| |||

| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sulfuric acid
| |||
| Other names
Oil of vitriol
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.763 | ||
| EC Number | 231-639-5 | ||
| E number | E513 | ||
| 2122 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | WS5600000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1830 | ||
| Properties | |||
| H 2SO 4 | |||
| Molar mass | 98.079 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | odorless | ||
| Density | 1.8302 g/cm3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | 10.31 °C (50.56 °F; 283.46 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 337 °C (639 °F; 610 K) When sulfuric acid is above 300 °C (572 °F), it will decompose slowly | ||
| miscible, exothermic | |||
| Vapor pressure | 0.001 mmHg (20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | −3, 1.99 | ||
| Conjugate base | Hydrogen sulfate | ||
| Viscosity | 26.7 cP (20 °C) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S |
157 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−814 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| H314 | |||
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P363, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| 15 mg/m3 (IDLH), 1 mg/m3 (TWA), 2 mg/m3 (STEL) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
2140 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
50 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 8 hr) 510 mg/m3 (rat, 2 hr) 320 mg/m3 (mouse, 2 hr) 18 mg/m3 (guinea pig) | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
87 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 2.75 hr) | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
15 mg/m3 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related strong acids
|
Selenic acid Hydrochloric acid Nitric acid Chromic acid | ||
Related compounds
|
Sulfurous acid Peroxymonosulfuric acid Sulfur trioxide Oleum | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Sulfuric acid (alternative spelling sulphuric acid), also known as vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and syrupy liquid that is soluble in water, in a reaction that is highly exothermic.
Its corrosiveness can be mainly ascribed to its strong acidic nature, and, if at a high concentration, its dehydrating and oxidizing properties. It is also hygroscopic, readily absorbing water vapor from the air. Upon contact, sulfuric acid can cause severe chemical burns and even secondary thermal burns; it is very dangerous even at moderate concentrations.
Sulfuric acid is a very important commodity chemical, and indeed, a nation's sulfuric acid production is a good indicator of its industrial strength. It is widely produced with different methods, such as contact process, wet sulfuric acid process, lead chamber process and some other methods.
The most common use of sulfuric acid is for fertilizer manufacture. It is also a central substance in the chemical industry. Principal uses include fertilizer manufacturing (and other mineral processing), oil refining, wastewater processing, and chemical synthesis. It has a wide range of end applications including in domestic acidic drain cleaners, as an electrolyte in lead-acid batteries and in various cleaning agents.
Physical properties
Grades of sulfuric acid
Although nearly 100% sulfuric acid can be made, the subsequent loss of SO
3 at the boiling point brings the concentration to 98.3% acid. The 98.3% grade is more stable in storage, and is the usual form of what is described as "concentrated sulfuric acid". Other concentrations are used for different purposes. Some common concentrations are:
3 at the boiling point brings the concentration to 98.3% acid. The 98.3% grade is more stable in storage, and is the usual form of what is described as "concentrated sulfuric acid". Other concentrations are used for different purposes. Some common concentrations are:
| Mass fraction H2SO4 |
Density (kg/L) |
Concentration (mol/L) |
Common name |
|---|---|---|---|
| l.t. 29% | 1.00-1.25 | l.t. 4.2 | diluted sulfuric acid |
| 29–32% | 1.25–1.28 | 4.2–5.0 | battery acid (used in lead–acid batteries) |
| 62–70% | 1.52–1.60 | 9.6–11.5 | chamber acid fertilizer acid |
| 78–80% | 1.70–1.73 | 13.5–14.0 | tower acid Glover acid |
| 98.3% | 1.84 | 18.4 | concentrated sulfuric acid |
"Chamber acid" and "tower acid" were the two concentrations of sulfuric acid produced by the lead chamber process, chamber acid being the acid produced in the lead chamber itself (less than 70% to avoid contamination with nitrosylsulfuric acid) and tower acid being the acid recovered from the bottom of the Glover tower.
They are now obsolete as commercial concentrations of sulfuric acid,
although they may be prepared in the laboratory from concentrated
sulfuric acid if needed. In particular, "10M" sulfuric acid (the modern
equivalent of chamber acid, used in many titrations)
is prepared by slowly adding 98% sulfuric acid to an equal volume of
water, with good stirring: the temperature of the mixture can rise to
80 °C (176 °F) or higher.
Sulfuric acid reacts with its anhydride, SO
3, to form H
2S
2O
7, called pyrosulfuric acid, fuming sulfuric acid, Disulfuric acid or oleum or, less commonly, Nordhausen acid. Concentrations of oleum are either expressed in terms of % SO
3 (called % oleum) or as % H
2SO
4 (the amount made if H
2O were added); common concentrations are 40% oleum (109% H
2SO
4) and 65% oleum (114.6% H
2SO
4). Pure H
2S
2O
7 is a solid with melting point of 36 °C.
3, to form H
2S
2O
7, called pyrosulfuric acid, fuming sulfuric acid, Disulfuric acid or oleum or, less commonly, Nordhausen acid. Concentrations of oleum are either expressed in terms of % SO
3 (called % oleum) or as % H
2SO
4 (the amount made if H
2O were added); common concentrations are 40% oleum (109% H
2SO
4) and 65% oleum (114.6% H
2SO
4). Pure H
2S
2O
7 is a solid with melting point of 36 °C.
Pure sulfuric acid has a vapor pressure of less than 0.001 mmHg at 25 °C and 1 mmHg at 145.8 °C, and 98% sulfuric acid has a less than 1 mmHg vapor pressure at 40 °C.
Pure sulfuric acid is a viscous clear liquid, like oil, and this explains the old name of the acid ('oil of vitriol').
Commercial sulfuric acid is sold in several different purity grades. Technical grade H
2SO
4 is impure and often colored, but is suitable for making fertilizer. Pure grades, such as United States Pharmacopeia (USP) grade, are used for making pharmaceuticals and dyestuffs. Analytical grades are also available.
2SO
4 is impure and often colored, but is suitable for making fertilizer. Pure grades, such as United States Pharmacopeia (USP) grade, are used for making pharmaceuticals and dyestuffs. Analytical grades are also available.
Nine hydrates are known, but four of them were confirmed to be tetrahydrate (H2SO4·4H2O), hemihexahydrate (H2SO4·6 1⁄2H2O) and octahydrate (H2SO4·8H2O).
Polarity and conductivity
| Species | mMol/kg |
|---|---|
| HSO− 4 |
15.0 |
| H 3SO+ 4 |
11.3 |
| H 3O+ |
8.0 |
| HS 2O− 7 |
4.4 |
| H 2S 2O 7 |
3.6 |
| H 2O |
0.1 |
Anhydrous H
2SO
4 is a very polar liquid, having a dielectric constant of around 100. It has a high electrical conductivity, caused by dissociation through protonating itself, a process known as autoprotolysis.
2SO
4 is a very polar liquid, having a dielectric constant of around 100. It has a high electrical conductivity, caused by dissociation through protonating itself, a process known as autoprotolysis.
- 2 H
2SO
4 ⇌ H
3SO+
4 + HSO−
4
The equilibrium constant for the autoprotolysis is
- Kap (25 °C) = [H
3SO+
4][HSO−
4] = 2.7×10−4
The comparable equilibrium constant for water, Kw is 10−14, a factor of 1010 (10 billion) smaller.
In spite of the viscosity of the acid, the effective conductivities of the H
3SO+
4 and HSO−
4 ions are high due to an intramolecular proton-switch mechanism (analogous to the Grotthuss mechanism in water), making sulfuric acid a good conductor of electricity. It is also an excellent solvent for many reactions.
3SO+
4 and HSO−
4 ions are high due to an intramolecular proton-switch mechanism (analogous to the Grotthuss mechanism in water), making sulfuric acid a good conductor of electricity. It is also an excellent solvent for many reactions.
Chemical properties
Reaction with water and dehydrating property
Drops of concentrated sulfuric acid rapidly decompose a piece of cotton towel by dehydration.
Because the hydration reaction of sulfuric acid is highly exothermic, dilution should always be performed by adding the acid to the water rather than the water to the acid.
Because the reaction is in an equilibrium that favors the rapid
protonation of water, addition of acid to the water ensures that the acid is the limiting reagent. This reaction is best thought of as the formation of hydronium ions:
- H
2SO
4 + H
2O → H
3O+ + HSO−
4 Ka1 = 2.4×106 (strong acid) - HSO−
4 + H
2O → H
3O+ + SO2−
4 Ka2 = 1.0×10−2
HSO−
4 is the bisulfate anion and SO2−
4 is the sulfate anion. Ka1 and Ka2 are the acid dissociation constants.
4 is the bisulfate anion and SO2−
4 is the sulfate anion. Ka1 and Ka2 are the acid dissociation constants.
Because the hydration of sulfuric acid is thermodynamically favorable and the affinity of it for water is sufficiently strong, sulfuric acid is an excellent dehydrating agent. Concentrated sulfuric acid has a very powerful dehydrating property, removing water (H2O) from other chemical compounds including sugar and other carbohydrates and producing carbon, heat, steam.
In the laboratory, this is often demonstrated by mixing table sugar
(sucrose) into sulfuric acid. The sugar changes from white to dark
brown and then to black as carbon is formed. A rigid column of black,
porous carbon will emerge as well. The carbon will smell strongly of caramel due to the heat generated.
Similarly, mixing starch into concentrated sulfuric acid will give elemental carbon
and water as absorbed by the sulfuric acid (which becomes slightly
diluted). The effect of this can be seen when concentrated sulfuric acid
is spilled on paper which is composed of cellulose; the cellulose reacts to give a burnt appearance, the carbon appears much as soot would in a fire.
Although less dramatic, the action of the acid on cotton, even in diluted form, will destroy the fabric.
The reaction with copper(II) sulfate
can also demonstrate the dehydration property of sulfuric acid. The
blue crystal is changed into white powder as water is removed.
Acid-base properties
As an acid, sulfuric acid reacts with most bases to give the corresponding sulfate. For example, the blue copper salt copper(II) sulfate, commonly used for electroplating and as a fungicide, is prepared by the reaction of copper(II) oxide with sulfuric acid:
- CuO (s) + H
2SO
4 (aq) → CuSO
4 (aq) + H
2O (l)
Sulfuric acid can also be used to displace weaker acids from their salts. Reaction with sodium acetate, for example, displaces acetic acid, CH
3COOH, and forms sodium bisulfate:
3COOH, and forms sodium bisulfate:
- H
2SO
4 + CH
3COONa → NaHSO
4 + CH
3COOH
Similarly, reacting sulfuric acid with potassium nitrate can be used to produce nitric acid and a precipitate of potassium bisulfate. When combined with nitric acid, sulfuric acid acts both as an acid and a dehydrating agent, forming the nitronium ion NO+
2, which is important in nitration reactions involving electrophilic aromatic substitution. This type of reaction, where protonation occurs on an oxygen atom, is important in many organic chemistry reactions, such as Fischer esterification and dehydration of alcohols.
2, which is important in nitration reactions involving electrophilic aromatic substitution. This type of reaction, where protonation occurs on an oxygen atom, is important in many organic chemistry reactions, such as Fischer esterification and dehydration of alcohols.
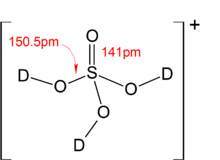
Solid state structure of the [D3SO4]+ ion present in [D3SO4]+[SbF6]−, synthesized by using DF in place of HF. (see text)
When allowed to react with superacids, sulfuric acid can act as a base and be protonated, forming the [H3SO4]+ ion. Salt of [H3SO4]+ have been prepared using the following reaction in liquid HF:
- ((CH3)3SiO)2SO2 + 3 HF + SbF5 → [H3SO4]+[SbF6]− + 2 (CH3)3SiF
The above reaction is thermodynamically favored due to the high bond enthalpy of the Si–F bond in the side product. Protonation using simply HF/SbF5, however, have met with failure, as pure sulfuric acid undergoes self-ionization to give [H3O]+ ions, which prevents the conversion of H2SO4 to [H3SO4]+ by the HF/SbF5 system:
- 2 H2SO4 ⇌ [H3O]+ + [HS2O7]−
Reactions with metals and strong oxidizing property
Dilute sulfuric acid reacts with metals via a single displacement reaction as with other typical acids, producing hydrogen gas and salts (the metal sulfate). It attacks reactive metals (metals at positions above copper in the reactivity series) such as iron, aluminium, zinc, manganese, magnesium, and nickel.
- Fe (s) + H
2SO
4 (aq) → H
2 (g) + FeSO
4 (aq)
However, concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and does not react with metals in the same way as other typical acids. Sulfur dioxide, water and SO2−
4 ions are evolved instead of the hydrogen and salts.
4 ions are evolved instead of the hydrogen and salts.
- 2 H2SO4 + 2 e− → SO2 + 2 H2O + SO2−
4
- Cu + 2 H2SO4 → SO2 + 2 H2O + SO2−
4 + Cu2+
Reactions with non-metals
- C + 2 H2SO4 → CO2 + 2 SO2 + 2 H2O
- S + 2 H2SO4 → 3 SO2 + 2 H2O
Reaction with sodium chloride
- NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Benzene undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution with sulfuric acid to give the corresponding sulfonic acids:
Occurrence
Rio Tinto with its highly acidic water
Pure sulfuric acid is not encountered naturally on Earth in anhydrous form, due to its great affinity for water. Dilute sulfuric acid is a constituent of acid rain, which is formed by atmospheric oxidation of sulfur dioxide in the presence of water – i.e., oxidation of sulfurous acid. Sulfur dioxide is the main byproduct produced when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal or oil are burned.
Sulfuric acid is formed naturally by the oxidation of sulfide
minerals, such as iron sulfide. The resulting water can be highly acidic
and is called acid mine drainage
(AMD) or acid rock drainage (ARD). This acidic water is capable of
dissolving metals present in sulfide ores, which results in brightly
colored, toxic streams. The oxidation of pyrite (iron sulfide) by molecular oxygen produces iron(II), or Fe2+:
- 2 FeS
2 (s) + 7 O
2 + 2 H2O → 2 Fe2+ + 4 SO2−
4 + 4 H+
The Fe2+ can be further oxidized to Fe3+:
- 4 Fe2+ + O
2 + 4 H+ → 4 Fe3+ + 2 H2O
- Fe3+ + 3 H2O → Fe(OH)
3↓ + 3 H+
The iron(III) ion ("ferric iron") can also oxidize pyrite:
- FeS
2(s) + 14 Fe3+ + 8 H2O → 15 Fe2+ + 2 SO2−
4 + 16 H+
When iron(III) oxidation of pyrite occurs, the process can become rapid. pH values below zero have been measured in ARD produced by this process.
ARD can also produce sulfuric acid at a slower rate, so that the acid neutralizing capacity (ANC) of the aquifer can neutralize the produced acid. In such cases, the total dissolved solids
(TDS) concentration of the water can be increased from the dissolution
of minerals from the acid-neutralization reaction with the minerals.
Sulfuric acid is used as a defense by certain marine species, for example, the phaeophyte alga Desmarestia munda (order Desmarestiales) concentrates sulfuric acid in cell vacuoles.
Stratospheric aerosol
In the stratosphere,
the atmosphere's second layer that is generally between 10 and 50 km
above Earth's surface, sulfuric acid is formed by the oxidation of
volcanic sulfur dioxide by the hydroxyl radical:
- SO
2 + HO• → HSO
3 - HSO
3 + O
2 → SO
3 + HO
2 - SO
3 + H2O → H
2SO
4
Because sulfuric acid reaches supersaturation
in the stratosphere, it can nucleate aerosol particles and provide a
surface for aerosol growth via condensation and coagulation with other
water-sulfuric acid aerosols. This results in the stratospheric aerosol layer.
Extraterrestrial sulfuric acid
Venus
Sulfuric acid is produced in the upper atmosphere of Venus by the Sun's photochemical action on carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and water vapor. Ultraviolet photons of wavelengths less than 169 nm can photodissociate carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide and atomic oxygen.
Atomic oxygen is highly reactive. When it reacts with sulfur dioxide, a
trace component of the Venusian atmosphere, the result is sulfur trioxide,
which can combine with water vapor, another trace component of Venus's
atmosphere, to yield sulfuric acid. In the upper, cooler portions of
Venus's atmosphere, sulfuric acid exists as a liquid, and thick sulfuric
acid clouds completely obscure the planet's surface when viewed from
above. The main cloud layer extends from 45–70 km above the planet's
surface, with thinner hazes extending as low as 30 km and as high as
90 km above the surface. The permanent Venusian clouds produce a
concentrated acid rain, as the clouds in the atmosphere of Earth produce
water rain.
The atmosphere exhibits a sulfuric acid cycle. As sulfuric acid
rain droplets fall down through the hotter layers of the atmosphere's
temperature gradient, they are heated up and release water vapor,
becoming more and more concentrated. When they reach temperatures above
300 °C, sulfuric acid begins to decompose into sulfur trioxide
and water, both in the gas phase. Sulfur trioxide is highly reactive
and dissociates into sulfur dioxide and atomic oxygen, which oxidizes
traces of carbon monoxide to form carbon dioxide. Sulfur dioxide and
water vapor rise on convection currents from the mid-level atmospheric
layers to higher altitudes, where they will be transformed again into
sulfuric acid, and the cycle repeats.
Europa
Infrared spectra taken by NASA's Galileo spacecraft show distinct absorptions on Jupiter's moon Europa that have been attributed to one or more sulfuric acid hydrates. Sulfuric acid in solution with water causes significant freezing-point depression of water's melting point, down to 210 K (−63 °C), and this would make the existence of liquid solutions beneath Europa's
icy crust more likely. The interpretation of the spectra is somewhat
controversial. Some planetary scientists prefer to assign the spectral
features to the sulfate ion, perhaps as part of one or more minerals on
Europa's surface.
Manufacture
Sulfuric acid is produced from sulfur, oxygen and water via the conventional contact process (DCDA) or the wet sulfuric acid process (WSA).
Contact process
In the first step, sulfur is burned to produce sulfur dioxide.
- S (s) + O
2 (g) → SO
2 (g)
This is then oxidized to sulfur trioxide using oxygen in the presence of a vanadium(V) oxide catalyst. This reaction is reversible and the formation of the sulfur trioxide is exothermic.
- 2 SO
2 (g) + O
2 (g) ⇌ 2 SO
3 (g) (in presence of V
2O
5)
The sulfur trioxide is absorbed into 97–98% H
2SO
4 to form oleum (H
2S
2O
7), also known as fuming sulfuric acid. The oleum is then diluted with water to form concentrated sulfuric acid.
2SO
4 to form oleum (H
2S
2O
7), also known as fuming sulfuric acid. The oleum is then diluted with water to form concentrated sulfuric acid.
- H
2SO
4 (l) + SO
3 (g)→ H
2S
2O
7 (l) - H
2S
2O
7 (l) + H
2O (l) → 2 H
2SO
4 (l)
Directly dissolving SO
3 in water is not practical due to the highly exothermic nature of the reaction between sulfur trioxide and water. The reaction forms a corrosive aerosol that is very difficult to separate, instead of a liquid.
3 in water is not practical due to the highly exothermic nature of the reaction between sulfur trioxide and water. The reaction forms a corrosive aerosol that is very difficult to separate, instead of a liquid.
- SO
3 (g) + H
2O (l) → H
2SO
4 (l)
Wet sulfuric acid process
In the first step, sulfur is burned to produce sulfur dioxide:
- S(s) + O
2(g) → SO
2(g)
- 2 H
2S + 3 O
2 → 2 H
2O + 2 SO
2 (−518 kJ/mol)
This is then oxidized to sulfur trioxide using oxygen with vanadium(V) oxide as catalyst.
- 2 SO
2 + O
2 → 2 SO
3 (−99 kJ/mol) (reaction is reversible)
The sulfur trioxide is hydrated into sulfuric acid H
2SO
4:
2SO
4:
- SO
3 + H
2O → H
2SO
4(g) (−101 kJ/mol)
The last step is the condensation of the sulfuric acid to liquid 97–98% H
2SO
4:
2SO
4:
- H
2SO
4(g) → H
2SO
4(l) (−69 kJ/mol)
Other methods
Another method is the less well-known metabisulfite method, in which metabisulfite is placed at the bottom of a beaker, and 12.6 molar concentration hydrochloric acid is added. The resulting gas is bubbled through nitric acid,
which will release brown/red vapors. The completion of the reaction is
indicated by the ceasing of the fumes. This method does not produce an
inseparable mist, which is quite convenient.
- SO2 + HNO3 + H2O→ H2SO4 + NO
Sulfuric acid can be produced in the laboratory by burning sulfur in air and dissolving the gas produced in a hydrogen peroxide solution.
- SO2 + H2O2 → H2SO4
Prior to 1900, most sulfuric acid was manufactured by the lead chamber process. As late as 1940, up to 50% of sulfuric acid manufactured in the United States was produced by chamber process plants.
In early to mid nineteenth century "vitriol" plants existed, among other places, in Prestonpans in Scotland, Shropshire and the Lagan Valley
in County Antrim Ireland where it was used as a bleach for linen. Early
bleaching of linen was done using lactic acid from sour milk but this
was a slow process and the use of vitriol sped up the bleaching process.
Uses
Sulfuric acid production in 2000
Sulfuric acid is a very important commodity chemical, and indeed, a
nation's sulfuric acid production is a good indicator of its industrial
strength. World production in 2004 was about 180 million tonnes,
with the following geographic distribution: Asia 35%, North America
(including Mexico) 24%, Africa 11%, Western Europe 10%, Eastern Europe
and Russia 10%, Australia and Oceania 7%, South America 7%.
Most of this amount (≈60%) is consumed for fertilizers, particularly
superphosphates, ammonium phosphate and ammonium sulfates. About 20% is
used in chemical industry for production of detergents, synthetic
resins, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals, petroleum catalysts, insecticides
and antifreeze,
as well as in various processes such as oil well acidifing, aluminum
reduction, paper sizing, water treatment. About 6% of uses are related
to pigments and include paints, enamels,
printing inks, coated fabrics and paper, and the rest is dispersed into
a multitude of applications such as production of explosives, cellophane, acetate and viscose textiles, lubricants, non-ferrous metals, and batteries.
Industrial production of chemicals
The major use for sulfuric acid is in the "wet method" for the production of phosphoric acid, used for manufacture of phosphate fertilizers.
In this method, phosphate rock is used, and more than 100 million
tonnes are processed annually. This raw material is shown below as fluorapatite, though the exact composition may vary. This is treated with 93% sulfuric acid to produce calcium sulfate, hydrogen fluoride (HF) and phosphoric acid. The HF is removed as hydrofluoric acid. The overall process can be represented as:
Ammonium sulfate, an important nitrogen fertilizer, is most commonly produced as a byproduct from coking plants supplying the iron and steel making plants. Reacting the ammonia produced in the thermal decomposition of coal
with waste sulfuric acid allows the ammonia to be crystallized out as a
salt (often brown because of iron contamination) and sold into the
agro-chemicals industry.
Another important use for sulfuric acid is for the manufacture of aluminium sulfate, also known as paper maker's alum. This can react with small amounts of soap on paper pulp fibers to give gelatinous aluminium carboxylates, which help to coagulate the pulp fibers into a hard paper surface. It is also used for making aluminium hydroxide, which is used at water treatment plants to filter out impurities, as well as to improve the taste of the water. Aluminium sulfate is made by reacting bauxite with sulfuric acid:
- 2 AlO(OH) + 3 H
2SO
4 → Al
2(SO
4)
3 + 4 H
2O
Sulfuric acid is also important in the manufacture of dyestuffs solutions.
Sulfur–iodine cycle
The sulfur–iodine cycle is a series of thermo-chemical processes used to obtain hydrogen. It consists of three chemical reactions whose net reactant is water and whose net products are hydrogen and oxygen. Step one of cycle is the Bunsen reaction.
2 H
2SO
4 → 2 SO
2 + 2 H
2O + O
2(830 °C) I
2 + SO
2 + 2 H
2O → 2 HI + H
2SO
4(120 °C) 2 HI → I
2 + H
2(320 °C)
The sulfur and iodine compounds are recovered and reused, hence the consideration of the process as a cycle. This process is endothermic and must occur at high temperatures, so energy in the form of heat has to be supplied.
The sulfur–iodine cycle has been proposed as a way to supply hydrogen for a hydrogen-based economy. It does not require hydrocarbons like current methods of steam reforming. But note that all of the available energy in the hydrogen so produced is supplied by the heat used to make it.
The sulfur–iodine cycle is currently being researched as a
feasible method of obtaining hydrogen, but the concentrated, corrosive
acid at high temperatures poses currently insurmountable safety hazards
if the process were built on a large scale.
Industrial cleaning agent
Sulfuric acid is used in large quantities by the iron and steelmaking industry to remove oxidation, rust, and scaling from rolled sheet and billets prior to sale to the automobile and major appliances industry. Used acid is often recycled using a spent acid regeneration (SAR) plant. These plants combust spent acid with natural gas, refinery gas, fuel oil or other fuel sources. This combustion process produces gaseous sulfur dioxide (SO
2) and sulfur trioxide (SO
3) which are then used to manufacture "new" sulfuric acid. SAR plants are common additions to metal smelting plants, oil refineries, and other industries where sulfuric acid is consumed in bulk, as operating a SAR plant is much cheaper than the recurring costs of spent acid disposal and new acid purchases.
2) and sulfur trioxide (SO
3) which are then used to manufacture "new" sulfuric acid. SAR plants are common additions to metal smelting plants, oil refineries, and other industries where sulfuric acid is consumed in bulk, as operating a SAR plant is much cheaper than the recurring costs of spent acid disposal and new acid purchases.
Hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) can be added to sulfuric acid to produce piranha solution, a powerful but very toxic cleaning solution with which substrate surfaces can be cleaned. Piranha solution is typically used in the microelectronics industry, and also in laboratory settings to clean glassware.
2O
2) can be added to sulfuric acid to produce piranha solution, a powerful but very toxic cleaning solution with which substrate surfaces can be cleaned. Piranha solution is typically used in the microelectronics industry, and also in laboratory settings to clean glassware.
Catalyst
Sulfuric
acid is used for a variety of other purposes in the chemical industry.
For example, it is the usual acid catalyst for the conversion of cyclohexanone oxime to caprolactam, used for making nylon. It is used for making hydrochloric acid from salt via the Mannheim process. Much H
2SO
4 is used in petroleum refining, for example as a catalyst for the reaction of isobutane with isobutylene to give isooctane, a compound that raises the octane rating of gasoline (petrol). Sulfuric acid is also often used as a dehydrating or oxidizing agent in industrial reactions, such as the dehydration of various sugars to form solid carbon.
2SO
4 is used in petroleum refining, for example as a catalyst for the reaction of isobutane with isobutylene to give isooctane, a compound that raises the octane rating of gasoline (petrol). Sulfuric acid is also often used as a dehydrating or oxidizing agent in industrial reactions, such as the dehydration of various sugars to form solid carbon.
Electrolyte
Acidic drain cleaners usually contain sulfuric acid at a high concentration which turns a piece of pH paper red and chars it instantly, demonstrating both the strong acidic nature and dehydrating property.
Sulfuric acid acts as the electrolyte in lead–acid batteries (lead-acid accumulator):
At anode:
- Pb + SO
42− ⇌ PbSO
4 + 2 e−
At cathode:
- PbO
2 + 4 H+ + SO
42− + 2 e− ⇌ PbSO
4 + 2 H2O
An acidic drain cleaner can be used to dissolve grease, hair and even tissue paper inside water pipes.
Overall:
- Pb + PbO
2 + 4 H+ + 2 SO
42− ⇌ 2 PbSO
4 + 2 H2O
Domestic uses
Sulfuric acid at high concentrations is frequently the major ingredient in acidic drain cleaners which are used to remove grease, hair, tissue paper, etc. Similar to their alkaline versions, such drain openers can dissolve fats and proteins via hydrolysis.
Moreover, as concentrated sulfuric acid has a strong dehydrating
property, it can remove tissue paper via dehydrating process as well.
Since the acid may react with water vigorously, such acidic drain
openers should be added slowly into the pipe to be cleaned.
History
John Dalton's 1808 sulfuric acid molecule shows a central sulfur atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, or sulfur trioxide, the anhydride of sulfuric acid.
The study of vitriol, a category of glassy minerals from which the acid can be derived, began in ancient times. Sumerians
had a list of types of vitriol that they classified according to the
substances' color. Some of the earliest discussions on the origin and
properties of vitriol is in the works of the Greek physician Dioscorides (first century AD) and the Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD). Galen
also discussed its medical use. Metallurgical uses for vitriolic
substances were recorded in the Hellenistic alchemical works of Zosimos of Panopolis, in the treatise Phisica et Mystica, and the Leyden papyrus X.
Medieval Islamic era alchemists, Jābir ibn Hayyān (c. 721 – c. 815 AD, also known as Geber), Razi (865 – 925 AD), and Jamal Din al-Watwat (d. 1318, wrote the book Mabāhij al-fikar wa-manāhij al-'ibar), included vitriol in their mineral classification lists. Ibn Sina focused on its medical uses and different varieties of vitriol.
Sulfuric acid was called "oil of vitriol" by medieval European alchemists because it was prepared by roasting "green vitriol" (iron(II) sulfate) in an iron retort. There are references to it in the works of Vincent of Beauvais and in the Compositum de Compositis ascribed to Saint Albertus Magnus. A passage from Pseudo-Geber´s Summa Perfectionis was long considered to be the first recipe for sulfuric acid, but this was a misinterpretation.
In the seventeenth century, the German-Dutch chemist Johann Glauber prepared sulfuric acid by burning sulfur together with saltpeter (potassium nitrate, KNO
3), in the presence of steam. As saltpeter decomposes, it oxidizes the sulfur to SO
3, which combines with water to produce sulfuric acid. In 1736, Joshua Ward, a London pharmacist, used this method to begin the first large-scale production of sulfuric acid.
3), in the presence of steam. As saltpeter decomposes, it oxidizes the sulfur to SO
3, which combines with water to produce sulfuric acid. In 1736, Joshua Ward, a London pharmacist, used this method to begin the first large-scale production of sulfuric acid.
In 1746 in Birmingham, John Roebuck adapted this method to produce sulfuric acid in lead-lined
chambers, which were stronger, less expensive, and could be made larger
than the previously used glass containers. This process allowed the
effective industrialization of sulfuric acid production. After several
refinements, this method, called the lead chamber process or "chamber process", remained the standard for sulfuric acid production for almost two centuries.
Sulfuric acid created by John Roebuck's process approached a 65%
concentration. Later refinements to the lead chamber process by French
chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac and British chemist John Glover improved concentration to 78%. However, the manufacture of some dyes and other chemical processes require a more concentrated product. Throughout the 18th century, this could only be made by dry distilling minerals in a technique similar to the original alchemical processes. Pyrite (iron disulfide, FeS
2) was heated in air to yield iron(II) sulfate, FeSO
4, which was oxidized by further heating in air to form iron(III) sulfate, Fe2(SO4)3, which, when heated to 480 °C, decomposed to iron(III) oxide and sulfur trioxide, which could be passed through water to yield sulfuric acid in any concentration. However, the expense of this process prevented the large-scale use of concentrated sulfuric acid.
2) was heated in air to yield iron(II) sulfate, FeSO
4, which was oxidized by further heating in air to form iron(III) sulfate, Fe2(SO4)3, which, when heated to 480 °C, decomposed to iron(III) oxide and sulfur trioxide, which could be passed through water to yield sulfuric acid in any concentration. However, the expense of this process prevented the large-scale use of concentrated sulfuric acid.
In 1831, British vinegar merchant Peregrine Phillips patented the contact process,
which was a far more economical process for producing sulfur trioxide
and concentrated sulfuric acid. Today, nearly all of the world's
sulfuric acid is produced using this method.
Safety
Laboratory hazards
Drops
of 98% sulfuric acid char a piece of tissue paper instantly. Carbon is
left after the dehydration reaction staining the paper black.
Superficial chemical burn caused by two 98% sulfuric acid splashes (forearm skin)
Sulfuric acid is capable of causing very severe burns, especially when it is at high concentrations. In common with other corrosive acids and alkali, it readily decomposes proteins and lipids through amide and ester hydrolysis upon contact with living tissues, such as skin and flesh. In addition, it exhibits a strong dehydrating property on carbohydrates, liberating extra heat and causing secondary thermal burns. Accordingly, it rapidly attacks the cornea and can induce permanent blindness if splashed onto eyes. If ingested, it damages internal organs irreversibly and may even be fatal.[5] Protective equipment should hence always be used when handling it. Moreover, its strong oxidizing property makes it highly corrosive to many metals and may extend its destruction on other materials. Because of such reasons, damage posed by sulfuric acid is potentially more severe than that by other comparable strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid and nitric acid.
Sulfuric acid must be stored carefully in containers made of
nonreactive material (such as glass). Solutions equal to or stronger
than 1.5 M are labeled "CORROSIVE", while solutions greater than 0.5 M
but less than 1.5 M are labeled "IRRITANT". However, even the normal
laboratory "dilute" grade (approximately 1 M, 10%) will char paper if
left in contact for a sufficient time.
The standard first aid treatment for acid spills on the skin is, as for other corrosive agents,
irrigation with large quantities of water. Washing is continued for at
least ten to fifteen minutes to cool the tissue surrounding the acid
burn and to prevent secondary damage. Contaminated clothing is removed
immediately and the underlying skin washed thoroughly.
Dilution hazards
Preparation
of the diluted acid can be dangerous due to the heat released in the
dilution process. To avoid splattering, the concentrated acid is usually
added to water and not the other way around. Water has a higher heat
capacity than the acid, and so a vessel of cold water will absorb heat
as acid is added.
| Physical property | H2SO4 | Water | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.84 | 1.0 | kg/L |
| Volumetric heat capacity | 2.54 | 4.18 | kJ/L |
| Boiling point | 337 | 100 | °C |
Also, because the acid is denser than water, it sinks to the bottom.
Heat is generated at the interface between acid and water, which is at
the bottom of the vessel. Acid will not boil, because of its higher
boiling point. Warm water near the interface rises due to convection, which cools the interface, and prevents boiling of either acid or water.
In contrast, addition of water to concentrated sulfuric acid
results in a thin layer of water on top of the acid. Heat generated in
this thin layer of water can boil, leading to the dispersal of a
sulfuric acid aerosol or worse, an explosion.
Preparation of solutions greater than 6 M (35%) in concentration
is most dangerous, because the heat produced may be sufficient to boil
the diluted acid: efficient mechanical stirring and external cooling
(such as an ice bath) are essential.
Reaction rates double for about every 10 degree Celsius increase in temperature.
Therefore, the reaction will become more violent as dilution proceeds,
unless the mixture is given time to cool. Adding acid to warm water will
cause a violent reaction.
On a laboratory scale, sulfuric acid can be diluted by pouring
concentrated acid onto crushed ice made from de-ionized water. The ice
melts in an endothermic process while dissolving the acid. The amount of
heat needed to melt the ice in this process is greater than the amount
of heat evolved by dissolving the acid so the solution remains cold.
After all the ice has melted, further dilution can take place using
water.
Industrial hazards
Sulfuric acid is non-flammable.
The main occupational risks posed by this acid are skin contact
leading to burns (see above) and the inhalation of aerosols. Exposure to
aerosols at high concentrations leads to immediate and severe
irritation of the eyes, respiratory tract and mucous membranes: this
ceases rapidly after exposure, although there is a risk of subsequent pulmonary edema
if tissue damage has been more severe. At lower concentrations, the
most commonly reported symptom of chronic exposure to sulfuric acid
aerosols is erosion of the teeth, found in virtually all studies:
indications of possible chronic damage to the respiratory tract
are inconclusive as of 1997. Repeated occupational exposure to sulfuric
acid mists may increase the chance of lung cancer by up to 64 percent. In the United States, the permissible exposure limit (PEL) for sulfuric acid is fixed at 1 mg/m3: limits in other countries are similar. There have been reports of sulfuric acid ingestion leading to vitamin B12 deficiency with subacute combined degeneration. The spinal cord is most often affected in such cases, but the optic nerves may show demyelination, loss of axons and gliosis.
Legal restrictions
International commerce of sulfuric acid is controlled under the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988,
which lists sulfuric acid under Table II of the convention as a
chemical frequently used in the illicit manufacture of narcotic drugs or
psychotropic substances.



![{\displaystyle \overbrace {{\ce {C12H22O11}}} ^{\text{sucrose}}\ {\ce {->[{\ce {H2SO4}}]}}\ {\underset {\text{(black graphitic foam)}}{{\ce {12C}}}}+{\ce {11H2O}}_{\text{(g,l)}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/195318b5774cf1e346fdf02beb203c9754e56880)
![{\displaystyle \overbrace {\ce {(C6H10O5)_{\mathit {n}}}} ^{\text{polysaccharide}}\ {\ce {->[{\ce {H2SO4}}]}}\ 6n{\ce {C}}+5n{\ce {H2O}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/547e4aa6ec4deb58f140807dbef295c5d9965771)