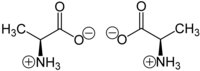
Two enantiomers of a generic amino acid that is chiral
Chirality /kaɪˈrælɪtiː/ is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word chirality is derived from the Greek χειρ (kheir), "hand," a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is chiral if it is distinguishable from its mirror image; that is, it cannot be superposed onto it. Conversely, a mirror image of an achiral object, such as a sphere, cannot be distinguished from the object. A chiral object and its mirror image are called enantiomorphs (Greek, "opposite forms") or, when referring to molecules, enantiomers. A non-chiral object is called achiral (sometimes also amphichiral) and can be superposed on its mirror image.
The term was first used by Lord Kelvin in 1893 in the second Robert Boyle Lecture at the Oxford University Junior Scientific Club which was published in 1894:
I call any geometrical figure, or group of points, 'chiral', and say that it has chirality if its image in a plane mirror, ideally realized, cannot be brought to coincide with itself.
Human hands
are perhaps the most universally recognized example of chirality. The
left hand is a non-superimposable mirror image of the right hand; no
matter how the two hands are oriented, it is impossible for all the
major features of both hands to coincide across all axes.
This difference in symmetry becomes obvious if someone attempts to
shake the right hand of a person using their left hand, or if a
left-handed glove is placed on a right hand. In mathematics, chirality is the property of a figure that is not identical to its mirror image.
Mathematics
An achiral 3D object without central symmetry or a plane of symmetry
A table of all prime knots with seven crossings or fewer (not including mirror images).
In mathematics, a figure is chiral (and said to have chirality) if it cannot be mapped to its mirror image by rotations and translations alone. For example, a right shoe is different from a left shoe, and clockwise is different from anticlockwise.
A chiral object and its mirror image are said to be enantiomorphs. The word enantiomorph stems from the Greek ἐναντίος (enantios) 'opposite' + μορφή (morphe) 'form'. A non-chiral figure is called achiral or amphichiral.
The helix (and by extension a spun string, a screw, a propeller, etc.) and Möbius strip are chiral two-dimensional objects in three-dimensional ambient space. The J, L, S and Z-shaped tetrominoes of the popular video game Tetris also exhibit chirality, but only in a two-dimensional space.
Many other familiar objects exhibit the same chiral symmetry of
the human body, such as gloves, glasses (where two lenses differ in
prescription), and shoes. A similar notion of chirality is considered in
knot theory, as explained below.
Some chiral three-dimensional objects, such as the helix, can be assigned a right or left handedness, according to the right-hand rule.
Geometry
In geometry a figure is achiral if and only if its symmetry group contains at least one orientation-reversing isometry.
In two dimensions, every figure that possesses an axis of symmetry is achiral, and it can be shown that every bounded achiral figure must have an axis of symmetry.
In three dimensions, every figure that possesses a plane of symmetry or a center of symmetry is achiral. There are, however, achiral figures lacking both plane and center of symmetry.
In terms of point groups, all chiral figures lack an improper axis of rotation (Sn).
This means that they cannot contain a center of inversion (i) or a
mirror plane (σ). Only figures with a point group designation of C1, Cn, Dn, T, O, or I can be chiral.
Knot theory
A knot is called achiral if it can be continuously deformed into its mirror image, otherwise it is called chiral. For example, the unknot and the figure-eight knot are achiral, whereas the trefoil knot is chiral.
Physics
Animation of left-handed (anticlockwise) circularly polarized light, as defined from the direction of the source in agreement with physics and astronomy conventions.
In physics, chirality may be found in the spin of a particle, where the handedness of the object is determined by the direction in which the particle spins. Not to be confused with helicity,
which is the projection of the spin along the linear momentum of a
subatomic particle, chirality is a purely quantum mechanical phenomenon
like spin. Although both can have left-handed or right-handed
properties, only in the massless case do they have a simple relation.
In particular for a massless particle the helicity is the same as the
chirality while for an antiparticle they have opposite sign.
The handedness in both chirality and helicity relate to
the rotation of a particle while it proceeds in linear motion with
reference to the human hands. The thumb of the hand points towards the
direction of linear motion whilst the fingers curl into the palm,
representing the direction of rotation of the particle (i.e. clockwise
and counterclockwise). Depending on the linear and rotational motion,
the particle can either be defined by left-handedness or
right-handedness. A symmetry transformation between the two is called parity. Invariance under parity by a Dirac fermion is called chiral symmetry.
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetic wave propagation as handedness is wave polarization and described in terms of helicity (occurs as a helix). Polarization of an electromagnetic wave is the property that describes the orientation, i.e., the time-varying, direction (vector), and amplitude of the electric field vector.
Chiral mirrors are a class of metamaterials that reflect
circularly polarized light of a certain helicity in a
handedness-preserving manner, while absorbing circular polarization of
the opposite handedness.
However, most absorbing chiral mirrors operate only in a narrow
frequency band, as limited by the causality principle. Employing a
different design methodology that allows undesired waves to pass through
instead of absorbing the undesired waveform, chiral mirrors are able to
show good performance in broadband.
Chemistry
(S)-Alanine (left) and (R)-alanine (right) in zwitterionic form at neutral pH
A chiral molecule is a type of molecule that has a non-superposable mirror image. The feature that is most often the cause of chirality in molecules is the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom.
The term "chiral" in general is used to describe the object that is non-superposable on its mirror image.
In chemistry, chirality usually refers to molecules. Two mirror images of a chiral molecule are called enantiomers or optical isomers. Pairs of enantiomers are often designated as "right-",
"left-handed" or, if they have no bias, "achiral". As polarized light
passes through a chiral molecule, the plane of polarization, when viewed
along the axis toward the source, will be rotated clockwise (to the
right) or anticlockwise (to the left). A right handed rotation is
dextrorotary (d); that to the left is levorotary (l). The d- and
l-isomers are the same compound but are called enantiomers. An equimolar mixture of the two optical isomers will produce no net rotation of polarized light as it passes through. Left handed molecules have l- prefixed to their names; d- is prefixed to right handed molecules.
Molecular chirality is of interest because of its application to stereochemistry in inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry, physical chemistry, biochemistry, and supramolecular chemistry.
More recent developments in chiral chemistry include the
development of chiral inorganic nanoparticles that may have the similar
tetrahedral geometry as chiral centers associated with sp3 carbon atoms
traditionally associated with chiral compounds, but at larger scale. Helical and other symmetries of chiral nanomaterials were also obtained.
Biology
All of the known life-forms show specific chiral properties in
chemical structures as well as macroscopic anatomy, development and
behavior.
In any specific organism or evolutionarily related set thereof,
individual compounds, organs, or behavior are found in the same single
enantiomorphic form. Deviation (having the opposite form) could be found
in a small number of chemical compounds, or certain organ or behavior
but that variation strictly depends upon the genetic make up of the
organism. From chemical level (molecular scale), biological systems show
extreme stereospecificity in synthesis, uptake, sensing, metabolic
processing. A living system usually deals with two enantiomers of the
same compound in drastically different ways.
In biology, homochirality is a common property of amino acids and carbohydrates. The chiral protein-making amino acids, which are translated through the ribosome from genetic coding, occur in the L form. However, D-amino acids are also found in nature. The monosaccharides (carbohydrate-units) are commonly found in D-configuration. DNA double helix is chiral (as any kind of helix is chiral), and B-form of DNA shows a right-handed turn.
Sometimes, when two enantiomers of a compound found in organisms,
they significantly differ in their taste, smell and other biological
actions. For example, (+)-limonene found in orange (causing its smell),
and (–)-limonene found in lemons (causing its smell), show different
smells due to different biochemical interactions at human nose. (+)-Carvone is responsible for the smell of caraway seed oil, whereas (–)-carvone is responsible for smell of spearmint oil.
(S)-(+)-Carvone occurs in caraway seed oil, and (R)-(-)-carvone occurs in spearmint
Also, for artificial compounds, including medicines, in case of
chiral drugs, the two enantiomers sometimes show remarkable difference
in effect of their biological actions. Darvon (dextropropoxyphene) is a painkiller, whereas its enantiomer, Novrad (levopropoxyphene) is an anti-cough agent. In case of penicillamine, the (S-isomer used in treatment of primary chronic arthritis, whereas the (R)-isomer has no therapeutic effect as well as being highly toxic. In some cases the less therapeutically active enantiomer can cause side effects. For example, (S-naproxen is an analgesic but the (R-isomer cause renal problems. The naturally occurring plant form of alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E)
is RRR-α-tocopherol whereas the synthetic form (all-racemic vitamin E,
or dl-tocopherol) is equal parts of the stereoisomers RRR, RRS, RSS,
SSS, RSR, SRS, SRR and SSR with progressively decreasing biological
equivalency, so that 1.36 mg of dl-tocopherol is considered equivalent
to 1.0 mg of d-tocopherol.
A natural left-handed helix, made by a certain climber plant's tendril.
Macroscopic examples of chirality are found in the plant kingdom, the
animal kingdom and all other groups of organism. A simple example is
the coiling direction of any climber plant, which can grow to form
either a left- or right-handed helix.
Shells of two different species of sea snail: on the left is the normally sinistral (left-handed) shell of Neptunea angulata, on the right is the normally dextral (right-handed) shell of Neptunea despecta
In anatomy, chirality is found in the imperfect mirror image symmetry of many kinds of animal bodies. Organisms such as gastropods exhibit chirality in their coiled shells, resulting in an asymmetrical appearance. Over 90% of gastropod species have dextral (right-handed) shells in their coiling, but a small minority of species and genera are virtually always sinistral (left-handed). A very few species (for example Amphidromus perversus) show an equal mixture of dextral and sinistral individuals.
In humans, chirality (also referred to as handedness or laterality) is an attribute of humans defined by their unequal distribution of fine motor skill between the left and right hands. An individual who is more dexterous with the right hand is called right-handed, and one who is more skilled with the left is said to be left-handed. Chirality is also seen in the study of facial asymmetry.
In flatfish, the Summer flounder or fluke are left-eyed, while halibut are right-eyed.
Popular Culture
Chirality, chiral theory and even "knots" of a sort feature very heavily in the 2019 video game Death Stranding, by Hideo Kojima and Kojima Productions.