| Anopheles | |
|---|---|

| |
| Anopheles stephensi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Culicidae |
| Subfamily: | Anophelinae |
| Genus: | Anopheles Meigen 1818 |
| |
| Anopheles range map | |
Anopheles (/əˈnɒfɪliːz/) is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognised; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which cause malaria in humans in endemic areas. Anopheles gambiae is one of the best known, because of its predominant role in the transmission of the most dangerous malaria parasite species (to humans) – Plasmodium falciparum.
The name comes from the Ancient Greek word ἀνωφελής anōphelḗs 'useless', derived from ἀν- an-, 'not', 'un-' and ὄφελος óphelos 'profit'.
Mosquitoes in other genera (Aedes, Culex, Culiseta, Haemagogus, and Ochlerotatus) can also serve as vectors of disease agents, but not human malaria.
Evolution
The ancestors of Drosophila and the mosquitoes diverged 260 million years ago. The culicine and Anopheles clades of mosquitoes diverged between 120 million years ago and 150 million years ago. The Old and New World Anopheles species subsequently diverged between 80 million years ago and 95 million years ago. Anopheles darlingi diverged from the African and Asian malaria vectors ∼100 million years ago. The Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles funestus clades diverged between 80 million years ago and 36 million years ago. A molecular study of several genes in seven species has provided additional support for an expansion of this genus during the Cretaceous period.
The Anopheles genome, at 230–284 million base pairs (Mbp), is comparable in size to that of Drosophila,
but considerably smaller than those found in other culicine genomes
(528 Mbp–1.9 Gbp). Like most culicine species, the genome is diploid with six chromosomes.
The only known fossils of this genus are those of Anopheles (Nyssorhynchus) dominicanus Zavortink & Poinar contained in Dominican amber from the Late Eocene (40.4 million years ago to 33.9 million years ago) and Anopheles rottensis Statz contained in German amber from the Late Oligocene (28.4 million years ago to 23 million years ago).
Systematics
The genus Anopheles Meigen (nearly worldwide distribution) belongs to the subfamily Anophelinae together with another two genera: Bironella Theobald (Australia only) and Chagasia Cruz (Neotropics).
The taxonomy remains incompletely settled. Classification into species
is based on morphological characteristics – wing spots, head anatomy,
larval and pupal anatomy, chromosome structure, and more recently, on
DNA sequences. In the taxonomy published by Harbach et al in 2016, it
was shown that three species of Bironella: confusa, gracilis, and hollandi are phylogenetically similar Anopheles kyondawensis than other Bironella species. The same phylogeny also argues that, based on genetic similarity, Anopheles implexus is actually divergent from the common ancestor to the Anopheles genus, raising new questions regarding taxonomy and classification.
The genus has been subdivided into seven subgenera based primarily on the number and positions of specialized setae on the gonocoxites of the male genitalia. The system of subgenera originated with the work of Christophers, who in 1915 described three subgenera: Anopheles (widely distributed), Myzomyia (later renamed Cellia) (Old World) and Nyssorhynchus (Neotropical). Nyssorhynchus was first described as Lavernia by Frederick Vincent Theobald. Frederick Wallace Edwards in 1932 added the subgenus Stethomyia (Neotropical distribution). Kerteszia was also described by Edwards in 1932, but then recognised as a subgrouping of Nyssorhynchus.
It was elevated to subgenus status by Komp in 1937, and it is also
found in the Neotropics. Two additional subgenera have since been
recognised: Baimaia (Southeast Asia only) by Harbach et al. in 2005 and Lophopodomyia (Neotropical) by Antunes in 1937.
Two main groupings within the genus Anopheles are used: one formed by the Celia and Anopheles subgenera and a second by Kerteszia, Lophopodomyia and Nyssorhynchus. Subgenus Stethomyia is an outlier with respect to these two taxa. Within the second group, Kerteszia and Nyssorhynchus appear to be sister taxa.
The number of species currently recognised within the subgenera is given here in parentheses: Anopheles (206 species), Baimaia (1), Cellia (216), Kerteszia (12), Lophopodomyia (6), Nyssorhynchus (34) and Stethomyia (5).
Taxonomic units between subgenus and species are not currently
recognised as official zoological names. In practice, a number of
taxonomic levels have been introduced. The larger subgenera (Anopheles, Cellia and Nyssorhynchus)
have been subdivided into sections and series which in turn have been
divided into groups and subgroups. Below subgroup but above species
level is the species complex. Taxonomic levels above species complex can
be distinguished on morphological grounds. Species within a species
complex are either morphologically identical or extremely similar and
can only be reliably separated by microscopic examination of the
chromosomes or DNA sequencing. The classification continues to be
revised.
Subgenus Nyssorhynchus has been divided in three sections: Albimanus (19 species), Argyritarsis (11 species) and Myzorhynchella (4 species). The Argyritarsis section has been subdivided into Albitarsis and Argyritarsis groups.
The Anopheles group was divided by Edwards into four series: Anopheles (worldwide), Myzorhynchus (Palearctic, Oriental, Australasian and Afrotropical), Cycloleppteron (Neotropical) and Lophoscelomyia (Oriental); and two groups, Arribalzagia (Neotropical) and Christya (Afrotropical). Reid and Knight (1961) modified this classification and consequently subdivided the subgenus Anopheles into two sections, Angusticorn and Laticorn and six series. The Arribalzagia and Christya Groups were considered to be series. The Laticorn Section includes the Arribalzagia (24 species), Christya and Myzorhynchus series. The Angusticorn section includes members of the Anopheles, Cycloleppteron and Lophoscelomyia series.
All species known to carry human malaria lie within either the Myzorhynchus or the Anopheles series.
Life stages
Like all mosquitoes, anophelines go through four stages in their life cycles: egg, larva, pupa, and imago.
The first three stages are aquatic and together last 5–14 days,
depending on the species and the ambient temperature. The adult stage is
when the female Anopheles mosquito acts as malaria vector. The adult females can live up to a month (or more in captivity), but most probably do not live more than two weeks in nature.
Eggs
Anopheles egg
Adult females lay 50–200 eggs per oviposition.
The eggs are quite small (about 0.5 × 0.2 mm). Eggs are laid singly and
directly on water. They are unique in that they have floats on either
side. Eggs are not resistant to drying and hatch within 2–3 days,
although hatching may take up to 2–3 weeks in colder climates.
Larvae
Anopheles larva from southern Germany, about 8 mm long
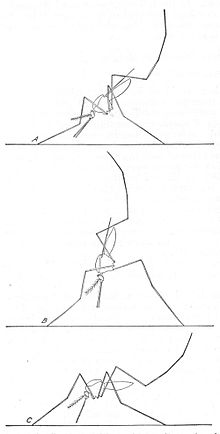
Feeding position of an Anopheles larva (A), compared to that of a nonanopheline mosquito (B)
The mosquito larva has a well-developed head with mouth brushes used for feeding, a large thorax and a nine-segment abdomen. It has no legs. In contrast to other mosquitoes, the Anopheles larva lacks a respiratory siphon, so it positions itself so that its body is parallel to the surface of the water.
In contrast, the feeding larva of a nonanopheline mosquito species
attaches itself to the water surface with its posterior siphon, with its
body pointing downwards.
Larvae breathe through spiracles
located on the eighth abdominal segment, so must come to the surface
frequently. The larvae spend most of their time feeding on algae, bacteria,
and other microorganisms in the surface microlayer. They dive below the
surface only when disturbed. Larvae swim either by jerky movements of
the entire body or through propulsion with the mouth brushes.
Larvae develop through four stages, or instars, after which they metamorphose into pupae. At the end of each instar, the larvae molt, shedding their exoskeletons, or skin, to allow for further growth. First-stage larvae are about 1 mm in length; fourth-stage larvae are normally 5–8 mm in length.
The process from egg-laying to emergence of the adult is temperature dependent, with a minimum time of seven days.
The larvae occur in a wide range of habitats, but most species prefer clean, unpolluted water. Larvae of Anopheles
mosquitoes have been found in freshwater or saltwater marshes, mangrove
swamps, rice fields, grassy ditches, the edges of streams and rivers,
and small, temporary rain pools. Many species prefer habitats with
vegetation. Others prefer habitats with none. Some breed in open,
sun-lit pools, while others are found only in shaded breeding sites in
forests. A few species breed in tree holes or the leaf axils of some
plants.
Pupae
Pupa is also known as tumbler.The pupa is comma-shaped when viewed from the side. The head and thorax are merged into a cephalothorax
with the abdomen curving around underneath. As with the larvae, pupae
must come to the surface frequently to breathe, which they do through a
pair of respiratory trumpets on their cephalothoraces. After a few days
as a pupa, the dorsal surface of the cephalothorax splits and the adult
mosquito emerges. The pupal stage lasts around 2–3 days in temperate areas.
Adults
Resting positions of adult Anopheles (A, B), compared to a nonanopheline mosquito (C)
The duration from egg to adult varies considerably among species, and
is strongly influenced by ambient temperature. Mosquitoes can develop
from egg to adult in as little as five days, but it can take 10–14 days
in tropical conditions.
Like all mosquitoes, adult Anopheles species have slender bodies with three sections: head, thorax and abdomen.
The head is specialized for acquiring sensory information and for
feeding. It contains the eyes and a pair of long, many-segmented antennae.
The antennae are important for detecting host odors, as well as odors
of breeding sites where females lay eggs. The head also has an
elongated, forward-projecting proboscis used for feeding, and two maxillary palps. These palps also carry the receptors for carbon dioxide, a major attractant for the location of the mosquito's host.
The thorax is specialized for locomotion. Three pairs of legs and a pair of wings are attached to the thorax.
The abdomen is specialized for food digestion and egg
development. This segmented body part expands considerably when a female
takes a blood meal. The blood is digested over time, serving as a
source of protein for the production of eggs, which gradually fill the abdomen.
Anopheles mosquitoes can be distinguished from other mosquitoes by the palps,
which are as long as the proboscis, and by the presence of discrete
blocks of black and white scales on the wings. Adults can also be
identified by their typical resting position: males and females rest
with their abdomens sticking up in the air rather than parallel to the
surface on which they are resting.
Adult mosquitoes usually mate within a few days after emerging from the pupal stage. In most species, the males form large swarms, usually around dusk, and the females fly into the swarms to mate.
Males live for about a week, feeding on nectar and other sources of sugar.
Males cannot feed on blood, as it appears to produce toxic effects and
kills them within a few days, around the same lifespan as a water-only
diet.
Females will also feed on sugar sources for energy, but usually require
a blood meal for the development of eggs. After obtaining a full blood
meal, the female will rest for a few days while the blood is digested
and eggs are developed. This process depends on the temperature, but
usually takes 2–3 days in tropical conditions. Once the eggs are fully
developed, the female lays them and resumes host-seeking.
The cycle repeats itself until the female dies. While females can
live longer than a month in captivity, most do not live longer than one
to two weeks in nature. Their lifespans depend on temperature,
humidity, and their ability to successfully obtain a blood meal while
avoiding host defenses.
In a study by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
researchers found that female mosquitoes carrying malaria parasites are
significantly more attracted to human breath and odours than uninfected
mosquitoes. The research team infected laboratory-raised Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes with Plasmodium
parasites, leaving a control group uninfected. Then tests were run on
the two groups to record their attraction to human smells. Female
mosquitoes are particularly drawn to foot odours, and one of the tests
showed infected mosquitoes landing and biting a prospective host
repeatedly. The team speculates that the parasite improves the
mosquitoes' sense of smell. It may also reduce its risk aversion.
Habitat
Although malaria is nowadays limited to tropical areas, most notoriously the regions of sub-Saharan Africa, many Anopheles species live in colder latitudes. Indeed, malaria outbreaks have, in the past, occurred in
colder climates, for example during the construction of the Rideau Canal in Canada during the 1820s. Since then, the Plasmodium parasite (not the Anopheles mosquito) has been eliminated from first world countries.
The CDC warns, however, that "Anopheles that can transmit
malaria are found not only in malaria-endemic areas, but also in areas
where malaria has been eliminated. The latter areas are thus constantly
at risk of reintroduction of the disease.
Susceptibility to become a vector of disease
Some species are poor vectors of malaria, as the parasites
do not develop well (or at all) within them. There is also variation
within species. In the laboratory, it is possible to select strains of A. gambiae that are refractory to infection by malaria parasites. These refractory strains have an immune response that encapsulates and kills the parasites after they have invaded the mosquito's stomach wall. Scientists are studying the genetic
mechanism for this response. Genetically modified mosquitoes refractory
to malaria possibly could replace wild mosquitoes, thereby limiting or
eliminating malaria transmission.
Malaria transmission and control
Understanding the biology and behavior of Anopheles
mosquitoes can help understand how malaria is transmitted, and can aid
in designing appropriate control strategies. Factors affecting a
mosquito's facility to transmit malaria include its innate
susceptibility to Plasmodium,
its host choice and its longevity. Factors that should be taken into
consideration when designing a control program include the
susceptibility of malaria vectors to insecticides and the preferred feeding and resting location of adult mosquitoes.
On December 21, 2007, a study published in PLoS Pathogens found the hemolytic C-type lectin CEL-III from Cucumaria echinata, a sea cucumber found in the Bay of Bengal, impaired the development of the malaria parasite when produced by transgenic A. stephensi.
This could potentially be used to control malaria by spreading
genetically modified mosquitoes refractory to the parasites, although
numerous scientific and ethical issues must be overcome before such a
control strategy could be implemented.
Preferred sources for blood meals
One important behavioral factor is the degree to which an Anopheles species prefers to feed on humans (anthropophily) or animals such as cattle or birds (zoophily). Anthropophilic Anopheles are more likely to transmit the malaria parasites from one person to another. Most Anopheles mosquitoes are not exclusively anthropophilic or zoophilic, including the primary malaria vector in the western United States, A. freeborni. However, the primary malaria vectors in Africa, A. gambiae and A. funestus, are strongly anthropophilic and, consequently, are two of the most efficient malaria vectors in the world.
Once ingested by a mosquito, malaria parasites must undergo
development within the mosquito before they are infectious to humans.
The time required for development in the mosquito (the extrinsic incubation period)
ranges from 10–21 days, depending on the parasite species and the
temperature. If a mosquito does not survive longer than the extrinsic
incubation period, then she will not be able to transmit any malaria
parasites.
It is not possible to measure directly the lifespans of
mosquitoes in nature, but indirect estimates of daily survivorship have
been made for several Anopheles species. Estimates of daily survivorship of A. gambiae in Tanzania ranged from 0.77 to 0.84, meaning at the end of one day, between 77% and 84% will have survived.
Assuming this survivorship is constant through the adult life of a mosquito, less than 10% of female A. gambiae
would survive longer than a 14-day extrinsic incubation period. If
daily survivorship increased to 0.9, over 20% of mosquitoes would
survive longer than the same period. Control measures that rely on insecticides (e.g. indoor residual spraying) may actually impact malaria transmission more through their effect on adult longevity than through their effect on the population of adult mosquitoes.
Patterns of feeding and resting
Most Anopheles mosquitoes are crepuscular (active at dusk or dawn) or nocturnal
(active at night). Some feed indoors (endophagic), while others feed
outdoors (exophagic). After feeding, some blood mosquitoes prefer to
rest indoors (endophilic), while others prefer to rest outdoors
(exophilic),
though this can differ regionally based on local vector ecotype, and
vector chromosomal makeup, as well as housing type and local
microclimatic conditions. Biting by nocturnal, endophagic Anopheles mosquitoes can be markedly reduced through the use of insecticide-treated bed nets or through improved housing construction to prevent mosquito entry (e.g. window screens).
Endophilic mosquitoes are readily controlled by indoor spraying of
residual insecticides. In contrast, exophagic/exophilic vectors are best
controlled through source reduction (destruction of the breeding
sites).
Gut flora
Because
transmission of disease by the mosquito requires ingestion of blood,
the gut flora may have a bearing on the success of infection of the
mosquito host. This aspect of disease transmission has not been
investigated until recently. The larval and pupal gut is largely colonised by photosynthetic cyanobacteria, while in the adult, Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes predominate. Blood meals drastically reduce the diversity of organisms and favor enteric bacteria.
Insecticide resistance
Insecticide-based
control measures (e.g. indoor spraying with insecticides, bed nets) are
the principal ways to kill mosquitoes that bite indoors. However, after
prolonged exposure to an insecticide over several generations, mosquito populations, like those of other insects,
may evolve resistance, a capacity to survive contact with an
insecticide. Since mosquitoes can have many generations per year, high
levels of resistance can evolve very quickly. Resistance of mosquitoes
to some insecticides has been documented with just within a few years
after the insecticides were introduced. Over 125 mosquito species
have documented resistance to one or more insecticides. The evolution
of resistance to insecticides used for indoor residual spraying was a
major impediment during the Global Malaria Eradication Campaign.
Judicious use of insecticides for mosquito control can limit the
evolution and spread of resistance. However, use of insecticides in
agriculture has often been implicated as contributing to resistance in
mosquito populations. Detection of evolving resistance in mosquito
populations is possible, so control programs are well advised to conduct
surveillance for this potential problem. In Malawi and other places, a shrub known as mpungabwi (Ocimum americanum) is used to repel mosquitoes.
Eradication
With substantial numbers of malaria cases affecting people around the globe, in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, where millions of children are killed by this infectious disease, eradication is back on the global health agenda.
Although malaria has existed since ancient times, its eradication was possible in Europe, North America, the Caribbean and parts of Asia
and southern Central America during the first regional elimination
campaigns in the late 1940s. However, the same results were not achieved
in sub-Saharan Africa.
Though the World Health Organization adopted a formal policy on the control and eradication of the malaria parasite since 1955,
only recently, after the Gates Malaria Forum in October 2007, did key
organizations start the debate on the pros and cons of redefining
eradication as a goal to control malaria.
Clearly, the cost of preventing malaria is much less than
treating the disease, in the long run. However, eradication of
mosquitoes is not an easy task. For effective prevention of malaria,
some conditions should be met, such as conducive conditions in the
country, data collection about the disease, targeted technical
approaches to the problem, very active and committed leadership, total
governmental support, sufficient monetary resources, community
involvement, and skilled technicians from different fields, as well as
an adequate implementation.
Currently, there are proposals to eradicate Anopheles gambiae, the main vector for malaria, with a CRISPR-Cas9 gene drive system.
This system aims to eradicate the species through introducing a gene
that would cause female sterility, thus causing the gene to be unable to
replicate. It has been demonstrated in a study by Kyrou et al that such
a gene drive system can suppress an entire caged An. gambiae population through targeting and deleting the dsx gene, which is vital for female fertility.
By utilizing the conservation tendencies of selfish genes, Kyrou et al
demonstrated full suppression of the population within 7-11 generations,
which is about less than a year. Of course, this has raised concerns
with both the efficiency of a gene drive system as well as the ethical
and ecological impact of such an eradication program. Therefore, there have been efforts to use the gene drive system to more efficiently introduce genes of Plasmodium resistance into the species, such as targeting and knocking out the FREP1 gene in Anopheles gambiae.
Such systems may generate less ecological impact, as the species are
not removed from the ecosystem, though concerns regarding efficiency
still linger.
Researchers in Burkina Faso have created a strain of the fungus metarhizium pinghaense genetically engineered to produce the venom of an Australian funnel-web spider; exposure to the fungus caused populations of Anopheles mosquitoes to crash by 99% in a controlled trial.
A wide range of strategies is needed to achieve malaria
eradication, starting from simple steps to complicated strategies which
may not be possible to enforce with the current tools.
Although mosquito control is an important component of malaria
control strategy, elimination of malaria in an area does not require the
elimination of all Anopheles mosquitoes. For instance, in North America and Europe, although the vector Anopheles
mosquitoes are still present, the parasite has been eliminated. Some
socioeconomic improvements (e.g., houses with screened windows, air conditioning),
once combined with vector reduction efforts and effective treatment,
lead to the elimination of malaria without the complete elimination of
the vectors. Some important measures in mosquito control to be followed
are: discourage egg-laying, prevent development of eggs into larvae and
adults, kill the adult mosquitoes, do not allow adult mosquitoes into
places of human dwelling, prevent mosquitoes from biting human beings
and deny them blood meals.
Research in this sense continues, and a study has suggested
sterile mosquitoes might be the answer to malaria elimination. This
research suggests using the sterile insect technique,
in which sexually sterile male insects are released to wipe out a pest
population, could be a solution to the problem of malaria in Africa.
This technique brings hope, as female mosquitoes only mate once during
their lifetimes, and in doing so with sterile male mosquitoes, the
insect population would decrease.
This is another option to be considered by local and international
authorities that may be combined with other methods and tools to achieve
malaria eradication in sub-Saharan Africa.
Parasites
A number of parasites of this genus are known to exist, including microsporidia of the genera Amblyospora, Crepidulospora, Senoma and Parathelohania.
Microsporidia infecting the aquatic stages of insects, a group that includes mosquitoes and black flies,
and copepods appear to form a distinct clade from those infecting
terrestrial insects and fish. Two distinct life cycles are found in this
group. In the first type, the parasite is transmitted by the oral
route and is relatively species nonspecific. In the second, while again
the oral route is the usual route of infection, the parasite is ingested
within an already infected intermediate host. Infection of the insect
larval form is frequently tissue-specific, and commonly involves the fat body. Vertical (transovarial) transmission is also known to occur.
Few phylogenetic studies of these parasites have been done, and
their relationship to their mosquito hosts is still being determined.
One study suggested Parathelohania is an early diverging genus within this group.
The parasite Wolbachia bacteria have also been studied for use as control agents.