In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics and is used to construct physical models of subatomic particles (in particle physics) and quasiparticles (in condensed matter physics).
QFT treats particles as excited states (also called quanta) of their underlying fields,
which are—in a sense—more fundamental than the basic particles.
Interactions between particles are described by interaction terms in the
Lagrangian involving their corresponding fields. Each interaction can be visually represented by Feynman diagrams, which are formal computational tools, in the process of relativistic perturbation theory.
History
As
a successful theoretical framework today, quantum field theory emerged
from the work of generations of theoretical physicists spanning much of
the 20th century. Its development began in the 1920s with the
description of interactions between light and electrons, culminating in the first quantum field theory — quantum electrodynamics.
A major theoretical obstacle soon followed with the appearance and
persistence of various infinities in perturbative calculations, a
problem only resolved in the 1950s with the invention of the renormalization procedure. A second major barrier came with QFT's apparent inability to describe the weak and strong interactions, to the point where some theorists called for the abandonment of the field theoretic approach. The development of gauge theory and the completion of the Standard Model in the 1970s led to a renaissance of quantum field theory.
Theoretical background
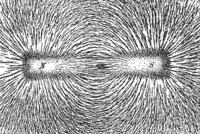
Magnetic field lines visualized using iron filings.
When a piece of paper is sprinkled with iron filings and placed above a
bar magnet, the filings align according to the direction of the
magnetic field, forming arcs.
Quantum field theory is the result of the combination of classical field theory, quantum mechanics, and special relativity. A brief overview of these theoretical precursors is in order.
The earliest successful classical field theory is one that emerged from Newton's law of universal gravitation, despite the complete absence of the concept of fields from his 1687 treatise Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica. The force of gravity as described by Newton is an "action at a distance" — its effects on faraway objects are instantaneous, no matter the distance. In an exchange of letters with Richard Bentley,
however, Newton stated that "it is inconceivable that inanimate brute
matter should, without the mediation of something else which is not
material, operate upon and affect other matter without mutual contact."
It was not until the 18th century that mathematical physicists
discovered a convenient description of gravity based on fields — a
numerical quantity (a vector (mathematics and physics))
assigned to every point in space indicating the action of gravity on
any particle at that point. However, this was considered merely a
mathematical trick.
Fields began to take on an existence of their own with the development of electromagnetism in the 19th century. Michael Faraday
coined the English term "field" in 1845. He introduced fields as
properties of space (even when it is devoid of matter) having physical
effects. He argued against "action at a distance", and proposed that
interactions between objects occur via space-filling "lines of force".
This description of fields remains to this day.
The theory of classical electromagnetism was completed in 1862 with Maxwell's equations, which described the relationship between the electric field, the magnetic field, electric current, and electric charge. Maxwell's equations implied the existence of electromagnetic waves,
a phenomenon whereby electric and magnetic fields propagate from one
spatial point to another at a finite speed, which turns out to be the speed of light. Action-at-a-distance was thus conclusively refuted.
Despite the enormous success of classical electromagnetism, it was unable to account for the discrete lines in atomic spectra, nor for the distribution of blackbody radiation in different wavelengths. Max Planck's
study of blackbody radiation marked the beginning of quantum mechanics.
He treated atoms, which absorb and emit electromagnetic radiation, as
tiny oscillators
with the crucial property that their energies can only take on a series
of discrete, rather than continuous, values. These are known as quantum harmonic oscillators. This process of restricting energies to discrete values is called quantization. Building on this idea, Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 an explanation for the photoelectric effect, that light is composed of individual packets of energy called photons
(the quanta of light). This implied that the electromagnetic radiation,
while being waves in the classical electromagnetic field, also exists
in the form of particles.
In 1913, Niels Bohr introduced the Bohr model of atomic structure, wherein electrons
within atoms can only take on a series of discrete, rather than
continuous, energies. This is another example of quantization. The Bohr
model successfully explained the discrete nature of atomic spectral
lines. In 1924, Louis de Broglie proposed the hypothesis of wave-particle duality, that microscopic particles exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties under different circumstances. Uniting these scattered ideas, a coherent discipline, quantum mechanics, was formulated between 1925 and 1926, with important contributions from de Broglie, Werner Heisenberg, Max Born, Erwin Schrödinger, Paul Dirac, and Wolfgang Pauli.
In the same year as his paper on the photoelectric effect, Einstein published his theory of special relativity, built on Maxwell's electromagnetism. New rules, called Lorentz transformation,
were given for the way time and space coordinates of an event change
under changes in the observer's velocity, and the distinction between
time and space was blurred. It was proposed that all physical laws must be the same for observers at different velocities, i.e. that physical laws be invariant under Lorentz transformations.
Two difficulties remained. Observationally, the Schrödinger equation underlying quantum mechanics could explain the stimulated emission
of radiation from atoms, where an electron emits a new photon under the
action of an external electromagnetic field, but it was unable to
explain spontaneous emission,
where an electron spontaneously decreases in energy and emits a photon
even without the action of an external electromagnetic field.
Theoretically, the Schrödinger equation could not describe photons and
was inconsistent with the principles of special relativity — it treats
time as an ordinary number while promoting spatial coordinates to linear operators.
Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum
field theory naturally began with the study of electromagnetic
interactions, as the electromagnetic field was the only known classical
field as of the 1920s.
Through the works of Born, Heisenberg, and Pascual Jordan in 1925-1926, a quantum theory of the free electromagnetic field (one with no interactions with matter) was developed via canonical quantization by treating the electromagnetic field as a set of quantum harmonic oscillators.
With the exclusion of interactions, however, such a theory was yet
incapable of making quantitative predictions about the real world.
In his seminal 1927 paper The quantum theory of the emission and absorption of radiation, Dirac coined the term quantum electrodynamics (QED), a theory that adds upon the terms describing the free electromagnetic field an additional interaction term between electric current density and the electromagnetic vector potential. Using first-order perturbation theory, he successfully explained the phenomenon of spontaneous emission. According to the uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics, quantum harmonic oscillators cannot remain stationary, but they have a non-zero minimum energy and must always be oscillating, even in the lowest energy state (the ground state). Therefore, even in a perfect vacuum, there remains an oscillating electromagnetic field having zero-point energy. It is this quantum fluctuation of electromagnetic fields in the vacuum that "stimulates" the spontaneous emission of radiation by electrons in atoms. Dirac's theory was hugely successful in explaining both the emission and absorption of radiation by atoms; by applying second-order perturbation theory, it was able to account for the scattering of photons, resonance fluorescence, as well as non-relativistic Compton scattering. Nonetheless, the application of higher-order perturbation theory was plagued with problematic infinities in calculations.
In 1928, Dirac wrote down a wave equation that described relativistic electrons — the Dirac equation. It had the following important consequences: the spin of an electron is 1/2; the electron g-factor is 2; it led to the correct Sommerfeld formula for the fine structure of the hydrogen atom; and it could be used to derive the Klein-Nishina formula
for relativistic Compton scattering. Although the results were
fruitful, the theory also apparently implied the existence of negative
energy states, which would cause atoms to be unstable, since they could
always decay to lower energy states by the emission of radiation.
The prevailing view at the time was that the world was composed
of two very different ingredients: material particles (such as
electrons) and quantum fields (such as photons). Material particles were
considered to be eternal, with their physical state described by the
probabilities of finding each particle in any given region of space or
range of velocities. On the other hand photons were considered merely
the excited states
of the underlying quantized electromagnetic field, and could be freely
created or destroyed. It was between 1928 and 1930 that Jordan, Eugene Wigner, Heisenberg, Pauli, and Enrico Fermi
discovered that material particles could also be seen as excited states
of quantum fields. Just as photons are excited states of the quantized
electromagnetic field, so each type of particle had its corresponding
quantum field: an electron field, a proton field, etc. Given enough
energy, it would now be possible to create material particles. Building
on this idea, Fermi proposed in 1932 an explanation for β decay known as Fermi's interaction. Atomic nuclei do not contain electrons per se,
but in the process of decay, an electron is created out of the
surrounding electron field, analogous to the photon created from the
surrounding electromagnetic field in the radiative decay of an excited
atom.
It was realized in 1929 by Dirac and others that negative energy states implied by the Dirac equation could be removed by assuming the existence of particles with the same mass as electrons but opposite electric charge. This not only ensured the stability of atoms, but it was also the first proposal of the existence of antimatter. Indeed, the evidence for positrons was discovered in 1932 by Carl David Anderson in cosmic rays. With enough energy, such as by absorbing a photon, an electron-positron pair could be created, a process called pair production; the reverse process, annihilation, could also occur with the emission of a photon. This showed that particle numbers need not be fixed during an interaction. Historically, however, positrons were at first thought of as "holes" in an infinite electron sea, rather than a new kind of particle, and this theory was referred to as the Dirac hole theory. QFT naturally incorporated antiparticles in its formalism.
Infinities and renormalization
Robert Oppenheimer showed in 1930 that higher-order perturbative calculations in QED always resulted in infinite quantities, such as the electron self-energy and the vacuum zero-point energy of the electron and photon fields,
suggesting that the computational methods at the time could not
properly deal with interactions involving photons with extremely high
momenta. It was not until 20 years later that a systematic approach to remove such infinities was developed.
A series of papers were published between 1934 and 1938 by Ernst Stueckelberg
that established a relativistically invariant formulation of QFT. In
1947, Stueckelberg also independently developed a complete
renormalization procedure. Unfortunately, such achievements were not
understood and recognized by the theoretical community.
Faced with these infinities, John Archibald Wheeler and Heisenberg proposed, in 1937 and 1943 respectively, to supplant the problematic QFT with the so-called S-matrix theory.
Since the specific details of microscopic interactions are inaccessible
to observations, the theory should only attempt to describe the
relationships between a small number of observables (e.g. the energy of an atom) in an interaction, rather than be concerned with the microscopic minutiae of the interaction. In 1945, Richard Feynman and Wheeler daringly suggested abandoning QFT altogether and proposed action-at-a-distance as the mechanism of particle interactions.
In 1947, Willis Lamb and Robert Retherford measured the minute difference in the 2S1/2 and 2P1/2 energy levels of the hydrogen atom, also called the Lamb shift. By ignoring the contribution of photons whose energy exceeds the electron mass, Hans Bethe successfully estimated the numerical value of the Lamb shift. Subsequently, Norman Myles Kroll, Lamb, James Bruce French, and Victor Weisskopf
again confirmed this value using an approach in which infinities
cancelled other infinities to result in finite quantities. However, this
method was clumsy and unreliable and could not be generalized to other
calculations.
The breakthrough eventually came around 1950 when a more robust method for eliminating infinities was developed Julian Schwinger, Feynman, Freeman Dyson, and Shinichiro Tomonaga.
The main idea is to replace the initial, so-called "bare", parameters
(mass, electric charge, etc.), which have no physical meaning, by their
finite measured values. To cancel the apparently infinite parameters,
one has to introduce additional, infinite, "counterterms" into the
Lagrangian. This systematic computational procedure is known as renormalization and can be applied to arbitrary order in perturbation theory.
By applying the renormalization procedure, calculations were finally made to explain the electron's anomalous magnetic moment (the deviation of the electron g-factor from 2) and vacuum polarisation.
These results agreed with experimental measurements to a remarkable
degree, thus marking the end of a "war against infinities".
At the same time, Feynman introduced the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics and Feynman diagrams.
The latter can be used to visually and intuitively organize and to help
compute terms in the perturbative expansion. Each diagram can be
interpreted as paths of particles in an interaction, with each vertex
and line having a corresponding mathematical expression, and the product
of these expressions gives the scattering amplitude of the interaction represented by the diagram.
It was with the invention of the renormalization procedure and
Feynman diagrams that QFT finally arose as a complete theoretical
framework.
Non-renormalizability
Given
the tremendous success of QED, many theorists believed, in the few
years after 1949, that QFT could soon provide an understanding of all
microscopic phenomena, not only the interactions between photons,
electrons, and positrons. Contrary to this optimism, QFT entered yet
another period of depression that lasted for almost two decades.
The first obstacle was the limited applicability of the
renormalization procedure. In perturbative calculations in QED, all
infinite quantities could be eliminated by redefining a small (finite)
number of physical quantities (namely the mass and charge of the
electron). Dyson proved in 1949 that this is only possible for a small
class of theories called "renormalizable theories", of which QED is an
example. However, most theories, including the Fermi theory of the weak interaction,
are "non-renormalizable". Any perturbative calculation in these
theories beyond the first order would result in infinities that could
not be removed by redefining a finite number of physical quantities.
The second major problem stemmed from the limited validity of the
Feynman diagram method, which are based on a series expansion in
perturbation theory. In order for the series to converge and low-order
calculations to be a good approximation, the coupling constant, in which the series is expanded, must be a sufficiently small number. The coupling constant in QED is the fine-structure constant α ≈ 1/137,
which is small enough that only the simplest, lowest order, Feynman
diagrams need to be considered in realistic calculations. In contrast,
the coupling constant in the strong interaction
is roughly of the order of one, making complicated, higher order,
Feynman diagrams just as important as simple ones. There was thus no way
of deriving reliable quantitative predictions for the strong
interaction using perturbative QFT methods.
With these difficulties looming, many theorists began to turn away from QFT. Some focused on symmetry principles and conservation laws,
while others picked up the old S-matrix theory of Wheeler and
Heisenberg. QFT was used heuristically as guiding principles, but not as
a basis for quantitative calculations.
Standard Model
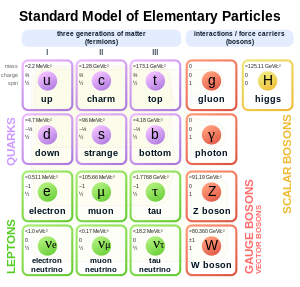
Elementary particles of the Standard Model: six types of matter quarks, four types of gauge bosons that carry fundamental interactions, as well as the Higgs boson, which endow elementary particles with mass.
In 1954, Yang Chen-Ning and Robert Mills generalized the local symmetry of QED, leading to non-Abelian gauge theories (also known as Yang-Mills theories), which are based on more complicated local symmetry groups.
In QED, (electrically) charged particles interact via the exchange of
photons, while in non-Abelian gauge theory, particles carrying a new
type of "charge" interact via the exchange of massless gauge bosons. Unlike photons, these gauge bosons themselves carry charge.
Sheldon Glashow developed a non-Abelian gauge theory that unified the electromagnetic and weak interactions in 1960. In 1964, Abdul Salam and John Clive Ward arrived at the same theory through a different path. This theory, nevertheless, was non-renormalizable.
Peter Higgs, Robert Brout, and François Englert proposed in 1964 that the gauge symmetry in Yang-Mills theories could be broken by a mechanism called spontaneous symmetry breaking, through which originally massless gauge bosons could acquire mass.
By combining the earlier theory of Glashow, Salam, and Ward with the idea of spontaneous symmetry breaking, Steven Weinberg wrote down in 1967 a theory describing electroweak interactions between all leptons and the effects of the Higgs boson. His theory was at first mostly ignored, until it was brought back to light in 1971 by Gerard 't Hooft's
proof that non-Abelian gauge theories are renormalizable. The
electroweak theory of Weinberg and Salam was extended from leptons to quarks in 1970 by Glashow, John Iliopoulos, and Luciano Maiani, marking its completion.
Harald Fritzsch, Murray Gell-Mann, and Heinrich Leutwyler discovered in 1971 that certain phenomena involving the strong interaction could also be explained by non-Abelian gauge theory. Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) was born. In 1973, David Gross, Frank Wilczek, and Hugh David Politzer showed that non-Abelian gauge theories are "asymptotically free",
meaning that under renormalization, the coupling constant of the strong
interaction decreases as the interaction energy increases. (Similar
discoveries had been made numerous times prior, but they had been
largely ignored.)
Therefore, at least in high-energy interactions, the coupling constant
in QCD becomes sufficiently small to warrant a perturbative series
expansion, making quantitative predictions for the strong interaction
possible.
These theoretical breakthroughs brought about a renaissance in
QFT. The full theory, which includes the electroweak theory and
chromodynamics, is referred to today as the Standard Model of elementary particles. The Standard Model successfully describes all fundamental interactions except gravity, and its many predictions have been met with remarkable experimental confirmation in subsequent decades. The Higgs boson, central to the mechanism of spontaneous symmetry breaking, was finally detected in 2012 at CERN, marking the complete verification of the existence of all constituents of the Standard Model.
Other developments
The 1970s saw the development of non-perturbative methods in non-Abelian gauge theories. The 't Hooft-Polyakov monopole was discovered by 't Hooft and Alexander Polyakov, flux tubes by Holger Bech Nielsen and Poul Olesen, and instantons by Polyakov et al.. These objects are inaccessible through perturbation theory.
Supersymmetry also appeared in the same period. The first supersymmetric QFT in four dimensions was built by Yuri Golfand and Evgeny Likhtman in 1970, but their result failed to garner widespread interest due to the Iron Curtain. Supersymmetry only took off in the theoretical community after the work of Julius Wess and Bruno Zumino in 1973.
Among the four fundamental interactions, gravity remains the only
one that lacks a consistent QFT description. Various attempts at a
theory of quantum gravity led to the development of string theory, itself a type of two-dimensional QFT with conformal symmetry. Joël Scherk and John Schwarz first proposed in 1974 that string theory could be the quantum theory of gravity.
Condensed matter physics
Although
quantum field theory arose from the study of interactions between
elementary particles, it has been successfully applied to other physical
systems, particularly to many-body systems in condensed matter physics.
Historically, the Higgs mechanism of spontaneous symmetry breaking was a result of Yoichiro Nambu's application of superconductor theory to elementary particles, while the concept of renormalization came out of the study of second-order phase transitions in matter.
Soon after the introduction of photons, Einstein performed the
quantization procedure on vibrations in a crystal, leading to the first quasiparticle — phonons.
Lev Landau claimed that low-energy excitations in many condensed matter
systems could be described in terms of interactions between a set of
quasiparticles. The Feynman diagram method of QFT was naturally well
suited to the analysis of various phenomena in condensed matter systems.
Gauge theory is used to describe the quantization of magnetic flux in superconductors, the resistivity in the quantum Hall effect, as well as the relation between frequency and voltage in the AC Josephson effect.
Principles
For simplicity, natural units are used in the following sections, in which the reduced Planck constant ħ and the speed of light c are both set to one.
Classical fields
A classical field is a function of spatial and time coordinates. Examples include the gravitational field in Newtonian gravity g(x, t) and the electric field E(x, t) and magnetic field B(x, t) in classical electromagnetism.
A classical field can be thought of as a numerical quantity assigned to
every point in space that changes in time. Hence, it has infinite degrees of freedom.
Many phenomena exhibiting quantum mechanical properties cannot be explained by classical fields alone. Phenomena such as the photoelectric effect are best explained by discrete particles (photons),
rather than a spatially continuous field. The goal of quantum field
theory is to describe various quantum mechanical phenomena using a
modified concept of fields.
Canonical quantisation and path integrals are two common formulations of QFT. To motivate the fundamentals of QFT, an overview of classical field theory is in order.
The simplest classical field is a real scalar field — a real number at every point in space that changes in time. It is denoted as ϕ(x, t), where x is the position vector, and t is the time. Suppose the Lagrangian of the field is
where is the time-derivative of the field, ∇ is the divergence operator, and m is a real parameter (the "mass" of the field). Applying the Euler–Lagrange equation on the Lagrangian:
we obtain the equations of motion for the field, which describe the way it varies in time and space:
This is known as the Klein–Gordon equation.
The Klein–Gordon equation is a wave equation, so its solutions can be expressed as a sum of normal modes (obtained via Fourier transform) as follows:
where a is a complex number (normalised by convention), * denotes complex conjugation, and ωp is the frequency of the normal mode:
Thus each normal mode corresponding to a single p can be seen as a classical harmonic oscillator with frequency ωp.
Canonical quantisation
The quantization procedure for the above classical field is analogous to the promotion of a classical harmonic oscillator to a quantum harmonic oscillator.
The displacement of a classical harmonic oscillator is described by
where a is a complex number (normalised by convention), and ω is the oscillator's frequency. Note that x
is the displacement of a particle in simple harmonic motion from the
equilibrium position, which should not be confused with the spatial
label x of a field.
Complex numbers a and a* are replaced by the annihilation operator and the creation operator , respectively, where † denotes Hermitian conjugation. The commutation relation between the two is
The vacuum state , which is the lowest energy state, is defined by
Any quantum state of a single harmonic oscillator can be obtained from by successively applying the creation operator :
By the same token, the aforementioned real scalar field ϕ, which corresponds to x in the single harmonic oscillator, is also promoted to an operator , while ap and ap* are replaced by the annihilation operator and the creation operator for a particular p, respectively:
Their commutation relations are:
Any quantum state of the field can be obtained from by successively applying creation operators , e.g.
Although the field appearing in the Lagrangian is spatially
continuous, the quantum states of the field are discrete. While the
state space of a single quantum harmonic oscillator contains all the
discrete energy states of one oscillating particle, the state space of a
quantum field contains the discrete energy levels of an arbitrary
number of particles. The latter space is known as a Fock space, which can account for the fact that particle numbers are not fixed in relativistic quantum systems.
The process of quantizing an arbitrary number of particles instead of a
single particle is often also called second quantization.
The preceding procedure is a direct application of
non-relativistic quantum mechanics and can be used to quantise (complex)
scalar fields, Dirac fields, vector fields (e.g. the electromagnetic field), and even strings.
However, creation and annihilation operators are only well defined in
the simplest theories that contain no interactions (so-called free
theory). In the case of the real scalar field, the existence of these
operators was a consequence of the decomposition of solutions of the
classical equations of motion into a sum of normal modes. To perform
calculations on any realistic interacting theory, perturbation theory would be necessary.
The Lagrangian of any quantum field in nature would contain
interaction terms in addition to the free theory terms. For example, a quartic interaction term could be introduced to the Lagrangian of the real scalar field:
where μ is a spacetime index, , etc. The summation over the index μ has been omitted following the Einstein notation. If the parameter λ
is sufficiently small, then the interacting theory described by the
above Lagrangian can be considered as a small perturbation from the free
theory.
Path integrals
The path integral formulation of QFT is concerned with the direct computation of the scattering amplitude of a certain interaction process, rather than the establishment of operators and state spaces. To calculate the probability amplitude for a system to evolve from some initial state at time t = 0 to some final state at t = T, the total time T is divided into N
small intervals. The overall amplitude is the product of the amplitude
of evolution within each interval, integrated over all intermediate
states. Let H be the Hamiltonian (i.e. generator of time evolution), then
Taking the limit N → ∞, the above product of integrals becomes the Feynman path integral:
where L is the Lagrangian involving ϕ and its derivatives with respect to spatial and time coordinates, obtained from the Hamiltonian H via Legendre transform. The initial and final conditions of the path integral are respectively
In other words, the overall amplitude is the sum over the amplitude
of every possible path between the initial and final states, where the
amplitude of a path is given by the exponential in the integrand.
Two-point correlation function
Now we assume that the theory contains interactions whose Lagrangian terms are a small perturbation from the free theory.
In calculations, one often encounters such expressions:
where x and y are position four-vectors, T is the time ordering operator (namely, it orders x and y according to their time-component, later time on the left and earlier time on the right), and is the ground state (vacuum state) of the interacting theory. This expression, known as the two-point correlation function or the two-point Green's function, represents the probability amplitude for the field to propagate from y to x.
In canonical quantization, the two-point correlation function can be written as:
where ε is an infinitesimal number, ϕI is the field operator under the free theory, and HI is the interaction Hamiltonian term. For the ϕ4 theory, it is
Since λ is a small parameter, the exponential function exp can be expanded into a Taylor series in λ
and computed term by term. This equation is useful in that it expresses
the field operator and ground state in the interacting theory, which
are difficult to define, in terms of their counterparts in the free
theory, which are well defined.
In the path integral formulation, the two-point correlation function can be written as:
where
is the Lagrangian density. As in the previous paragraph, the
exponential factor involving the interaction term can also be expanded
as a series in λ.
According to Wick's theorem, any n-point
correlation function in the free theory can be written as a sum of
products of two-point correlation functions. For example,
Since correlation functions in the interacting theory can be
expressed in terms of those in the free theory, only the latter need to
be evaluated in order to calculate all physical quantities in the
(perturbative) interacting theory.
Either through canonical quantization or path integrals, one can obtain:
This is known as the Feynman propagator for the real scalar field.
Feynman diagram
Correlation functions in the interacting theory can be written as a
perturbation series. Each term in the series is a product of Feynman
propagators in the free theory and can be represented visually by a Feynman diagram. For example, the λ1 term in the two-point correlation function in the ϕ4 theory is
After applying Wick's theorem, one of the terms is
whose corresponding Feynman diagram is
Every point corresponds to a single ϕ field factor. Points labelled with x and y are called external points, while those in the interior are called internal points or vertices (there is one in this diagram). The value of the corresponding term can be obtained from the diagram by following "Feynman rules": assign to every vertex and the Feynman propagator to every line with end points x1 and x2. The product of factors corresponding to every element in the diagram, divided by the "symmetry factor" (2 for this diagram), gives the expression for the term in the perturbation series.
In order to compute the n-point correlation function to the k-th order, list all valid Feynman diagrams with n external points and k or fewer vertices, and then use Feynman rules to obtain the expression for each term. To be precise,
is equal to the sum of (expressions corresponding to) all connected diagrams with n
external points. (Connected diagrams are those in which every vertex is
connected to an external point through lines. Components that are
totally disconnected from external lines are sometimes called "vacuum
bubbles".) In the ϕ4 interaction theory discussed above, every vertex must have four legs.
In realistic applications, the scattering amplitude of a certain interaction or the decay rate of a particle can be computed from the S-matrix, which itself can be found using the Feynman diagram method.
Feynman diagrams devoid of "loops" are called tree-level diagrams, which describe the lowest-order interaction processes; those containing n loops are referred to as n-loop diagrams, which describe higher-order contributions, or radiative corrections, to the interaction. Lines whose end points are vertices can be thought of as the propagation of virtual particles.
Renormalisation
Feynman rules can be used to directly evaluate tree-level diagrams.
However, naïve computation of loop diagrams such as the one shown above
will result in divergent momentum integrals, which seems to imply that
almost all terms in the perturbative expansion are infinite. The renormalisation procedure is a systematic process for removing such infinities.
Parameters appearing in the Lagrangian, such as the mass m and the coupling constant λ, have no physical meaning — m, λ, and the field strength ϕ
are not experimentally measurable quantities and are referred to here
as the bare mass, bare coupling constant, and bare field, respectively.
The physical mass and coupling constant are measured in some interaction
process and are generally different from the bare quantities. While
computing physical quantities from this interaction process, one may
limit the domain of divergent momentum integrals to be below some
momentum cut-off Λ, obtain expressions for the physical quantities, and then take the limit Λ → ∞. This is an example of regularisation, a class of methods to treat divergences in QFT, with Λ being the regulator.
The approach illustrated above is called bare perturbation
theory, as calculations involve only the bare quantities such as mass
and coupling constant. A different approach, called renormalised
perturbation theory, is to use physically meaningful quantities from the
very beginning. In the case of ϕ4 theory, the field strength is first redefined:
where ϕ is the bare field, ϕr is the renormalised field, and Z is a constant to be determined. The Lagrangian density becomes:
where mr and λr are the experimentally measurable, renormalised, mass and coupling constant, respectively, and
are constants to be determined. The first three terms are the ϕ4
Lagrangian density written in terms of the renormalised quantities,
while the latter three terms are referred to as "counterterms". As the
Lagrangian now contains more terms, so the Feynman diagrams should
include additional elements, each with their own Feynman rules. The
procedure is outlined as follows. First select a regularisation scheme
(such as the cut-off regularisation introduced above or dimensional regularization); call the regulator Λ. Compute Feynman diagrams, in which divergent terms will depend on Λ. Then, define δZ, δm, and δλ
such that Feynman diagrams for the counterterms will exactly cancel the
divergent terms in the normal Feynman diagrams when the limit Λ → ∞ is taken. In this way, meaningful finite quantities are obtained.
It is only possible to eliminate all infinities to obtain a finite result in renormalisable theories, whereas in non-renormalisable theories infinities cannot be removed by the redefinition of a small number of parameters. The Standard Model of elementary particles is a renormalisable QFT, while quantum gravity is non-renormalisable.
Renormalisation group
The renormalisation group, developed by Kenneth Wilson,
is a mathematical apparatus used to study the changes in physical
parameters (coefficients in the Lagrangian) as the system is viewed at
different scales. The way in which each parameter changes with scale is described by its β function. Correlation functions, which underlie quantitative physical predictions, change with scale according to the Callan–Symanzik equation.
As an example, the coupling constant in QED, namely the elementary charge e, has the following β function:
where Λ is the energy scale under which the measurement of e is performed. This differential equation implies that the observed elementary charge increases as the scale increases. The renormalized coupling constant, which changes with the energy scale, is also called the running coupling constant.
The coupling constant g in quantum chromodynamics, a non-Abelian gauge theory based on the symmetry group SU(3), has the following β function:
where Nf is the number of quark flavors. In the case where Nf ≤ 16 (the Standard Model has Nf = 6), the coupling constant g
decreases as the energy scale increases. Hence, while the strong
interaction is strong at low energies, it becomes very weak in
high-energy interactions, a phenomenon known as asymptotic freedom.
Conformal field theories (CFTs) are special QFTs that admit conformal symmetry. They are insensitive to changes in the scale, as all their coupling constants have vanishing β function. (The converse is not true, however — the vanishing of all β functions does not imply conformal symmetry of the theory.) Examples include string theory and N = 4 supersymmetric Yang–Mills theory.
According to Wilson's picture, every QFT is fundamentally accompanied by its energy cut-off Λ, i.e. that the theory is no longer valid at energies higher than Λ, and all degrees of freedom above the scale Λ
are to be omitted. For example, the cut-off could be the inverse of the
atomic spacing in a condensed matter system, and in elementary particle
physics it could be associated with the fundamental "graininess" of
spacetime caused by quantum fluctuations in gravity. The cut-off scale
of theories of particle interactions lies far beyond current
experiments. Even if the theory were very complicated at that scale, as
long as its couplings are sufficiently weak, it must be described at low
energies by a renormalisable effective field theory.
The difference between renormalisable and non-renormalisable theories
is that the former are insensitive to details at high energies, whereas
the latter do depend of them.
According to this view, non-renormalisable theories are to be seen as
low-energy effective theories of a more fundamental theory. The failure
to remove the cut-off Λ from calculations in such a theory merely indicates that new physical phenomena appear at scales above Λ, where a new theory is necessary.
Other theories
The quantisation and renormalisation procedures outlined in the preceding sections are performed for the free theory and ϕ4 theory of the real scalar field. A similar process can be done for other types of fields, including the complex scalar field, the vector field, and the Dirac field, as well as other types of interaction terms, including the electromagnetic interaction and the Yukawa interaction.
As an example, quantum electrodynamics contains a Dirac field ψ representing the electron field and a vector field Aμ representing the electromagnetic field (photon field). (Despite its name, the quantum electromagnetic "field" actually corresponds to the classical electromagnetic four-potential, rather than the classical electric and magnetic fields.) The full QED Lagrangian density is:
where γμ are Dirac matrices, , and is the electromagnetic field strength. The parameters in this theory are the (bare) electron mass m and the (bare) elementary charge e.
The first and second terms in the Lagrangian density correspond to the
free Dirac field and free vector fields, respectively. The last term
describes the interaction between the electron and photon fields, which
is treated as a perturbation from the free theories.
Shown above is an example of a tree-level Feynman diagram in QED. It describes an electron and a positron annihilating, creating an off-shell photon, and then decaying into a new pair of electron and positron. Time runs from left to right. Arrows pointing forward in time represent the propagation of positrons, while those pointing backward in time represent the propagation of electrons. A wavy line represents the propagation of a photon. Each vertex in QED Feynman diagrams must have an incoming and an outgoing fermion (positron/electron) leg as well as a photon leg.
Gauge symmetry
If the following transformation to the fields is performed at every spacetime point x (a local transformation), then the QED Lagrangian remains unchanged, or invariant:
where α(x) is any function of spacetime coordinates. If a theory's Lagrangian (or more precisely the action) is invariant under a certain local transformation, then the transformation is referred to as a gauge symmetry of the theory. Gauge symmetries form a group at every spacetime point. In the case of QED, the successive application of two different local symmetry transformations and is yet another symmetry transformation . For any α(x), is an element of the U(1) group, thus QED is said to have U(1) gauge symmetry. The photon field Aμ may be referred to as the U(1) gauge boson.
U(1) is an Abelian group, meaning that the result is the same regardless of the order in which its elements are applied. QFTs can also be built on non-Abelian groups, giving rise to non-Abelian gauge theories (also known as Yang–Mills theories). Quantum chromodynamics, which describes the strong interaction, is a non-Abelian gauge theory with an SU(3) gauge symmetry. It contains three Dirac fields ψi, i = 1,2,3 representing quark fields as well as eight vector fields Aa,μ, a = 1,...,8 representing gluon fields, which are the SU(3) gauge bosons. The QCD Lagrangian density is:
where Dμ is the gauge covariant derivative:
where g is the coupling constant, ta are the eight generators of SU(3) in the fundamental representation (3×3 matrices),
and fabc are the structure constants of SU(3). Repeated indices i,j,a are implicitly summed over following Einstein notation. This Lagrangian is invariant under the transformation:
where U(x) is an element of SU(3) at every spacetime point x:
The preceding discussion of symmetries is on the level of the
Lagrangian. In other words, these are "classical" symmetries. After
quantisation, some theories will no longer exhibit their classical
symmetries, a phenomenon called anomaly. For instance, in the path integral formulation, despite the invariance of the Lagrangian density under a certain local transformation of the fields, the measure of the path integral may change.
For a theory describing nature to be consistent, it must not contain
any anomaly in its gauge symmetry. The Standard Model of elementary
particles is a gauge theory based on the group SU(3) × SU(2) × U(1), in which all anomalies exactly cancel.
The theoretical foundation of general relativity, the equivalence principle, can also be understood as a form of gauge symmetry, making general relativity a gauge theory based on the Lorentz group.
Noether's theorem states that every continuous symmetry, i.e. the parameter in the symmetry transformation being continuous rather than discrete, leads to a corresponding conservation law. For example, the U(1) symmetry of QED implies charge conservation.
Gauge transformations do not relate distinct quantum states.
Rather, it relates two equivalent mathematical descriptions of the same
quantum state. As an example, the photon field Aμ, being a four-vector,
has four apparent degrees of freedom, but the actual state of a photon
is described by its two degrees of freedom corresponding to the polarisation. The remaining two degrees of freedom are said to be "redundant" — apparently different ways of writing Aμ
can be related to each other by a gauge transformation and in fact
describe the same state of the photon field. In this sense, gauge
invariance is not a "real" symmetry, but are a reflection of the
"redundancy" of the chosen mathematical description.
To account for the gauge redundancy in the path integral formulation, one must perform the so-called Faddeev–Popov gauge fixing
procedure. In non-Abelian gauge theories, such a procedure introduces
new fields called "ghosts". Particles corresponding to the ghost fields
are called ghost particles, which cannot be detected externally. A more rigorous generalisation of the Faddeev–Popov procedure is given by BRST quantization.
Spontaneous symmetry breaking
Spontaneous symmetry breaking is a mechanism whereby the symmetry of the Lagrangian is violated by the system described by it.
To illustrate the mechanism, consider a linear sigma model containing N real scalar fields, described by the Lagrangian density:
The lowest energy state (ground state or vacuum state) of the classical theory is any uniform field ϕ0 satisfying
Without loss of generality, let the ground state be in the N-th direction:
The original N fields can be rewritten as:
and the original Lagrangian density as:
where k = 1,...,N-1. The original O(N) global symmetry is no longer manifest, leaving only the subgroup O(N-1). The larger symmetry before spontaneous symmetry breaking is said to be "hidden" or spontaneously broken.
Goldstone's theorem
states that under spontaneous symmetry breaking, every broken
continuous global symmetry leads to a massless field called the
Goldstone boson. In the above example, O(N) has N(N-1)/2 continuous symmetries (the dimension of its Lie algebra), while O(N-1) has (N-1)(N-2)/2. The number of broken symmetries is their difference, N-1, which corresponds to the N-1 massless fields πk.
On the other hand, when a gauge (as opposed to global) symmetry
is spontaneously broken, the resulting Goldstone boson is "eaten" by the
corresponding gauge boson by becoming an additional degree of freedom
for the gauge boson. The Goldstone boson equivalence theorem states that
at high energy, the amplitude for emission or absorption of a
longitudinally polarised massive gauge boson becomes equal to the
amplitude for emission or absorption of the Goldstone boson that was
eaten by the gauge boson.
In the QFT of ferromagnetism, spontaneous symmetry breaking can explain the alignment of magnetic dipoles at low temperatures. In the Standard Model of elementary particles, the W and Z bosons, which would otherwise be massless as a result of gauge symmetry, acquire mass through spontaneous symmetry breaking of the Higgs boson, a process called the Higgs mechanism.
Supersymmetry
All experimentally known symmetries in nature relate bosons to bosons and fermions to fermions. Theorists have hypothesised the existence of a type of symmetry, called supersymmetry, that relates bosons and fermions.
The Standard Model obeys Poincaré symmetry, whose generators are spacetime translation Pμ and Lorentz transformation Jμν. In addition to these generators, supersymmetry in (3+1)-dimensions includes additional generators Qα, called supercharges, which themselves transform as Weyl fermions. The symmetry group generated by all these generators is known as the super-Poincaré group. In general there can be more than one set of supersymmetry generators, QαI, I = 1, ..., N, which generate the corresponding N = 1 supersymmetry, N = 2 supersymmetry, and so on. Supersymmetry can also be constructed in other dimensions, most notably in (1+1) dimensions for its application in superstring theory.
The Lagrangian of a supersymmetric theory must be invariant under the action of the super-Poincaré group. Examples of such theories include: Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (MSSM), N = 4 supersymmetric Yang–Mills theory, and superstring theory. In a supersymmetric theory, every fermion has a bosonic superpartner and vice versa.
If supersymmetry is promoted to a local symmetry, then the resultant gauge theory is an extension of general relativity called supergravity.
Supersymmetry is a potential solution to many current problems in physics. For example, the hierarchy problem
of the Standard Model — why the mass of the Higgs boson is not
radiatively corrected (under renormalisation) to a very high scale such
as the grand unified scale or the Planck scale — can be resolved by relating the Higgs field and its superpartner, the Higgsino.
Radiative corrections due to Higgs boson loops in Feynman diagrams are
cancelled by corresponding Higgsino loops. Supersymmetry also offers
answers to the grand unification of all gauge coupling constants in the
Standard Model as well as the nature of dark matter.
Nevertheless, as of 2018, experiments have yet to provide
evidence for the existence of supersymmetric particles. If supersymmetry
were a true symmetry of nature, then it must be a broken symmetry, and
the energy of symmetry breaking must be higher than those achievable by
present-day experiments.
Other spacetimes
The ϕ4 theory, QED, QCD, as well as the whole Standard Model all assume a (3+1)-dimensional Minkowski space (3 spatial and 1 time dimensions) as the background on which the quantum fields are defined. However, QFT a priori imposes no restriction on the number of dimensions nor the geometry of spacetime.
In condensed matter physics, QFT is used to describe (2+1)-dimensional electron gases. In high-energy physics, string theory is a type of (1+1)-dimensional QFT, while Kaluza–Klein theory uses gravity in extra dimensions to produce gauge theories in lower dimensions.
In Minkowski space, the flat metric ημν is used to raise and lower spacetime indices in the Lagrangian, e.g.
where ημν is the inverse of ημν satisfying ημρηρν = δμν. For QFTs in curved spacetime on the other hand, a general metric (such as the Schwarzschild metric describing a black hole) is used:
where gμν is the inverse of gμν. For a real scalar field, the Lagrangian density in a general spacetime background is
where g = det(gμν), and ∇μ denotes the covariant derivative.
The Lagrangian of a QFT, hence its calculational results and physical
predictions, depends on the geometry of the spacetime background.
Topological quantum field theory
The correlation functions and physical predictions of a QFT depend on the spacetime metric gμν. For a special class of QFTs called topological quantum field theories (TQFTs), all correlation functions are independent of continuous changes in the spacetime metric. QFTs in curved spacetime generally change according to the geometry (local structure) of the spacetime background, while TQFTs are invariant under spacetime diffeomorphisms but are sensitive to the topology (global structure) of spacetime. This means that all calculational results of TQFTs are topological invariants of the underlying spacetime. Chern–Simons theory is an example of TQFT. Applications of TQFT include the fractional quantum Hall effect and topological quantum computers.
Perturbative and non-perturbative methods
Using perturbation theory, the total effect of a small interaction term can be approximated order by order by a series expansion in the number of virtual particles
participating in the interaction. Every term in the expansion may be
understood as one possible way for (physical) particles to interact with
each other via virtual particles, expressed visually using a Feynman diagram. The electromagnetic force
between two electrons in QED is represented (to first order in
perturbation theory) by the propagation of a virtual photon. In a
similar manner, the W and Z bosons carry the weak interaction, while gluons
carry the strong interaction. The interpretation of an interaction as a
sum of intermediate states involving the exchange of various virtual
particles only makes sense in the framework of perturbation theory. In
contrast, non-perturbative methods in QFT treat the interacting
Lagrangian as a whole without any series expansion. Instead of particles
that carry interactions, these methods have spawned such concepts as 't Hooft–Polyakov monopole, domain wall, flux tube, and instanton.
Mathematical rigor
In
spite of its overwhelming success in particle physics and condensed
matter physics, QFT itself lacks a formal mathematical foundation. For
example, according to Haag's theorem, there does not exist a well-defined interaction picture for QFT, which implies that perturbation theory of QFT, which underlies the entire Feynman diagram method, is fundamentally not rigorous.
Since the 1950s, theoretical physicists and mathematicians have attempted to organise all QFTs into a set of axioms,
in order to establish the existence of concrete models of relativistic
QFT in a mathematically rigorous way and to study their properties. This
line of study is called constructive quantum field theory, a subfield of mathematical physics, which has led to such results as CPT theorem, spin-statistics theorem, and Goldstone's theorem.
Compared to ordinary QFT, topological quantum field theory and conformal field theory are better supported mathematically — both can be classified in the framework of representations of cobordisms.
Algebraic quantum field theory
is another approach to the axiomatisation of QFT, in which the
fundamental objects are local operators and the algebraic relations
between them. Axiomatic systems following this approach include Wightman axioms and Haag-Kastler axioms. One way to construct theories satisfying Wightman axioms is to use Osterwalder-Schrader axioms, which give the necessary and sufficient conditions for a real time theory to be obtained from an imaginary time theory by analytic continuation (Wick rotation).
Yang-Mills existence and mass gap, one of the Millenium Prize Problems, concerns the well-defined existence of Yang-Mills theories as set out by the above axioms. The full problem statement is as follows.
| Prove that for any compact simple gauge group G, a non-trivial quantum Yang–Mills theory exists on and has a mass gap Δ greater than 0. Existence includes establishing axiomatic properties at least as strong as those cited in Streater and Wightman (1964), Osterwalder and Schrader (1973) and Osterwalder and Schrader (1975). |








![{\displaystyle [{\hat {a}},{\hat {a}}^{\dagger }]=1.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/10235c596afd2a1fe9ee7522ffd66f35dd06618e)

















![{\displaystyle \langle \Omega |T\{\phi (x)\phi (y)\}|\Omega \rangle =\lim _{T\to \infty (1-i\epsilon )}{\frac {\int {\mathcal {D}}\phi \,\phi (x)\phi (y)\exp \left[i\int _{-T}^{T}d^{4}z\,{\mathcal {L}}\right]}{\int {\mathcal {D}}\phi \,\exp \left[i\int _{-T}^{T}d^{4}z\,{\mathcal {L}}\right]}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6a53cf57879d423ddf41fcff180629b0917de9fa)













![{\displaystyle e^{i[\alpha (x)+\alpha '(x)]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/171b083b739b394140c10da874c3e4c7d23fe601)




![{\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}[\phi ,\partial _{\mu }\phi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/562e89f35d6535c06ecb8c3cc70aa8da84920ed5)








