| Part of a series on |
| Biology |
|---|
 |
| Key components |
|
| Subdiciplines |
| Research |
| Applications |
In biology, homeostasis is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium and calcium ions, as well as that of the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life.
Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in the optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms. All homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components for the variable being regulated: a receptor, a control centre, and an effector. The receptor is the sensing component that monitors and responds to changes in the environment, either external or internal. Receptors include thermoreceptors, and mechanoreceptors. Control centres include the respiratory centre, and the renin–angiotensin system. An effector is the target acted on, to bring about the change back to the normal state. At the cellular level, receptors include nuclear receptors that bring about changes in gene expression through up-regulation or down-regulation, and act in negative feedback mechanisms. An example of this is in the control of bile acids in the liver.
Some centers, such as the renin–angiotensin system, control more than one variable. When the receptor senses a stimulus, it reacts by sending action potentials to a control center. The control center sets the maintenance range—the acceptable upper and lower limits—for the particular variable, such as temperature. The control center responds to the signal by determining an appropriate response and sending signals to an effector, which can be one or more muscles, an organ, or a gland. When the signal is received and acted on, negative feedback is provided to the receptor that stops the need for further signaling.
The cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), located at the presynaptic neuron, is a receptor that can stop stressful neurotransmitter release to the postsynaptic neuron; it is activated by endocannabinoids (ECs) such as anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamide; AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) via a retrograde signaling process in which these compounds are synthesized by and released from postsynaptic neurons, and travel back to the presynaptic terminal to bind to the CB1 receptor for modulation of neurotransmitter release to obtain homeostasis.
The polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are lipid derivatives of omega-3 (docosahexaenoic acid, DHA, and eicosapentaenoic acid, EPA) or of omega-6 (arachidonic acid, ARA) are synthesized from membrane phospholipids and used as a precursor for endocannabinoids (ECs) mediate significant effects in the fine-tune adjustment of body homeostasis.
History
The concept of the regulation of the internal environment was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1849, and the word homeostasis was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. In 1932, Joseph Barcroft a British physiologist, was the first to say that higher brain function required the most stable internal environment. Thus, to Barcroft homeostasis was not only organized by the brain—homeostasis served the brain. Homeostasis is an almost exclusively biological term, referring to the concepts described by Bernard and Cannon, concerning the constancy of the internal environment in which the cells of the body live and survive. The term cybernetics is applied to technological control systems such as thermostats, which function as homeostatic mechanisms, but is often defined much more broadly than the biological term of homeostasis.
Etymology
The word homeostasis (/ˌhoʊmioʊˈsteɪsɪs/) uses combining forms of homeo- and -stasis, New Latin from Greek: ὅμοιος homoios, "similar" and στάσις stasis, "standing still", yielding the idea of "staying the same".
Overview
The metabolic processes of all organisms can only take place in very specific physical and chemical environments. The conditions vary with each organism, and with whether the chemical processes take place inside the cell or in the interstitial fluid bathing the cells. The best known homeostatic mechanisms in humans and other mammals are regulators that keep the composition of the extracellular fluid (or the "internal environment") constant, especially with regard to the temperature, pH, osmolality, and the concentrations of sodium, potassium, glucose, carbon dioxide, and oxygen. However, a great many other homeostatic mechanisms, encompassing many aspects of human physiology, control other entities in the body. Where the levels of variables are higher or lower than those needed, they are often prefixed with hyper- and hypo-, respectively such as hyperthermia and hypothermia or hypertension and hypotension.
If an entity is homeostatically controlled it does not imply that its value is necessarily absolutely steady in health. Core body temperature is, for instance, regulated by a homeostatic mechanism with temperature sensors in, amongst others, the hypothalamus of the brain. However, the set point of the regulator is regularly reset. For instance, core body temperature in humans varies during the course of the day (i.e. has a circadian rhythm), with the lowest temperatures occurring at night, and the highest in the afternoons. Other normal temperature variations include those related to the menstrual cycle. The temperature regulator's set point is reset during infections to produce a fever. Organisms are capable of adjusting somewhat to varied conditions such as temperature changes or oxygen levels at altitude, by a process of acclimatisation.
Homeostasis does not govern every activity in the body. For instance the signal (be it via neurons or hormones) from the sensor to the effector is, of necessity, highly variable in order to convey information about the direction and magnitude of the error detected by the sensor. Similarly the effector's response needs to be highly adjustable to reverse the error – in fact it should be very nearly in proportion (but in the opposite direction) to the error that is threatening the internal environment. For instance, the arterial blood pressure in mammals is homeostatically controlled, and measured by stretch receptors in the walls of the aortic arch and carotid sinuses at beginnings of the internal carotid arteries. The sensors send messages via sensory nerves to the medulla oblongata of the brain indicating whether the blood pressure has fallen or risen, and by how much. The medulla oblongata then distributes messages along motor or efferent nerves belonging to the autonomic nervous system to a wide variety of effector organs, whose activity is consequently changed to reverse the error in the blood pressure. One of the effector organs is the heart whose rate is stimulated to rise (tachycardia) when the arterial blood pressure falls, or to slow down (bradycardia) when the pressure rises above set point. Thus the heart rate (for which there is no sensor in the body) is not homeostatically controlled, but is one of effector responses to errors in the arterial blood pressure. Another example is the rate of sweating. This is one of the effectors in the homeostatic control of body temperature, and therefore highly variable in rough proportion to the heat load that threatens to destabilize the body's core temperature, for which there is a sensor in the hypothalamus of the brain.
Controls of variables
Core temperature
Mammals regulate their core temperature using input from thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus, brain, spinal cord, internal organs, and great veins. Apart from the internal regulation of temperature, a process called allostasis can come into play that adjusts behaviour to adapt to the challenge of very hot or cold extremes (and to other challenges). These adjustments may include seeking shade and reducing activity, or seeking warmer conditions and increasing activity, or huddling. Behavioural thermoregulation takes precedence over physiological thermoregulation since necessary changes can be affected more quickly and physiological thermoregulation is limited in its capacity to respond to extreme temperatures.
When core temperature falls, the blood supply to the skin is reduced by intense vasoconstriction. The blood flow to the limbs (which have a large surface area) is similarly reduced, and returned to the trunk via the deep veins which lie alongside the arteries (forming venae comitantes). This acts as a counter-current exchange system which short-circuits the warmth from the arterial blood directly into the venous blood returning into the trunk, causing minimal heat loss from the extremities in cold weather. The subcutaneous limb veins are tightly constricted, not only reducing heat loss from this source, but also forcing the venous blood into the counter-current system in the depths of the limbs.
The metabolic rate is increased, initially by non-shivering thermogenesis, followed by shivering thermogenesis if the earlier reactions are insufficient to correct the hypothermia.
When core temperature rises are detected by thermoreceptors, the sweat glands in the skin are stimulated via cholinergic sympathetic nerves to secrete sweat onto the skin, which, when it evaporates, cools the skin and the blood flowing through it. Panting is an alternative effector in many vertebrates, which cools the body also by the evaporation of water, but this time from the mucous membranes of the throat and mouth.
Blood glucose
Blood sugar levels are regulated within fairly narrow limits. In mammals the primary sensors for this are the beta cells of the pancreatic islets. The beta cells respond to a rise in the blood sugar level by secreting insulin into the blood, and simultaneously inhibiting their neighboring alpha cells from secreting glucagon into the blood. This combination (high blood insulin levels and low glucagon levels) act on effector tissues, chief of which are the liver, fat cells and muscle cells. The liver is inhibited from producing glucose, taking it up instead, and converting it to glycogen and triglycerides. The glycogen is stored in the liver, but the triglycerides are secreted into the blood as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles which are taken up by adipose tissue, there to be stored as fats. The fat cells take up glucose through special glucose transporters (GLUT4), whose numbers in the cell wall are increased as a direct effect of insulin acting on these cells. The glucose that enters the fat cells in this manner is converted into triglycerides (via the same metabolic pathways as are used by the liver) and then stored in those fat cells together with the VLDL-derived triglycerides that were made in the liver. Muscle cells also take glucose up through insulin-sensitive GLUT4 glucose channels, and convert it into muscle glycogen.
A fall in blood glucose, causes insulin secretion to be stopped, and glucagon to be secreted from the alpha cells into the blood. This inhibits the uptake of glucose from the blood by the liver, fats cells and muscle. Instead the liver is strongly stimulated to manufacture glucose from glycogen (through glycogenolysis) and from non-carbohydrate sources (such as lactate and de-aminated amino acids) using a process known as gluconeogenesis. The glucose thus produced is discharged into the blood correcting the detected error (hypoglycemia). The glycogen stored in muscles remains in the muscles, and is only broken down, during exercise, to glucose-6-phosphate and thence to pyruvate to be fed into the citric acid cycle or turned into lactate. It is only the lactate and the waste products of the citric acid cycle that are returned to the blood. The liver can take up only the lactate, and by the process of energy consuming gluconeogenesis convert it back to glucose.
Iron levels
Copper regulation
Levels of blood gases
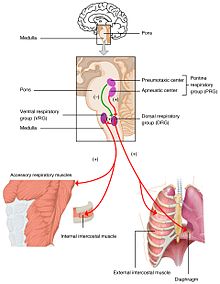
Changes in the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and plasma pH are sent to the respiratory center, in the brainstem where they are regulated. The partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the arterial blood is monitored by the peripheral chemoreceptors (PNS) in the carotid artery and aortic arch. A change in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is detected as altered pH in the cerebrospinal fluid by central chemoreceptors (CNS) in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. Information from these sets of sensors is sent to the respiratory center which activates the effector organs – the diaphragm and other muscles of respiration. An increased level of carbon dioxide in the blood, or a decreased level of oxygen, will result in a deeper breathing pattern and increased respiratory rate to bring the blood gases back to equilibrium.
Too little carbon dioxide, and, to a lesser extent, too much oxygen in the blood can temporarily halt breathing, a condition known as apnea, which freedivers use to prolong the time they can stay underwater.
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is more of a deciding factor in the monitoring of pH. However, at high altitude (above 2500 m) the monitoring of the partial pressure of oxygen takes priority, and hyperventilation keeps the oxygen level constant. With the lower level of carbon dioxide, to keep the pH at 7.4 the kidneys secrete hydrogen ions into the blood, and excrete bicarbonate into the urine. This is important in the acclimatization to high altitude.
Blood oxygen content
The kidneys measure the oxygen content rather than the partial pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood. When the oxygen content of the blood is chronically low, oxygen-sensitive cells secrete erythropoietin (EPO) into the blood. The effector tissue is the red bone marrow which produces red blood cells (RBCs)(erythrocytes). The increase in RBCs leads to an increased hematocrit in the blood, and subsequent increase in hemoglobin that increases the oxygen carrying capacity. This is the mechanism whereby high altitude dwellers have higher hematocrits than sea-level residents, and also why persons with pulmonary insufficiency or right-to-left shunts in the heart (through which venous blood by-passes the lungs and goes directly into the systemic circulation) have similarly high hematocrits.
Regardless of the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood, the amount of oxygen that can be carried, depends on the hemoglobin content. The partial pressure of oxygen may be sufficient for example in anemia, but the hemoglobin content will be insufficient and subsequently as will be the oxygen content. Given enough supply of iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid, EPO can stimulate RBC production, and hemoglobin and oxygen content restored to normal.
Arterial blood pressure
The brain can regulate blood flow over a range of blood pressure values by vasoconstriction and vasodilation of the arteries.
High pressure receptors called baroreceptors in the walls of the aortic arch and carotid sinus (at the beginning of the internal carotid artery) monitor the arterial blood pressure. Rising pressure is detected when the walls of the arteries stretch due to an increase in blood volume. This causes heart muscle cells to secrete the hormone atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) into the blood. This acts on the kidneys to inhibit the secretion of renin and aldosterone causing the release of sodium, and accompanying water into the urine, thereby reducing the blood volume. This information is then conveyed, via afferent nerve fibers, to the solitary nucleus in the medulla oblongata. From here motor nerves belonging to the autonomic nervous system are stimulated to influence the activity of chiefly the heart and the smallest diameter arteries, called arterioles. The arterioles are the main resistance vessels in the arterial tree, and small changes in diameter cause large changes in the resistance to flow through them. When the arterial blood pressure rises the arterioles are stimulated to dilate making it easier for blood to leave the arteries, thus deflating them, and bringing the blood pressure down, back to normal. At the same time, the heart is stimulated via cholinergic parasympathetic nerves to beat more slowly (called bradycardia), ensuring that the inflow of blood into the arteries is reduced, thus adding to the reduction in pressure, and correction of the original error.
Low pressure in the arteries, causes the opposite reflex of constriction of the arterioles, and a speeding up of the heart rate (called tachycardia). If the drop in blood pressure is very rapid or excessive, the medulla oblongata stimulates the adrenal medulla, via "preganglionic" sympathetic nerves, to secrete epinephrine (adrenaline) into the blood. This hormone enhances the tachycardia and causes severe vasoconstriction of the arterioles to all but the essential organ in the body (especially the heart, lungs, and brain). These reactions usually correct the low arterial blood pressure (hypotension) very effectively.
Calcium levels
The plasma ionized calcium (Ca2+) concentration is very tightly controlled by a pair of homeostatic mechanisms. The sensor for the first one is situated in the parathyroid glands, where the chief cells sense the Ca2+ level by means of specialized calcium receptors in their membranes. The sensors for the second are the parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland. The parathyroid chief cells secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) in response to a fall in the plasma ionized calcium level; the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland secrete calcitonin in response to a rise in the plasma ionized calcium level.
The effector organs of the first homeostatic mechanism are the bones, the kidney, and, via a hormone released into the blood by the kidney in response to high PTH levels in the blood, the duodenum and jejunum. Parathyroid hormone (in high concentrations in the blood) causes bone resorption, releasing calcium into the plasma. This is a very rapid action which can correct a threatening hypocalcemia within minutes. High PTH concentrations cause the excretion of phosphate ions via the urine. Since phosphates combine with calcium ions to form insoluble salts (see also bone mineral), a decrease in the level of phosphates in the blood, releases free calcium ions into the plasma ionized calcium pool. PTH has a second action on the kidneys. It stimulates the manufacture and release, by the kidneys, of calcitriol into the blood. This steroid hormone acts on the epithelial cells of the upper small intestine, increasing their capacity to absorb calcium from the gut contents into the blood.
The second homeostatic mechanism, with its sensors in the thyroid gland, releases calcitonin into the blood when the blood ionized calcium rises. This hormone acts primarily on bone, causing the rapid removal of calcium from the blood and depositing it, in insoluble form, in the bones.
The two homeostatic mechanisms working through PTH on the one hand, and calcitonin on the other can very rapidly correct any impending error in the plasma ionized calcium level by either removing calcium from the blood and depositing it in the skeleton, or by removing calcium from it. The skeleton acts as an extremely large calcium store (about 1 kg) compared with the plasma calcium store (about 180 mg). Longer term regulation occurs through calcium absorption or loss from the gut.
Another example are the most well-characterised endocannabinoids like anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamide; AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), whose synthesis occurs through the action of a series of intracellular enzymes activated in response to a rise in intracellular calcium levels to introduce homeostasis and prevention of tumor development through putative protective mechanisms that prevent cell growth and migration by activation of CB1 and/or CB2 and adjoining receptors.
Sodium concentration
The homeostatic mechanism which controls the plasma sodium concentration is rather more complex than most of the other homeostatic mechanisms described on this page.
The sensor is situated in the juxtaglomerular apparatus of kidneys, which senses the plasma sodium concentration in a surprisingly indirect manner. Instead of measuring it directly in the blood flowing past the juxtaglomerular cells, these cells respond to the sodium concentration in the renal tubular fluid after it has already undergone a certain amount of modification in the proximal convoluted tubule and loop of Henle. These cells also respond to rate of blood flow through the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which, under normal circumstances, is directly proportional to the arterial blood pressure, making this tissue an ancillary arterial blood pressure sensor.
In response to a lowering of the plasma sodium concentration, or to a fall in the arterial blood pressure, the juxtaglomerular cells release renin into the blood. Renin is an enzyme which cleaves a decapeptide (a short protein chain, 10 amino acids long) from a plasma α-2-globulin called angiotensinogen. This decapeptide is known as angiotensin I. It has no known biological activity. However, when the blood circulates through the lungs a pulmonary capillary endothelial enzyme called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) cleaves a further two amino acids from angiotensin I to form an octapeptide known as angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a hormone which acts on the adrenal cortex, causing the release into the blood of the steroid hormone, aldosterone. Angiotensin II also acts on the smooth muscle in the walls of the arterioles causing these small diameter vessels to constrict, thereby restricting the outflow of blood from the arterial tree, causing the arterial blood pressure to rise. This, therefore, reinforces the measures described above (under the heading of "Arterial blood pressure"), which defend the arterial blood pressure against changes, especially hypotension.
The angiotensin II-stimulated aldosterone released from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal glands has an effect on particularly the epithelial cells of the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts of the kidneys. Here it causes the reabsorption of sodium ions from the renal tubular fluid, in exchange for potassium ions which are secreted from the blood plasma into the tubular fluid to exit the body via the urine. The reabsorption of sodium ions from the renal tubular fluid halts further sodium ion losses from the body, and therefore preventing the worsening of hyponatremia. The hyponatremia can only be corrected by the consumption of salt in the diet. However, it is not certain whether a "salt hunger" can be initiated by hyponatremia, or by what mechanism this might come about.
When the plasma sodium ion concentration is higher than normal (hypernatremia), the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus is halted, ceasing the production of angiotensin II, and its consequent aldosterone-release into the blood. The kidneys respond by excreting sodium ions into the urine, thereby normalizing the plasma sodium ion concentration. The low angiotensin II levels in the blood lower the arterial blood pressure as an inevitable concomitant response.
The reabsorption of sodium ions from the tubular fluid as a result of high aldosterone levels in the blood does not, of itself, cause renal tubular water to be returned to the blood from the distal convoluted tubules or collecting ducts. This is because sodium is reabsorbed in exchange for potassium and therefore causes only a modest change in the osmotic gradient between the blood and the tubular fluid. Furthermore, the epithelium of the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts is impermeable to water in the absence of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the blood. ADH is part of the control of fluid balance. Its levels in the blood vary with the osmolality of the plasma, which is measured in the hypothalamus of the brain. Aldosterone's action on the kidney tubules prevents sodium loss to the extracellular fluid (ECF). So there is no change in the osmolality of the ECF, and therefore no change in the ADH concentration of the plasma. However, low aldosterone levels cause a loss of sodium ions from the ECF, which could potentially cause a change in extracellular osmolality and therefore of ADH levels in the blood.
Potassium concentration
High potassium concentrations in the plasma cause depolarization of the zona glomerulosa cells' membranes in the outer layer of the adrenal cortex. This causes the release of aldosterone into the blood.
Aldosterone acts primarily on the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts of the kidneys, stimulating the excretion of potassium ions into the urine. It does so, however, by activating the basolateral Na+/K+ pumps of the tubular epithelial cells. These sodium/potassium exchangers pump three sodium ions out of the cell, into the interstitial fluid and two potassium ions into the cell from the interstitial fluid. This creates an ionic concentration gradient which results in the reabsorption of sodium (Na+) ions from the tubular fluid into the blood, and secreting potassium (K+) ions from the blood into the urine (lumen of collecting duct).
Fluid balance
The total amount of water in the body needs to be kept in balance. Fluid balance involves keeping the fluid volume stabilized, and also keeping the levels of electrolytes in the extracellular fluid stable. Fluid balance is maintained by the process of osmoregulation and by behavior. Osmotic pressure is detected by osmoreceptors in the median preoptic nucleus in the hypothalamus. Measurement of the plasma osmolality to give an indication of the water content of the body, relies on the fact that water losses from the body, (through unavoidable water loss through the skin which is not entirely waterproof and therefore always slightly moist, water vapor in the exhaled air, sweating, vomiting, normal feces and especially diarrhea) are all hypotonic, meaning that they are less salty than the body fluids (compare, for instance, the taste of saliva with that of tears. The latter has almost the same salt content as the extracellular fluid, whereas the former is hypotonic with respect to the plasma. Saliva does not taste salty, whereas tears are decidedly salty). Nearly all normal and abnormal losses of body water therefore cause the extracellular fluid to become hypertonic. Conversely, excessive fluid intake dilutes the extracellular fluid causing the hypothalamus to register hypotonic hyponatremia conditions.
When the hypothalamus detects a hypertonic extracellular environment, it causes the secretion of an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) called vasopressin which acts on the effector organ, which in this case is the kidney. The effect of vasopressin on the kidney tubules is to reabsorb water from the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts, thus preventing aggravation of the water loss via the urine. The hypothalamus simultaneously stimulates the nearby thirst center causing an almost irresistible (if the hypertonicity is severe enough) urge to drink water. The cessation of urine flow prevents the hypovolemia and hypertonicity from getting worse; the drinking of water corrects the defect.
Hypo-osmolality results in very low plasma ADH levels. This results in the inhibition of water reabsorption from the kidney tubules, causing high volumes of very dilute urine to be excreted, thus getting rid of the excess water in the body.
Urinary water loss, when the body water homeostat is intact, is a compensatory water loss, correcting any water excess in the body. However, since the kidneys cannot generate water, the thirst reflex is the all-important second effector mechanism of the body water homeostat, correcting any water deficit in the body.
Blood pH
The plasma pH can be altered by respiratory changes in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide; or altered by metabolic changes in the carbonic acid to bicarbonate ion ratio. The bicarbonate buffer system regulates the ratio of carbonic acid to bicarbonate to be equal to 1:20, at which ratio the blood pH is 7.4 (as explained in the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation). A change in the plasma pH gives an acid–base imbalance. In acid–base homeostasis there are two mechanisms that can help regulate the pH. Respiratory compensation a mechanism of the respiratory center, adjusts the partial pressure of carbon dioxide by changing the rate and depth of breathing, to bring the pH back to normal. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide also determines the concentration of carbonic acid, and the bicarbonate buffer system can also come into play. Renal compensation can help the bicarbonate buffer system. The sensor for the plasma bicarbonate concentration is not known for certain. It is very probable that the renal tubular cells of the distal convoluted tubules are themselves sensitive to the pH of the plasma. The metabolism of these cells produces carbon dioxide, which is rapidly converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate through the action of carbonic anhydrase. When the ECF pH falls (becoming more acidic) the renal tubular cells excrete hydrogen ions into the tubular fluid to leave the body via urine. Bicarbonate ions are simultaneously secreted into the blood that decreases the carbonic acid, and consequently raises the plasma pH. The converse happens when the plasma pH rises above normal: bicarbonate ions are excreted into the urine, and hydrogen ions released into the plasma.
When hydrogen ions are excreted into the urine, and bicarbonate into the blood, the latter combines with the excess hydrogen ions in the plasma that stimulated the kidneys to perform this operation. The resulting reaction in the plasma is the formation of carbonic acid which is in equilibrium with the plasma partial pressure of carbon dioxide. This is tightly regulated to ensure that there is no excessive build-up of carbonic acid or bicarbonate. The overall effect is therefore that hydrogen ions are lost in the urine when the pH of the plasma falls. The concomitant rise in the plasma bicarbonate mops up the increased hydrogen ions (caused by the fall in plasma pH) and the resulting excess carbonic acid is disposed of in the lungs as carbon dioxide. This restores the normal ratio between bicarbonate and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide and therefore the plasma pH. The converse happens when a high plasma pH stimulates the kidneys to secrete hydrogen ions into the blood and to excrete bicarbonate into the urine. The hydrogen ions combine with the excess bicarbonate ions in the plasma, once again forming an excess of carbonic acid which can be exhaled, as carbon dioxide, in the lungs, keeping the plasma bicarbonate ion concentration, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide and, therefore, the plasma pH, constant.
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) allows for regulation of the distribution of substances between cells of the brain, and neuroendocrine factors, to which slight changes can cause problems or damage to the nervous system. For example, high glycine concentration disrupts temperature and blood pressure control, and high CSF pH causes dizziness and syncope.
Neurotransmission
Inhibitory neurons in the central nervous system play a homeostatic role in the balance of neuronal activity between excitation and inhibition. Inhibitory neurons using GABA, make compensating changes in the neuronal networks preventing runaway levels of excitation. An imbalance between excitation and inhibition is seen to be implicated in a number of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Neuroendocrine system
The neuroendocrine system is the mechanism by which the hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, regulating metabolism, reproduction, eating and drinking behaviour, energy utilization, osmolarity and blood pressure.
The regulation of metabolism, is carried out by hypothalamic interconnections to other glands. Three endocrine glands of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis (HPG axis) often work together and have important regulatory functions. Two other regulatory endocrine axes are the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis) and the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis (HPT axis).
The liver also has many regulatory functions of the metabolism. An important function is the production and control of bile acids. Too much bile acid can be toxic to cells and its synthesis can be inhibited by activation of FXR a nuclear receptor.
Gene regulation
At the cellular level, homeostasis is carried out by several mechanisms including transcriptional regulation that can alter the activity of genes in response to changes.
Energy balance
The amount of energy taken in through nutrition needs to match the amount of energy used. To achieve energy homeostasis appetite is regulated by two hormones, grehlin and leptin. Grehlin stimulates hunger and the intake of food and leptin acts to signal satiety (fullness).
A 2019 review of weight-change interventions, including dieting, exercise and overeating, found that body weight homeostasis could not precisely correct for "energetic errors", the loss or gain of calories, in the short-term.
Clinical significance
Many diseases are the result of a homeostatic failure. Almost any homeostatic component can malfunction either as a result of an inherited defect, an inborn error of metabolism, or an acquired disease. Some homeostatic mechanisms have inbuilt redundancies, which ensures that life is not immediately threatened if a component malfunctions; but sometimes a homeostatic malfunction can result in serious disease, which can be fatal if not treated. A well-known example of a homeostatic failure is shown in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Here blood sugar regulation is unable to function because the beta cells of the pancreatic islets are destroyed and cannot produce the necessary insulin. The blood sugar rises in a condition known as hyperglycemia.
The plasma ionized calcium homeostat can be disrupted by the constant, unchanging, over-production of parathyroid hormone by a parathyroid adenoma resulting in the typically features of hyperparathyroidism, namely high plasma ionized Ca2+ levels and the resorption of bone, which can lead to spontaneous fractures. The abnormally high plasma ionized calcium concentrations cause conformational changes in many cell-surface proteins (especially ion channels and hormone or neurotransmitter receptors) giving rise to lethargy, muscle weakness, anorexia, constipation and labile emotions.
The body water homeostat can be compromised by the inability to secrete ADH in response to even the normal daily water losses via the exhaled air, the feces, and insensible sweating. On receiving a zero blood ADH signal, the kidneys produce huge unchanging volumes of very dilute urine, causing dehydration and death if not treated.
As organisms age, the efficiency of their control systems becomes reduced. The inefficiencies gradually result in an unstable internal environment that increases the risk of illness, and leads to the physical changes associated with aging.
Various chronic diseases are kept under control by homeostatic compensation, which masks a problem by compensating for it (making up for it) in another way. However, the compensating mechanisms eventually wear out or are disrupted by a new complicating factor (such as the advent of a concurrent acute viral infection), which sends the body reeling through a new cascade of events. Such decompensation unmasks the underlying disease, worsening its symptoms. Common examples include decompensated heart failure, kidney failure, and liver failure.
Biosphere
In the Gaia hypothesis, James Lovelock stated that the entire mass of living matter on Earth (or any planet with life) functions as a vast homeostatic superorganism that actively modifies its planetary environment to produce the environmental conditions necessary for its own survival. In this view, the entire planet maintains several homeostasis (the primary one being temperature homeostasis). Whether this sort of system is present on Earth is open to debate. However, some relatively simple homeostatic mechanisms are generally accepted. For example, it is sometimes claimed that when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels rise, certain plants may be able to grow better and thus act to remove more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, warming has exacerbated droughts, making water the actual limiting factor on land. When sunlight is plentiful and the atmospheric temperature climbs, it has been claimed that the phytoplankton of the ocean surface waters, acting as global sunshine, and therefore heat sensors, may thrive and produce more dimethyl sulfide (DMS). The DMS molecules act as cloud condensation nuclei, which produce more clouds, and thus increase the atmospheric albedo, and this feeds back to lower the temperature of the atmosphere. However, rising sea temperature has stratified the oceans, separating warm, sunlit waters from cool, nutrient-rich waters. Thus, nutrients have become the limiting factor, and plankton levels have actually fallen over the past 50 years, not risen. As scientists discover more about Earth, vast numbers of positive and negative feedback loops are being discovered, that, together, maintain a metastable condition, sometimes within a very broad range of environmental conditions.
Predictive
Predictive homeostasis is an anticipatory response to an expected challenge in the future, such as the stimulation of insulin secretion by gut hormones which enter the blood in response to a meal. This insulin secretion occurs before the blood sugar level rises, lowering the blood sugar level in anticipation of a large influx into the blood of glucose resulting from the digestion of carbohydrates in the gut. Such anticipatory reactions are open loop systems which are based, essentially, on "guess work", and are not self-correcting. Anticipatory responses always require a closed loop negative feedback system to correct the 'over-shoots' and 'under-shoots' to which the anticipatory systems are prone.
Other fields
The term has come to be used in other fields, for example:
Risk
An actuary may refer to risk homeostasis, where (for example) people who have anti-lock brakes have no better safety record than those without anti-lock brakes, because the former unconsciously compensate for the safer vehicle via less-safe driving habits. Previous to the innovation of anti-lock brakes, certain maneuvers involved minor skids, evoking fear and avoidance: Now the anti-lock system moves the boundary for such feedback, and behavior patterns expand into the no-longer punitive area. It has also been suggested that ecological crises are an instance of risk homeostasis in which a particular behavior continues until proven dangerous or dramatic consequences actually occur.
Stress
Sociologists and psychologists may refer to stress homeostasis, the tendency of a population or an individual to stay at a certain level of stress, often generating artificial stresses if the "natural" level of stress is not enough.
Jean-François Lyotard, a postmodern theorist, has applied this term to societal 'power centers' that he describes in The Postmodern Condition, as being 'governed by a principle of homeostasis,' for example, the scientific hierarchy, which will sometimes ignore a radical new discovery for years because it destabilizes previously accepted norms.
Technology
Familiar technological homeostatic mechanisms include:
- A thermostat operates by switching heaters or air-conditioners on and off in response to the output of a temperature sensor.
- Cruise control adjusts a car's throttle in response to changes in speed.
- An autopilot operates the steering controls of an aircraft or ship in response to deviation from a pre-set compass bearing or route.
- Process control systems in a chemical plant or oil refinery maintain fluid levels, pressures, temperature, chemical composition, etc. by controlling heaters, pumps and valves.
- The centrifugal governor of a steam engine, as designed by James Watt in 1788, reduces the throttle valve in response to increases in the engine speed, or opens the valve if the speed falls below the pre-set rate.