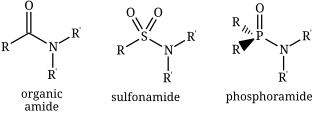
Structures of three kinds of amides: an organic amide, a sulfonamide, and a phosphoramide.
An amide is a compound with the functional group RnE(O)xNR′2 (R and R′ refer to H or organic groups). Most common are carboxamides (organic amides) (n = 1, E = C, x = 1), but many other important types of amides are known, including phosphoramides (n = 2, E = P, x = 1 and many related formulas) and sulfonamides (E = S, x = 2). The term amide refers both to classes of compounds and to the functional group (RnE(O)xNR′2) within those compounds.
Amide can also refer to the conjugate base of ammonia (the anion H2N−) or of an organic amine (an anion R2N−)..
Due to the dual use of the word 'amide', there is debate as to how to properly and unambiguously name the derived anions of amides in the first sense (i.e., deprotonated acylated amines), a few of which are commonly used as nonreactive counterions.
Structure and bonding
The simplest amides are derivatives of ammonia wherein one hydrogen atom has been replaced by an acyl group. The ensemble is generally represented as RC(O)NH2 and is described as a primary amide. Closely related and even more numerous are secondary amides which can be derived from primary amines (R′NH2) and have the formula RC(O)NHR′. Tertiary amides are commonly derived from secondary amines (R′R″NH) and have the general structure RC(O)NR′R″. Amides are usually regarded as derivatives of carboxylic acids in which the hydroxyl group has been replaced by an amine or ammonia.
The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen is delocalized into the carbonyl, thus forming a partial double bond between N and the carbonyl carbon. Consequently, the nitrogen in amides is not pyramidal. It is estimated that acetamide is described by resonance structure
A for 62% and by B for 28% (which does not sum to 100% because there
are additional resonance forms that are not depicted in the above
Figure). One final thing to note when looking at the bonds of an amide
is that there is also a hydrogen bond present between the active groups
hydrogen and nitrogen atoms.
Amides possess a conjugated system spread over the O, C and N atoms, consisting of molecular orbitals occupied by delocalized electrons. One of the π molecular orbitals in formamide is shown above.
Nomenclature
In the usual nomenclature, one adds the term "amide" to the stem of
the parent acid's name. For instance, the amide derived from acetic acid is named acetamide (CH3CONH2). IUPAC recommends ethanamide,
but this and related formal names are rarely encountered. When the
amide is derived from a primary or secondary amine, the substituents on
nitrogen are indicated first in the name. Thus, the amide formed from dimethylamine and acetic acid is N,N-dimethylacetamide (CH3CONMe2, where Me = CH3). Usually even this name is simplified to dimethylacetamide. Cyclic amides are called lactams; they are necessarily secondary or tertiary amides. Functional groups consisting of –P(O)NR2 and –SO2NR2 are phosphonamides and sulfonamides, respectively.
Properties
Basicity
Compared to amines, amides are very weak bases. While the conjugate acid of an amine has a pKa of about 9.5, the conjugate acid of an amide has a pKa around −0.5. Therefore, amides don't have as clearly noticeable acid–base properties in water. This relative lack of basicity is explained by the electron-withdrawing nature of the carbonyl group where the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen is delocalized by resonance. On the other hand, amides are much stronger bases than carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes, and ketones (their conjugate acids' pKas are between −6 and −10). It is estimated in silico that acetamide is represented by resonance structure A for 62% and by B for 28%. Resonance is largely prevented in the very strained quinuclidone.
Because of the greater electronegativity of oxygen, the carbonyl
(C=O) is a stronger dipole than the N–C dipole. The presence of a C=O
dipole and, to a lesser extent a N–C dipole, allows amides to act as
H-bond acceptors. In primary and secondary amides, the presence of N–H
dipoles allows amides to function as H-bond donors as well. Thus amides
can participate in hydrogen bonding with water and other protic
solvents; the oxygen atom can accept hydrogen bonds from water and the
N–H hydrogen atoms can donate H-bonds. As a result of interactions such
as these, the water solubility of amides is greater than that of
corresponding hydrocarbons.
The proton of a primary or secondary amide does not dissociate readily under normal conditions; its pKa is usually well above 15. Conversely, under extremely acidic conditions, the carbonyl oxygen can become protonated with a pKa of roughly −1.
Solubility
The solubilities
of amides and esters are roughly comparable. Typically amides are less
soluble than comparable amines and carboxylic acids since these
compounds can both donate and accept hydrogen bonds. Tertiary amides,
with the important exception of N,N-dimethylformamide, exhibit low solubility in water.
Characterization
The
presence of the functional group is generally easily established, at
least in small molecules. They are the most common non-basic functional
group. They can be distinguished from nitro and cyano groups by their IR spectra. Amides exhibit a moderately intense νCO band near 1650 cm−1. By 1H NMR spectroscopy, CONHR
signals occur at low fields. In X-ray crystallography, the C(O)N center
together with the three immediately adjacent atoms characteristically
define a plane.
Applications and occurrence
Amides
are pervasive in nature and technology as structural materials. The
amide linkage is easily formed, confers structural rigidity, and resists
hydrolysis. Nylons are polyamides, as are the very resilient materials Aramid, Twaron, and Kevlar. Amide linkages constitute a defining molecular feature of proteins, the secondary structure of which is due in part to the hydrogen bonding abilities of amides. Amide linkages in a biochemical context are called peptide bonds when they occur in the main chain of a protein and isopeptide bonds when they occur to a side-chain of the protein. Proteins can have structural roles, such as in hair or spider silk, but also nearly all enzymes are proteins. Low molecular weight amides, such as dimethylformamide (HC(O)N(CH3)2), are common solvents. Many drugs are amides, including paracetamol, penicillin and LSD. Moreover, plant N-alkylamides have a wide range of biological functionalities.
Amide synthesis
Many methods exist in amide synthesis. On paper, the simplest method for making amides is by coupling a carboxylic acid with an amine. In general this reaction is thermodynamically favorable, however it suffers from a high activation energy,
largely due to the amine first deprotonating the carboxylic acid, which
reduces its reactivity. As such the direct reaction often requires high
temperatures.
- RCO2H + R′R″NH ⇌ RCO−
2 + R′R″NH+
2 ⇌ RC(O)NR′R″ + H2O
Many methods are known for driving the equilibrium to the right. For
the most part these reactions involve "activating" the carboxylic acid
by first converting it to a better electrophile; such as esters, acid chlorides (Schotten-Baumann reaction) or anhydrides (Lumière–Barbier method). Conventional methods in peptide synthesis use coupling agents such as HATU, HOBt, or PyBOP.
In recent years there has also been a surge in the development of Boron
reagents for amide bond formation, including catalytic use of
2-IodoPhenylBoronic acid or MIBA, and Tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate.
| Reaction name | Substrate | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Beckmann rearrangement | Cyclic ketone | Reagent: hydroxylamine and acid |
| Schmidt reaction | Ketones | Reagent: hydrazoic acid |
| Nitrile hydrolysis | Nitrile | Reagent: water; acid catalyst |
| Willgerodt–Kindler reaction | Aryl alkyl ketones | Sulfur and morpholine |
| Passerini reaction | Carboxylic acid, ketone or aldehyde |
|
| Ugi reaction | Isocyanide, carboxylic acid, ketone, primary amine |
|
| Bodroux reaction | Carboxylic acid, Grignard reagent with an aniline derivative ArNHR′ | |
| Chapman rearrangement[ | Aryl imino ether | For N,N-diaryl amides. The reaction mechanism is based on a nucleophilic aromatic substitution. 
|
| Leuckart amide synthesis | Isocyanate | Reaction of arene with isocyanate catalysed by aluminium trichloride, formation of aromatic amide. |
| Ritter reaction | Alkenes, alcohols, or other carbonium ion sources | Secondary amides via an addition reaction between a nitrile and a carbonium ion in the presence of concentrated acids. |
| Photolytic addition of formamide to olefins | Terminal alkenes | A free radical homologation reaction between a terminal alkene and formamide. |
| Ester aminolysis | Esters | Base catalyzed reaction of esters with various amines to form alcohols and amides. |
Other methods
Dehydrogenative acylation of amines is catalyzed by organoruthenium complexes:
The reaction proceed by one dehydrogenation of the alcohol to the aldehyde followed by formation of a hemiaminal, which undergoes a second dehydrogenation to the amide. Elimination of water in the hemiaminal to the imine is not observed.
Transamidation is typically very slow, but it is accelerated with Lewis acid and organometallic catalysts:
- RC(O)NR'2 + HNR"2 → RC(O)NR"2 + HNR'2
Primary amides (RC(O)NH2) are more amenable to this reaction.
Amide reactions
Mechanism for acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an amide.
| Reaction name | Product | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | Nitrile | Reagent: phosphorus pentoxide; benzenesulfonyl chloride; TFAA/py |
| Hofmann rearrangement | Amine with one fewer carbon atom | Reagents: bromine and sodium hydroxide |
| Amide reduction | Amine | Reagent: lithium aluminium hydride followed by hydrolysis |
| Vilsmeier–Haack reaction | Aldehyde (via imine) | POCl3, aromatic substrate, formamide |
| Bischler–Napieralski reaction | Cyclic imine | POCl3, SOCl2, etc. |