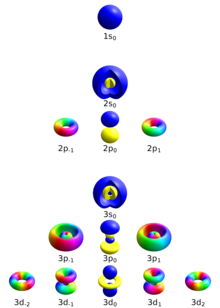Quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of a quantum system.
In the case of electrons, the quantum numbers can be defined as "the
sets of numerical values which give acceptable solutions to the Schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom". An important aspect of quantum mechanics is the quantization of the observable quantities, since quantum numbers are discrete sets of integers or half-integers, although they could approach infinity in some cases. This distinguishes quantum mechanics from classical mechanics
where the values that characterize the system such as mass, charge, or
momentum, range continuously. Quantum numbers often describe
specifically the energy levels of electrons in atoms, but other possibilities include angular momentum, spin, etc. An important family is flavour quantum numbers – internal quantum numbers which determine the type of a particle and its interactions with other particles through the forces. Any quantum system can have one or more quantum numbers; it is thus difficult to list all possible quantum numbers.
How many quantum numbers exist?
The question of how many quantum numbers are needed to describe any given system
has no universal answer. Hence for each system one must find the answer
for a full analysis of the system. A quantized system requires at least
one quantum number. The dynamics of any quantum system are described by
a quantum Hamiltonian, H. There is one quantum number of the system corresponding to the energy, i.e., the eigenvalue of the Hamiltonian. There is also one quantum number for each operator O that commutes with the Hamiltonian. These are all the quantum numbers that the system can have. Note that the operators O defining the quantum numbers should be independent
of each other. Often, there is more than one way to choose a set of
independent operators. Consequently, in different situations different
sets of quantum numbers may be used for the description of the same
system.
Spatial and angular momentum numbers
Single electron orbitals for hydrogen-like atoms with quantum numbers n=1,2,3 (blocks), ℓ (rows) and m (columns). The spin s is not visible, because it has no spatial dependence.
Four quantum numbers can describe an electron in an atom completely.
As per the following model, these nearly-compatible quantum numbers are:
- Principal quantum number (n)
- Azimuthal quantum number (ℓ)
- Magnetic quantum number (m)
- Spin quantum number (s)
The spin-orbital interaction, however, relates these numbers. Thus, a
complete description of the system can be given with fewer quantum
numbers, if orthogonal choices are made for these basis vectors.
Traditional nomenclatures
Hund-Mulliken molecular orbital theory
Many different models have been proposed throughout the history of quantum mechanics, but the most prominent system of nomenclature spawned from the Hund-Mulliken molecular orbital theory of Friedrich Hund, Robert S. Mulliken, and contributions from Schrödinger, Slater and John Lennard-Jones. This system of nomenclature incorporated Bohr energy levels, Hund-Mulliken orbital theory, and observations on electron spin based on spectroscopy and Hund's rules.
This model describes electrons using four quantum numbers, n, ℓ, mℓ, ms,
given below. It is also the common nomenclature in the classical
description of nuclear particle states (e.g. protons and neutrons). A
quantum description of molecular orbitals require different quantum numbers, because the Hamiltonian and its symmetries are quite different.
- The principal quantum number (n) describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an electron. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom, i.e.
- n = 1, 2, ... .
For particles in a time-independent potential (see Schrödinger equation), it also labels the nth eigenvalue of Hamiltonian (H), i.e. the energy, E with the contribution due to angular momentum (the term involving J2) left out. This number therefore has a dependence only on the distance between the electron and the nucleus (i.e., the radial coordinate, r). The average distance increases with n, and hence quantum states with different principal quantum numbers are said to belong to different shells. - The azimuthal quantum number (ℓ) (also known as the angular quantum number or orbital quantum number) describes the subshell, and gives the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum through the relation
- L2 = ħ2 ℓ (ℓ + 1).
- ℓ = 0, 1, 2,..., n − 1.
- The magnetic quantum number (mℓ) describes the specific orbital (or "cloud") within that subshell, and yields the projection of the orbital angular momentum along a specified axis:
- Lz = mℓ ħ.
- The spin projection quantum number (ms) describes the spin (intrinsic angular momentum) of the electron within that orbital, and gives the projection of the spin angular momentum S along the specified axis:
- Sz = ms ħ.
- ms = −s, −s + 1, −s + 2, ..., s − 2, s − 1, s.
Note that there is no universal fixed value for mℓ and ms values. Rather, the mℓ and ms
values are random. The only requirement is that the naming schematic
used within a particular set of calculations or descriptions must be
consistent (e.g. the orbital occupied by the first electron in a p
orbital could be described as mℓ = −1 or mℓ = 0 or mℓ = 1, but the mℓ value of the next unpaired electron in that orbital must be different; yet, the mℓ assigned to electrons in other orbitals again can be mℓ = −1 or mℓ = 0, or mℓ = 1 ).
These rules are summarized as follows:
Name Symbol Orbital meaning Range of values Value examples principal quantum number n shell 1 ≤ n n = 1, 2, 3, … azimuthal quantum number (angular momentum) ℓ subshell (s orbital is listed as 0, p orbital as 1 etc.) 0 ≤ ℓ ≤ n − 1 for n = 3: ℓ = 0, 1, 2 (s, p, d) magnetic quantum number, (projection of angular momentum) mℓ energy shift (orientation of the subshell's shape) −ℓ ≤ mℓ ≤ ℓ for ℓ = 2: mℓ = −2, −1, 0, 1, 2 spin projection quantum number ms spin of the electron (−½ = "spin down", ½ = "spin up") −s ≤ ms ≤ s for an electron s = ½,
so ms = −½, ½
Example: The quantum numbers used to refer to the outermost valence electrons of the Carbon (C) atom, which are located in the 2p atomic orbital, are; n = 2 (2nd electron shell), ℓ = 1 (p orbital subshell), mℓ = 1, 0 or −1, ms = ½ (parallel spins).
Results from spectroscopy
indicated that up to two electrons can occupy a single orbital. However
two electrons can never have the same exact quantum state nor the same
set of quantum numbers according to Hund's rules, which addresses the Pauli exclusion principle. A fourth quantum number with two possible values was added as an ad hoc
assumption to resolve the conflict; this supposition could later be
explained in detail by relativistic quantum mechanics and from the
results of the renowned Stern–Gerlach experiment.
Total angular momenta numbers
Total momentum of a particle
When one takes the spin–orbit interaction into consideration, the L and S operators no longer commute with the Hamiltonian, and their eigenvalues therefore change over time. Thus another set of quantum numbers should be used. This set includes
- The total angular momentum quantum number:
- j = |ℓ ± s|,
- J2 = ħ2 j (j + 1).
- The projection of the total angular momentum along a specified axis:
- mj = −j, −j + 1, −j + 2, ..., j − 2, j − 1, j
analogous to the above and satisfies
- mj = mℓ + ms and |mℓ + ms| ≤ j.
- Parity
This is the eigenvalue under reflection: positive (+1) for states which came from even ℓ and negative (−1) for states which came from odd ℓ. The former is also known as even parity and the latter as odd parity, and is given by
- P = (−1)ℓ.
For example, consider the following 8 states, defined by their quantum numbers:
# n ℓ mℓ ms ℓ + s ℓ − s mℓ + ms 1. 2 1 1 +1/2 3/2 1/23/2 2. 2 1 1 −1/2 3/2 1/2 1/2 3. 2 1 0 +1/2 3/2 1/2 1/2 4. 2 1 0 −1/2 3/2 1/2 −1/2 5. 2 1 −1 +1/2 3/2 1/2 −1/2 6. 2 1 −1 −1/2 3/2 1/2−3/2 7. 2 0 0 +1/2 1/2 −1/2 1/2 8. 2 0 0 −1/2 1/2 −1/2 −1/2
The [quantum state]s in the system can be described as linear combination of these 8 states. However, in the presence of spin–orbit interaction, if one wants to describe the same system by 8 states that are eigenvectors of the Hamiltonian (i.e. each represents a state that does not mix with others over time), we should consider the following 8 states:
j mj parity 3/2 3/2 odd (coming from state (1) above) 3/2 1/2 odd (coming from states (2) and (3) above) 3/2 −1/2 odd (coming from states (4) and (5) above) 3/2 −3/2 odd (coming from state (6) above) 1/2 1/2 odd (coming from states (2) and (3) above) 1/2 −1/2 odd (coming from states (4) and (5) above) 1/2 1/2 even (coming from state (7) above) 1/2 −1/2 even (coming from state (8) above)
Nuclear angular momentum quantum numbers
In nuclei, the entire assembly of protons and neutrons (nucleons) has a resultant angular momentum due to the angular momenta of each nucleon, usually denoted 'I'. If the total angular momentum of a neutron is jn = ℓ + s and for a proton is jp = ℓ + s (where s for protons and neutrons happens to be ½ again) then the nuclear angular momentum quantum numbers I are given by:
- I = |jn − jp|, |jn − jp| + 1, |jn − jp| + 2, ...,
- (jn + jp) − 2, (jn + jp) − 1, (jn + jp)
Parity with the number I is used to label nuclear angular momentum states, examples for some isotopes of Hydrogen (H), Carbon (C), and Sodium (Na) are;
1
1HI = (1/2)+ 9
6CI = (3/2)− 20
11NaI = 2+ 2
1HI = 1+ 10
6CI = 0+ 21
11NaI = (3/2)+ 3
1HI = (1/2)+ 11
6CI = (3/2)− 22
11NaI = 3+ 12
6CI = 0+ 23
11NaI = (3/2)+ 13
6CI = (1/2)− 24
11NaI = 4+ 14
6CI = 0+ 25
11NaI = (5/2)+ 15
6CI = (1/2)+ 26
11NaI = 3+
The reason for the unusual fluctuations in I,
even by differences of just one nucleon, are due to the odd/even
numbers of protons and neutrons - pairs of nucleons have a total angular
momentum of zero (just like electrons in orbitals), leaving an odd/even
numbers of unpaired nucleons. The property of nuclear spin is an
important factor for the operation of NMR spectroscopy in organic chemistry, and MRI in nuclear medicine, due to the nuclear magnetic moment interacting with an external magnetic field.
Elementary particles
Elementary particles
contain many quantum numbers which are usually said to be intrinsic to
them. However, it should be understood that the elementary particles are
quantum states of the standard model of particle physics, and hence the quantum numbers of these particles bear the same relation to the Hamiltonian of this model as the quantum numbers of the Bohr atom does to its Hamiltonian. In other words, each quantum number denotes a symmetry of the problem. It is more useful in quantum field theory to distinguish between spacetime and internal symmetries.
Typical quantum numbers related to spacetime symmetries are spin (related to rotational symmetry), the parity, C-parity and T-parity (related to the Poincaré symmetry of spacetime). Typical internal symmetries are lepton number and baryon number or the electric charge. (For a full list of quantum numbers of this kind see the article on flavor.)
Multiplicative quantum numbers
A
minor but often confusing point is as follows: most conserved quantum
numbers are additive, so in an elementary particle reaction, the sum of the quantum numbers should be the same before and after the reaction. However, some, usually called a parity, are multiplicative; i.e., their product
is conserved. All multiplicative quantum numbers belong to a symmetry
(like parity) in which applying the symmetry transformation twice is
equivalent to doing nothing (involution).