Cocaine, also known as coke, is a strong stimulant mostly used as a recreational drug. It is commonly snorted, inhaled as smoke, or dissolved and injected into a vein. Mental effects may include loss of contact with reality, an intense feeling of happiness, or agitation. Physical symptoms may include a fast heart rate, sweating, and large pupils. High doses can result in very high blood pressure or body temperature. Effects begin within seconds to minutes of use and last between five and ninety minutes. Cocaine has a small number of accepted medical uses such as numbing and decreasing bleeding during nasal surgery.
Cocaine is addictive due to its effect on the reward pathway in the brain. After a short period of use, there is a high risk that dependence will occur. Its use also increases the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, lung problems in those who smoke it, blood infections, and sudden cardiac death. Cocaine sold on the street is commonly mixed with local anesthetics, cornstarch, quinine, or sugar, which can result in additional toxicity. Following repeated doses a person may have decreased ability to feel pleasure and be very physically tired.
Cocaine acts by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. This results in greater concentrations of these three neurotransmitters in the brain. It can easily cross the blood–brain barrier and may lead to the breakdown of the barrier. Cocaine is a naturally occurring substance found in the coca plant which is mostly grown in South America. In 2013, 419 kilograms were produced legally. It is estimated that the illegal market for cocaine is 100 to US$500 billion each year. With further processing crack cocaine can be produced from cocaine.
Cocaine is the second most frequently used illegal drug globally, after cannabis. Between 14 and 21 million people use the drug each year. Use is highest in North America followed by Europe and South America. Between one and three percent of people in the developed world have used cocaine at some point in their life. In 2013, cocaine use directly resulted in 4,300 deaths, up from 2,400 in 1990. The leaves of the coca plant have been used by Peruvians since ancient times. Cocaine was first isolated from the leaves in 1860. Since 1961, the international Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs has required countries to make recreational use of cocaine a crime.
Uses
Medical
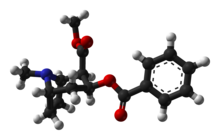
Cocaine hydrochloride
Topical cocaine can be used as a local numbing agent to help with painful procedures in the mouth or nose.
Cocaine is now predominantly used for nasal and lacrimal duct surgery. The major disadvantages of this use are cocaine's potential for cardiovascular toxicity, glaucoma, and pupil dilation. Medicinal use of cocaine has decreased as other synthetic local anesthetics such as benzocaine, proparacaine, lidocaine, and tetracaine are now used more often.
If vasoconstriction is desired for a procedure (as it reduces
bleeding), the anesthetic is combined with a vasoconstrictor such as phenylephrine or epinephrine. Some ENT specialists occasionally use cocaine within the practice when performing procedures such as nasal cauterization.
In this scenario dissolved cocaine is soaked into a ball of cotton
wool, which is placed in the nostril for the 10–15 minutes immediately
before the procedure, thus performing the dual role of both numbing the
area to be cauterized, and vasoconstriction. Even when used this way,
some of the used cocaine may be absorbed through oral or nasal mucosa
and give systemic effects. An alternative method of administration for ENT surgery is mixed with adrenaline and sodium bicarbonate, as Moffett's solution.
Recreational
Cocaine is a powerful nervous system stimulant.
Its effects can last from 15 or 30 minutes to an hour. The duration of
cocaine's effects depends on the amount taken and the route of
administration.
Cocaine can be in the form of fine white powder, bitter to the taste.
When inhaled or injected, it causes a numbing effect. Crack cocaine is a
smokeable form of cocaine made into small "rocks" by processing cocaine
with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and water. Crack cocaine is referred to as "crack" because of the crackling sounds it makes when heated.
Cocaine use leads to increases in alertness, feelings of well-being and euphoria, increased energy and motor activity, and increased feelings of competence and sexuality.
Coca leaves
Coca leaves are typically mixed with an alkaline substance (such as lime) and chewed into a wad that is retained in the mouth between gum and cheek (much the same as chewing tobacco
is chewed) and sucked of its juices. The juices are absorbed slowly by
the mucous membrane of the inner cheek and by the gastrointestinal tract
when swallowed. Alternatively, coca leaves can be infused in liquid and
consumed like tea. Ingesting coca leaves generally is an inefficient
means of administering cocaine.
Because cocaine is hydrolyzed
and rendered inactive in the acidic stomach, it is not readily absorbed
when ingested alone. Only when mixed with a highly alkaline substance
(such as lime)
can it be absorbed into the bloodstream through the stomach. The
efficiency of absorption of orally administered cocaine is limited by
two additional factors. First, the drug is partly catabolized by the
liver. Second, capillaries in the mouth and esophagus constrict after
contact with the drug, reducing the surface area over which the drug can
be absorbed. Nevertheless, cocaine metabolites can be detected in the
urine of subjects that have sipped even one cup of coca leaf infusion.
Orally administered cocaine takes approximately 30 minutes to
enter the bloodstream. Typically, only a third of an oral dose is
absorbed, although absorption has been shown to reach 60% in controlled
settings. Given the slow rate of absorption, maximum physiological and psychotropic
effects are attained approximately 60 minutes after cocaine is
administered by ingestion. While the onset of these effects is slow, the
effects are sustained for approximately 60 minutes after their peak is
attained.
Contrary to popular belief, both ingestion and insufflation
result in approximately the same proportion of the drug being absorbed:
30 to 60%. Compared to ingestion, the faster absorption of insufflated
cocaine results in quicker attainment of maximum drug effects. Snorting
cocaine produces maximum physiological effects within 40 minutes and
maximum psychotropic effects within 20 minutes, however, a more
realistic activation period is closer to 5 to 10 minutes. Physiological
and psychotropic effects from nasally insufflated cocaine are sustained
for approximately 40–60 minutes after the peak effects are attained.
Coca tea,
an infusion of coca leaves, is also a traditional method of
consumption. The tea has often been recommended for travelers in the
Andes to prevent altitude sickness. However, its actual effectiveness has never been systematically studied.
In 1986 an article in the Journal of the American Medical Association revealed that U.S. health food stores were selling dried coca leaves to be prepared as an infusion as "Health Inca Tea."
While the packaging claimed it had been "decocainized," no such process
had actually taken place. The article stated that drinking two cups of
the tea per day gave a mild stimulation, increased heart rate, and mood elevation, and the tea was essentially harmless. Despite this, the DEA seized several shipments in Hawaii, Chicago, Georgia, and several locations on the East Coast of the United States, and the product was removed from the shelves.
Insufflation
Lines of cocaine prepared for insufflation
Nasal insufflation (known colloquially as "snorting", "sniffing", or "blowing") is a common method of ingestion of recreational powdered cocaine. The drug coats and is absorbed through the mucous membranes lining the nasal passages.
Cocaine's desired euphoric effects are delayed when snorted through the
nose by about five minutes. This occurs because cocaine's absorption is
slowed by its constricting effect on the blood vessels of the nose. Insufflation of cocaine also leads to the longest duration of its effects (60–90 minutes).
When insufflating cocaine, absorption through the nasal membranes is
approximately 30–60%, with higher doses leading to increased absorption
efficiency. Any material not directly absorbed through the mucous membranes is collected in mucus and swallowed (this "drip" is considered pleasant by some and unpleasant by others).
In a study of cocaine users, the average time taken to reach peak subjective effects was 14.6 minutes.
Any damage to the inside of the nose is because cocaine highly
constricts blood vessels – and therefore blood and oxygen/nutrient flow –
to that area. Nosebleeds after cocaine insufflation are due to
irritation and damage of mucus membranes by foreign particles and adulterants and not the cocaine itself; as a vasoconstrictor, cocaine acts to reduce bleeding.
Rolled up banknotes, hollowed-out pens, cut straws, pointed ends of keys, specialized spoons, long fingernails,
and (clean) tampon applicators are often used to insufflate cocaine.
Such devices are often called "tooters" by users. The cocaine typically
is poured onto a flat, hard surface (such as a mirror, CD case or book)
and divided into "bumps," "lines" or "rails," and then insufflated.
The amount of cocaine in a line varies widely from person to person and
occasion to occasion (the purity of the cocaine is also a factor), but
one line is generally considered to be a single dose and is typically
35 mg (a "bump") to 100 mg (a "rail"). As tolerance builds rapidly in the short-term (hours), many lines are often snorted to produce greater effects. A 2001 study reported that the sharing of straws used to "snort" cocaine can spread blood diseases such as hepatitis C.
Injection
Drug injection
by turning the drug into a solution provides the highest blood levels
of drug in the shortest amount of time. Subjective effects not commonly
shared with other methods of administration include a ringing in the
ears moments after injection (usually when in excess of 120 milligrams)
lasting two to 5 minutes including tinnitus
and audio distortion. This is colloquially referred to as a "bell
ringer". In a study of cocaine users, the average time taken to reach
peak subjective effects was 3.1 minutes. The euphoria passes quickly. Aside from the toxic effects of cocaine, there is also danger of circulatory emboli
from the insoluble substances that may be used to cut the drug. As with
all injected illicit substances, there is a risk of the user
contracting blood-borne infections if sterile injecting equipment is not
available or used. Additionally, because cocaine is a vasoconstrictor,
and usage often entails multiple injections within several hours or
less, subsequent injections are progressively more difficult to
administer, which in turn may lead to more injection attempts and more
consequences from improperly performed injection.
An injected mixture of cocaine and heroin, known as "speedball"
is a particularly dangerous combination, as the converse effects of the
drugs actually complement each other, but may also mask the symptoms of
an overdose. It has been responsible for numerous deaths, including
celebrities such as comedians/actors John Belushi and Chris Farley, Mitch Hedberg, River Phoenix, grunge singer Layne Staley and actor Philip Seymour Hoffman. Experimentally, cocaine injections can be delivered to animals such as fruit flies to study the mechanisms of cocaine addiction.
Inhalation
Inhalation by smoking cocaine is one of the several ways the drug is
consumed. The onset of cocaine's desired euphoric effects is fastest
with inhaling cocaine and begins after 3–5 seconds. In contrast, inhalation of cocaine leads to the shortest duration of its effects (5–15 minutes). The two main ways cocaine is smoked are freebasing and by using cocaine which has been converted to smokable "crack cocaine". Cocaine is smoked by inhaling the vapor produced when solid cocaine is heated to the point that it sublimates.
In a 2000 Brookhaven National Laboratory medical department study,
based on self reports of 32 abusers who participated in the study,"peak
high" was found at mean of 1.4min +/- 0.5 minutes. Pyrolysis products of cocaine that occur only when heated/smoked have been shown to change the effect profile, i.e. anhydroecgonine methyl ester when co-administered with cocaine increases the dopamine in CPu and NAc brain regions, and has M1- and M3- receptor affinity.
Smoking freebase or crack cocaine is most often accomplished using a pipe made from a small glass tube, often taken from "love roses", small glass tubes with a paper rose that are promoted as romantic gifts.
These are sometimes called "stems", "horns", "blasters" and "straight
shooters". A small piece of clean heavy copper or occasionally stainless
steel scouring pad – often called a "brillo" (actual Brillo Pads contain soap, and are not used) or "chore" (named for Chore Boy
brand copper scouring pads) – serves as a reduction base and flow
modulator in which the "rock" can be melted and boiled to vapor. Crack
smokers also sometimes smoke through a soda can with small holes on the side or bottom.
Crack is smoked by placing it at the end of the pipe; a flame held
close to it produces vapor, which is then inhaled by the smoker. The
effects, felt almost immediately after smoking, are very intense and do
not last long – usually 2 to 10 minutes. When smoked, cocaine is sometimes combined with other drugs, such as cannabis, often rolled into a joint or blunt. Powdered cocaine is also sometimes smoked, though heat destroys much of the chemical; smokers often sprinkle it on cannabis.[citation needed]
The language referring to paraphernalia and practices of smoking
cocaine vary, as do the packaging methods in the street level sale.
Suppository
Another way users consume cocaine is by making it into a suppository
which they then insert into the anus or vagina. The drug is then
absorbed by the membranes of these body parts. Little research has been
focused on the suppository (anal or vaginal insertion) method of
administration, also known as "plugging". This method of administration
is commonly administered using an oral syringe.
Cocaine can be dissolved in water and withdrawn into an oral syringe
which may then be lubricated and inserted into the anus or vagina before
the plunger is pushed. Anecdotal evidence of its effects is
infrequently discussed, possibly due to social taboos in many cultures.
The rectum and the vaginal canal is where the majority of the drug would
be taken up through the membranes lining its walls.
Adverse effects
Acute
With excessive or prolonged use, the drug can cause itching, fast heart rate, hallucinations, and paranoid delusions. Overdoses cause hyperthermia and a marked elevation of blood pressure, which can be life-threatening, arrhythmias, and death.
Anxiety, paranoia,
and restlessness can also occur, especially during the comedown. With
excessive dosage, tremors, convulsions and increased body temperature
are observed. Severe cardiac adverse events, particularly sudden cardiac death, become a serious risk at high doses due to cocaine's blocking effect on cardiac sodium channels.
- Delphic analysis regarding 20 popular recreational drugs based on expert opinion. Cocaine was ranked the 2nd in dependence and physical harm and 3rd in social harm.
Chronic
Side effects of chronic cocaine use
Chronic cocaine intake causes strong imbalances of transmitter levels
in order to compensate extremes. Thus, receptors disappear from the
cell surface or reappear on it, resulting more or less in an "off" or
"working mode" respectively, or they change their susceptibility for
binding partners (ligands) – mechanisms called downregulation and upregulation. However, studies suggest cocaine abusers do not show normal age-related loss of striatal dopamine transporter (DAT) sites, suggesting cocaine has neuroprotective properties for dopamine neurons.
Possible side effects include insatiable hunger, aches,
insomnia/oversleeping, lethargy, and persistent runny nose. Depression
with suicidal ideation may develop in very heavy users. Finally, a loss
of vesicular monoamine transporters,
neurofilament proteins, and other morphological changes appear to
indicate a long term damage of dopamine neurons. All these effects
contribute a rise in tolerance thus requiring a larger dosage to achieve
the same effect.
The lack of normal amounts of serotonin and dopamine in the brain is the
cause of the dysphoria and depression felt after the initial high.
Physical withdrawal is not dangerous. Physiological changes caused by
cocaine withdrawal include vivid and unpleasant dreams, insomnia or
hypersomnia, increased appetite and psychomotor retardation or
agitation.
Physical side effects from chronic smoking of cocaine include coughing up blood, bronchospasm, itching, fever, diffuse alveolar infiltrates without effusions, pulmonary and systemic eosinophilia, chest pain, lung trauma, sore throat, asthma, hoarse voice, dyspnea (shortness of breath), and an aching, flu-like syndrome. Cocaine constricts blood vessels, dilates pupils,
and increases body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. It can
also cause headaches and gastrointestinal complications such as
abdominal pain and nausea. A common but untrue belief is that the
smoking of cocaine chemically breaks down tooth enamel and causes tooth decay. However, cocaine does often cause involuntary tooth grinding, known as bruxism, which can deteriorate tooth enamel and lead to gingivitis. Additionally, stimulants like cocaine, methamphetamine, and even caffeine cause dehydration and dry mouth.
Since saliva is an important mechanism in maintaining one's oral pH
level, chronic stimulant abusers who do not hydrate sufficiently may
experience demineralization of their teeth due to the pH of the tooth
surface dropping too low (below 5.5). Cocaine use also promotes the formation of blood clots. This increase in blood clot formation is attributed to cocaine-associated increases in the activity of plasminogen activator inhibitor, and an increase in the number, activation, and aggregation of platelets.
Chronic intranasal usage can degrade the cartilage separating the nostrils (the septum nasi),
leading eventually to its complete disappearance. Due to the absorption
of the cocaine from cocaine hydrochloride, the remaining hydrochloride
forms a dilute hydrochloric acid.
Cocaine may also greatly increase this risk of developing rare autoimmune or connective tissue diseases such as lupus, Goodpasture syndrome, vasculitis, glomerulonephritis, Stevens–Johnson syndrome, and other diseases. It can also cause a wide array of kidney diseases and kidney failure.
Cocaine use leads to an increased risk of hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. Cocaine use also increases the risk of having a heart attack.
Addiction
Cocaine addiction occurs through ΔFosB overexpression in the nucleus accumbens, which results in altered transcriptional regulation in neurons within the nucleus accumbens.
ΔFosB levels have been found to increase upon the use of cocaine.
Each subsequent dose of cocaine continues to increase ΔFosB levels with
no ceiling of tolerance. Elevated levels of ΔFosB leads to increases in
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, which in turn increases the number of dendritic branches and spines present on neurons involved with the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex areas of the brain. This change can be identified rather quickly, and may be sustained weeks after the last dose of the drug.
Transgenic mice exhibiting inducible expression of ΔFosB primarily in the nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum exhibit sensitized behavioural responses to cocaine. They self-administer cocaine at lower doses than control, but have a greater likelihood of relapse when the drug is withheld. ΔFosB increases the expression of AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 and also decreases expression of dynorphin, thereby enhancing sensitivity to reward.
Dependence and withdrawal
Cocaine dependence is a form of psychological dependence that develops from regular cocaine use and produces a withdrawal state with emotional-motivational deficits upon cessation of cocaine use.
During pregnancy
Cocaine is known to have a number of deleterious effects during
pregnancy. Pregnant people who use cocaine have an elevated risk of placental abruption, a condition where the placenta detaches from the uterus and causes bleeding. Due to its vasoconstrictive and hypertensive effects, they are also at risk for hemorrhagic stroke and myocardial infarction.
Cocaine is also teratogenic, meaning that it can cause birth defects
and fetal malformations. In-utero exposure to cocaine is associated with
behavioral abnormalities, cognitive impairment, cardiovascular
malformations, intrauterine growth restriction, preterm birth, urinary tract malformations, and cleft lip and palate.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of cocaine involve the complex relationships of neurotransmitters (inhibiting monoamine uptake in rats with ratios of about: serotonin:dopamine = 2:3, serotonin:norepinephrine = 2:5). The most extensively studied effect of cocaine on the central nervous system is the blockade of the dopamine transporter protein. Dopamine transmitter
released during neural signaling is normally recycled via the
transporter; i.e., the transporter binds the transmitter and pumps it
out of the synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic neuron, where it is taken up into storage vesicles.
Cocaine binds tightly at the dopamine transporter forming a complex
that blocks the transporter's function. The dopamine transporter can no
longer perform its reuptake function, and thus dopamine accumulates in the synaptic cleft.
The increased concentration of dopamine in the synapse activates
post-synaptic dopamine receptors, which makes the drug rewarding and
promotes the compulsive use of cocaine.
Cocaine affects certain serotonin (5-HT) receptors; in particular, it has been shown to antagonize the 5-HT3 receptor, which is a ligand-gated ion channel.
The overabundance of 5-HT3 receptors in cocaine conditioned rats
display this trait, however the exact effect of 5-HT3 in this process is
unclear. The 5-HT2 receptor (particularly the subtypes 5-HT2AR, 5-HT2BR and 5-HT2CR) are involved in the locomotor-activating effects of cocaine.
Cocaine has been demonstrated to bind as to directly stabilize
the DAT transporter on the open outward-facing conformation. Further,
cocaine binds in such a way as to inhibit a hydrogen bond innate to DAT.
Cocaine's binding properties are such that it attaches so this hydrogen
bond will not form and is blocked from formation due to the tightly
locked orientation of the cocaine molecule. Research studies have
suggested that the affinity for the transporter is not what is involved
in habituation of the substance so much as the conformation and binding
properties to where and how on the transporter the molecule binds.
Sigma receptors are affected by cocaine, as cocaine functions as a sigma ligand agonist. Further specific receptors it has been demonstrated to function on are NMDA and the D1 dopamine receptor.
Cocaine also blocks sodium channels, thereby interfering with the propagation of action potentials; thus, like lignocaine and novocaine,
it acts as a local anesthetic. It also functions on the binding sites
to the dopamine and serotonin sodium dependent transport area as targets
as separate mechanisms from its reuptake of those transporters; unique
to its local anesthetic value which makes it in a class of functionality
different from both its own derived phenyltropanes analogues which have
that removed. In addition to this cocaine has some target binding to
the site of the Kappa-opioid receptor as well. Cocaine also causes vasoconstriction,
thus reducing bleeding during minor surgical procedures. The locomotor
enhancing properties of cocaine may be attributable to its enhancement
of dopaminergic transmission from the substantia nigra. Recent research points to an important role of circadian mechanisms and clock genes in behavioral actions of cocaine.
Cocaine can often cause reduced food intake, many chronic users
lose their appetite and can experience severe malnutrition and
significant weight loss. Cocaine effects, further, are shown to be
potentiated for the user when used in conjunction with new surroundings
and stimuli, and otherwise novel environs.
Pharmacokinetics
Cocaine has a short half life of 0.7-1.5 hours and is extensively metabolized by cholinesterase enzymes (primarily in the liver and plasma), with only about 1% excreted unchanged in the urine. The metabolism is dominated by hydrolytic ester cleavage, so the eliminated metabolites consist mostly of benzoylecgonine (BE), the major metabolite, and other significant metabolites in lesser amounts such as ecgonine methyl ester (EME) and ecgonine. Further minor metabolites of cocaine include norcocaine, p-hydroxycocaine, m-hydroxycocaine, p-hydroxybenzoylecgonine (pOHBE), and m-hydroxybenzoylecgonine. If consumed with alcohol, cocaine combines with alcohol in the liver to form cocaethylene. Studies have suggested cocaethylene is both more euphoric, and has a higher cardiovascular toxicity than cocaine by itself.
Depending on liver and kidney function, cocaine metabolites are
detectable in urine. Benzoylecgonine can be detected in urine within
four hours after cocaine intake and remains detectable in concentrations
greater than 150 ng/mL typically for up to eight days after cocaine is
used. Detection of cocaine metabolites in hair is possible in regular
users until the sections of hair grown during use are cut or fall out.
Chemistry
Appearance
A pile of cocaine hydrochloride
A piece of compressed cocaine powder
Cocaine in its purest form is a white, pearly product. Cocaine appearing in powder form is a salt, typically cocaine hydrochloride. Street cocaine is often adulterated or "cut" with talc, lactose, sucrose, glucose, mannitol, inositol, caffeine, procaine, phencyclidine, phenytoin, lignocaine, strychnine, amphetamine, or heroin.
The color of "crack" cocaine depends upon several factors including the origin of the cocaine used, the method of preparation – with ammonia or baking soda
– and the presence of impurities. It will generally range from white to
a yellowish cream to a light brown. Its texture will also depend on the
adulterants, origin and processing of the powdered cocaine, and the
method of converting the base. It ranges from a crumbly texture,
sometimes extremely oily, to a hard, almost crystalline nature.
Forms
Salts
Cocaine – a tropane alkaloid – is a weakly alkaline compound, and can therefore combine with acidic compounds to form salts. The hydrochloride (HCl) salt of cocaine is by far the most commonly encountered, although the sulfate (SO42-) and the nitrate (NO3−)
salts are occasionally seen. Different salts dissolve to a greater or
lesser extent in various solvents – the hydrochloride salt is polar in
character and is quite soluble in water.
Base
As the name implies, "freebase" is the base form of cocaine, as opposed to the salt form. It is practically insoluble in water whereas hydrochloride salt is water-soluble.
Smoking freebase cocaine has the additional effect of releasing methylecgonidine into the user's system due to the pyrolysis of the substance (a side effect which insufflating
or injecting powder cocaine does not create). Some research suggests
that smoking freebase cocaine can be even more cardiotoxic than other routes of administration because of methylecgonidine's effects on lung tissue and liver tissue.
Pure cocaine is prepared by neutralizing its compounding salt
with an alkaline solution, which will precipitate to non-polar basic
cocaine. It is further refined through aqueous-solvent liquid–liquid extraction.
Crack cocaine
A woman smoking crack cocaine
"Rocks" of crack cocaine
Crack is a lower purity form of free-base cocaine that is usually
produced by neutralization of cocaine hydrochloride with a solution of
baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3) and water, producing
a very hard/brittle, off-white-to-brown colored, amorphous material
that contains sodium carbonate, entrapped water, and other by-products
as the main impurities.
The "freebase" and "crack" forms of cocaine are usually
administered by vaporization of the powdered substance into smoke, which
is then inhaled.
The origin of the name "crack" comes from the "crackling" sound (and hence the onomatopoeic
moniker "crack") that is produced when the cocaine and its impurities
(i.e. water, sodium bicarbonate) are heated past the point of
vaporization.
Pure cocaine base/crack can be smoked because it vaporizes smoothly, with little or no decomposition at 98 °C (208 °F), which is below the boiling point of water.
In contrast, cocaine hydrochloride does not vaporize until heated
to a much higher temperature (about 197 °C), and considerable
decomposition/burning occurs at these high temperatures. This
effectively destroys some of the cocaine and yields a sharp, acrid, and
foul-tasting smoke.
Smoking or vaporizing cocaine and inhaling it into the lungs
produces an almost immediate "high" that can be very powerful (and
addicting) quite rapidly – this initial crescendo of stimulation is
known as a "rush". While the stimulating effects may last for hours, the
euphoric sensation is very brief, prompting the user to smoke more
immediately.
Coca leaf infusions
Coca herbal infusion (also referred to as coca tea)
is used in coca-leaf producing countries much as any herbal medicinal
infusion would elsewhere in the world. The free and legal
commercialization of dried coca leaves under the form of filtration bags
to be used as "coca tea" has been actively promoted by the governments
of Peru and Bolivia for many years as a drink having medicinal powers. In Peru, the National Coca Company,
a state-run corporation, sells cocaine-infused teas and other medicinal
products and also exports leaves to the U.S. for medicinal use.
Visitors to the city of Cuzco in Peru, and La Paz
in Bolivia are greeted with the offering of coca leaf infusions
(prepared in teapots with whole coca leaves) purportedly to help the
newly arrived traveler overcome the malaise of high altitude
sickness.The effects of drinking coca tea are a mild stimulation and
mood lift.
It does not produce any significant numbing of the mouth nor does it
give a rush like snorting cocaine. In order to prevent the demonization
of this product, its promoters publicize the unproven concept that much
of the effect of the ingestion of coca leaf infusion would come from the
secondary alkaloids, as being not only quantitatively different from
pure cocaine but also qualitatively different.
It has been promoted as an adjuvant for the treatment of cocaine
dependence. In one controversial study, coca leaf infusion was used—in
addition to counseling—to treat 23 addicted coca-paste smokers in Lima,
Peru. Relapses fell from an average of four times per month before
treatment with coca tea to one during the treatment. The duration of
abstinence increased from an average of 32 days prior to treatment to
217 days during treatment. These results suggest that the administration
of coca leaf infusion plus counseling would be an effective method for
preventing relapse during treatment for cocaine addiction.
Importantly, these results also suggest strongly that the primary
pharmacologically active metabolite in coca leaf infusions is actually
cocaine and not the secondary alkaloids. The cocaine metabolite benzoylecgonine can be detected in the urine of people a few hours after drinking one cup of coca leaf infusion.
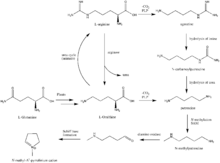
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis of N-methyl-pyrrolinium cation
Biosynthesis of cocaine
Robinson biosynthesis of tropane
Reduction of tropinone
The first synthesis and elucidation of the cocaine molecule was by Richard Willstätter in 1898. Willstätter's synthesis derived cocaine from tropinone. Since then, Robert Robinson and Edward Leete have made significant contributions to the mechanism of the synthesis. (-NO3)
The additional carbon atoms required for the synthesis of cocaine
are derived from acetyl-CoA, by addition of two acetyl-CoA units to the
N-methyl-Δ1-pyrrolinium cation. The first addition is a Mannich-like reaction with the enolate anion from acetyl-CoA acting as a nucleophile
towards the pyrrolinium cation. The second addition occurs through a
Claisen condensation. This produces a racemic mixture of the
2-substituted pyrrolidine, with the retention of the thioester from the
Claisen condensation. In formation of tropinone from racemic ethyl [2,3-13C2]4(Nmethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)-3-oxobutanoate there is no preference for either stereoisomer.
In the biosynthesis of cocaine, however, only the (S)-enantiomer can
cyclize to form the tropane ring system of cocaine. The
stereoselectivity of this reaction was further investigated through
study of prochiral methylene hydrogen discrimination. This is due to the extra chiral center at C-2.
This process occurs through an oxidation, which regenerates the
pyrrolinium cation and formation of an enolate anion, and an
intramolecular Mannich reaction. The tropane ring system undergoes hydrolysis, SAM-dependent methylation, and reduction via NADPH for the formation of methylecgonine. The benzoyl moiety required for the formation of the cocaine diester is synthesized from phenylalanine via cinnamic acid. Benzoyl-CoA then combines the two units to form cocaine.
N-methyl-pyrrolinium cation
The biosynthesis begins with L-Glutamine, which is derived to L-ornithine in plants. The major contribution of L-ornithine and L-arginine as a precursor to the tropane ring was confirmed by Edward Leete. Ornithine then undergoes a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent
decarboxylation to form putrescine. In animals, however, the urea cycle
derives putrescine from ornithine. L-ornithine is converted to
L-arginine, which is then decarboxylated via PLP to form agmatine. Hydrolysis of the imine derives N-carbamoylputrescine
followed with hydrolysis of the urea to form putrescine. The separate
pathways of converting ornithine to putrescine in plants and animals
have converged. A SAM-dependent N-methylation of putrescine gives the N-methylputrescine
product, which then undergoes oxidative deamination by the action of
diamine oxidase to yield the aminoaldehyde. Schiff base formation
confirms the biosynthesis of the N-methyl-Δ1-pyrrolinium cation.
Robert Robinson's acetonedicarboxylate
The biosynthesis of the tropane alkaloid,
however, is still uncertain. Hemscheidt proposes that Robinson's
acetonedicarboxylate emerges as a potential intermediate for this
reaction. Condensation of N-methylpyrrolinium and acetonedicarboxylate would generate the oxobutyrate. Decarboxylation leads to tropane alkaloid formation.
Reduction of tropinone
The reduction of tropinone is mediated by NADPH-dependent reductase enzymes, which have been characterized in multiple plant species.
These plant species all contain two types of the reductase enzymes,
tropinone reductase I and tropinone reductase II. TRI produces tropine
and TRII produces pseudotropine. Due to differing kinetic and
pH/activity characteristics of the enzymes and by the 25-fold higher
activity of TRI over TRII, the majority of the tropinone reduction is
from TRI to form tropine.
Detection in body fluids
Cocaine and its major metabolites may be quantified in blood, plasma,
or urine to monitor for abuse, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning, or
assist in the forensic investigation of a traffic or other criminal
violation or a sudden death. Most commercial cocaine immunoassay
screening tests cross-react appreciably with the major cocaine
metabolites, but chromatographic techniques can easily distinguish and
separately measure each of these substances. When interpreting the
results of a test, it is important to consider the cocaine usage history
of the individual, since a chronic user can develop tolerance to doses
that would incapacitate a cocaine-naive individual, and the chronic user
often has high baseline values of the metabolites in his system.
Cautious interpretation of testing results may allow a distinction
between passive or active usage, and between smoking versus other routes
of administration.
In 2011, researchers at John Jay College of Criminal Justice reported
that dietary zinc supplements can mask the presence of cocaine and other
drugs in urine. Similar claims have been made in web forums on that
topic.
Usage
| Substance | Best estimate |
Low estimate |
High estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine- type stimulants |
34.16 | 13.42 | 55.24 |
| Cannabis | 192.15 | 165.76 | 234.06 |
| Cocaine | 18.20 | 13.87 | 22.85 |
| Ecstasy | 20.57 | 8.99 | 32.34 |
| Opiates | 19.38 | 13.80 | 26.15 |
| Opioids | 34.26 | 27.01 | 44.54 |
According to a 2016 United Nations report, England and Wales are the countries with the highest rate of cocaine usage (2.4% of adults in the previous year).
Other countries where the usage rate meets or exceeds 1.5% are Spain
and Scotland (2.2%), the United States (2.1%), Australia (2.1%), Uruguay
(1.8%), Brazil (1.75%), Chile (1.73%), the Netherlands (1.5%) and
Ireland (1.5%).
Europe
Cocaine is the second most popular illegal recreational drug in Europe (behind cannabis).
Since the mid-1990s, overall cocaine usage in Europe has been on the
rise, but usage rates and attitudes tend to vary between countries.
European countries with the highest usage rates are the United Kingdom,
Spain, Italy, and the Republic of Ireland.
Approximately 17 million Europeans (5.1%) have used cocaine at
least once and 3.5 millions (1.1%) in the last year. About 1.9% (2.3
million) of young adults (15–34 years old) have used cocaine in the last
year (latest data available as of 2018).
Usage is particularly prevalent among this demographic: 4% to 7%
of males have used cocaine in the last year in Spain, Denmark, Republic
of Ireland, Italy, and the United Kingdom. The ratio of male to female
users is approximately 3.8:1, but this statistic varies from 1:1 to 13:1
depending on country.
In 2014 London had the highest amount of cocaine in its sewage out of 50 European cities.
United States
Cocaine is the second most popular illegal recreational drug in the United States (behind cannabis) and the U.S. is the world's largest consumer of cocaine.
Cocaine is commonly used in middle to upper-class communities and is
known as a "rich man's drug". It is also popular amongst college
students, as a party drug. A study throughout the entire United States
has reported that around 48 percent of people who graduated from high
school in 1979 have used cocaine recreationally during some point in
their lifetime, compared to approximately 20 percent of students who
graduated between the years of 1980 and 1995.
Its users span over different ages, races, and professions. In the 1970s and 1980s, the drug became particularly popular in the disco culture as cocaine usage was very common and popular in many discos such as Studio 54.
History
Discovery
For over a thousand years South American indigenous peoples have chewed the leaves of Erythroxylon coca, a plant that contains vital nutrients as well as numerous alkaloids, including cocaine. The coca leaf was, and still is, chewed almost universally by some indigenous communities.
The remains of coca leaves have been found with ancient Peruvian
mummies, and pottery from the time period depicts humans with bulged
cheeks, indicating the presence of something on which they are chewing. There is also evidence that these cultures used a mixture of coca leaves and saliva as an anesthetic for the performance of trepanation.
When the Spanish arrived in South America,
most at first ignored aboriginal claims that the leaf gave them
strength and energy, and declared the practice of chewing it the work of
the Devil. But after discovering that these claims were true, they legalized and taxed the leaf, taking 10% off the value of each crop. In 1569, Spanish botanist Nicolás Monardes described the indigenous peoples' practice of chewing a mixture of tobacco and coca leaves to induce "great contentment":
When they wished to make themselves drunk and out of judgment they chewed a mixture of tobacco and coca leaves which make them go as they were out of their wittes.
In 1609, Padre Blas Valera wrote:
Coca protects the body from many ailments, and our doctors use it in powdered form to reduce the swelling of wounds, to strengthen broken bones, to expel cold from the body or prevent it from entering, and to cure rotten wounds or sores that are full of maggots. And if it does so much for outward ailments, will not its singular virtue have even greater effect in the entrails of those who eat it?
Isolation and naming
Although the stimulant and hunger-suppressant properties of coca had
been known for many centuries, the isolation of the cocaine alkaloid
was not achieved until 1855. Various European scientists had attempted
to isolate cocaine, but none had been successful for two reasons: the
knowledge of chemistry required was insufficient at the time,
and contemporary conditions of sea-shipping from South America could
degrade the cocaine in the plant samples available to European chemists.
The cocaine alkaloid was first isolated by the German chemist Friedrich Gaedcke in 1855. Gaedcke named the alkaloid "erythroxyline", and published a description in the journal Archiv der Pharmazie.
In 1856, Friedrich Wöhler asked Dr. Carl Scherzer, a scientist aboard the Novara (an Austrian frigate sent by Emperor Franz Joseph
to circle the globe), to bring him a large amount of coca leaves from
South America. In 1859, the ship finished its travels and Wöhler
received a trunk full of coca. Wöhler passed on the leaves to Albert Niemann, a Ph.D. student at the University of Göttingen in Germany, who then developed an improved purification process.
Niemann described every step he took to isolate cocaine in his dissertation titled Über eine neue organische Base in den Cocablättern (On a New Organic Base in the Coca Leaves), which was published in 1860—it earned him his Ph.D. and is now in the British Library.
He wrote of the alkaloid's "colourless transparent prisms" and said
that "Its solutions have an alkaline reaction, a bitter taste, promote
the flow of saliva and leave a peculiar numbness, followed by a sense of
cold when applied to the tongue." Niemann named the alkaloid "cocaine"
from "coca" (from Quechua "cuca") + suffix "ine". Because of its use as a local anesthetic, a suffix "-caine" was later extracted and used to form names of synthetic local anesthetics.
The first synthesis and elucidation of the structure of the cocaine molecule was by Richard Willstätter in 1898. It was the first biomimetic synthesis of an organic structure recorded in academic chemical literature. The synthesis started from tropinone, a related natural product and took five steps.
Medicalization
"Cocaine toothache drops", 1885 advertisement of cocaine for dental pain in children
Advertisement in the January 1896 issue of McClure's Magazine for Burnett's Cocaine "for the hair".
With the discovery of this new alkaloid, Western medicine was quick to exploit the possible uses of this plant.
In 1879, Vassili von Anrep, of the University of Würzburg,
devised an experiment to demonstrate the analgesic properties of the
newly discovered alkaloid. He prepared two separate jars, one containing
a cocaine-salt solution, with the other containing merely salt water.
He then submerged a frog's legs into the two jars, one leg in the
treatment and one in the control solution, and proceeded to stimulate
the legs in several different ways. The leg that had been immersed in
the cocaine solution reacted very differently from the leg that had been
immersed in salt water.
Karl Koller (a close associate of Sigmund Freud, who would write about cocaine later) experimented with cocaine for ophthalmic
usage. In an infamous experiment in 1884, he experimented upon himself
by applying a cocaine solution to his own eye and then pricking it with
pins. His findings were presented to the Heidelberg Ophthalmological
Society. Also in 1884, Jellinek demonstrated the effects of cocaine as a
respiratory system anesthetic. In 1885, William Halsted demonstrated nerve-block anesthesia, and James Leonard Corning demonstrated peridural anesthesia. 1898 saw Heinrich Quincke use cocaine for spinal anesthesia.
Popularization
Pope Leo XIII purportedly carried a hip flask of the coca-treated Vin Mariani with him, and awarded a Vatican gold medal to Angelo Mariani.
In 1859, an Italian doctor, Paolo Mantegazza, returned from Peru,
where he had witnessed first-hand the use of coca by the local
indigenous peoples. He proceeded to experiment on himself and upon his
return to Milan
he wrote a paper in which he described the effects. In this paper he
declared coca and cocaine (at the time they were assumed to be the same)
as being useful medicinally, in the treatment of "a furred tongue in
the morning, flatulence, and whitening of the teeth."
A chemist named Angelo Mariani
who read Mantegazza's paper became immediately intrigued with coca and
its economic potential. In 1863, Mariani started marketing a wine called Vin Mariani, which had been treated with coca leaves, to become cocawine. The ethanol
in wine acted as a solvent and extracted the cocaine from the coca
leaves, altering the drink's effect. It contained 6 mg cocaine per ounce
of wine, but Vin Mariani which was to be exported contained 7.2 mg per
ounce, to compete with the higher cocaine content of similar drinks in
the United States. A "pinch of coca leaves" was included in John Styth Pemberton's original 1886 recipe for Coca-Cola, though the company began using decocainized leaves in 1906 when the Pure Food and Drug Act was passed.
In 1879 cocaine began to be used to treat morphine addiction. Cocaine was introduced into clinical use as a local anesthetic in Germany in 1884, about the same time as Sigmund Freud published his work Über Coca, in which he wrote that cocaine causes:
Exhilaration and lasting euphoria, which in no way differs from the normal euphoria of the healthy person. You perceive an increase of self-control and possess more vitality and capacity for work. In other words, you are simply normal, and it is soon hard to believe you are under the influence of any drug. Long intensive physical work is performed without any fatigue. This result is enjoyed without any of the unpleasant after-effects that follow exhilaration brought about by alcoholic beverages. No craving for the further use of cocaine appears after the first, or even after repeated taking of the drug.
In 1885 the U.S. manufacturer Parke-Davis
sold cocaine in various forms, including cigarettes, powder, and even a
cocaine mixture that could be injected directly into the user's veins
with the included needle. The company promised that its cocaine products
would "supply the place of food, make the coward brave, the silent
eloquent and render the sufferer insensitive to pain."
In this 1904 advice column from the Tacoma Times, "Madame Falloppe" recommended that cold sores be treated with a solution of borax, cocaine, and morphine.
By the late Victorian era, cocaine use had appeared as a vice in literature. For example, it was injected by Arthur Conan Doyle's fictional Sherlock Holmes, generally to offset the boredom he felt when he was not working on a case.
In early 20th-century Memphis, Tennessee, cocaine was sold in neighborhood drugstores on Beale Street,
costing five or ten cents for a small boxful. Stevedores along the
Mississippi River used the drug as a stimulant, and white employers
encouraged its use by black laborers.
In 1909, Ernest Shackleton took "Forced March" brand cocaine tablets to Antarctica, as did Captain Scott a year later on his ill-fated journey to the South Pole.
During the mid-1940s, amidst World War II, cocaine was considered
for inclusion as an ingredient of a future generation of 'pep pills'
for the German military, code named D-IX.
In modern popular culture references to the drug are prevalent,
in it the drug has a glamorous image associated with the rich, famous
and powerful with it also making users to "feel rich and beautiful". In addition the pace of modern society − such as in finance − gives many the incentive to make use of the drug.
Women purchase cocaine capsules in Berlin, 1924
Modern usage
D.C. Mayor Marion Barry captured on a surveillance camera smoking crack cocaine during a sting operation by the FBI and D.C. Police.
In many countries, cocaine is a popular recreational drug. In the United States, the development of "crack" cocaine
introduced the substance to a generally poorer inner-city market. Use
of the powder form has stayed relatively constant, experiencing a new
height of use during the late 1990s and early 2000s in the U.S., and has
become much more popular in the last few years in the UK.
Cocaine use is prevalent across all socioeconomic strata,
including age, demographics, economic, social, political, religious, and
livelihood.
The estimated U.S. cocaine market exceeded US$70 billion in
street value for the year 2005, exceeding revenues by corporations such
as Starbucks. There is a tremendous demand for cocaine in the U.S. market, particularly among those who are making incomes affording luxury spending, such as single adults and professionals with discretionary income. Cocaine's status as a club drug shows its immense popularity among the "party crowd".
In 1995 the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute
(UNICRI) announced in a press release the publication of the results of
the largest global study on cocaine use ever undertaken. However, a
decision by an American representative in the World Health Assembly
banned the publication of the study, because it seemed to make a case
for the positive uses of cocaine. An excerpt of the report strongly
conflicted
with accepted paradigms, for example "that occasional cocaine use does
not typically lead to severe or even minor physical or social problems."
In the sixth meeting of the B committee, the US representative
threatened that "If World Health Organization activities relating to
drugs failed to reinforce proven drug control approaches, funds for the
relevant programs should be curtailed". This led to the decision to
discontinue publication. A part of the study was recuperated and
published in 2010, including profiles of cocaine use in 20 countries,
but are unavailable as of 2015.
In October 2010 it was reported that the use of cocaine in Australia has doubled since monitoring began in 2003.
A problem with illegal cocaine use, especially in the higher
volumes used to combat fatigue (rather than increase euphoria) by
long-term users, is the risk of ill effects or damage caused by the
compounds used in adulteration. Cutting or "stepping on" the drug is
commonplace, using compounds which simulate ingestion effects, such as Novocain
(procaine) producing temporary anesthaesia, as many users believe a
strong numbing effect is the result of strong and/or pure cocaine,
ephedrine or similar stimulants that are to produce an increased heart
rate. The normal adulterants for profit are inactive sugars, usually
mannitol, creatine or glucose, so introducing active adulterants gives
the illusion of purity and to 'stretch' or make it so a dealer can sell
more product than without the adulterants.
The adulterant of sugars allows the dealer to sell the product for a
higher price because of the illusion of purity and allows sale of more
of the product at that higher price, enabling dealers to significantly
increase revenue with little additional cost for the adulterants. A 2007
study by the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction showed that the purity levels for street purchased cocaine was often under 5% and on average under 50% pure.
Society and culture
Legal status
The production, distribution, and sale of cocaine products is
restricted (and illegal in most contexts) in most countries as regulated
by the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.
In the United States the manufacture, importation, possession, and
distribution of cocaine are additionally regulated by the 1970 Controlled Substances Act.
Some countries, such as Peru and Bolivia, permit the cultivation of coca leaf for traditional consumption by the local indigenous population, but nevertheless, prohibit the production, sale, and consumption of cocaine. The provisions as to how much a coca farmer can yield annually is protected by laws such as the Bolivian Cato accord. In addition, some parts of Europe, the United States, and Australia allow processed cocaine for medicinal uses only.
Australia
Cocaine is a Schedule 8 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (July 2016).
A schedule 8 substance is a controlled Drug – Substances which should
be available for use but require restriction of manufacture, supply,
distribution, possession and use to reduce abuse, misuse and physical or
psychological dependence.
In Western Australia under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1981
4.0g of cocaine is the amount of prohibited drugs determining a court
of trial, 2.0g is the amount of cocaine required for the presumption of
intention to sell or supply and 28.0g is the amount of cocaine required
for purposes of drug trafficking.
United States
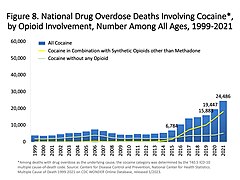
Drug overdoses killed more than 72,000 Americans in 2017, with cocaine overdoses making up 14,556 of those deaths.
The US federal government instituted a national labeling requirement
for cocaine and cocaine-containing products through the Pure Food and
Drug Act of 1906. The next important federal regulation was the Harrison Narcotics Tax Act
of 1914. While this act is often seen as the start of prohibition, the
act itself was not actually a prohibition on cocaine, but instead set up
a regulatory and licensing regime.
The Harrison Act did not recognize addiction as a treatable condition
and therefore the therapeutic use of cocaine, heroin or morphine to such
individuals was outlawed – leading a 1915 editorial in the journal American Medicine
to remark that the addict "is denied the medical care he urgently
needs, open, above-board sources from which he formerly obtained his
drug supply are closed to him, and he is driven to the underworld where
he can get his drug, but of course, surreptitiously and in violation of
the law." The Harrison Act left manufacturers of cocaine untouched so long as they met certain purity and labeling standards.
Despite that cocaine was typically illegal to sell and legal outlets
were rarer, the quantities of legal cocaine produced declined very
little. Legal cocaine quantities did not decrease until the Jones–Miller Act of 1922 put serious restrictions on cocaine manufactures.
Interdiction
In 2004, according to the United Nations, 589 tonnes of cocaine were seized globally by law enforcement authorities. Colombia seized 188 t, the United States 166 t, Europe 79 t, Peru 14 t, Bolivia 9 t, and the rest of the world 133 t.
Economics
Because of the drug's potential for addiction and overdose, cocaine is generally treated as a "hard drug",
with severe penalties for possession and trafficking. Demand remains
high, and consequently, black market cocaine is quite expensive.
Unprocessed cocaine, such as coca leaves,
are occasionally purchased and sold, but this is exceedingly rare as it
is much easier and more profitable to conceal and smuggle it in
powdered form. The scale of the market is immense: 770 tonnes times $100 per gram retail = up to $77 billion.
Production
Until 2012, Colombia was the world's leading producer of cocaine.
Three-quarters of the world's annual yield of cocaine has been produced
in Colombia, both from cocaine base imported from Peru (primarily the Huallaga Valley)
and Bolivia, and from locally grown coca. There was a 28% increase from
the amount of potentially harvestable coca plants which were grown in
Colombia in 1998. This, combined with crop reductions in Bolivia and
Peru, made Colombia the nation with the largest area of coca under cultivation
after the mid-1990s. Coca grown for traditional purposes by indigenous
communities, a use which is still present and is permitted by Colombian
laws, only makes up a small fragment of total coca production, most of
which is used for the illegal drug trade.
An interview with a coca farmer published in 2003 described a mode of production by acid-base extraction that has changed little since 1905. Roughly 625 pounds (283 kg) of leaves were harvested per hectare,
six times per year. The leaves were dried for half a day, then chopped
into small pieces with a string trimmer and sprinkled with a small
amount of powdered cement (replacing sodium carbonate
from former times). Several hundred pounds of this mixture were soaked
in 50 US gallons (190 L) of gasoline for a day, then the gasoline was
removed and the leaves were pressed for remaining liquid, after which
they could be discarded. Then battery acid (weak sulfuric acid) was used, one bucket per 55 lb (25 kg) of leaves, to create a phase separation in which the cocaine free base in the gasoline was acidified and extracted into a few buckets of "murky-looking smelly liquid". Once powdered caustic soda
was added to this, the cocaine precipitated and could be removed by
filtration through a cloth. The resulting material, when dried, was
termed pasta and sold by the farmer. The 3750 pound yearly harvest of leaves from a hectare produced 6 lb (2.5 kg) of pasta, approximately 40–60% cocaine. Repeated recrystallization from solvents, producing pasta lavada and eventually crystalline cocaine were performed at specialized laboratories after the sale.
Attempts to eradicate coca fields through the use of defoliants
have devastated part of the farming economy in some coca growing
regions of Colombia, and strains appear to have been developed that are
more resistant or immune to their use. Whether these strains are natural
mutations or the product of human tampering is unclear. These strains
have also shown to be more potent than those previously grown,
increasing profits for the drug cartels responsible for the exporting of
cocaine. Although production fell temporarily, coca crops rebounded in
numerous smaller fields in Colombia, rather than the larger plantations.
The cultivation of coca has become an attractive economic
decision for many growers due to the combination of several factors,
including the lack of other employment alternatives, the lower
profitability of alternative crops in official crop substitution
programs, the eradication-related damages to non-drug farms, the spread
of new strains of the coca plant due to persistent worldwide demand.
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net cultivation km2 (sq mi) | 1,875 (724) | 2,218 (856) | 2,007.5 (775.1) | 1,663 (642) | 1,662 (642) |
| Potential pure cocaine production (tonnes) | 770 | 925 | 830 | 680 | 645 |
The latest estimate provided by the U.S. authorities on the annual production of cocaine in Colombia refers to 290 metric tons.
As of the end of 2011, the seizure operations of Colombian cocaine
carried out in different countries have totaled 351.8 metric tons of
cocaine, i.e. 121.3% of Colombia's annual production according to the
U.S. Department of State's estimates.
Synthesis
Synthetic cocaine would be highly desirable to the illegal drug
industry as it would eliminate the high visibility and low reliability
of offshore sources and international smuggling, replacing them with
clandestine domestic laboratories, as are common for illicit methamphetamine.
However, natural cocaine remains the lowest cost and highest quality
supply of cocaine. Actual full synthesis of cocaine is rarely done.
Formation of inactive stereoisomers (cocaine has 4 chiral centres – 1R, 2R, 3S, and 5S,
2 of them dependent, hence a total potential of 8 possible
stereoisomers) plus synthetic by-products limits the yield and purity.
Names like "synthetic cocaine" and "new cocaine" have been misapplied to phencyclidine (PCP) and various designer drugs.
Trafficking and distribution
Cocaine smuggled in a charango, 2008
Organized criminal
gangs operating on a large scale dominate the cocaine trade. Most
cocaine is grown and processed in South America, particularly in
Colombia, Bolivia, Peru, and smuggled into the United States and Europe, the United States being the world's largest consumer of cocaine, where it is sold at huge markups; usually in the US at $80–120 for 1 gram, and $250–300 for 3.5 grams (1/8 of an ounce, or an "eight ball").
Caribbean and Mexican routes
As of 2005, cocaine shipments from South America transported through Mexico or Central America
were generally moved over land or by air to staging sites in northern
Mexico. The cocaine is then broken down into smaller loads for smuggling
across the U.S.–Mexico border. The primary cocaine importation points in the United States have been in Arizona, southern California, southern Florida, and Texas.
Typically, land vehicles are driven across the U.S.–Mexico border.
Sixty-five percent of cocaine enters the United States through Mexico,
and the vast majority of the rest enters through Florida. As of 2015, the Sinaloa Cartel is the most active drug cartel involved in smuggling illicit drugs like cocaine into the United States and trafficking them throughout the United States.
Cocaine traffickers from Colombia and Mexico have established a labyrinth of smuggling routes throughout the Caribbean, the Bahama Island chain, and South Florida. They often hire traffickers from Mexico or the Dominican Republic
to transport the drug using a variety of smuggling techniques to U.S.
markets. These include airdrops of 500 to 700 kg (1,100 to 1,500 lb) in
the Bahama Islands or off the coast of Puerto Rico,
mid-ocean boat-to-boat transfers of 500 to 2,000 kg (1,100 to
4,400 lb), and the commercial shipment of tonnes of cocaine through the
port of Miami.
Chilean route
Another route of cocaine traffic goes through Chile, which is
primarily used for cocaine produced in Bolivia since the nearest
seaports lie in northern Chile. The arid Bolivia–Chile border is easily
crossed by 4×4 vehicles that then head to the seaports of Iquique and Antofagasta.
While the price of cocaine is higher in Chile than in Peru and Bolivia,
the final destination is usually Europe, especially Spain where drug
dealing networks exist among South American immigrants.
Techniques
Cocaine is also carried in small, concealed, kilogram quantities across the border by couriers known as "mules"
(or "mulas"), who cross a border either legally, for example, through a
port or airport, or illegally elsewhere. The drugs may be strapped to
the waist or legs or hidden in bags, or hidden in the body. If the mule
gets through without being caught, the gangs will reap most of the
profits. If he or she is caught, however, gangs will sever all links and
the mule will usually stand trial for trafficking alone.
Bulk cargo ships are also used to smuggle cocaine to staging sites in the western Caribbean–Gulf of Mexico
area. These vessels are typically 150–250-foot (50–80 m) coastal
freighters that carry an average cocaine load of approximately 2.5
tonnes. Commercial fishing vessels are also used for smuggling
operations. In areas with a high volume of recreational traffic,
smugglers use the same types of vessels, such as go-fast boats, as those used by the local populations.
Sophisticated drug subs
are the latest tool drug runners are using to bring cocaine north from
Colombia, it was reported on 20 March 2008. Although the vessels were
once viewed as a quirky sideshow in the drug war, they are becoming
faster, more seaworthy, and capable of carrying bigger loads of drugs
than earlier models, according to those charged with catching them.
Sales to consumers
Cocaine adulterated with fruit flavoring
Cocaine is readily available in all major countries' metropolitan areas. According to the Summer 1998 Pulse Check, published by the U.S. Office of National Drug Control Policy, cocaine use had stabilized across the country, with a few increases reported in San Diego, Bridgeport, Miami, and Boston. In the West, cocaine usage was lower, which was thought to be due to a switch to methamphetamine
among some users; methamphetamine is cheaper, three and a half times
more powerful, and lasts 12–24 times longer with each dose. Nevertheless, the number of cocaine users remain high, with a large concentration among urban youth.
In addition to the amounts previously mentioned, cocaine can be sold in "bill sizes": As of 2007
for example, $10 might purchase a "dime bag", a very small amount
(0.1–0.15 g) of cocaine. Twenty dollars might purchase 0.15–0.3 g.
However, in lower Texas, it is sold cheaper due to it being easier to
receive: a dime for $10 is 0.4 g, a 20 is 0.8–1.0 g and an 8-ball (3.5
g) is sold for $60 to $80, depending on the quality and dealer.
These amounts and prices are very popular among young people because
they are inexpensive and easily concealed on one's body. Quality and
price can vary dramatically depending on supply and demand, and on
geographic region.
In 2008, the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
reports that the typical retail price of cocaine varied between €50 and
€75 per gram in most European countries, although Cyprus, Romania,
Sweden and Turkey reported much higher values.
Consumption
World annual cocaine consumption, as of 2000, stood at around 600
tonnes, with the United States consuming around 300 t, 50% of the total,
Europe about 150 t, 25% of the total, and the rest of the world the
remaining 150 t or 25%. It is estimated that 1.5 million people in the United States used cocaine in 2010 down from 2.4 million in 2006. Conversely, cocaine use appears to be increasing in Europe with the highest prevalences in Spain, the United Kingdom, Italy, and Ireland.
The 2010 UN World Drug Report
concluded that "it appears that the North American cocaine market has
declined in value from US$47 billion in 1998 to US$38 billion in 2008.
Between 2006 and 2008, the value of the market remained basically
stable".
Research
In 2005, researchers proposed the use of cocaine in conjunction with phenylephrine administered in the form of an eye drop as a diagnostic test for Parkinson's disease.