| Christensen's Types of Innovation |
|---|
|
Sustaining
Disruptive
|
In business theory, disruptive innovation is innovation that creates a new market and value network or enters at the bottom of an existing market and eventually displaces established market-leading firms, products, and alliances. The concept was developed by the American academic Clayton Christensen and his collaborators beginning in 1995, and has been called the most influential business idea of the early 21st century. Lingfei Wu, Dashun Wang, and James A. Evans generalized this term to identify disruptive science and technological advances from more than 65 million papers, patents and software products that span the period 1954–2014. Their work was featured as the cover of the February 2019 issue of Nature and was included among the Altmetric 100 most-discussed work in 2019.
Not all innovations are disruptive, even if they are revolutionary. For example, the first automobiles in the late 19th century were not a disruptive innovation, because early automobiles were expensive luxury items that did not disrupt the market for horse-drawn vehicles. The market for transportation essentially remained intact until the debut of the lower-priced Ford Model T in 1908. The mass-produced automobile was a disruptive innovation, because it changed the transportation market, whereas the first thirty years of automobiles did not.
Disruptive innovations tend to be produced by outsiders and entrepreneurs in startups, rather than existing market-leading companies. The business environment of market leaders does not allow them to pursue disruptive innovations when they first arise, because they are not profitable enough at first and because their development can take scarce resources away from sustaining innovations (which are needed to compete against current competition). Small teams are more likely to create disruptive innovations than large teams. A disruptive process can take longer to develop than by the conventional approach and the risk associated to it is higher than the other more incremental, architectural or evolutionary forms of innovations, but once it is deployed in the market, it achieves a much faster penetration and higher degree of impact on the established markets.
Beyond business and economics disruptive innovations can also be considered to disrupt complex systems, including economic and business-related aspects. Through identifying and analyzing systems for possible points of intervention, one can then design changes focused on disruptive interventions.
Usage history
The term disruptive technologies was coined by Clayton M. Christensen and introduced in his 1995 article Disruptive Technologies: Catching the Wave, which he cowrote with Joseph Bower. The article is aimed at both management executives who make the funding or purchasing decisions in companies, as well as the research community, which is largely responsible for introducing the disruptive vector to the consumer market. He describes the term further in his book The Innovator's Dilemma. Innovator's Dilemma explored the case of the disk drive industry (the disk drive and memory industry, with its rapid technological evolution, is to the study of technology what fruit flies are to the study of genetics, as Christensen was told in the 1990s) and the excavating and Earth-moving industry (where hydraulic actuation slowly, yet eventually, displaced cable-actuated machinery). In his sequel with Michael E. Raynor, The Innovator's Solution, Christensen replaced the term disruptive technology with disruptive innovation because he recognized that most technologies are not intrinsically disruptive or sustaining in character; rather, it is the business model that identifies the crucial idea that potentiates profound market success and subsequently serves as the disruptive vector. Comprehending Christensen's business model, which takes the disruptive vector from the idea borne from the mind of the innovator to a marketable product, is central to understanding how novel technology facilitates the rapid destruction of established technologies and markets by the disruptor. Christensen and Mark W. Johnson, who cofounded the management consulting firm Innosight, described the dynamics of "business model innovation" in the 2008 Harvard Business Review article "Reinventing Your Business Model". The concept of disruptive technology continues a long tradition of identifying radical technological change in the study of innovation by economists, and its implementation and execution by its management at a corporate or policy level.
According to Christensen, "the term 'disruptive innovation' is misleading when it is used to refer to the derivative, or 'instantaneous value', of the market behavior of the product or service, rather than the integral, or 'sum over histories', of the product's market behavior."
In the late 1990s, the automotive sector began to embrace a perspective of "constructive disruptive technology" by working with the consultant David E. O'Ryan, whereby the use of current off-the-shelf technology was integrated with newer innovation to create what he called "an unfair advantage". The process or technology change as a whole had to be "constructive" in improving the current method of manufacturing, yet disruptively impact the whole of the business case model, resulting in a significant reduction of waste, energy, materials, labor, or legacy costs to the user.
In keeping with the insight that a persuasive advertising campaign can be just as effective as technological sophistication at bringing a successful product to market, Christensen's theory explains why many disruptive innovations are not advanced or useful technologies, rather combinations of existing off-the-shelf components, applied shrewdly to a fledgling value network.
Online news site TechRepublic proposes an end using the term, and similar related terms, suggesting that, as of 2014, it is overused jargon.
Definition
- Disruption is a process, not a product or service, that occurs from the nascent to the mainstream
- Originates in low-end (less demanding customers) or new market (where none existed) footholds
- New firms don't catch on with mainstream customers until quality catches up with their standards
- Success is not a requirement and some business can be disruptive but fail
- New firm's business model differs significantly from incumbent
Christensen continues to develop and refine the theory and has accepted that not all examples of disruptive innovation perfectly fit into his theory. For example, he conceded that originating in the low end of the market is not always a cause of disruptive innovation, but rather it fosters competitive business models, using Uber as an example. In an interview with Forbes magazine he stated:
"Uber helped me realize that it isn’t that being at the bottom of the market is the causal mechanism, but that it’s correlated with a business model that is unattractive to its competitor".
Theory
The current theoretical understanding of disruptive innovation is different from what might be expected by default, an idea that Clayton M. Christensen called the "technology mudslide hypothesis". This is the simplistic idea that an established firm fails because it doesn't "keep up technologically" with other firms. In this hypothesis, firms are like climbers scrambling upward on crumbling footing, where it takes constant upward-climbing effort just to stay still, and any break from the effort (such as complacency born of profitability) causes a rapid downhill slide. Christensen and colleagues have shown that this simplistic hypothesis is wrong; it doesn't model reality. What they have shown is that good firms are usually aware of the innovations, but their business environment does not allow them to pursue them when they first arise, because they are not profitable enough at first and because their development can take scarce resources away from that of sustaining innovations (which are needed to compete against current competition). In Christensen's terms, a firm's existing value networks place insufficient value on the disruptive innovation to allow its pursuit by that firm. Meanwhile, start-up firms inhabit different value networks, at least until the day that their disruptive innovation is able to invade the older value network. At that time, the established firm in that network can at best only fend off the market share attack with a me-too entry, for which survival (not thriving) is the only reward.
In the technology mudslide hypothesis, Christensen differentiated disruptive innovation from sustaining innovation. He explained that the latter's goal is to improve existing product performance. On the other hand, he defines a disruptive innovation as a product or service designed for a new set of customers.
Generally, disruptive innovations were technologically straightforward, consisting of off-the-shelf components put together in a product architecture that was often simpler than prior approaches. They offered less of what customers in established markets wanted and so could rarely be initially employed there. They offered a different package of attributes valued only in emerging markets remote from, and unimportant to, the mainstream.
Christensen also noted that products considered as disruptive innovations tend to skip stages in the traditional product design and development process to quickly gain market traction and competitive advantage. He argued that disruptive innovations can hurt successful, well-managed companies that are responsive to their customers and have excellent research and development. These companies tend to ignore the markets most susceptible to disruptive innovations, because the markets have very tight profit margins and are too small to provide a good growth rate to an established (sizable) firm. Thus, disruptive technology provides an example of an instance when the common business-world advice to "focus on the customer" (or "stay close to the customer", or "listen to the customer") can be strategically counterproductive.
While Christensen argued that disruptive innovations can hurt successful, well-managed companies, O'Ryan countered that "constructive" integration of existing, new, and forward-thinking innovation could improve the economic benefits of these same well-managed companies, once decision-making management understood the systemic benefits as a whole.
Christensen distinguishes between "low-end disruption", which targets customers who do not need the full performance valued by customers at the high end of the market, and "new-market disruption", which targets customers who have needs that were previously unserved by existing incumbents.
Low-end disruption
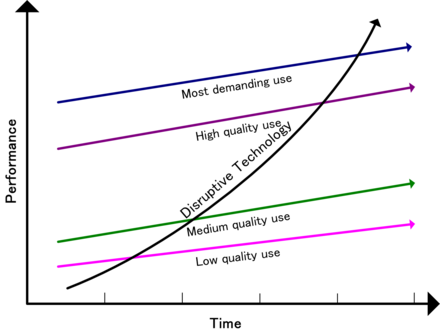
"Low-end disruption" occurs when the rate at which products improve exceeds the rate at which customers can adopt the new performance. Therefore, at some point the performance of the product overshoots the needs of certain customer segments. At this point, a disruptive technology may enter the market and provide a product that has lower performance than the incumbent but that exceeds the requirements of certain segments, thereby gaining a foothold in the market.
In low-end disruption, the disruptor is focused initially on serving the least profitable customer, who is happy with a good enough product. This type of customer is not willing to pay premium for enhancements in product functionality. Once the disruptor has gained a foothold in this customer segment, it seeks to improve its profit margin. To get higher profit margins, the disruptor needs to enter the segment where the customer is willing to pay a little more for higher quality. To ensure this quality in its product, the disruptor needs to innovate. The incumbent will not do much to retain its share in a not-so-profitable segment, and will move up-market and focus on its more attractive customers. After a number of such encounters, the incumbent is squeezed into smaller markets than it was previously serving. And then, finally, the disruptive technology meets the demands of the most profitable segment and drives the established company out of the market.
New market disruption
"New market disruption" occurs when a product fits a new or emerging market segment that is not being served by existing incumbents in the industry. Some scholars note that the creation of a new market is a defining feature of disruptive innovation, particularly in the way it tend to improve products or services differently in comparison to normal market drivers. It initially caters to a niche market and proceeds on defining the industry over time once it is able to penetrate the market or induce consumers to defect from the existing market into the new market it created.
The extrapolation of the theory to all aspects of life has been challenged, as has the methodology of relying on selected case studies as the principal form of evidence. Jill Lepore points out that some companies identified by the theory as victims of disruption a decade or more ago, rather than being defunct, remain dominant in their industries today (including Seagate Technology, U.S. Steel, and Bucyrus). Lepore questions whether the theory has been oversold and misapplied, as if it were able to explain everything in every sphere of life, including not just business but education and public institutions.
Disruptive technology
In 2009, Milan Zeleny described high technology as disruptive technology and raised the question of what is being disrupted. The answer, according to Zeleny, is the support network of high technology. For example, introducing electric cars disrupts the support network for gasoline cars (network of gas and service stations). Such disruption is fully expected and therefore effectively resisted by support net owners. In the long run, high (disruptive) technology bypasses, upgrades, or replaces the outdated support network.
Questioning the concept of a disruptive technology, Haxell (2012) questions how such technologies get named and framed, pointing out that this is a positioned and retrospective act.
Technology, being a form of social relationship, always evolves. No technology remains fixed. Technology starts, develops, persists, mutates, stagnates, and declines, just like living organisms. The evolutionary life cycle occurs in the use and development of any technology. A new high-technology core emerges and challenges existing technology support nets (TSNs), which are thus forced to coevolve with it. New versions of the core are designed and fitted into an increasingly appropriate TSN, with smaller and smaller high-technology effects. High technology becomes regular technology, with more efficient versions fitting the same support net. Finally, even the efficiency gains diminish, emphasis shifts to product tertiary attributes (appearance, style), and technology becomes TSN-preserving appropriate technology. This technological equilibrium state becomes established and fixated, resisting being interrupted by a technological mutation; then new high technology appears and the cycle is repeated.
Regarding this evolving process of technology, Christensen said:
The technological changes that damage established companies are usually not radically new or difficult from a technological point of view. They do, however, have two important characteristics: First, they typically present a different package of performance attributes—ones that, at least at the outset, are not valued by existing customers. Second, the performance attributes that existing customers do value improve at such a rapid rate that the new technology can later invade those established markets.
The World Bank's 2019 World Development Report on The Changing Nature of Work examines how technology shapes the relative demand for certain skills in labor markets and expands the reach of firms - robotics and digital technologies, for example, enable firms to automate, replacing labor with machines to become more efficient, and innovate, expanding the number of tasks and products. Joseph Bower explained the process of how disruptive technology, through its requisite support net, dramatically transforms a certain industry.
When the technology that has the potential for revolutionizing an industry emerges, established companies typically see it as unattractive: it’s not something their mainstream customers want, and its projected profit margins aren’t sufficient to cover big-company cost structure. As a result, the new technology tends to get ignored in favor of what’s currently popular with the best customers. But then another company steps in to bring the innovation to a new market. Once the disruptive technology becomes established there, smaller-scale innovation rapidly raise the technology’s performance on attributes that mainstream customers’ value.
For example, the automobile was high technology with respect to the horse carriage. It evolved into technology and finally into appropriate technology with a stable, unchanging TSN. The main high-technology advance in the offing is some form of electric car—whether the energy source is the sun, hydrogen, water, air pressure, or traditional charging outlet. Electric cars preceded the gasoline automobile by many decades and are now returning to replace the traditional gasoline automobile. The printing press was a development that changed the way that information was stored, transmitted, and replicated. This allowed empowered authors but it also promoted censorship and information overload in writing technology.
Milan Zeleny described the above phenomenon. He also wrote that:
Implementing high technology is often resisted. This resistance is well understood on the part of active participants in the requisite TSN. The electric car will be resisted by gas-station operators in the same way automated teller machines (ATMs) were resisted by bank tellers and automobiles by horsewhip makers. Technology does not qualitatively restructure the TSN and therefore will not be resisted and never has been resisted. Middle management resists business process reengineering because BPR represents a direct assault on the support net (coordinative hierarchy) they thrive on. Teamwork and multi-functionality is resisted by those whose TSN provides the comfort of narrow specialization and command-driven work.
Social media could be considered a disruptive innovation within sports. More specifically, the way that news in sports circulates nowadays versus the pre-internet era where sports news was mainly on T.V., radio, and newspapers. Social media has created a new market for sports that was not around before in the sense that players and fans have instant access to information related to sports.
High-technology effects
High technology is a technology core that changes the very architecture (structure and organization) of the components of the technology support net. High technology therefore transforms the qualitative nature of the TSN's tasks and their relations, as well as their requisite physical, energy, and information flows. It also affects the skills required, the roles played, and the styles of management and coordination—the organizational culture itself.
This kind of technology core is different from regular technology core, which preserves the qualitative nature of flows and the structure of the support and only allows users to perform the same tasks in the same way, but faster, more reliably, in larger quantities, or more efficiently. It is also different from appropriate technology core, which preserves the TSN itself with the purpose of technology implementation and allows users to do the same thing in the same way at comparable levels of efficiency, instead of improving the efficiency of performance.
On differences between high and low technologies, Milan Zeleny wrote:
The effects of high technology always breaks the direct comparability by changing the system itself, therefore requiring new measures and new assessments of its productivity. High technology cannot be compared and evaluated with the existing technology purely on the basis of cost, net present value or return on investment. Only within an unchanging and relatively stable TSN would such direct financial comparability be meaningful. For example, you can directly compare a manual typewriter with an electric typewriter, but not a typewriter with a word processor. Therein lies the management challenge of high technology.
Not all modern technologies are high technologies, only those used and functioning as such, and embedded in their requisite TSNs. They have to empower the individual because only through the individual can they empower knowledge. Not all information technologies have integrative effects. Some information systems are still designed to improve the traditional hierarchy of command and thus preserve and entrench the existing TSN. The administrative model of management, for instance, further aggravates the division of task and labor, further specializes knowledge, separates management from workers, and concentrates information and knowledge in centers.
As knowledge surpasses capital, labor, and raw materials as the dominant economic resource, technologies are also starting to reflect this shift. Technologies are rapidly shifting from centralized hierarchies to distributed networks. Nowadays knowledge does not reside in a super-mind, super-book, or super-database, but in a complex relational pattern of networks brought forth to coordinate human action.
Internal auditor response
Internal audit plays a critical role maintaining effective control mitigating emerging risks. Businesses will increase risk or bypass opportunity if auditors do not address disruption-related risks. Michael G. Alles has discussed that Big Data is a disruptive innovation that auditors must incorporate in practice. A 2019 study, Internal Auditors' Response to Disruptive Innovation, reports on the evolution of internal audit to react to changes. Disruptions examined include data analytics, agile processes, cloud computing, robotic process automation, continuous auditing, regulatory change, and artificial intelligence.
Proactive approach
A proactive approach to addressing the challenge posited by disruptive innovations has been debated by scholars. Petzold criticized the lack of acknowledgment of underlying process of the change to study the disruptive innovation over time from a process view and complexify the concept to support the understanding of its unfolding and advance its manageability. Keeping in view the multidimensional nature of disruptive innovation a measurement framework has been developed by Guo to enable a systemic assessment of disruptive potential of innovations, providing insights for the decisions in product/service launch and resource allocation. Middle managers play an important role in long term sustainability of any firm and thus have been studied to have a proactive role in exploitation of the disruptive innovation process.
Examples
In the practical world, the popularization of personal computers illustrates how knowledge contributes to the ongoing technology innovation. The original centralized concept (one computer, many persons) is a knowledge-defying idea of the prehistory of computing, and its inadequacies and failures have become clearly apparent. The era of personal computing brought powerful computers "on every desk" (one person, one computer). This short transitional period was necessary for getting used to the new computing environment, but was inadequate from the vantage point of producing knowledge. Adequate knowledge creation and management come mainly from networking and distributed computing (one person, many computers). Each person's computer must form an access point to the entire computing landscape or ecology through the Internet of other computers, databases, and mainframes, as well as production, distribution, and retailing facilities, and the like. For the first time, technology empowers individuals rather than external hierarchies. It transfers influence and power where it optimally belongs: at the loci of the useful knowledge. Even though hierarchies and bureaucracies do not innovate, free and empowered individuals do; knowledge, innovation, spontaneity, and self-reliance are becoming increasingly valued and promoted.
Uber is not an example of disruption because it did not originate in a low-end or new market footholds. One of the conditions for the business to be considered disruptive according to Clayton M. Christensen is that the business should originate on a) low-end or b) new-market footholds. Instead, Uber was launched in San Francisco, a large urban city with an established taxi service and did not target low-end customers or created a new market (from the consumer perspective). In contrast, UberSELECT, an option that provides luxurious cars such as limousine at a discounted price, is an example of disruption innovation because it originates from low-end customers segment - customers who would not have entered the traditional luxurious market.
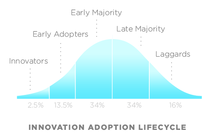
The technology adoption lifecycle is a sociological model that describes the adoption or acceptance of a new product or innovation, according to the demographic and psychological characteristics of defined adopter groups. The process of adoption over time is typically illustrated as a classical normal distribution or "bell curve". The model indicates that the first group of people to use a new product is called "innovators", followed by "early adopters". Next come the early majority and late majority, and the last group to eventually adopt a product are called "Laggards" or "phobics." For example, a phobic may only use a cloud service when it is the only remaining method of performing a required task, but the phobic may not have an in-depth technical knowledge of how to use the service.
The demographic and psychological (or "psychographic") profiles of each adoption group were originally specified by the North Central Rural Sociology Committee (Subcommittee for the Study of the Diffusion of Farm Practices) by agricultural researchers Beal and Bohlen in 1957.
The report summarized the categories as:
- innovators – had larger farms, were more educated, more prosperous and more risk-oriented
- early adopters – younger, more educated, tended to be community leaders, less prosperous
- early majority – more conservative but open to new ideas, active in community and influence to neighbors
- late majority – older, less educated, fairly conservative and less socially active
- laggards – very conservative, had small farms and capital, oldest and least educated
The model has subsequently been adapted for many areas of technology adoption in the late 20th century.
Adaptations of the model
The model has spawned a range of adaptations that extend the concept or apply it to specific domains of interest.
In his book Crossing the Chasm, Geoffrey Moore proposes a variation of the original lifecycle. He suggests that for discontinuous innovations, which may result in a Foster disruption based on an s-curve, there is a gap or chasm between the first two adopter groups (innovators/early adopters), and the vertical markets.
Disruption as it is used today are of the Clayton M. Christensen variety. These disruptions are not s-curve based.
In educational technology, Lindy McKeown has provided a similar model (a pencil metaphor) describing the Information and Communications Technology uptake in education.
In medical sociology, Carl May has proposed normalization process theory that shows how technologies become embedded and integrated in health care and other kinds of organization.
Wenger, White and Smith, in their book Digital habitats: Stewarding technology for communities, talk of technology stewards: people with sufficient understanding of the technology available and the technological needs of a community to steward the community through the technology adoption process.
Rayna and Striukova (2009) propose that the choice of initial market segment has crucial importance for crossing the chasm, as adoption in this segment can lead to a cascade of adoption in the other segments. This initial market segment has, at the same time, to contain a large proportion of visionaries, to be small enough for adoption to be observed from within the segment and from other segment and be sufficiently connected with other segments. If this is the case, the adoption in the first segment will progressively cascade into the adjacent segments, thereby triggering the adoption by the mass-market.
Stephen L. Parente (1995) implemented a Markov Chain to model economic growth across different countries given different technological barriers.
In Product marketing, Warren Schirtzinger proposed an expansion of the original lifecycle (the Customer Alignment Lifecycle) which describes the configuration of five different business disciplines that follow the sequence of technology adoption.
Examples
One way to model product adoption is to understand that people's behaviors are influenced by their peers and how widespread they think a particular action is. For many format-dependent technologies, people have a non-zero payoff for adopting the same technology as their closest friends or colleagues. If two users both adopt product A, they might get a payoff a > 0; if they adopt product B, they get b > 0. But if one adopts A and the other adopts B, they both get a payoff of 0.
A threshold can be set for each user to adopt a product. Say that a node v in a graph has d neighbors: then v will adopt product A if a fraction p of its neighbors is greater than or equal to some threshold. For example, if v's threshold is 2/3, and only one of its two neighbors adopts product A, then v will not adopt A. Using this model, we can deterministically model product adoption on sample networks.
History
The technology adoption lifecycle is a sociological model that is an extension of an earlier model called the diffusion process, which was originally published in 1957 by Joe M. Bohlen, George M. Beal and Everett M. Rogers at Iowa State University and which was originally published only for its application to agriculture and home economics, building on earlier research conducted there by Neal C. Gross and Bryce Ryan. Their original purpose was to track the purchase patterns of hybrid seed corn by farmers.
Bohlen, Beal and Rogers together developed a model called the diffusion process and later, Rogers generalized the use of it in his widely acclaimed 1962 book Diffusion of Innovations (now in its fifth edition), describing how new ideas and technologies spread in different cultures. Others have since used the model to describe how innovations spread between states in the U.S.