| Yellow fever | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Yellow jack, yellow plague, bronze john |
 | |
| A TEM micrograph of yellow fever virus (234,000× magnification) | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, chills, muscle pain, headache, yellow skin |
| Complications | Liver failure, bleeding |
| Usual onset | 3–6 days post exposure |
| Duration | 3–4 days |
| Causes | Yellow fever virus spread by mosquitoes |
| Diagnostic method | Blood test |
| Prevention | Yellow fever vaccine |
| Treatment | Supportive care |
| Frequency | ~127,000 severe cases (2013) |
| Deaths | 5,100 (2015) |
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains particularly in the back, and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems is increased.
The disease is caused by yellow fever virus and is spread by the bite of an infected female mosquito. It infects only humans, other primates, and several types of mosquitoes. In cities, it is spread primarily by Aedes aegypti, a type of mosquito found throughout the tropics and subtropics. The virus is an RNA virus of the genus Flavivirus. The disease may be difficult to tell apart from other illnesses, especially in the early stages. To confirm a suspected case, blood-sample testing with polymerase chain reaction is required.
A safe and effective vaccine against yellow fever exists, and some countries require vaccinations for travelers. Other efforts to prevent infection include reducing the population of the transmitting mosquitoes. In areas where yellow fever is common, early diagnosis of cases and immunization of large parts of the population are important to prevent outbreaks. Once infected, management is symptomatic with no specific measures effective against the virus. Death occurs in up to half of those who get severe disease.
In 2013, yellow fever resulted in about 127,000 severe infections and 45,000 deaths, with nearly 90 percent of these occurring in African nations. Nearly a billion people live in an area of the world where the disease is common. It is common in tropical areas of the continents of South America and Africa, but not in Asia. Since the 1980s, the number of cases of yellow fever has been increasing. This is believed to be due to fewer people being immune, more people living in cities, people moving frequently, and changing climate increasing the habitat for mosquitoes. The disease originated in Africa and spread to South America with the slave trade in the 17th century. Since the 17th century, several major outbreaks of the disease have occurred in the Americas, Africa, and Europe. In the 18th and 19th centuries, yellow fever was seen as one of the most dangerous infectious diseases. In 1927, yellow fever virus became the first human virus to be isolated.
Signs and symptoms
Yellow fever begins after an incubation period of three to six days.
Most cases only cause a mild infection with fever, headache, chills,
back pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, muscle pain, nausea, and vomiting. In these cases, the infection lasts only three to four days.
In 15% of cases, though, people enter a second, toxic phase of
the disease with recurring fever, this time accompanied by jaundice due
to liver damage, as well as abdominal pain. Bleeding in the mouth, nose, the eyes, and the gastrointestinal tract cause vomit containing blood, hence the Spanish name for yellow fever, vómito negro ("black vomit"). There may also be kidney failure, hiccups, and delirium.
Among those who develop jaundice, the fatality rate is 20 to 50%, while the overall fatality rate is about 5%. Severe cases may have a mortality greater than 50%.
Surviving the infection provides lifelong immunity, and normally no permanent organ damage results.
Cause
| Yellow fever virus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Family: | Flaviviridae |
| Genus: | Flavivirus |
| Species: |
Yellow fever virus
|
Yellow fever is caused by yellow fever virus, an enveloped RNA virus 40–50 nm in width, the type species and namesake of the family Flaviviridae. It was the first illness shown to be transmissible by filtered human serum and transmitted by mosquitoes, by Walter Reed around 1900. The positive-sense, single-stranded RNA is around 11,000 nucleotides long and has a single open reading frame encoding a polyprotein. Host proteases
cut this polyprotein into three structural (C, prM, E) and seven
nonstructural proteins (NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5); the
enumeration corresponds to the arrangement of the protein coding genes in the genome. Minimal yellow fever virus
(YFV) 3'UTR region is required for stalling of the host 5'-3'
exonuclease XRN1. The UTR contains PKS3 pseudoknot structure, which
serves as a molecular signal to stall the exonuclease and is the only
viral requirement for subgenomic flavivirus RNA (sfRNA) production. The
sfRNAs are a result of incomplete degradation of the viral genome by the
exonuclease and are important for viral pathogenicity. Yellow fever belongs to the group of hemorrhagic fevers.
The viruses infect, amongst others, monocytes, macrophages, Schwann cells, and dendritic cells. They attach to the cell surfaces via specific receptors and are taken up by an endosomal vesicle. Inside the endosome, the decreased pH induces the fusion of the endosomal membrane with the virus envelope. The capsid enters the cytosol, decays, and releases the genome. Receptor binding, as well as membrane fusion, are catalyzed by the protein E, which changes its conformation at low pH, causing a rearrangement of the 90 homodimers to 60 homotrimers.
After entering the host cell, the viral genome is replicated in the rough endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) and in the so-called vesicle packets. At first, an immature form
of the virus particle is produced inside the ER, whose M-protein is not
yet cleaved to its mature form, so is denoted as precursor M (prM) and
forms a complex with protein E. The immature particles are processed in
the Golgi apparatus by the host protein furin, which cleaves prM to M. This releases E from the complex, which can now take its place in the mature, infectious virion.
Transmission
Aedes aegypti feeding
Adults of the yellow fever mosquito A. aegypti: The male is on the left, females are on the right. Only the female mosquito bites humans to transmit the disease.
Yellow fever virus is mainly transmitted through the bite of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti, but other mostly Aedes mosquitoes such as the tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) can also serve as a vector for this virus. Like other arboviruses, which are transmitted by mosquitoes, yellow fever virus
is taken up by a female mosquito when it ingests the blood of an
infected human or another primate. Viruses reach the stomach of the
mosquito, and if the virus concentration is high enough, the virions can
infect epithelial cells and replicate there. From there, they reach the haemocoel (the blood system of mosquitoes) and from there the salivary glands.
When the mosquito next sucks blood, it injects its saliva into the
wound, and the virus reaches the bloodstream of the bitten person. Transovarial and transstadial transmission of yellow fever virus within A. aegypti,
that is, the transmission from a female mosquito to her eggs and then
larvae, are indicated. This infection of vectors without a previous
blood meal seems to play a role in single, sudden breakouts of the
disease.
Three epidemiologically different infectious cycles occur in which the virus is transmitted from mosquitoes to humans or other primates. In the "urban cycle", only the yellow fever mosquito A. aegypti is involved. It is well adapted to urban areas, and can also transmit other diseases, including Zika fever, dengue fever, and chikungunya.
The urban cycle is responsible for the major outbreaks of yellow fever
that occur in Africa. Except for an outbreak in Bolivia in 1999, this
urban cycle no longer exists in South America.
Besides the urban cycle, both in Africa and South America, a sylvatic cycle (forest or jungle cycle) is present, where Aedes africanus (in Africa) or mosquitoes of the genus Haemagogus and Sabethes
(in South America) serve as vectors. In the jungle, the mosquitoes
infect mainly nonhuman primates; the disease is mostly asymptomatic in
African primates. In South America, the sylvatic cycle is currently the
only way humans can become infected, which explains the low incidence of
yellow fever cases on the continent. People who become infected in the
jungle can carry the virus to urban areas, where A. aegypti acts
as a vector. Because of this sylvatic cycle, yellow fever cannot be
eradicated except by eradicating the mosquitoes that serve as vectors.
In Africa, a third infectious cycle known as "savannah cycle" or
intermediate cycle, occurs between the jungle and urban cycles.
Different mosquitoes of the genus Aedes are involved. In recent years, this has been the most common form of transmission of yellow fever in Africa.
Concern exists about yellow fever spreading to southeast Asia, where its vector A. aegypti already occurs.
Pathogenesis
After transmission from a mosquito, the viruses replicate in the lymph nodes and infect dendritic cells in particular. From there, they reach the liver and infect hepatocytes (probably indirectly via Kupffer cells), which leads to eosinophilic degradation of these cells and to the release of cytokines. Apoptotic masses known as Councilman bodies appear in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes.
Diagnosis
Yellow fever is most frequently a clinical diagnosis,
made from symptoms and where the infected person was before becoming
ill. Mild courses of the disease can only be confirmed virologically.
Since mild courses of yellow fever can also contribute significantly to
regional outbreaks, every suspected case of yellow fever (involving
symptoms of fever, pain, nausea, and vomiting 6–10 days after leaving
the affected area) is treated seriously.
If yellow fever is suspected, the virus cannot be confirmed until
6–10 days after the illness. A direct confirmation can be obtained by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, where the genome of the virus is amplified. Another direct approach is the isolation of the virus and its growth in cell culture using blood plasma; this can take 1–4 weeks.
Serologically, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay during the acute phase of the disease using specific IgM against yellow fever or an increase in specific IgG titer
(compared to an earlier sample) can confirm yellow fever. Together with
clinical symptoms, the detection of IgM or a four-fold increase in IgG
titer is considered sufficient indication for yellow fever. Since these
tests can cross-react with other flaviviruses, such as dengue virus, these indirect methods cannot conclusively prove yellow fever infection.
Liver biopsy can verify inflammation and necrosis of hepatocytes and detect viral antigens. Because of the bleeding tendency of yellow fever patients, a biopsy is only advisable post mortem to confirm the cause of death.
In a differential diagnosis, infections with yellow fever must be distinguished from other feverish illnesses such as malaria. Other viral hemorrhagic fevers, such as Ebola virus, Lassa virus, Marburg virus, and Junin virus, must be excluded as the cause.
Prevention
Personal
prevention of yellow fever includes vaccination and avoidance of
mosquito bites in areas where yellow fever is endemic. Institutional
measures for prevention of yellow fever include vaccination programmes
and measures of controlling mosquitoes. Programmes for distribution of
mosquito nets for use in homes are providing reductions in cases of both
malaria and yellow fever. Use of EPA-registered insect repellent is
recommended when outdoors. Exposure for even a short time is enough for a
potential mosquito bite. Long-sleeved clothing, long pants, and socks
are useful for prevention. The application of larvicides to
water-storage containers can help eliminate potential mosquito breeding
sites. EPA-registered insecticide spray decreases the transmission of
yellow fever.
- Use insect repellent when outdoors such as those containing DEET, picaridin, ethyl butylacetylaminopropionate (IR3535), or oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin.
- Wear proper clothing to reduce mosquito bites. When weather permits, wear long sleeves, long pants, and socks when outdoors. Mosquitoes may bite through thin clothing, so spraying clothes with repellent containing permethrin or another EPA-registered repellent gives extra protection. Clothing treated with permethrin is commercially available. Mosquito repellents containing permethrin are not approved for application directly to the skin.
- The peak biting times for many mosquito species are dusk to dawn. However, A. aegypti, one of the mosquitoes that transmits yellow fever virus, feeds during the daytime. Staying in accommodations with screened or air-conditioned rooms, particularly during peak biting times, also reduces the risk of mosquito bites.
Vaccination
The cover of a certificate that confirms the holder has been vaccinated against yellow fever
Vaccination
is recommended for those traveling to affected areas, because
non-native people tend to develop more severe illness when infected.
Protection begins by the 10th day after vaccine administration in 95% of
people, and had been reported to last for at least 10 years. The World Health Organization (WHO) now states that a single dose of vaccination is sufficient to confer lifelong immunity against yellow fever disease." The attenuated live vaccine stem 17D was developed in 1937 by Max Theiler. The WHO recommends routine vaccinations for people living in affected areas between the 9th and 12th month after birth.
Up to one in four people experience fever, aches, and local soreness and redness at the site of injection. In rare cases (less than one in 200,000 to 300,000),
the vaccination can cause yellow fever vaccine-associated viscerotropic
disease, which is fatal in 60% of cases. It is probably due to the
genetic morphology of the immune system. Another possible side effect is
an infection of the nervous system, which occurs in one in 200,000 to
300,000 cases, causing yellow fever vaccine-associated neurotropic
disease, which can lead to meningoencephalitis and is fatal in less than 5% of cases.
The Yellow Fever Initiative, launched by the WHO in 2006,
vaccinated more than 105 million people in 14 countries in West Africa.[36] No outbreaks were reported during 2015. The campaign was supported by the GAVI Alliance,
and governmental organizations in Europe and Africa. According to the
WHO, mass vaccination cannot eliminate yellow fever because of the vast
number of infected mosquitoes in urban areas of the target countries,
but it will significantly reduce the number of people infected.
Demand for the yellow fever vaccine has continued to increase due
to the growing number of countries implementing yellow fever
vaccination as part of their routine immunization programmes.
Recent upsurges in yellow fever outbreaks in Angola (2015), the
Democratic Republic of Congo (2016), Uganda (2016), and more recently in
Nigeria and Brazil in 2017 have further increased demand, while
straining global vaccine supply.
Therefore, to vaccinate susceptible populations in preventive mass
immunization campaigns during outbreaks, fractional dosing of the
vaccine is being considered as a dose-sparing strategy to maximize
limited vaccine supplies.
Fractional dose yellow fever vaccination refers to administration of a
reduced volume of vaccine dose, which has been reconstituted as per
manufacturer recommendations.
The first practical use of fractional dose yellow fever vaccination was
in response to a large yellow fever outbreak in the Democratic Republic
of the Congo in mid-2016.
In March 2017, the WHO launched a vaccination campaign in Brazil with 3.5 million doses from an emergency stockpile. In March 2017 the WHO recommended vaccination for travellers to certain parts of Brazil.
In March 2018, Brazil shifted its policy and announced it planned to
vaccinate all 77.5 million currently unvaccinated citizens by April
2019.
Compulsory vaccination
Some
countries in Asia are theoretically in danger of yellow fever epidemics
(mosquitoes with the capability to transmit yellow fever and
susceptible monkeys are present), although the disease does not yet
occur there. To prevent introduction of the virus, some countries demand
previous vaccination of foreign visitors if they have passed through
yellow fever areas. Vaccination has to be proved by the production of a
vaccination certificate, which is valid 10 days after the vaccination
and lasts for 10 years. Although the WHO on 17 May 2013 advised that
subsequent booster vaccinations are unnecessary, an older (than 10
years) certificate may not be acceptable at all border posts in all
affected countries. A list of the countries that require yellow fever
vaccination is published by the WHO.
If the vaccination cannot be conducted for some reasons, dispensation
may be possible. In this case, an exemption certificate issued by a
WHO-approved vaccination center is required. Although 32 of 44 countries
where yellow fever occurs endemically do have vaccination programmes,
in many of these countries, less than 50% of their population is
vaccinated.
Vector control
Control of the yellow fever mosquito A. aegypti is of major importance, especially because the same mosquito can also transmit dengue fever and chikungunya disease. A. aegypti
breeds preferentially in water, for example in installations by
inhabitants of areas with precarious drinking water supply, or in
domestic waste, especially tires, cans, and plastic bottles. These
conditions are common in urban areas in developing countries.
Two main strategies are employed to reduce mosquito populations.
One approach is to kill the developing larvae. Measures are taken to
reduce the water accumulations in which the larvae develop. Larvicides are used, as well as larvae-eating fish and copepods, which reduce the number of larvae. For many years, copepods of the genus Mesocyclops have been used in Vietnam
for preventing dengue fever. It eradicated the mosquito vector in
several areas. Similar efforts may be effective against yellow fever. Pyriproxyfen is recommended as a chemical larvicide, mainly because it is safe for humans and effective even in small doses.
The second strategy is to reduce populations of the adult yellow fever mosquito. Lethal ovitraps can reduce Aedes
populations, but with a decreased amount of pesticide because it
targets the mosquitoes directly. Curtains and lids of water tanks can be
sprayed with insecticides, but application inside houses is not
recommended by the WHO. Insecticide-treated mosquito nets are effective, just as they are against the Anopheles mosquito that carries malaria.
Treatment
As for other Flavivirus
infections, no cure is known for yellow fever. Hospitalization is
advisable and intensive care may be necessary because of rapid
deterioration in some cases. Different methods for acute treatment of
the disease have been shown not to be very successful; passive
immunization after the emergence of symptoms is probably without effect.
Ribavirin and other antiviral drugs, as well as treatment with interferons, do not have a positive effect in patients. Asymptomatic treatment includes rehydration and pain relief with drugs such as paracetamol. Acetylsalicylic acid
should not be given because of its anticoagulant effect, which can be
devastating in the case of internal bleeding that can occur with yellow
fever.
Epidemiology
Yellow fever is common
in tropical and subtropical areas of South America and Africa.
Worldwide, about 600 million people live in endemic areas. The WHO
estimates 200,000 cases of disease and 30,000 deaths a year occur. But
the number of officially reported cases is far lower.
Africa
Areas with risk of yellow fever in Africa (2017)
An estimated 90% of the infections occur on the African continent. In 2008, the largest number of recorded cases was in Togo. In 2016, a large outbreak originated in Angola
and spread to neighboring countries before being contained by a massive
vaccination campaign. In March and April 2016, 11 cases were reported
in China, the first appearance of the disease in Asia in recorded
history.
Phylogenetic analysis has identified seven genotypes of yellow fever viruses, and they are assumed to be differently adapted to humans and to the vector A. aegypti.
Five genotypes (Angola, Central/East Africa, East Africa, West Africa
I, and West Africa II) occur only in Africa. West Africa genotype I is
found in Nigeria and the surrounding areas.
This appears to be especially virulent or infectious, as this type is
often associated with major outbreaks. The three genotypes in East and
Central Africa occur in areas where outbreaks are rare. Two recent
outbreaks in Kenya (1992–1993) and Sudan (2003 and 2005) involved the
East African genotype, which had remained unknown until these outbreaks
occurred.
South America
Areas with risk of yellow fever in South America (2018)
In South America, two genotypes have been identified (South American genotypes I and II). Based on phylogenetic analysis these two genotypes appear to have originated in West Africa and were first introduced into Brazil. The date of introduction into South America appears to be 1822 (95% confidence interval 1701 to 1911).
The historical record shows an outbreak of yellow fever occurred in
Recife, Brazil, between 1685 and 1690. The disease seems to have
disappeared, with the next outbreak occurring in 1849. It was likely
introduced with the importation of slaves through the slave trade from Africa. Genotype I has been divided into five subclades, A through E.
In late 2016, a large outbreak began in Minas Gerais state of Brazil that was characterized as a sylvan or jungle epizootic. It began as an outbreak in brown howler monkeys, which serve as a sentinel species for yellow fever, that then spread to men working in the jungle. No cases had been transmitted between humans by the A. aegypti
mosquito, which can sustain urban outbreaks that can spread rapidly. In
April 2017, the sylvan outbreak continued moving toward the Brazilian
coast, where most people were unvaccinated.
By the end of May the outbreak appeared to be declining after more than
3,000 suspected cases, 758 confirmed and 264 deaths confirmed to be
yellow fever. The Health Ministry launched a vaccination campaign and was concerned about spread during the Carnival season in February and March. The CDC issued a Level 2 alert (practice enhanced precautions.)
A Bayesian analysis of genotypes I and II has shown that genotype I accounts for virtually all the current infections in Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Trinidad and Tobago, while genotype II accounted for all cases in Peru.
Genotype I originated in the northern Brazilian region around 1908 (95%
highest posterior density interval [HPD]: 1870–1936). Genotype II
originated in Peru in 1920 (95% HPD: 1867–1958). The estimated rate of
mutation for both genotypes was about 5 × 10−4 substitutions/site/year, similar to that of other RNA viruses.
Asia
The main vector (A. aegypti)
also occurs in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, the Pacific,
and Australia, but yellow fever has never occurred there, until jet
travel introduced 11 cases from the 2016 Angola and DR Congo yellow fever outbreak in Africa. Proposed explanations include:
- That the strains of the mosquito in the east are less able to transmit yellow fever virus.
- That immunity is present in the populations because of other diseases caused by related viruses (for example, dengue).
- That the disease was never introduced because the shipping trade was insufficient.
But none is considered satisfactory. Another proposal is the absence of a slave trade to Asia on the scale of that to the Americas. The trans-Atlantic slave trade probably introduced yellow fever into the Western Hemisphere from Africa.
History
Early history
The
evolutionary origins of yellow fever most likely lie in Africa, with
transmission of the disease from nonhuman primates to humans.
The virus is thought to have originated in East or Central Africa and
spread from there to West Africa. As it was endemic in Africa, the
natives had developed some immunity to it. When an outbreak of yellow
fever would occur in an African village where colonists resided, most
Europeans died, while the native population usually suffered nonlethal
symptoms resembling influenza.
This phenomenon, in which certain populations develop immunity to
yellow fever due to prolonged exposure in their childhood, is known as acquired immunity. The virus, as well as the vector A. aegypti, were probably transferred to North and South America with the importation of slaves from Africa, part of the Columbian Exchange following European exploration and colonization.
The first definitive outbreak of yellow fever in the New World was in 1647 on the island of Barbados. An outbreak was recorded by Spanish colonists in 1648 in the Yucatán Peninsula, where the indigenous Mayan people called the illness xekik ("blood vomit"). In 1685, Brazil suffered its first epidemic in Recife. The first mention of the disease by the name "yellow fever" occurred in 1744. McNeill argues that the environmental and ecological disruption caused by the introduction of sugar plantations created the conditions for mosquito and viral reproduction, and subsequent outbreaks of yellow fever. Deforestation reduced populations of insectivorous birds and other creatures that fed on mosquitoes and their eggs.
Sugar curing house, 1762: Sugar pots and jars on sugar plantations served as breeding place for larvae of A. aegypti, the vector of yellow fever.
In Colonial times and during the Napoleonic Wars,
the West Indies were known as a particularly dangerous posting for
soldiers due to yellow fever being endemic in the area. The mortality
rate in British garrisons in Jamaica was seven times that of garrisons in Canada, mostly because of yellow fever and other tropical diseases.
Both English and French forces posted there were seriously affected by
the "yellow jack." Wanting to regain control of the lucrative sugar
trade in Saint-Domingue
(Hispaniola), and with an eye on regaining France's New World empire,
Napoleon sent an army under the command of his brother-in-law General Charles Leclerc
to Saint-Domingue to seize control after a slave revolt. The historian
J. R. McNeill asserts that yellow fever accounted for about 35,000 to
45,000 casualties of these forces during the fighting.
Only one third of the French troops survived for withdrawal and return
to France. Napoleon gave up on the island and his plans for North
America, selling the Louisiana Purchase to the US in 1803. In 1804, Haiti
proclaimed its independence as the second republic in the Western
Hemisphere. Considerable debate exists over whether the number of deaths
caused by disease in the Haitian Revolution was exaggerated.
Although yellow fever is most prevalent in tropical-like
climates, the northern United States were not exempted from the fever.
The first outbreak in English-speaking North America occurred in New York City in 1668. English colonists in Philadelphia and the French in the Mississippi River Valley recorded major outbreaks in 1669, as well as additional yellow fever epidemics in Philadelphia, Baltimore, and New York City in the 18th and 19th centuries. The disease traveled along steamboat routes from New Orleans, causing some 100,000–150,000 deaths in total. The yellow fever epidemic of 1793
in Philadelphia, which was then the capital of the United States,
resulted in the deaths of several thousand people, more than 9% of the
population. The national government fled the city, including President George Washington.
Headstones of people who died in the yellow fever epidemic of 1878 can be found in New Orleans' cemeteries.
The southern city of New Orleans
was plagued with major epidemics during the 19th century, most notably
in 1833 and 1853. Its residents called the disease "yellow jack." Urban
epidemics continued in the United States until 1905, with the last
outbreak affecting New Orleans.
At least 25 major outbreaks took place in the Americas during the
18th and 19th centuries, including particularly serious ones in Cartagena, Chile, in 1741; Cuba in 1762 and 1900; Santo Domingo in 1803; and Memphis, Tennessee, in 1878.
In the early nineteenth century, the prevalence of yellow fever
in the Caribbean "led to serious health problems" and alarmed the United States Navy as numerous deaths and sickness curtailed naval operations and destroyed morale. A tragic episode began in April of 1822 when the frigate USS Macedonian left Boston and became part of Commodore James Biddle's West India Squadron. Secretary of the Navy Smith Thompson
had assigned the squadron to guard United States merchant shipping and
suppress piracy. During their time on deployment from 26 May to 3 August
1822, seventy-six of the Macedonian's officers and men died, including
Dr. John Cadle, Surgeon USN. Seventy-four of these deaths were
attributed to yellow fever. Biddle reported that another fifty-two of
his crew were on sick-list. In their report to the Secretary of the
Navy, Biddle and Surgeon's Mate Dr. Charles Chase stated the cause as
"fever." As a consequence of this loss, Biddle noted that his squadron
was forced to return to Norfolk Navy Yard early. Upon arrival, the
Macedonian's crew were provided medical care and quarantined at Craney
Island, Virginia.
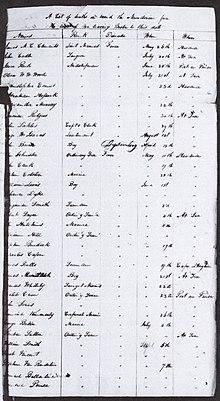
A
page from Commodore James Biddle's list of the seventy-six dead
(seventy-four of yellow fever) aboard the USS Macedonian, dated 3 August
1822
In 1853, Cloutierville, Louisiana,
had a late-summer outbreak of yellow fever that quickly killed 68 of
the 91 inhabitants. A local doctor concluded that some unspecified
infectious agent had arrived in a package from New Orleans. In 1854, 650 residents of Savannah, Georgia died from yellow fever. In 1858, St. Matthew's German Evangelical Lutheran Church in Charleston, South Carolina, suffered 308 yellow fever deaths, reducing the congregation by half. A ship carrying persons infected with the virus arrived in Hampton Roads in southeastern Virginia in June 1855. The disease spread quickly through the community, eventually killing over 3,000 people, mostly residents of Norfolk and Portsmouth. In 1873, Shreveport, Louisiana,
lost 759 citizens in an 80-day period to a yellow fever epidemic, with
over 400 additional victims eventually succumbing. The total death toll
from August through November was approximately 1,200.
In 1878, about 20,000 people died in a widespread epidemic in the Mississippi River Valley.
That year, Memphis had an unusually large amount of rain, which led to
an increase in the mosquito population. The result was a huge epidemic
of yellow fever.
The steamship John D. Porter took people fleeing Memphis northward in
hopes of escaping the disease, but passengers were not allowed to
disembark due to concerns of spreading yellow fever. The ship roamed the
Mississippi River for the next two months before unloading her
passengers.
Major outbreaks have also occurred in southern Europe. Gibraltar lost many lives to outbreaks in 1804, 1814, and 1828. Barcelona suffered the loss of several thousand citizens during an outbreak in 1821. The Duke de Richelieu deployed 30,000 French troops to the border between France and Spain in the Pyrenees Mountains, to establish a cordon sanitaire in order to prevent the epidemic from spreading from Spain into France.
Causes and transmission
Ezekiel Stone Wiggins, known as the Ottawa Prophet, proposed that the cause of a yellow fever epidemic in Jacksonville, Florida, in 1888, was astrological.
The planets were in the same line as the sun and earth and this produced, besides Cyclones, Earthquakes, etc., a denser atmosphere holding more carbon and creating microbes. Mars had an uncommonly dense atmosphere, but its inhabitants were probably protected from the fever by their newly discovered canals, which were perhaps made to absorb carbon and prevent the disease.
In 1848, Josiah C. Nott
suggested that yellow fever was spread by insects such as moths or
mosquitoes, basing his ideas on the pattern of transmission of the
disease. Carlos Finlay, a Cuban doctor and scientist, proposed in 1881 that yellow fever might be transmitted by mosquitoes rather than direct human contact. Since the losses from yellow fever in the Spanish–American War in the 1890s were extremely high, Army doctors began research experiments with a team led by Walter Reed, and composed of doctors James Carroll, Aristides Agramonte, and Jesse William Lazear.
They successfully proved Finlay's ″mosquito hypothesis″. Yellow fever
was the first virus shown to be transmitted by mosquitoes. The physician
William Gorgas applied these insights and eradicated yellow fever from Havana. He also campaigned against yellow fever during the construction of the Panama Canal.
A previous effort of canal building by the French had failed in part
due to mortality from the high incidence of yellow fever and malaria,
which killed many workers.
Although Dr. Walter Reed has received much of the credit in
United States history books for "beating" yellow fever, he had fully
credited Dr. Finlay with the discovery of the yellow fever vector, and
how it might be controlled. Reed often cited Finlay's papers in his own
articles, and also credited him for the discovery in his personal
correspondence. The acceptance of Finlay's work was one of the most important and far-reaching effects of the Walter Reed Commission of 1900.
Applying methods first suggested by Finlay, the United States
government and Army eradicated yellow fever in Cuba and later in Panama,
allowing completion of the Panama Canal. While Reed built on the
research of Finlay, historian François Delaporte notes that yellow fever
research was a contentious issue. Scientists, including Finlay and
Reed, became successful by building on the work of less prominent
scientists, without always giving them the credit they were due. Reed's research was essential in the fight against yellow fever. He is also credited for using the first type of medical consent
form during his experiments in Cuba, an attempt to ensure that
participants knew they were taking a risk by being part of testing.
Like Cuba and Panama, Brazil also led a highly successful sanitation
campaign against mosquitoes and yellow fever. Beginning in 1903, the
campaign led by Oswaldo Cruz,
then director general of public health, resulted not only in
eradicating the disease but also in reshaping the physical landscape of
Brazilian cities such as Rio de Janeiro. During rainy seasons, Rio de
Janeiro had regularly suffered floods, as water from the bay surrounding
the city overflowed into Rio's narrow streets. Coupled with the poor
drainage systems found throughout Rio, this created swampy conditions in
the city's neighborhoods. Pools of stagnant water stood year-long in
city streets and proved to be a fertile ground for disease-carrying
mosquitoes. Thus, under Cruz's direction, public health units known as
"mosquito inspectors" fiercely worked to combat yellow fever throughout
Rio by spraying, exterminating rats, improving drainage, and destroying
unsanitary housing. Ultimately, the city's sanitation and renovation
campaigns reshaped Rio de Janeiro's neighborhoods. Its poor residents
were pushed from city centers to Rio's suburbs, or to towns found in the
outskirts of the city. In later years, Rio's most impoverished
inhabitants would come to reside in favelas.
During 1920–23, the Rockefeller Foundation’s International Health Board undertook an expensive and successful yellow fever eradication campaign in Mexico.
The IHB gained the respect of Mexico's federal government because of
the success. The eradication of yellow fever strengthened the
relationship between the US and Mexico, which had not been very good in
the years prior. The eradication of yellow fever was also a major step
toward better global health.
In 1927, scientists isolated yellow fever virus in West Africa. Following this, two vaccines were developed in the 1930s. Vaccine 17D is still in use although newer vaccines, based on vero cells, are in development.
Current status
Using
vector control and strict vaccination programs, the urban cycle of
yellow fever was nearly eradicated from South America. Since 1943, only a
single urban outbreak in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia, has occurred. Since the 1980s, however, the number of yellow fever cases has been increasing again, and A. aegypti
has returned to the urban centers of South America. This is partly due
to limitations on available insecticides, as well as habitat
dislocations caused by climate change. It is also because the vector
control program was abandoned. Although no new urban cycle has yet been
established, scientists believe this could happen again at any point. An
outbreak in Paraguay in 2008 was thought to be urban in nature, but this ultimately proved not to be the case.
In Africa, virus eradication programs have mostly relied upon
vaccination. These programs have largely been unsuccessful because they
were unable to break the sylvatic cycle involving wild primates. With
few countries establishing regular vaccination programs, measures to
fight yellow fever have been neglected, making the future spread of the
virus more likely.
Research
In the hamster model of yellow fever, early administration of the antiviral ribavirin is an effective treatment of many pathological features of the disease.
Ribavirin treatment during the first five days after virus infection
improved survival rates, reduced tissue damage in the liver and spleen, prevented hepatocellular steatosis,
and normalised levels of alanine aminotransferase, a liver damage
marker. The mechanism of action of ribavirin in reducing liver pathology
in yellow fever virus infection may be similar to its activity in treatment of hepatitis C, a related virus.
Because ribavirin had failed to improve survival in a virulent rhesus
model of yellow fever infection, it had been previously discounted as a
possible therapy. Infection was reduced in mosquitoes with the wMel strain of Wolbachia.
Yellow fever has been researched by several countries as a potential biological weapon.