submitted to the European Space Agency (ESA). Named the Asteroidal Gravity Optical and Radar Analysis (AGORA), this spacecraft
was to launch some time in 1990–1994 and perform two flybys of large
asteroids. The preferred target for this mission was Vesta. AGORA would
reach the asteroid belt either by a gravitational slingshot trajectory past Mars or by means of a small ion engine. However, the proposal was refused by the ESA. A joint NASA–ESA asteroid mission was then drawn up for a Multiple Asteroid Orbiter with Solar Electric Propulsion (MAOSEP),
with one of the mission profiles including an orbit of Vesta. NASA
indicated they were not interested in an asteroid mission. Instead, the
ESA set up a technological study of a spacecraft with an ion drive.
Other missions to the asteroid belt were proposed in the 1980s by
France, Germany, Italy and the United States, but none were approved. Exploration of Vesta by fly-by and impacting penetrator was the second main target of the first plan of the multi-aimed Soviet Vesta mission, developed in cooperation with European countries for realisation in 1991–1994 but canceled due to the Soviet Union disbanding.
First image of asteroids (Ceres and Vesta) taken from Mars. The image was made by the Curiosity rover on 20 April 2014.
In the early 1990s, NASA initiated the Discovery Program,
which was intended to be a series of low-cost scientific missions. In
1996, the program's study team recommended a mission to explore the
asteroid belt using a spacecraft with an ion engine as a high priority.
Funding for this program remained problematic for several years, but by
2004 the Dawn vehicle had passed its critical design review and construction proceeded.
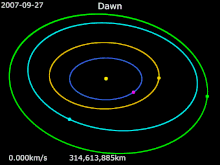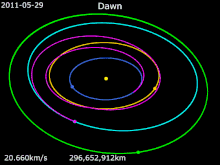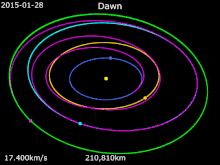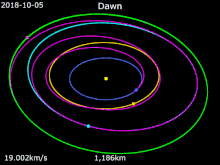
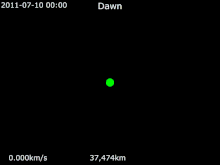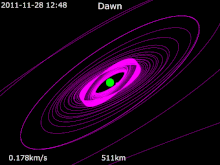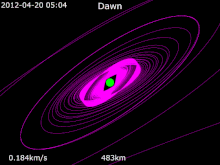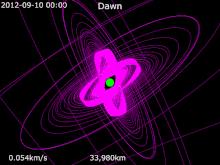
It launched on 27 September 2007 as the first space mission to Vesta. On 3 May 2011, Dawn acquired its first targeting image 1.2 million kilometers from Vesta. On 16 July 2011, NASA confirmed that it received telemetry from Dawn indicating that the spacecraft successfully entered Vesta's orbit. It was scheduled to orbit Vesta for one year, until July 2012. Dawn's arrival coincided with late summer in the southern hemisphere of Vesta, with the large crater at Vesta's south pole (Rheasilvia)
in sunlight. Because a season on Vesta lasts eleven months, the
northern hemisphere, including anticipated compression fractures
opposite the crater, would become visible to Dawn's cameras before it left orbit. Dawn left orbit around Vesta on 4 September 2012 11:26 p.m. PDT to travel to Ceres.
NASA/DLR released imagery and summary information from a survey
orbit, two high-altitude orbits (60–70 m/pixel) and a low-altitude
mapping orbit (20 m/pixel), including digital terrain models, videos and
atlases. Scientists also used Dawn to calculate Vesta's precise mass and gravity field. The subsequent determination of the J2 component yielded a core diameter estimate of about 220 km assuming a crustal density similar to that of the HED.
Dawn data can be accessed by the public at the UCLA website.
Observations from Earth orbit
- Albedo and spectral maps of 4 Vesta, as determined from Hubble Space Telescope images from November 1994
- Elevation diagram of 4 Vesta (as determined from Hubble Space Telescope images of May 1996) viewed from the south-east, showing Rheasilvia crater at the south pole and Feralia Planitia near the equator
- Vesta seen by the Hubble Space Telescope in May 2007
Observations from Dawn
Vesta comes into view as the Dawn spacecraft approaches and enters orbit:
True-color images
Detailed images retrieved during the high-altitude (60–70 m/pixel)
and low-altitude (~20 m/pixel) mapping orbits are available on the Dawn Mission website of JPL/NASA.
Visibility
Annotated image from Earth's surface in June 2007 with (4) Vesta
Its size and unusually bright surface make Vesta the brightest asteroid, and it is occasionally visible to the naked eye from dark skies (without light pollution). In May and June 2007, Vesta reached a peak magnitude of +5.4, the brightest since 1989. At that time, opposition and perihelion were only a few weeks apart. It was brighter still at its 22 June 2018 opposition, reaching a magnitude of +5.3.
Less favorable oppositions during late autumn 2008 in the Northern Hemisphere still had Vesta at a magnitude of from +6.5 to +7.3. Even when in conjunction with the Sun, Vesta will have a magnitude around +8.5; thus from a pollution-free sky it can be observed with binoculars even at elongations much smaller than near opposition.
2010–2011
In 2010, Vesta reached opposition in the constellation of Leo on the night of 17–18 February, at about magnitude 6.1, a brightness that makes it visible in binocular range but generally not for the naked eye.
Under perfect dark sky conditions where all light pollution is absent
it might be visible to an experienced observer without the use of a
telescope or binoculars. Vesta came to opposition again on 5 August
2011, in the constellation of Capricornus at about magnitude 5.6.
2012–2013
Vesta was at opposition again on 9 December 2012. According to Sky and Telescope magazine, this year Vesta came within about 6 degrees of 1 Ceres during the winter of 2012 and spring 2013.
Vesta orbits the Sun in 3.63 years and Ceres in 4.6 years, so every 17
years Vesta overtakes Ceres (the last overtaking was in 1996). On December 1, 2012, Vesta had a magnitude of 6.6, but decreasing to 8.4 by May 1, 2013.
2014
Conjunction of Ceres and Vesta on July 5, 2014 in Virgo
Ceres and Vesta came within one degree of each other in the night sky in July 2014.