Full moon as seen from North America in Earth's Northern Hemisphere
| |||||||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjectives | |||||||||||||
| Orbital characteristics | |||||||||||||
| Epoch J2000 | |||||||||||||
| Perigee | 362600 km (356400–370400 km) | ||||||||||||
| Apogee | 405400 km (404000–406700 km) | ||||||||||||
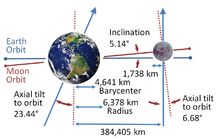
| 384399 km (0.00257 AU) | |||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.0549 | ||||||||||||
27.321661 d
(27 d 7 h 43 min 11.5 s) | |||||||||||||
29.530589 d
(29 d 12 h 44 min 2.9 s) | |||||||||||||
Average orbital speed
| 1.022 km/s | ||||||||||||
| Inclination | 5.145° to the ecliptic | ||||||||||||
Regressing by one revolution in 18.61 years
| |||||||||||||
Progressing by one revolution in 8.85 years
| |||||||||||||
| Satellite of | Earth | ||||||||||||
| Physical characteristics | |||||||||||||
Mean radius
| 1737.1 km (0.273 of Earth's) | ||||||||||||
Equatorial radius
| 1738.1 km (0.273 of Earth's) | ||||||||||||
Polar radius
| 1736.0 km (0.273 of Earth's) | ||||||||||||
| Flattening | 0.0012 | ||||||||||||
| Circumference | 10921 km (equatorial) | ||||||||||||
| 3.793×107 km2 (0.074 of Earth's) | |||||||||||||
| Volume | 2.1958×1010 km3 (0.020 of Earth's) | ||||||||||||
| Mass | 7.342×1022 kg (0.012300 of Earth's) | ||||||||||||
Mean density
| 3.344 g/cm3 0.606 × Earth | ||||||||||||
| 1.62 m/s2 (0.1654 g) | |||||||||||||
| 0.3929±0.0009 | |||||||||||||
| 2.38 km/s | |||||||||||||
Sidereal rotation period
| 27.321661 d (synchronous) | ||||||||||||
Equatorial rotation velocity
| 4.627 m/s | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
North pole right ascension
|
| ||||||||||||
North pole declination
| 65.64° | ||||||||||||
| Albedo | 0.136 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| 29.3 to 34.1 arcminutes | |||||||||||||
| Atmosphere | |||||||||||||
Surface pressure
| |||||||||||||
| Composition by volume | |||||||||||||
The Moon is an astronomical body that orbits planet Earth and is Earth's only permanent natural satellite. It is the fifth-largest natural satellite in the Solar System, and the largest among planetary satellites relative to the size of the planet that it orbits (its primary). The Moon is after Jupiter's satellite Io the second-densest satellite in the Solar System among those whose densities are known.
The Moon is thought to have formed about 4.51 billion years ago, not long after Earth. The most widely accepted explanation is that the Moon formed from the debris left over after a giant impact between Earth and a Mars-sized body called Theia.
The Moon is in synchronous rotation with Earth, and thus always shows the same side to Earth, the near side. The near side is marked by dark volcanic maria that fill the spaces between the bright ancient crustal highlands and the prominent impact craters. After the Sun, the Moon is the second-brightest regularly visible celestial object in Earth's sky. Its surface is actually dark, although compared to the night sky it appears very bright, with a reflectance just slightly higher than that of worn asphalt. Its gravitational influence produces the ocean tides, body tides, and the slight lengthening of the day.
The Moon's average orbital distance is 384,402 km (238,856 mi), or 1.28 light-seconds. This is about thirty times the diameter of Earth. The Moon's apparent size in the sky is almost the same as that of the Sun, since the star is about 400 times the lunar distance and diameter. Therefore, the Moon covers the Sun nearly precisely during a total solar eclipse. This matching of apparent visual size will not continue in the far future because the Moon's distance from Earth is gradually increasing.
The Moon was first reached in September 1959 by the Soviet Union's Luna 2, an unmanned spacecraft. The United States' NASA Apollo program achieved the only manned lunar missions to date, beginning with the first manned orbital mission by Apollo 8 in 1968, and six manned landings between 1969 and 1972, with the first being Apollo 11. These missions returned lunar rocks which have been used to develop a geological understanding of the Moon's origin, internal structure, and the Moon's later history. Since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972, the Moon has been visited only by unmanned spacecraft.
Both the Moon's natural prominence in the earthly sky and its regular cycle of phases as seen from Earth have provided cultural references and influences for human societies and cultures since time immemorial. Such cultural influences can be found in language, lunar calendar systems, art, and mythology.
Name and etymology
The Moon, tinted reddish, during a lunar eclipse
The usual English proper name for Earth's natural satellite is "the Moon", which in nonscientific texts is usually not capitalized. The noun moon is derived from Old English mōna, which (like all Germanic language cognates) stems from Proto-Germanic *mēnô, which comes from Proto-Indo-European *mḗh₁n̥s "moon", "month", which comes from the Proto-Indo-European root *meh₁- "to measure", the month being the ancient unit of time measured by the Moon.
Occasionally, the name "Luna" is used. In literature, especially
science fiction, "Luna" is used to distinguish it from other moons,
while in poetry, the name has been used to denote personification of our
moon.
The modern English adjective pertaining to the Moon is lunar, derived from the Latin word for the Moon, luna. The adjective selenic (usually only used to refer to the chemical element selenium) is so rarely used to refer to the Moon that this meaning is not recorded in most major dictionaries. It is derived from the Ancient Greek word for the Moon, σελήνη (selḗnē), from which is however also derived the prefix "seleno-", as in selenography, the study of the physical features of the Moon, as well as the element name selenium. Both the Greek goddess Selene and the Roman goddess Diana were alternatively called Cynthia. The names Luna, Cynthia, and Selene are reflected in terminology for lunar orbits in words such as apolune, pericynthion, and selenocentric. The name Diana comes from the Proto-Indo-European *diw-yo,
"heavenly", which comes from the PIE root *dyeu- "to shine," which in
many derivatives means "sky, heaven, and god" and is also the origin of
Latin dies, "day".
Formation
The Moon formed 4.51 billion years ago, some 60 million years after the origin of the Solar System. Several forming mechanisms have been proposed, including the fission of the Moon from Earth's crust through centrifugal force (which would require too great an initial spin of Earth), the gravitational capture of a pre-formed Moon (which would require an unfeasibly extended atmosphere of Earth to dissipate the energy of the passing Moon), and the co-formation of Earth and the Moon together in the primordial accretion disk (which does not explain the depletion of metals in the Moon). These hypotheses also cannot account for the high angular momentum of the Earth–Moon system.
The evolution of the Moon and a tour of the Moon
The prevailing hypothesis is that the Earth–Moon system formed after an impact of a Mars-sized body (named Theia) with the proto-Earth (giant impact). The impact blasted material into Earth's orbit and then the material accreted and formed the Moon.
The Moon's far side has a crust that is 30 mi (48 km) thicker
than that of the near side. This is thought to be because the Moon fused
from two different bodies.
This hypothesis, although not perfect, perhaps best explains the
evidence. Eighteen months prior to an October 1984 conference on lunar
origins, Bill Hartmann, Roger Phillips, and Jeff Taylor challenged
fellow lunar scientists: "You have eighteen months. Go back to your
Apollo data, go back to your computer, do whatever you have to, but make
up your mind. Don't come to our conference unless you have something to
say about the Moon's birth." At the 1984 conference at Kona, Hawaii,
the giant impact hypothesis emerged as the most popular.
Before the conference, there were partisans of the three "traditional" theories, plus a few people who were starting to take the giant impact seriously, and there was a huge apathetic middle who didn’t think the debate would ever be resolved. Afterward, there were essentially only two groups: the giant impact camp and the agnostics.
Giant impacts are thought to have been common in the early Solar
System. Computer simulations of giant impacts have produced results that
are consistent with the mass of the lunar core and the angular momentum
of the Earth–Moon system. These simulations also show that most of the
Moon derived from the impactor, rather than the proto-Earth. However, more recent simulations suggest a larger fraction of the Moon derived from the proto-Earth. Other bodies of the inner Solar System such as Mars and Vesta have, according to meteorites from them, very different oxygen and tungsten isotopic
compositions compared to Earth. However, Earth and the Moon have nearly
identical isotopic compositions. The isotopic equalization of the
Earth-Moon system might be explained by the post-impact mixing of the
vaporized material that formed the two, although this is debated.
The impact released a lot of energy and then the released
material re-accreted into the Earth–Moon system. This would have melted
the outer shell of Earth, and thus formed a magma ocean. Similarly, the newly formed Moon would also have been affected and had its own lunar magma ocean; its depth is estimated from about 500 km (300 miles) to 1,737 km (1,079 miles).
While the giant impact hypothesis might explain many lines of
evidence, some questions are still unresolved, most of which involve the
Moon's composition.
In 2001, a team at the Carnegie Institute of Washington reported the
most precise measurement of the isotopic signatures of lunar rocks. To their surprise, the rocks from the Apollo program
had the same isotopic signature as rocks from Earth, however they
differed from almost all other bodies in the Solar System. Indeed, this
observation was unexpected, because most of the material that formed the
Moon was thought to come from Theia and it was announced in 2007 that there was less than a 1% chance that Theia and Earth had identical isotopic signatures. Other Apollo lunar samples had in 2012 the same titanium isotopes composition as Earth, which conflicts
with what is expected if the Moon formed far from Earth or is derived
from Theia. These discrepancies may be explained by variations of the
giant impact hypothesis.
Physical characteristics
Internal structure
Structure of the Moon
| Compound | Formula | Composition (wt %) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maria | Highlands | ||
| silica | SiO2 | 45.4% | 45.5% |
| alumina | Al2O3 | 14.9% | 24.0% |
| lime | CaO | 11.8% | 15.9% |
| iron(II) oxide | FeO | 14.1% | 5.9% |
| magnesia | MgO | 9.2% | 7.5% |
| titanium dioxide | TiO2 | 3.9% | 0.6% |
| sodium oxide | Na2O | 0.6% | 0.6% |
| Total | 99.9% | 100.0% | |
The Moon is a differentiated body: it has a geochemically distinct crust, mantle, and core.
The Moon has a solid iron-rich inner core with a radius possibly as
small as 240 km (150 mi) and a fluid outer core primarily made of liquid
iron with a radius of roughly 300 km (190 mi). Around the core is a
partially molten boundary layer with a radius of about 500 km (310 mi). This structure is thought to have developed through the fractional crystallization of a global magma ocean shortly after the Moon's formation 4.5 billion years ago.
Crystallization of this magma ocean would have created a mafic mantle from the precipitation and sinking of the minerals olivine, clinopyroxene, and orthopyroxene; after about three-quarters of the magma ocean had crystallised, lower-density plagioclase minerals could form and float into a crust atop. The final liquids to crystallise would have been initially sandwiched between the crust and mantle, with a high abundance of incompatible and heat-producing elements.
Consistent with this perspective, geochemical mapping made from orbit suggests the crust of mostly anorthosite. The Moon rock
samples of the flood lavas that erupted onto the surface from partial
melting in the mantle confirm the mafic mantle composition, which is
more iron-rich than that of Earth.
The crust is on average about 50 km (31 mi) thick.
The Moon is the second-densest satellite in the Solar System, after Io. However, the inner core of the Moon is small, with a radius of about 350 km (220 mi) or less,
around 20% of the radius of the Moon. Its composition is not well
defined, but is probably metallic iron alloyed with a small amount of sulfur and nickel; analyses of the Moon's time-variable rotation suggest that it is at least partly molten.
Surface geology
Topography of the Moon
STL 3D model of the Moon with 10× elevation exaggeration rendered with data from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The topography of the Moon has been measured with laser altimetry and stereo image analysis. Its most visible topographic feature is the giant far-side South Pole–Aitken basin, some 2,240 km (1,390 mi) in diameter, the largest crater on the Moon and the second-largest confirmed impact crater in the Solar System. At 13 km (8.1 mi) deep, its floor is the lowest point on the surface of the Moon.
The highest elevations of the Moon's surface are located directly to
the northeast, and it has been suggested might have been thickened by
the oblique formation impact of the South Pole–Aitken basin. Other large impact basins, such as Imbrium, Serenitatis, Crisium, Smythii, and Orientale, also possess regionally low elevations and elevated rims. The far side of the lunar surface is on average about 1.9 km (1.2 mi) higher than that of the near side.
The discovery of fault scarp cliffs by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter suggest that the Moon has shrunk within the past billion years, by about 90 metres (300 ft). Similar shrinkage features exist on Mercury.
Volcanic features
Lunar nearside with major maria and craters labeled
The dark and relatively featureless lunar plains, clearly seen with the naked eye, are called maria (Latin for "seas"; singular mare), as they were once believed to be filled with water; they are now known to be vast solidified pools of ancient basaltic lava. Although similar to terrestrial basalts, lunar basalts have more iron and no minerals altered by water. The majority of these lavas erupted or flowed into the depressions associated with impact basins. Several geologic provinces containing shield volcanoes and volcanic domes are found within the near side "maria".
Evidence of young lunar volcanism
Almost all maria are on the near side of the Moon, and cover 31% of the surface of the near side, compared with 2% of the far side. This is thought to be due to a concentration of heat-producing elements under the crust on the near side, seen on geochemical maps obtained by Lunar Prospector's
gamma-ray spectrometer, which would have caused the underlying mantle
to heat up, partially melt, rise to the surface and erupt. Most of the Moon's mare basalts
erupted during the Imbrian period, 3.0–3.5 billion years ago, although
some radiometrically dated samples are as old as 4.2 billion years. Until recently, the youngest eruptions, dated by crater counting, appeared to have been only 1.2 billion years ago. In 2006, a study of Ina, a tiny depression in Lacus Felicitatis,
found jagged, relatively dust-free features that, because of the lack
of erosion by infalling debris, appeared to be only 2 million years old. Moonquakes and releases of gas also indicate some continued lunar activity. In 2014 NASA announced "widespread evidence of young lunar volcanism" at 70 irregular mare patches identified by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter,
some less than 50 million years old. This raises the possibility of a
much warmer lunar mantle than previously believed, at least on the near
side where the deep crust is substantially warmer because of the greater
concentration of radioactive elements. Just prior to this, evidence has been presented for 2–10 million years younger basaltic volcanism inside Lowell crater,
Orientale basin, located in the transition zone between the near and
far sides of the Moon. An initially hotter mantle and/or local
enrichment of heat-producing elements in the mantle could be responsible
for prolonged activities also on the far side in the Orientale basin.
The lighter-coloured regions of the Moon are called terrae, or more commonly highlands,
because they are higher than most maria. They have been radiometrically
dated to having formed 4.4 billion years ago, and may represent plagioclase cumulates of the lunar magma ocean. In contrast to Earth, no major lunar mountains are believed to have formed as a result of tectonic events.
The concentration of maria on the Near Side likely reflects the
substantially thicker crust of the highlands of the Far Side, which may
have formed in a slow-velocity impact of a second moon of Earth a few
tens of millions of years after their formation.
Impact craters
Lunar crater Daedalus on the Moon's far side
The other major geologic process that has affected the Moon's surface is impact cratering,
with craters formed when asteroids and comets collide with the lunar
surface. There are estimated to be roughly 300,000 craters wider than
1 km (0.6 mi) on the Moon's near side alone. The lunar geologic timescale is based on the most prominent impact events, including Nectaris, Imbrium, and Orientale,
structures characterized by multiple rings of uplifted material,
between hundreds and thousands of kilometres in diameter and associated
with a broad apron of ejecta deposits that form a regional stratigraphic horizon.
The lack of an atmosphere, weather and recent geological processes mean
that many of these craters are well-preserved. Although only a few
multi-ring basins have been definitively dated, they are useful for
assigning relative ages. Because impact craters accumulate at a nearly
constant rate, counting the number of craters per unit area can be used
to estimate the age of the surface. The radiometric ages of impact-melted rocks collected during the Apollo missions cluster between 3.8 and 4.1 billion years old: this has been used to propose a Late Heavy Bombardment of impacts.
Blanketed on top of the Moon's crust is a highly comminuted (broken into ever smaller particles) and impact gardened surface layer called regolith, formed by impact processes. The finer regolith, the lunar soil of silicon dioxide glass, has a texture resembling snow and a scent resembling spent gunpowder.
The regolith of older surfaces is generally thicker than for younger
surfaces: it varies in thickness from 10–20 km (6.2–12.4 mi) in the
highlands and 3–5 km (1.9–3.1 mi) in the maria. Beneath the finely comminuted regolith layer is the megaregolith, a layer of highly fractured bedrock many kilometres thick.
Comparison of high-resolution images obtained by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
has shown a contemporary crater-production rate significantly higher
than previously estimated. A secondary cratering process caused by distal ejecta
is thought to churn the top two centimetres of regolith a hundred times
more quickly than previous models suggested—on a timescale of 81,000
years.
Lunar swirls at Reiner Gamma
Lunar swirls
Lunar swirls are enigmatic features found across the Moon's surface.
They are characterized by a high albedo, appear optically immature (i.e.
the optical characteristics of a relatively young regolith), and have
often a sinuous shape. Their shape is often accentuated by low albedo
regions that wind between the bright swirls.
Presence of water
Liquid water cannot persist on the lunar surface. When exposed to
solar radiation, water quickly decomposes through a process known as photodissociation and is lost to space. However, since the 1960s, scientists have hypothesized that water ice may be deposited by impacting comets or possibly produced by the reaction of oxygen-rich lunar rocks, and hydrogen from solar wind, leaving traces of water which could possibly persist in cold, permanently shadowed craters at either pole on the Moon. Computer simulations suggest that up to 14,000 km2 (5,400 sq mi) of the surface may be in permanent shadow. The presence of usable quantities of water on the Moon is an important factor in rendering lunar habitation as a cost-effective plan; the alternative of transporting water from Earth would be prohibitively expensive.
In years since, signatures of water have been found to exist on the lunar surface. In 1994, the bistatic radar experiment located on the Clementine
spacecraft, indicated the existence of small, frozen pockets of water
close to the surface. However, later radar observations by Arecibo, suggest these findings may rather be rocks ejected from young impact craters. In 1998, the neutron spectrometer on the Lunar Prospector
spacecraft showed that high concentrations of hydrogen are present in
the first meter of depth in the regolith near the polar regions. Volcanic lava beads, brought back to Earth aboard Apollo 15, showed small amounts of water in their interior.
The 2008 Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft has since confirmed the existence of surface water ice, using the on-board Moon Mineralogy Mapper. The spectrometer observed absorption lines common to hydroxyl,
in reflected sunlight, providing evidence of large quantities of water
ice, on the lunar surface. The spacecraft showed that concentrations may
possibly be as high as 1,000 ppm.
Using the mapper's reflectance spectra, indirect lighting of areas in
shadow confirmed water ice within 20° latitude of both poles in 2018. In 2009, LCROSS
sent a 2,300 kg (5,100 lb) impactor into a permanently shadowed polar
crater, and detected at least 100 kg (220 lb) of water in a plume of
ejected material. Another examination of the LCROSS data showed the amount of detected water to be closer to 155 ± 12 kg (342 ± 26 lb).
In May 2011, 615–1410 ppm water in melt inclusions in lunar sample 74220 was reported, the famous high-titanium "orange glass soil" of volcanic origin collected during the Apollo 17
mission in 1972. The inclusions were formed during explosive eruptions
on the Moon approximately 3.7 billion years ago. This concentration is
comparable with that of magma in Earth's upper mantle.
Although of considerable selenological interest, this announcement
affords little comfort to would-be lunar colonists—the sample originated
many kilometers below the surface, and the inclusions are so difficult
to access that it took 39 years to find them with a state-of-the-art ion
microprobe instrument.
Analysis of the findings of the Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3)
revealed in August 2018 for the first time "definitive evidence" for
water-ice on the lunar surface. The data revealed the distinct reflective signatures of water-ice, as opposed to dust and other reflective substances.
The ice deposits were found on the North and South poles, although it
is more abundant in the South, where water is trapped in permanently
shadowed craters and cravices, allowing it to persist as ice on the
surface since they are shielded from the sun.
Gravitational field
GRAIL's gravity map of the Moon
The gravitational field of the Moon has been measured through tracking the Doppler shift of radio signals emitted by orbiting spacecraft. The main lunar gravity features are mascons, large positive gravitational anomalies associated with some of the giant impact basins, partly caused by the dense mare basaltic lava flows that fill those basins.
The anomalies greatly influence the orbit of spacecraft about the Moon.
There are some puzzles: lava flows by themselves cannot explain all of
the gravitational signature, and some mascons exist that are not linked
to mare volcanism.
Magnetic field
The Moon has an external magnetic field of about 1–100 nanoteslas, less than one-hundredth that of Earth. The Moon does not currently have a global dipolar magnetic field and only has crustal magnetization, probably acquired early in its history when a dynamo was still operating. Alternatively, some of the remnant magnetization may be from transient
magnetic fields generated during large impacts through the expansion of
an impact-generated plasma cloud in an ambient magnetic field. This is
supported by the apparent location of the largest crustal magnetizations
near the antipodes of the giant impact basins.
Atmosphere
Sketch by the Apollo 17 astronauts. The lunar atmosphere was later studied by LADEE.
The Moon has an atmosphere so tenuous as to be nearly vacuum, with a total mass of less than 10 metric tons (9.8 long tons; 11 short tons). The surface pressure of this small mass is around 3 × 10−15 atm (0.3 nPa); it varies with the lunar day. Its sources include outgassing and sputtering, a product of the bombardment of lunar soil by solar wind ions. Elements that have been detected include sodium and potassium, produced by sputtering (also found in the atmospheres of Mercury and Io); helium-4 and neon from the solar wind; and argon-40, radon-222, and polonium-210, outgassed after their creation by radioactive decay within the crust and mantle. The absence of such neutral species (atoms or molecules) as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and magnesium, which are present in the regolith, is not understood. Water vapour has been detected by Chandrayaan-1 and found to vary with latitude, with a maximum at ~60–70 degrees; it is possibly generated from the sublimation of water ice in the regolith.
These gases either return into the regolith because of the Moon's
gravity or are lost to space, either through solar radiation pressure
or, if they are ionized, by being swept away by the solar wind's
magnetic field.
Dust
A permanent asymmetric moon dust cloud exists around the Moon, created by small particles from comets.
Estimates are 5 tons of comet particles strike the Moon's surface each
24 hours. The particles strike the Moon's surface ejecting moon dust
above the Moon. The dust stays above the Moon approximately 10 minutes,
taking 5 minutes to rise, and 5 minutes to fall. On average, 120
kilograms of dust are present above the Moon, rising to 100 kilometers
above the surface. The dust measurements were made by LADEE's
Lunar Dust EXperiment (LDEX), between 20 and 100 kilometers above the
surface, during a six-month period. LDEX detected an average of one 0.3
micrometer moon dust particle each minute. Dust particle counts peaked
during the Geminid, Quadrantid, Northern Taurid, and Omicron Centaurid meteor showers,
when the Earth, and Moon, pass through comet debris. The cloud is
asymmetric, more dense near the boundary between the Moon's dayside and
nightside.
Past thicker atmosphere
In October 2017, NASA scientists at the Marshall Space Flight Center and the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston announced their finding, based on studies of Moon magma samples retrieved by the Apollo
missions, that the Moon had once possessed a relatively thick
atmosphere for a period of 70 million years between 3 and 4 billion
years ago. This atmosphere, sourced from gases ejected from lunar
volcanic eruptions, was twice the thickness of that of present-day Mars. The ancient lunar atmosphere was eventually stripped away by solar winds and dissipated into space.
Seasons
The Moon's axial tilt with respect to the ecliptic is only 1.5424°,
much less than the 23.44° of Earth. Because of this, the Moon's solar
illumination varies much less with season, and topographical details
play a crucial role in seasonal effects. From images taken by Clementine in 1994, it appears that four mountainous regions on the rim of Peary Crater at the Moon's north pole may remain illuminated for the entire lunar day, creating peaks of eternal light.
No such regions exist at the south pole. Similarly, there are places
that remain in permanent shadow at the bottoms of many polar craters, and these "craters of eternal darkness" are extremely cold: Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter measured the lowest summer temperatures in craters at the southern pole at 35 K (−238 °C; −397 °F) and just 26 K (−247 °C; −413 °F) close to the winter solstice in north polar Hermite Crater. This is the coldest temperature in the Solar System ever measured by a spacecraft, colder even than the surface of Pluto.
Average temperatures of the Moon's surface are reported, but
temperatures of different areas will vary greatly depending upon whether
they are in sunlight or shadow.
Earth-Moon system
Orbit
Earth–Moon system (schematic)
DSCOVR satellite sees the Moon passing in front of Earth
The Moon makes a complete orbit around Earth with respect to the fixed stars about once every 27.3 days (its sidereal period).
However, because Earth is moving in its orbit around the Sun at the
same time, it takes slightly longer for the Moon to show the same phase to Earth, which is about 29.5 days (its synodic period). Unlike most satellites of other planets, the Moon orbits closer to the ecliptic plane than to the planet's equatorial plane. The Moon's orbit is subtly perturbed by the Sun and Earth in many small, complex and interacting ways. For example, the plane of the Moon's orbit gradually rotates once every 18.61 years, which affects other aspects of lunar motion. These follow-on effects are mathematically described by Cassini's laws.
Relative size
The Moon is exceptionally large relative to Earth: Its diameter is more than a quarter and its mass is 1/81 of Earth's. It is the largest moon in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, though Charon is larger relative to the dwarf planet Pluto, at 1/9 Pluto's mass. The Earth and the Moon's barycentre, their common centre of mass, is located 1,700 km (1,100 mi) (about a quarter of Earth's radius) beneath Earth's surface.
The Earth revolves around the Earth-Moon barycentre once a
sidereal month, with 1/81 the speed of the Moon, or about 12.5 metres
(41 ft) per second. This motion is superimposed on the much larger
revolution of the Earth around the Sun at a speed of about 30 kilometres
(19 mi) per second.
Appearance from Earth
Moon setting in western sky over the High Desert in California
The Moon is in synchronous rotation as it orbits
Earth; it rotates about its axis in about the same time it takes to
orbit Earth. This results in it always keeping nearly the same face
turned towards Earth. However, because of the effect of libration, about 59% of the Moon's surface can actually be seen from Earth. The side of the Moon that faces Earth is called the near side, and the opposite the far side. The far side is often inaccurately called the "dark side", but it is in
fact illuminated as often as the near side: once every 29.5 Earth days.
During new moon, the near side is dark.
The Moon had once rotated at a faster rate, but early in its history, its rotation slowed and became tidally locked in this orientation as a result of frictional effects associated with tidal deformations caused by Earth.
With time, the energy of rotation of the Moon on its axis was
dissipated as heat, until there was no rotation of the Moon relative to
Earth. In 2016, planetary scientists, using data collected on the much
earlier NASA Lunar Prospector
mission, found two hydrogen-rich areas on opposite sides of the Moon,
probably in the form of water ice. It is speculated that these patches
were the poles of the Moon billions of years ago, before it was tidally
locked to Earth.
The Moon is prominently featured in Vincent van Gogh's 1889 painting, The Starry Night
The Moon has an exceptionally low albedo, giving it a reflectance that is slightly brighter than that of worn asphalt. Despite this, it is the brightest object in the sky after the Sun. This is due partly to the brightness enhancement of the opposition surge; the Moon at quarter phase is only one-tenth as bright, rather than half as bright, as at full moon. Additionally, color constancy in the visual system
recalibrates the relations between the colors of an object and its
surroundings, and because the surrounding sky is comparatively dark, the
sunlit Moon is perceived as a bright object. The edges of the full moon seem as bright as the centre, without limb darkening, because of the reflective properties of lunar soil, which retroreflects
light more towards the Sun than in other directions. The Moon does
appear larger when close to the horizon, but this is a purely
psychological effect, known as the moon illusion, first described in the 7th century BC. The full Moon's angular diameter is about 0.52° (on average) in the sky, roughly the same apparent size as the Sun.
The Moon's highest altitude at culmination varies by its phase and time of year. The full moon is highest in the sky during winter (for each hemisphere). The 18.61-year nodal cycle has an influence on lunar standstill. When the ascending node of the lunar orbit is in the vernal equinox, the lunar declination can reach up to plus or minus 28° each month. This means the Moon can pass overhead if viewed from latitudes up to 28° north or south (of the Equator), instead of only 18°. The orientation of the Moon's crescent also depends on the latitude of the viewing location; an observer in the tropics can see a smile-shaped crescent Moon. The Moon is visible for two weeks every 27.3 days at the North and South Poles. Zooplankton in the Arctic use moonlight when the Sun is below the horizon for months on end.
14 November 2016 supermoon was 356,511 kilometres (221,526 mi) away from the center of Earth, the closest occurrence since 26 January 1948. It will not be closer until 25 November 2034.
The distance between the Moon and Earth varies from around 356,400 km (221,500 mi) to 406,700 km (252,700 mi) at perigee (closest) and apogee (farthest), respectively. On 14 November 2016, it was closer to Earth when at full phase than it has been since 1948, 14% closer than its farthest position in apogee. Reported as a "supermoon", this closest point coincided within an hour of a full moon, and it was 30% more luminous than when at its greatest distance because its angular diameter is 14% greater and . At lower levels, the human perception of reduced brightness as a percentage is provided by the following formula:
When the actual reduction is 1.00 / 1.30, or about 0.770, the
perceived reduction is about 0.877, or 1.00 / 1.14. This gives a maximum
perceived increase of 14% between apogee and perigee moons of the same
phase.
There has been historical controversy over whether features on
the Moon's surface change over time. Today, many of these claims are
thought to be illusory, resulting from observation under different
lighting conditions, poor astronomical seeing, or inadequate drawings. However, outgassing does occasionally occur and could be responsible for a minor percentage of the reported lunar transient phenomena.
Recently, it has been suggested that a roughly 3 km (1.9 mi) diameter
region of the lunar surface was modified by a gas release event about a
million years ago.
The Moon's appearance, like the Sun's, can be affected by Earth's atmosphere. Common optical effects are the 22° halo ring, formed when the Moon's light is refracted through the ice crystals of high cirrostratus clouds, and smaller coronal rings when the Moon is seen through thin clouds.
The monthly changes in the angle between the direction of sunlight and view from Earth, and the phases of the Moon that result, as viewed from the Northern Hemisphere. The Earth–Moon distance is not to scale.
The illuminated area of the visible sphere (degree of illumination) is given by , where is the elongation (i.e., the angle between Moon, the observer (on Earth) and the Sun).
Tidal effects
The libration of the Moon over a single lunar month. Also visible is the slight variation in the Moon's visual size from Earth.
The gravitational attraction that masses have for one another decreases inversely with the square of the distance of those masses from each other. As a result, the slightly greater attraction that the Moon has for the side of Earth closest to the Moon, as compared to the part of the Earth opposite the Moon, results in tidal forces. Tidal forces affect both the Earth's crust and oceans.
The most obvious effect of tidal forces is to cause two bulges in the Earth's oceans, one on the side facing the Moon and the other on the side opposite. This results in elevated sea levels called ocean tides. As the Earth spins on its axis, one of the ocean bulges (high tide) is held in place "under" the Moon, while another such tide is opposite. As a result, there are two high tides, and two low tides in about 24 hours. Since the Moon is orbiting the Earth in the same direction of the Earth's rotation, the high tides occur about every 12 hours and 25 minutes; the 25 minutes is due to the Moon's time to orbit the Earth. The Sun has the same tidal effect on the Earth, but its forces of attraction are only 40% that of the Moon's; the Sun's and Moon's interplay is responsible for spring and neap tides. If the Earth were a water world (one with no continents) it would produce a tide of only one meter, and that tide would be very predictable, but the ocean tides are greatly modified by other effects: the frictional coupling of water to Earth's rotation through the ocean floors, the inertia of water's movement, ocean basins that grow shallower near land, the sloshing of water between different ocean basins. As a result, the timing of the tides at most points on the Earth is a product of observations that are explained, incidentally, by theory.
While gravitation causes acceleration and movement of the Earth's fluid oceans, gravitational coupling between the Moon and Earth's solid body is mostly elastic and plastic. The result is a further tidal effect of the Moon on the Earth that causes a bulge of the solid portion of the Earth nearest the Moon that acts as a torque in opposition to the Earth's rotation. This "drains" angular momentum and rotational kinetic energy from Earth's spin, slowing the Earth's rotation. That angular momentum, lost from the Earth, is transferred to the Moon in a process (confusingly known as tidal acceleration), which lifts the Moon into a higher orbit and results in its lower orbital speed about the Earth. Thus the distance between Earth and Moon is increasing, and the Earth's spin is slowing in reaction. Measurements from laser reflectors left during the Apollo missions (lunar ranging experiments) have found that the Moon's distance increases by 38 mm (1.5 in) per year (roughly the rate at which human fingernails grow). Atomic clocks also show that Earth's day lengthens by about 15 microseconds every year, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds. Left to run its course, this tidal drag would continue until the spin of Earth and the orbital period of the Moon matched, creating mutual tidal locking between the two. As a result, the Moon would be suspended in the sky over one meridian, as is already currently the case with Pluto and its moon Charon. However, the Sun will become a red giant engulfing the Earth-Moon system long before this occurrence.
In a like manner, the lunar surface experiences tides of around 10 cm (4 in) amplitude over 27 days, with two components: a fixed one due to Earth, because they are in synchronous rotation, and a varying component from the Sun. The Earth-induced component arises from libration, a result of the Moon's orbital eccentricity (if the Moon's orbit were perfectly circular, there would only be solar tides). Libration also changes the angle from which the Moon is seen, allowing a total of about 59% of its surface to be seen from Earth over time. The cumulative effects of stress built up by these tidal forces produces moonquakes. Moonquakes are much less common and weaker than are earthquakes, although moonquakes can last for up to an hour—significantly longer than terrestrial quakes—because of the absence of water to damp out the seismic vibrations. The existence of moonquakes was an unexpected discovery from seismometers placed on the Moon by Apollo astronauts from 1969 through 1972.
Eclipses
From Earth, the Moon and the Sun appear the same size, as seen in the 1999 solar eclipse (left), whereas from the STEREO-B (bottom) spacecraft in an Earth-trailing orbit, the Moon appears much smaller than the Sun (right).
Eclipses only occur when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are all in a straight line (termed "syzygy"). Solar eclipses occur at new moon, when the Moon is between the Sun and Earth. In contrast, lunar eclipses occur at full moon, when Earth is between the Sun and Moon. The apparent size of the Moon is roughly the same as that of the Sun, with both being viewed at close to one-half a degree wide. The Sun is much larger than the Moon but it is the vastly greater distance that gives it the same apparent size as the much closer and much smaller Moon from the perspective of Earth. The variations in apparent size, due to the non-circular orbits, are nearly the same as well, though occurring in different cycles. This makes possible both total (with the Moon appearing larger than the Sun) and annular (with the Moon appearing smaller than the Sun) solar eclipses. In a total eclipse, the Moon completely covers the disc of the Sun and the solar corona becomes visible to the naked eye. Because the distance between the Moon and Earth is very slowly increasing over time, the angular diameter of the Moon is decreasing. Also, as it evolves toward becoming a red giant, the size of the Sun, and its apparent diameter in the sky, are slowly increasing. The combination of these two changes means that hundreds of millions of years ago, the Moon would always completely cover the Sun on solar eclipses, and no annular eclipses were possible. Likewise, hundreds of millions of years in the future, the Moon will no longer cover the Sun completely, and total solar eclipses will not occur.
Because the Moon's orbit around Earth is inclined by about 5.145° (5° 9') to the orbit of Earth around the Sun, eclipses do not occur at every full and new moon. For an eclipse to occur, the Moon must be near the intersection of the two orbital planes. The periodicity and recurrence of eclipses of the Sun by the Moon, and of the Moon by Earth, is described by the saros, which has a period of approximately 18 years.
Because the Moon is continuously blocking our view of a half-degree-wide circular area of the sky, the related phenomenon of occultation occurs when a bright star or planet passes behind the Moon and is occulted: hidden from view. In this way, a solar eclipse is an occultation of the Sun. Because the Moon is comparatively close to Earth, occultations of individual stars are not visible everywhere on the planet, nor at the same time. Because of the precession of the lunar orbit, each year different stars are occulted.
Observation and exploration
Ancient and medieval studies
Map of the Moon by Johannes Hevelius from his Selenographia (1647), the first map to include the libration zones
A study of the Moon in Robert Hooke's Micrographia, 1665
Understanding of the Moon's cycles was an early development of astronomy: by the 5th century BC, Babylonian astronomers had recorded the 18-year Saros cycle of lunar eclipses, and Indian astronomers had described the Moon's monthly elongation. The Chinese astronomer Shi Shen (fl. 4th century BC) gave instructions for predicting solar and lunar eclipses. Later, the physical form of the Moon and the cause of moonlight became understood. The ancient Greek philosopher Anaxagoras (d. 428 BC) reasoned that the Sun and Moon were both giant spherical rocks, and that the latter reflected the light of the former. Although the Chinese of the Han Dynasty believed the Moon to be energy equated to qi, their 'radiating influence' theory also recognized that the light of the Moon was merely a reflection of the Sun, and Jing Fang (78–37 BC) noted the sphericity of the Moon. In the 2nd century AD, Lucian wrote the novel A True Story, in which the heroes travel to the Moon and meet its inhabitants. In 499 AD, the Indian astronomer Aryabhata mentioned in his Aryabhatiya that reflected sunlight is the cause of the shining of the Moon. The astronomer and physicist Alhazen (965–1039) found that sunlight was not reflected from the Moon like a mirror, but that light was emitted from every part of the Moon's sunlit surface in all directions. Shen Kuo (1031–1095) of the Song dynasty created an allegory equating the waxing and waning of the Moon to a round ball of reflective silver that, when doused with white powder and viewed from the side, would appear to be a crescent.
Galileo's sketches of the Moon from Sidereus Nuncius
In Aristotle's (384–322 BC) description of the universe, the Moon marked the boundary between the spheres of the mutable elements (earth, water, air and fire), and the imperishable stars of aether, an influential philosophy that would dominate for centuries. However, in the 2nd century BC, Seleucus of Seleucia correctly theorized that tides were due to the attraction of the Moon, and that their height depends on the Moon's position relative to the Sun. In the same century, Aristarchus computed the size and distance of the Moon from Earth, obtaining a value of about twenty times the radius of Earth for the distance. These figures were greatly improved by Ptolemy (90–168 AD): his values of a mean distance of 59 times Earth's radius and a diameter of 0.292 Earth diameters were close to the correct values of about 60 and 0.273 respectively.[180] Archimedes (287–212 BC) designed a planetarium that could calculate the motions of the Moon and other objects in the Solar System.
During the Middle Ages, before the invention of the telescope, the Moon was increasingly recognised as a sphere, though many believed that it was "perfectly smooth".
In 1609, Galileo Galilei drew one of the first telescopic drawings of the Moon in his book Sidereus Nuncius and noted that it was not smooth but had mountains and craters. Telescopic mapping of the Moon followed: later in the 17th century, the efforts of Giovanni Battista Riccioli and Francesco Maria Grimaldi led to the system of naming of lunar features in use today. The more exact 1834–36 Mappa Selenographica of Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler, and their associated 1837 book Der Mond, the first trigonometrically accurate study of lunar features, included the heights of more than a thousand mountains, and introduced the study of the Moon at accuracies possible in earthly geography. Lunar craters, first noted by Galileo, were thought to be volcanic until the 1870s proposal of Richard Proctor that they were formed by collisions. This view gained support in 1892 from the experimentation of geologist Grove Karl Gilbert, and from comparative studies from 1920 to the 1940s, leading to the development of lunar stratigraphy, which by the 1950s was becoming a new and growing branch of astrogeology.
By spacecraft
20th century
Soviet missions
Luna 2, the first human-made object to reach the surface of the Moon (left) and Soviet Moon rover Lunokhod 1
The Cold War-inspired Space Race between the Soviet Union and the U.S. led to an acceleration of interest in exploration of the Moon. Once launchers had the necessary capabilities, these nations sent unmanned probes on both flyby and impact/lander missions. Spacecraft from the Soviet Union's Luna program were the first to accomplish a number of goals: following three unnamed, failed missions in 1958, the first human-made object to escape Earth's gravity and pass near the Moon was Luna 1; the first human-made object to impact the lunar surface was Luna 2, and the first photographs of the normally occluded far side of the Moon were made by Luna 3, all in 1959.
The first spacecraft to perform a successful lunar soft landing was Luna 9 and the first unmanned vehicle to orbit the Moon was Luna 10, both in 1966. Rock and soil samples were brought back to Earth by three Luna sample return missions (Luna 16 in 1970, Luna 20 in 1972, and Luna 24 in 1976), which returned 0.3 kg total. Two pioneering robotic rovers landed on the Moon in 1970 and 1973 as a part of Soviet Lunokhod programme.
Luna 24 was the last Soviet/Russian mission to the Moon.
United States missions
Earthrise (Apollo 8, 1968, taken by William Anders)
During the late 1950s at the height of the Cold War, the United States Army conducted a classified feasibility study that proposed the construction of a manned military outpost on the Moon called Project Horizon with the potential to conduct a wide range of missions from scientific research to nuclear Earth bombardment. The study included the possibility of conducting a lunar-based nuclear test. The Air Force, which at the time was in competition with the Army for a leading role in the space program, developed its own similar plan called Lunex. However, both these proposals were ultimately passed over as the space program was largely transferred from the military to the civilian agency NASA.
Following President John F. Kennedy's 1961 commitment to a manned moon landing before the end of the decade, the United States, under NASA leadership, launched a series of unmanned probes to develop an understanding of the lunar surface in preparation for manned missions: the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Ranger program produced the first close-up pictures; the Lunar Orbiter program produced maps of the entire Moon; the Surveyor program landed its first spacecraft four months after Luna 9. The manned Apollo program was developed in parallel; after a series of unmanned and manned tests of the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit, and spurred on by a potential Soviet lunar flight, in 1968 Apollo 8 made the first manned mission to lunar orbit. The subsequent landing of the first humans on the Moon in 1969 is seen by many as the culmination of the Space Race.
Neil Armstrong working at the lunar module
Neil Armstrong became the first person to walk on the Moon as the commander of the American mission Apollo 11 by first setting foot on the Moon at 02:56 UTC on 21 July 1969. An estimated 500 million people worldwide watched the transmission by the Apollo TV camera, the largest television audience for a live broadcast at that time. The Apollo missions 11 to 17 (except Apollo 13, which aborted its planned lunar landing) returned 380.05 kilograms (837.87 lb) of lunar rock and soil in 2,196 separate samples. The American Moon landing and return was enabled by considerable technological advances in the early 1960s, in domains such as ablation chemistry, software engineering, and atmospheric re-entry technology, and by highly competent management of the enormous technical undertaking.
Scientific instrument packages were installed on the lunar surface during all the Apollo landings. Long-lived instrument stations, including heat flow probes, seismometers, and magnetometers, were installed at the Apollo 12, 14, 15, 16, and 17 landing sites. Direct transmission of data to Earth concluded in late 1977 because of budgetary considerations, but as the stations' lunar laser ranging corner-cube retroreflector arrays are passive instruments, they are still being used. Ranging to the stations is routinely performed from Earth-based stations with an accuracy of a few centimetres, and data from this experiment are being used to place constraints on the size of the lunar core.
1980s–2000
An artificially coloured mosaic constructed from a series of 53 images taken through three spectral filters by Galileo' s imaging system as the spacecraft flew over the northern regions of the Moon on 7 December 1992.
After the first Moon race there were years of near quietude but starting in the 1990s, many more countries have become involved in direct exploration of the Moon. In 1990, Japan became the third country to place a spacecraft into lunar orbit with its Hiten spacecraft. The spacecraft released a smaller probe, Hagoromo, in lunar orbit, but the transmitter failed, preventing further scientific use of the mission. In 1994, the U.S. sent the joint Defense Department/NASA spacecraft Clementine to lunar orbit. This mission obtained the first near-global topographic map of the Moon, and the first global multispectral images of the lunar surface. This was followed in 1998 by the Lunar Prospector mission, whose instruments indicated the presence of excess hydrogen at the lunar poles, which is likely to have been caused by the presence of water ice in the upper few meters of the regolith within permanently shadowed craters.
India, Japan, China, the United States, and the European Space Agency each sent lunar orbiters, and especially ISRO's Chandrayaan-1 has contributed to confirming the discovery of lunar water ice in permanently shadowed craters at the poles and bound into the lunar regolith. The post-Apollo era has also seen two rover missions: the final Soviet Lunokhod mission in 1973, and China's ongoing Chang'e 3 mission, which deployed its Yutu rover on 14 December 2013. The Moon remains, under the Outer Space Treaty, free to all nations to explore for peaceful purposes.
21st century
Artistic representation of a future Moon colony
The European spacecraft SMART-1, the second ion-propelled spacecraft, was in lunar orbit from 15 November 2004 until its lunar impact on 3 September 2006, and made the first detailed survey of chemical elements on the lunar surface.
The ambitious Chinese Lunar Exploration Program began with Chang'e 1, which successfully orbited the Moon from 5 November 2007 until its controlled lunar impact on 1 March 2009. It obtained a full image map of the Moon. Chang'e 2, beginning in October 2010, reached the Moon more quickly, mapped the Moon at a higher resolution over an eight-month period, then left lunar orbit for an extended stay at the Earth–Sun L2 Lagrangian point, before finally performing a flyby of asteroid 4179 Toutatis on 13 December 2012, and then heading off into deep space. On 14 December 2013, Chang'e 3 landed a lunar lander onto the Moon's surface, which in turn deployed a lunar rover, named Yutu (Chinese: 玉兔; literally "Jade Rabbit"). This was the first lunar soft landing since Luna 24 in 1976, and the first lunar rover mission since Lunokhod 2 in 1973. China intends to launch another rover mission (Chang'e 4) before 2020, followed by a sample return mission (Chang'e 5) soon after.
Between 4 October 2007 and 10 June 2009, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kaguya (Selene) mission, a lunar orbiter fitted with a high-definition video camera, and two small radio-transmitter satellites, obtained lunar geophysics data and took the first high-definition movies from beyond Earth orbit. India's first lunar mission, Chandrayaan I, orbited from 8 November 2008 until loss of contact on 27 August 2009, creating a high resolution chemical, mineralogical and photo-geological map of the lunar surface, and confirming the presence of water molecules in lunar soil. The Indian Space Research Organisation planned to launch Chandrayaan II in 2013, which would have included a Russian robotic lunar rover. However, the failure of Russia's Fobos-Grunt mission has delayed this project, and is now scheduled to be launched no earlier than January 2019.
Copernicus's central peaks as observed by the LRO, 2012
The Ina formation, 2009
The U.S. co-launched the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) and the LCROSS impactor and follow-up observation orbiter on 18 June 2009; LCROSS completed its mission by making a planned and widely observed impact in the crater Cabeus on 9 October 2009, whereas LRO is currently in operation, obtaining precise lunar altimetry and high-resolution imagery. In November 2011, the LRO passed over the large and bright Aristarchus crater. NASA released photos of the crater on 25 December 2011.
Two NASA GRAIL spacecraft began orbiting the Moon around 1 January 2012, on a mission to learn more about the Moon's internal structure. NASA's LADEE probe, designed to study the lunar exosphere, achieved orbit on 6 October 2013.
Upcoming lunar missions include Russia's Luna-Glob: an unmanned lander with a set of seismometers, and an orbiter based on its failed Martian Fobos-Grunt mission. Privately funded lunar exploration has been promoted by the Google Lunar X Prize, announced 13 September 2007, which offers US$20 million to anyone who can land a robotic rover on the Moon and meet other specified criteria. Shackleton Energy Company is building a program to establish operations on the south pole of the Moon to harvest water and supply their Propellant Depots.
NASA began to plan to resume manned missions following the call by U.S. President George W. Bush on 14 January 2004 for a manned mission to the Moon by 2019 and the construction of a lunar base by 2024. The Constellation program was funded and construction and testing begun on a manned spacecraft and launch vehicle, and design studies for a lunar base. However, that program has been cancelled in favor of a manned asteroid landing by 2025 and a manned Mars orbit by 2035. India has also expressed its hope to send a manned mission to the Moon by 2020.
On 28 February 2018, SpaceX, Vodafone, Nokia and Audi announced a collaboration to install a 4G wireless communication network on the Moon, with the aim of streaming live footage on the surface to Earth.
Planned commercial missions
In 2007, the X Prize Foundation together with Google launched the Google Lunar X Prize
to encourage commercial endeavors to the Moon. A prize of $20 million
was to be awarded to the first private venture to get to the Moon with a
robotic lander by the end of March 2018, with additional prizes worth
$10 million for further milestones. As of August 2016, 16 teams were reportedly participating in the competition.
In January 2018 the foundation announced that the prize would go
unclaimed as none of the finalist teams would be able to make a launch
attempt by the deadline.
In August 2016, the US government granted permission to US-based start-up Moon Express to land on the Moon. This marked the first time that a private enterprise was given the right to do so. The decision is regarded as a precedent helping to define regulatory standards for deep-space commercial activity in the future, as thus far companies' operation had been restricted to being on or around Earth.
On November 29, 2018 NASA announced that nine commercial companies would compete to win a contract to send small payloads to the Moon in what is known as Commercial Lunar Payload Services. According to NASA administrator Jim Bridenstine, "We are building a domestic American capability to get back and forth to the surface of the moon."
Astronomy from the Moon
A false-color image of Earth in ultraviolet light taken from the surface of the Moon on the Apollo 16 mission. The day-side reflects a lot of UV light from the Sun, but the night-side shows faint bands of UV emission from the aurora caused by charged particles.
For many years, the Moon has been recognized as an excellent site for telescopes. It is relatively nearby; astronomical seeing is not a concern; certain craters near the poles are permanently dark and cold, and thus especially useful for infrared telescopes; and radio telescopes on the far side would be shielded from the radio chatter of Earth. The lunar soil, although it poses a problem for any moving parts of telescopes, can be mixed with carbon nanotubes and epoxies and employed in the construction of mirrors up to 50 meters in diameter. A lunar zenith telescope can be made cheaply with an ionic liquid.
In April 1972, the Apollo 16 mission recorded various astronomical photos and spectra in ultraviolet with the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph.
Legal status
Although Luna landers scattered pennants of the Soviet Union on the Moon, and U.S. flags were symbolically planted at their landing sites by the Apollo astronauts, no nation claims ownership of any part of the Moon's surface. Russia and the U.S. are party to the 1967 Outer Space Treaty, which defines the Moon and all outer space as the "province of all mankind". This treaty also restricts the use of the Moon to peaceful purposes, explicitly banning military installations and weapons of mass destruction.
The 1979 Moon Agreement
was created to restrict the exploitation of the Moon's resources by any
single nation, but as of November 2016, it has been signed and ratified
by only 18 nations, none of which engages in self-launched human space exploration or has plans to do so. Although several individuals have made claims to the Moon in whole or in part, none of these are considered credible.
In culture
Luna, the Moon, from a 1550 edition of Guido Bonatti's Liber astronomiae
Mythology
Statue of Chandraprabha (means"as charming as moon")-8th Tirthankara in Jainism with the symbol of crescent moon below it.
Sun and Moon with faces (1493 woodcut)
A 5,000-year-old rock carving at Knowth, Ireland, may represent the Moon, which would be the earliest depiction discovered. The contrast between the brighter highlands and the darker maria creates the patterns seen by different cultures as the Man in the Moon, the rabbit and the buffalo, among others. In many prehistoric and ancient cultures, the Moon was personified as a deity or other supernatural phenomenon, and astrological views of the Moon continue to be propagated today.
In Proto-Indo-European religion, the moon was personified as the male god *Meh1not. The ancient Sumerians believed that the Moon was the god Nanna, who was the father of Inanna, the goddess of the planet Venus, and Utu, the god of the sun. Nanna was later known as Sîn, and was particularly associated with magic and sorcery. In Greco-Roman mythology, the Sun and the Moon are represented as male and female, respectively (Helios/Sol and Selene/Luna); this is a development unique to the eastern Mediterranean and traces of an earlier male moon god in the Greek tradition are preserved in the figure of Menelaus.
In Mesopotamian iconography, the crescent was the primary symbol of Nanna-Sîn. In ancient Greek art, the Moon goddess Selene was represented wearing a crescent on her headgear in an arrangement reminiscent of horns. The star and crescent arrangement also goes back to the Bronze Age, representing either the Sun and Moon, or the Moon and planet Venus, in combination. It came to represent the goddess Artemis or Hecate, and via the patronage of Hecate came to be used as a symbol of Byzantium.
An iconographic tradition of representing Sun and Moon with faces developed in the late medieval period.
Calendar
The Moon's regular phases make it a very convenient timepiece, and
the periods of its waxing and waning form the basis of many of the
oldest calendars. Tally sticks, notched bones dating as far back as 20–30,000 years ago, are believed by some to mark the phases of the Moon.
The ~30-day month is an approximation of the lunar cycle.
The English noun month and its cognates in other Germanic languages stem from Proto-Germanic *mǣnṓth-, which is connected to the above-mentioned Proto-Germanic *mǣnōn, indicating the usage of a lunar calendar among the Germanic peoples (Germanic calendar) prior to the adoption of a solar calendar. The PIE root of moon, *méh1nōt, derives from the PIE verbal root *meh1-, "to measure", "indicat[ing] a functional conception of the Moon, i.e. marker of the month" (cf. the English words measure and menstrual), and echoing the Moon's importance to many ancient cultures in measuring time (see Latin mensis and Ancient Greek μείς (meis) or μήν (mēn), meaning "month").
Most historical calendars are lunisolar. The 7th-century Islamic calendar is an exceptional example of a purely lunar calendar. Months are traditionally determined by the visual sighting of the hilal, or earliest crescent moon, over the horizon.
Moonrise, 1884, picture by Stanisław Masłowski (National Museum, Kraków, Gallery of Sukiennice Museum)
Lunacy
The Moon has long been associated with insanity and irrationality; the words lunacy and lunatic (popular shortening loony) are derived from the Latin name for the Moon, Luna. Philosophers Aristotle and Pliny the Elder
argued that the full moon induced insanity in susceptible individuals,
believing that the brain, which is mostly water, must be affected by the
Moon and its power over the tides, but the Moon's gravity is too slight
to affect any single person. Even today, people who believe in a lunar effect
claim that admissions to psychiatric hospitals, traffic accidents,
homicides or suicides increase during a full moon, but dozens of studies
invalidate these claims.