Gender inequality in the United States has been diminishing
throughout its history and significant advancements towards equality
have been made beginning mostly in the early 1900s. However, despite
this progress, gender inequality in the United States continues to
persist in many forms, including the disparity in women's political
representation and participation, occupational segregation, and the unequal distribution of household labor.
In the past 20 years there have been emerging issues for boys/men, an
achievement and attainment gap in education is a discussed subject. The
alleviation of gender inequality has been the goal of several major
pieces of legislation since 1920 and continuing to the present day. As
of 2017, the World Economic Forum ranks the United States 49th best in terms of gender equality out of 144 countries.
In addition to the inequality faced by transgender women, inequality, prejudice, and violence against transgender
men and women, as well as gender nonconforming individuals and
individuals who identify with genders outside the gender binary, are
also prevalent in the United States. Transgender individuals suffer from
prejudices in the workforce and employment, higher levels of domestic
violence, higher rates of hate crimes, especially murder, and higher
levels of police brutality when compared to the cisgender population.
Current issues for women
Political participation
The Center for American Women and Politics
reports that, as of 2013, 18.3% of congressional seats are held by
women and 23% of statewide elective offices are held by women; while the
percentage of Congress made up of women has steadily increased,
statewide elective positions held by women have decreased from their
peak of 27.6% in 2001. Women also make up, as of 2013, 24.2% of state
legislators in the United States. Among the one hundred largest cities
in the United States, ten had female mayors as of 2013.
In 1977, political science professor Susan Welch
presented three possible explanations for this underrepresentation of
women in politics: one, that women are socialized to avoid careers in
politics; two, that women's responsibilities in the home keep them away
out of both the work force and the political arena; and three, women are
more often than men members of other demographic groups with low
political participation rates. In 2001, M. Margaret Conway, political science professor at the University of Florida,
also presented three possible explanations for the continuation of this
disparity: one, similar to Welch's first explanation, sociological and
societal norm discourages women from running; two, women less frequently
acquire the necessary skills to hold a political leadership position
from nonpolitical activities; and three, gatekeeping in party politics
prevents women from running.
Work life and economics
The United States is falling behind other Western countries in the percentage of women engaged in the workforce. Researchers from the Institute for Women's Policy Research at the University of California Hastings College of Law
argue that this growing gap is due to a lack of governmental, business
and societal support for working women. They ranked the United States
last out of 20 industrialized countries in an index that measured such
programs as family leave, alternative work arrangements, part-time employment, and other means to make workplaces more flexible and family-friendly.
The United States is also the only industrialized nation that does not
have a paid parental leave policy mandated by law, and is one of only
four countries worldwide that does not; in addition, fully paid
maternity leave is only offered by around 16 percent of employers in the
United States.
Sex discrimination in employment
According to a study conducted by researchers at California State University, Northridge,
when an individual with a PhD applies for a position at a university,
that individual is significantly more likely to be offered a higher
level of appointment, receive an offer of an academic position leading
to tenure, and be offered a full professorship if they are a man when
compared to a woman of comparable qualifications.
However, these findings have been disputed, with one study finding
universities pushed to hire more women, resulting in females being given
a 2:1 advantage over males in science, technology engineering and
mathematics fields.
Another study found that women were significantly less likely to
receive a job offer or an interview for a high-paying waiter position
when compared to equally qualified men; this study also found that such
hiring discrimination may be caused in part by customer's discrimination
of preference for male wait staff. Similarly, research conducted at the University of California, Davis
focusing on academic dermatology revealed a significant downward trend
in the number of women receiving funding from the National Institutes of
Health, which the authors concluded was due to a lack of support for
women scientists at their home institutions.
Research from Lawrence University
has found that men were more likely to be hired in traditionally
masculine jobs, such as sales management, and women were more likely to
be hired in traditionally feminine jobs, such as receptionist or
secretary. However, individuals of either gender with masculine
personality traits were advantaged when applying for either masculine or
feminine jobs, indicating a possibly valuing of stereotypically male
traits above stereotypically female traits.
Occupational segregation by gender
Occupational gender segregation takes the form of both horizontal
segregation (the unequal gender distribution across occupations) and
vertical segregation (the overrepresentation of men in higher positions
in both traditionally male and traditionally female fields).
According to William A. Darity, Jr.
and Patrick L. Mason, there is a strong horizontal occupational
division in the United States on the basis of gender; in 1990, the index
of occupational dissimilarity was 53%, meaning 53% of women or 47% of
men would have to move to different career field in order for all
occupations to have equal gender composition.
While women have begun to more frequently enter traditionally
male-dominated professions, there have been much fewer men entering
female-dominated professions; professor of sociology Paula England cites
this horizontal segregation of careers as a contributing factor to the
gender pay gap.
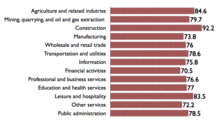
Pay gap
Women's median usual weekly earnings as percentage of men's, for full-time workers, by industry, 2009
With regards to the gender pay gap in the United States, International Labour Organization notes as of 2010 women in the United States earned about 81% of what their male counterparts did. While the gender pay gap has been narrowing since the passage of the Equal Pay Act, the convergence began to slow down in the 1990s.
In addition, overall wage inequality has been increasing since the
1980s as middle-wage jobs are decreasing replaced by larger percentages
of both high-paying and low-paying jobs, creating a highly polarized
environment.
However numerous studies dispute the claim that discrimination
accounts for the majority of the pay gap. When adjusting for industries
commonly chosen, hours worked, and benefits received, the pay gap
returns to 5%, which has been attributed to less aggressive pay
negotiating in women.
One study actually found that before 30, females made more than males,
and hypothesized that choosing a family over a career resulted in the
drop of the female wage advantage during the thirties.
According to researchers at the University of California, Berkeley and the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign,
the primary cause of this gap is discrimination manifested in the
tendency of women to be hired more frequently in lower paying
occupations, in addition to the fact that male dominated occupations are
higher paying than female dominated occupations, and that, even within
comparable occupations, women are often paid less than men.
In medicine, female physicians are compensated less,
despite the fact that evidence suggest that the quality of care female
physicians provide may be higher than that of male physicians.
In addition to the gender pay gap, a "family gap" also exists,
wherein women with children receive about 10-15% less pay when compared
to women without children. According to Jane Waldfogel, professor of social work and public affairs at Columbia University, this family gap is a contributing factor to the United States' large gender pay gap.
She also noted that men did not seem to be affected by this gap, as
married men (who are more likely to have children) generally earned
higher than unmarried men.
Social life
Researchers from the University of Michigan
have found that from 1970 to 1985, the percentage of men and women who
supported traditional social roles for wives and believed that maternal
employment damages mother-child relationships or children's development
decreased. Similarly, Jane Wilke from the University of Connecticut
found that men's support the idea that men should be the sole source of
income in a married couple decreased from 32 to 21 percent from 1972 to
1989; in practice only 15 percent of households were supported by a
male spouse's income alone at the time of the study.
However, more recent research in 2011 has found that attitudes
towards gender and societal roles have changed very little since the
mid-1990s, with attitudes hovering at about sixty to seventy percent
egalitarian. This study theorized that a "egalitarian but traditional"
gender frame emerged in popular culture during this period, which
supports each gender assuming their traditional roles without appearing
sexist or discriminatory, and is responsible for this backlash.
Stephanie Coontz, a professor of family history at Evergreen State College,
noted that one of the factors contributing to the gender inequality in
the United States is that most men still expect women and men to assume
traditional gender roles in the households and for women to carry out a larger share of the housework. This has been confirmed by a number of other studies; for example Makiko Fuwa from University of California, Irvine
noted that while there has been movement towards greater equality, "in
1995 American women still spent nearly twice as much time on housework
than men" and there is also a segregation of household tasks. This gendered division of household labor creates what is known as the second shift or double burden,
where working women in a heterosexual couple with a working partner
spend significally more time on childcare and household chores.
Researchers from the University of Maryland
have found that while men have steadily begun to perform more household
labor since 1965, most of the essential and traditionally feminine
tasks are still carried out by women; men generally carry out more
nonessential or infrequent tasks, such as taking out the trash or mowing
the lawn.
While both genders tend to have roughly equal amounts of leisure time,
men have more uninterrupted leisure time when compared to women. Working mothers also tend to get less sleep when compared to their working husbands.
Education
Literacy
and enrollment in primary and secondary education are at parity in the
United States, and women are overrepresented in tertiary education.
There is, however, a notably gender segregation in degree choice,
correlated with lower incomes for graduates with "feminine" degrees,
such as education or nursing, and higher incomes for those with
"masculine" degrees, such as engineering. In addition, men have a statistically significant advantage over women when applying for highly selective universities. Females started outnumbering males in higher education in 1992.
Other issues
Research conducted at Lycoming College
has found the enjoyment of sexist humor to be strongly correlated with
sexual aggression towards women among male college students.
In addition, studies have shown that exposure to sexist humor,
particularly humor related to sexual assault, can increase male
aggression and their tendency to discriminate against women.
One study also asserted that the attitudes behind such humor creates
an environment where such discriminatory and possibly violent behavior
is acceptable.
Men's tendency to self-report the likelihood that they would commit
sexually violent acts has also been found to increase after exposure to
sexist humor, as reported by researchers from the University of Kent.
Benevolent sexism,
sometimes referred to as chivalry, which holds women as something to be
protected, also has psychological effects. Women who hold these views
are more likely to have less ambitious career goals and men who hold
these views tend to have a polarized and stereotyped view of women, made
up of both very favorable and very unfavorable traits.
In such cases, the stereotyped view of women is "favorable in content
and yet prejudicial in [its] consequences," and attempts to provide
justification for discriminatory behaviors presented as helpful or
paternal.
Current issues for men
Achievement gap in school
For the past fifty years, there has been a gap in the educational achievement of males and females
in the United States, but which gender has been disadvantaged has
fluctuated over the years. In the 1970s and 1980s, data showed girls
trailing behind boys in a variety of academic performance measures,
specifically in test scores in math and science.
Data in the last twenty years shows the general trend of girls
outperforming boys in academic achievement in terms of class grades
across all subjects and college graduation rates, but boys scoring
higher on standardized tests and being better represented in the
higher-paying and more prestigious STEM fields (science, technology,
engineering, and math).
Graduation rates
According
to recent data (from 2007), 55 percent of college students are females
and 45 percent are males. From 1995 until 2005, the number of males
enrolled in college increased by 18 percent, while the number of female
students rose by 27 percent.
Males are enrolling in college in greater numbers than ever before, yet
fewer than two-thirds of them are graduating with a bachelor's degree.
The numbers of both men and women receiving a bachelor's degree have
increased significantly, but the increasing rate of female college
graduates exceeds the increasing rate for males.
A higher proportion of men (29.4%) hold bachelor's degrees than women (26.1%). In 2007, the United States Census Bureau
estimated that 18,423,000 males ages over the age of 18 held a
bachelor's degree, while 20,501,000 females over the age 18 held one. In
addition, fewer males held master's degrees: 6,472,000 males compared
to 7,283,000 females. However, more men held professional and doctoral
degrees than women. 2,033,000 males held professional degrees compared
to 1,079,000, and 1,678,000 males had received a doctoral degree
compared to 817,000 females.
Selective service
Congressman Alexander Pirnie (R-NY) drawing the first capsule for the Selective Service draft, Dec 1, 1969.
In the United States, most male US citizens and residents must register with the Selective Service System within 30 days of their 18th birthday.
Those who fail to register may be punished by up to five years in
prison and a fine of up to $250,000, although no non-registrants have
been prosecuted since January 1986.
They may also be ineligible for federal student financial aid, federal
job training and federal employment, and for certain states, state
employment and even driver's licenses .
Suicide
In the United States, the male-to-female teenage suicide death ratio is estimated at 3:1. Typically males are three to five times more likely to commit suicide than females.
Homelessness
At least 70% to 85% of all homeless are men.
Occupational segregation into dangerous jobs
Men are over-represented in dangerous jobs. The industries with the
highest death rates are mining, agriculture, forestry, fishing, and
construction, all of which employ more men than women. In one U.S. study, 93% of deaths on the job involved men, with a death rate approximately 11 times higher than women.
Prison
Men receive 65% longer prison sentences for the same crime as a women.
Benatar
Benatar
identified multiple areas in which men are currently disadvantaged
today. He identified military conscription and cited the fact that men
are more likely to be the victim of spousal abuse, while being taken
less seriously.
Benatar also identified the inequality experienced by men in the
justice system, such as the increased prison sentences received by
males, as well as the increased likelihood of a male being arrested if
the accuser is female. Furthermore, the disparity in legal custody
cases and alimony payment was cited, with females more frequently
getting custody of children.
Current issues for transgender people
Visibility, awareness, and public attitudes
One of the largest factors that causes and perpetuates transgender inequality is a lack of understanding and awareness among cisgender people.
A 2002 survey found that, of the American respondents polled, only 70%
had heard of the term transgender, while 67% agreed that it is possible
for a person to be born as one gender, but inside feel like another
gender.
In addition, the survey found that 61% of Americans believe that the
country needs anti-discrimination laws to protect transgender
individuals, 57% incorrectly believed that it was not legal to fire
someone on the basis of their gender identity if they are trans, 53%
believed being transgender was acceptable while 37% did not, 77%
believed that transgender students should be allowed to attend public
school, and 8% said they would refuse to work with a transgender co
worker.
A 2012 study found that the heterosexual cisgender individuals who
believe there are natural binary genders and there are natural
differences between men and women are more likely to have negative
attitudes toward transgender individuals.
Events in the LGBT+ community such as Transgender Awareness Week and the International Transgender Day of Visibility are focused on educating and informing the public about transgender individuals and the challenges they face.
Legal rights
According
to the Transformative Justice Law Project of Illinois, transgender
people are "over-represented in the criminal legal system due to
institutionalized oppression and increased poverty and criminalization."
Many transgender individuals have difficulties correcting their
name and gender on their ID and personal documents. According to the National Center for Transgender Equality,
"only one-fifth (21%) of transgender people who have transitioned in
the National Transgender Discrimination Survey have been able to update
all of their IDs and records with their new gender and one-third (33%)
had updated none of their IDs or records. At the time of the survey,
only 59% had been able to update their gender on their driver’s license
or state ID; 49% had updated their Social Security Record; 26% their
passport; and just 24% their birth certificate."
In addition, those transgender people who are successful in correcting
their ID and records often must undergo heavy invasions of privacy,
including presenting proof of gender reassignment surgery, and those who
cannot correct their identification documents often face higher levels
of discrimination, since it effectively "outs" them as transgender.
Some state appellate courts- including Kansas, Ohio, Texas,
Florida, and Illinois- have upheld that the gender an individual is
assigned at birth is their legal gender for life, even if the individual
has undergone gender reassignment surgery or similar treatments, and therefore refuse to acknowledge the gender that transgender people identify as.
There have been several legal cases in which transgender parents
have lost custody and other parental rights on the basis of their
gender.
There have also been cases of the validity and legality of married
heterosexual couples in which one partner is transgender being contested
and, in some cases, the marriage has been voided.
Work life and economics
A
2007 study reported that between fifteen and fifty-seven percent of
transgender individuals report some kind of employment discrimination;
of these thirteen to fifty-six percent reported being fired due to their
gender identity, thirteen to forty-seven percent reported that they
were denied employment due to their gender identity, twenty-two to
thirty-one percent reported harassment due to their gender identity,
and nineteen percent reported being denied promotion due to their gender
identity.
Another study found that transgender respondents reported twice the
national rate of unemployment, while transgender people of color
reported four times the national rate of unemployment. This study also found that 90% of respondents reported some kind of workplace harassment, mistreatment or discrimination.
Transgender pay gap
According to the American Psychology Association, around 64% of transgender people have annual incomes of less than $25,000.
Another study found that transgender individuals are nearly four times
more likely to make less than $10,000 annually when compared to the
general population; on the other end of the spectrum, only 14% of
transgender respondents reported making more than $100,000 annually
compared to 25% of the general population.
In addition, transgender women reported their wages decreasing by
nearly one-third following their gender transitions but transgender men
reported their wages increasing slightly (about 1.5%), according to one
study.
Social life
Since
many public spaces, including schools, are highly gendered with
features such as gendered bathrooms and locker rooms, transgender people
often face violence in these gendered areas.
Transgender people are often asked to present their ID or other
invasive question when using a public restroom designated for the gender
they identify as and can often face discrimination and violence if
their ID has not been correct or if they do not "pass" as the gender
they identify as.
One study found that 71% of transgender respondents made efforts
to hide their gender or gender transition to avoid discrimination, while
57% reported delaying their gender transition to avoid discrimination.
Transgender individuals also face discrimination within the LGBT+ community, especially from cisgender gay men and lesbians. As a result, they often do not receive the same social support from the community that other queer individuals do.
Education
One
study found that 78% of transgender individuals interviewed reported
harassment in primary or secondary school, 35% reported physical
assault, 12% reported sexual violence, and 6% reported being expelled.
According to the study, the effect of this harassment was so severe
that 15% of the respondents were forced to leave school at either the
primary, secondary, or tertiary level.
Transgender individuals also face barriers when applying to
higher education, as was the case with a transgender woman rejected from
the all-girls Smith College because she was not legally recognized as female in her home state.
Health and violence
Transgender
individuals, especially transgender women, are at a high risk of
suffering from domestic abuse due to invisibility, lack of access to
support facilities such as shelters, and a lack of legal and social
protection.
Transgender individuals are also more likely to be sexually and
physically assaulted, both by strangers and acquaintances, than
cisgender individuals are.
In addition, there are several factors that limit transgender people's
access to health care facilities and proper medical care, including
transphobia and the tendency of gender-segregated homeless and domestic
violence shelters to refuse service to transgender and gender
nonconforming individuals.
One study reported that 19% of transgender individuals interviewed
reported being refused medical care due to their gender identity, while
28% reported being harassed in a medical setting and 2% reported
violence toward them in a medical setting due to their gender identity.
In the same study, 50% percent of transgender respondents reported the
need to educate their medical providers about the health care needs of
transgender individuals.
Transgender individuals also reported four times the national
average of HIV infections when compared to cisgender individuals in one
study conducted by the National Center for Transgender Equality and the National Gay and Lesbian Task Force.
The NCAVP's
2012 Report on Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer, and
HIV-affected Hate Violence reported that over fifty percent of
anti-LGBTQ homicide victims in 2012 were transgender women, a
considerable increase from the percentage of transgender women victims
in 2011 at 40%.
In addition, the report also found that, compared to cisgender people,
transgender people were more than three times more likely to experience
police violence.
In terms of mental health, transgender individuals have much
higher rates of suicide attempts than cisgender individuals and it has
been reported that between nineteen and twenty-five of the trans
population have attempted suicide.
Government policy
In 1920, the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution,
which insured women's suffrage (although some individual states allowed
women the right to vote as early as 1869), was ratified. In addition,
the Women's Bureau of the Department of Labor was created to monitor
working conditions for women in the workforce.
In 1961, the President's Commission on the Status of Women was started, initially chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt. This commission found that women were suffering considerable workplace discrimination. In 1963, the Equal Pay Act was passed, which made it illegal for a woman to be paid less than a man working in the same position. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 also made discriminatory hiring on the basis of gender illegal. The affirmative action
policy of 1965 was expanded in 1967 to cover women as well as racial
minorities. In 1973, women's right to safe and legal abortion was
established by the Supreme Court's ruling in Roe v. Wade. In 1968, sex-segregated job advertisements were declared illegal by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission,
this decision was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1973; this allowed
women to apply for higher-paying jobs formally restricted only to male
applicants. In 1972, Title IX of the Education Amendments,
which reads "No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex,
be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be
subjected to discrimination under any educational program or activity
receiving federal financial assistance," was passed.
In 1986, in the decision of Meritor Savings Bank v. Vinson, sexual harassment was established as illegal and discriminatory. The Family Medical Leave Act
of 1993 guarantees that new parents can retain their jobs for 12 weeks
after the birth of the child; this unpaid leave is the only form of
paternal leave protected by law in the United States. In 1994, the Violence Against Women Act provided legal protection, as well as funds and services, for rape victims and victims of domestic violence. United States v. Virginia established in 1996 that gender-based admission practices violated the Fourteenth Amendment,
and establishing a separate all-female school would not suffice as an
alternative to integrating an all-male school. Most recently, in 2009
the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009 provides employees (usually female) who suffer from pay discrimination to file a complaint with the government.
The Equal Rights Amendment,
which reads, "Equality of rights under the law shall not be denied or
abridged by the United States or by any State on account of sex", was
first introduced to Congress in 1923 and successfully passed both houses
of Congress in 1972. However, it failed to be ratified by an adequate
number of states and died in 1982. The United States is one of only a few countries which have not ratified the UN Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (US has only signed the treaty).
Rankings
The World Economic Forum's Gender Gap Index for 2012 ranked United States 22nd best out of 135 countries for gender equality.
The primary indicators for inequality were related to political
empowerment, where the US was ranked 55th (32nd for women in ministerial
position and 78th for women in parliament).
USA was ranked 33rd for health and survival, 8th for economic
participation and opportunity, and tied for 1st (no inequality) in
education. Since the Gender Gap report was first published in 2006, the US position remains relatively stable in that index. However, the United States' score decreased between 2011 and 2012.
United Nation's Gender Inequality Index (part of the Human Development Report) for 2011 had US ranked 47th out of 173 countries. In addition, the OECD's Better Life Index discusses a number of differences, but does not stress any in particular when it comes to gender.