Food security is a measure of the availability of food and individuals' accessibility to it, where accessibility includes affordability. There is evidence of food security being a concern over 10,000 years ago, with central authorities in ancient China and ancient Egypt being known to release food from storage in times of famine. At the 1974 World Food Conference the term "food security" was defined with an emphasis on supply. Food security, they said, is the "availability at all times of adequate, nourishing, diverse, balanced and moderate world food supplies of basic foodstuffs to sustain a steady expansion of food consumption and to offset fluctuations in production and prices". Later definitions added demand and access issues to the definition. The final report of the 1996 World Food Summit states that food security "exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life".
Household food security exists when all members, at all times, have access to enough food for an active, healthy life. Individuals who are food secure do not live in hunger or fear of starvation.
Food insecurity, on the other hand, is a situation of "limited or
uncertain availability of nutritionally adequate and safe foods or
limited or uncertain ability to acquire acceptable foods in socially
acceptable ways", according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Food security incorporates a measure of resilience to future disruption
or unavailability of critical food supply due to various risk factors
including droughts, shipping disruptions, fuel shortages, economic
instability, and wars.
In the years 2011–2013, an estimated 842 million people were suffering from chronic hunger. The Food and Agriculture Organization
of the United Nations, or FAO, identified the four pillars of food
security as availability, access, utilization, and stability. The United Nations (UN) recognized the Right to Food in the Declaration of Human Rights in 1948, and has since noted that it is vital for the enjoyment of all other rights.
The 1996 World Summit on Food Security declared that "food should not be used as an instrument for political and economic pressure". According to the International Centre for Trade and Sustainable Development, failed agriculture market regulation and the lack of anti-dumping mechanisms cause much of the world's food scarcity and malnutrition.
The 1996 World Summit on Food Security declared that "food should not be used as an instrument for political and economic pressure". According to the International Centre for Trade and Sustainable Development, failed agriculture market regulation and the lack of anti-dumping mechanisms cause much of the world's food scarcity and malnutrition.
Measurement
Food security can be measured by calorie intake per person per day, available on a household budget.
In general the objective of food security indicators and measures is to
capture some or all of the main components of food security in terms of
food availability, access and utilization or adequacy. While
availability (production and supply) and utilization/adequacy
(nutritional status/anthropometric measures) seemed much easier to
estimate, thus more popular, access (ability to acquire sufficient
quantity and quality) remain largely elusive. The factors influencing household food access are often context specific.
Several measures have been developed that aim to capture the
access component of food security, with some notable examples developed
by the USAID-funded Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance (FANTA)
project, collaborating with Cornell and Tufts University and Africare
and World Vision. These include:
- Household Food Insecurity Access Scale (HFIAS) – continuous measure of the degree of food insecurity (access) in the household in the previous month
- Household Dietary Diversity Scale (HDDS) – measures the number of different food groups consumed over a specific reference period (24hrs/48hrs/7days).
- Household Hunger Scale (HHS) -- measures the experience of household food deprivation based on a set of predictable reactions, captured through a survey and summarized in a scale.
- Coping Strategies Index (CSI) – assesses household behaviours and rates them based on a set of varied established behaviours on how households cope with food shortages. The methodology for this research is based on collecting data on a single question: "What do you do when you do not have enough food, and do not have enough money to buy food?"
Food insecurity is measured in the United States by questions in the Census Bureau's Current Population Survey.
The questions asked are about anxiety that the household budget is
inadequate to buy enough food, inadequacy in the quantity or quality of
food eaten by adults and children in the household, and instances of
reduced food intake or consequences of reduced food intake for adults
and for children. A National Academy of Sciences
study commissioned by the USDA criticized this measurement and the
relationship of "food security" to hunger, adding "it is not clear
whether hunger is appropriately identified as the extreme end of the
food security scale."
The FAO, World Food Programme (WFP), and International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) collaborate to produce The State of Food Insecurity in the World.
The 2012 edition described improvements made by the FAO to the
prevalence of undernourishment (PoU) indicator that is used to measure
rates of food insecurity. New features include revised minimum dietary
energy requirements for individual countries, updates to the world population
data, and estimates of food losses in retail distribution for each
country. Measurements that factor into the indicator include dietary
energy supply, food production, food prices, food expenditures, and
volatility of the food system. The stages of food insecurity range from food secure situations to full-scale famine.
A new peer-reviewed journal, Food Security: The Science, Sociology and Economics of Food Production and Access to Food, began publishing in 2009.
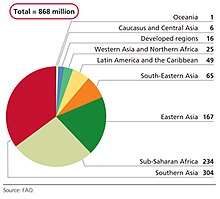
Rates
Number of people affected by undernourishment in 2010–12 (by region, in millions)
With its prevalence of undernourishment (PoU) indicator, the FAO
reported that almost 870 million people were chronically undernourished
in the years 2010–2012. This represents 12.5% of the global population,
or 1 in 8 people. Higher rates occur in developing countries, where 852
million people (about 15% of the population) are chronically
undernourished. The report noted that Asia and Latin America have
achieved reductions in rates of undernourishment that put these regions
on track for achieving the Millennium Development Goal of halving the
prevalence of undernourishment by 2015. The UN noted that about 2 billion people do not consume a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals.
In India, the second-most populous country in the world, 30 million
people have been added to the ranks of the hungry since the mid-1990s
and 46% of children are underweight.
Examples of food insecurity
Famines
have been frequent in world history. Some have killed millions and
substantially diminished the population of a large area. The most common
causes have been drought and war, but the greatest famines in history were caused by economic policy.
Food security by country
Afghanistan
In
Afghanistan about 35% of households are food insecure. The prevalence
of under-weight, stunting, and wasting in children under 5 years of age
is also very high.
Mexico
Food insecurity has distressed Mexico throughout its history and
continues to do so in the present. Food availability is not the issue;
rather, severe deficiencies in the accessibility of food contributes to
the insecurity. Between 2003 and 2005, the total Mexican food supply was
well above the sufficient to meet the requirements of the Mexican
population, averaging 3,270 kilocalories per daily capita, higher than
the minimum requirements of 1,850 kilocalories per daily capita.
However, at least 10 percent of the population in every Mexican state
suffers from inadequate food access. In nine states, 25–35 percent live
in food-insecure households. More than 10 percent of the populations of
seven Mexica states fall into the category of Serious Food Insecurity.
The issue of food inaccessibility is magnified by chronic child malnutrition as well as obesity in children, adolescents, and family.
Mexico is vulnerable to drought which can further cripple agriculture.
United States
The United States Department of Agriculture
defines food insecurity as "limited or uncertain availability of
nutritionally adequate and safe foods or limited or uncertain ability to
acquire acceptable foods in socially acceptable ways." Food security is defined by the USDA as "access by all people at all times to enough food for an active, healthy life."
National Food Security Surveys are the main survey tool used by the USDA to measure food security in the United States.
Based on respondents' answers to survey questions, the household can be
placed on a continuum of food security defined by the USDA. This
continuum has four categories: high food security, marginal food
security, low food security, and very low food security. Economic Research Service
report number 155 (ERS-155) estimates that 14.5 percent (17.6 million)
of US households were food insecure at some point in 2012. The
prevalence of food insecurity has been relatively in the United States
since the economic recession 2008.
In 2016:
- 12.3 percent (15.6 million) of U.S. households were food insecure at some time during 2016.
- 7.4 percent (9.4 million) of U.S. households had low food security in 2016.
- 4.9 percent (6.1 million) of U.S. households had very low food security at some time during 2016.
- Both children and adults were food insecure in 8.0 percent of households with children (3.1 million households).
Democratic Republic of Congo
The
Democratic Republic of Congo is the second largest country in Africa;
the country is dealing with food insecurity. Although they have an
abundance of natural resources, they lack accessibility of essential
foods makes it difficult for the Congolese people in their daily lives.
Malnutrition is high among children affects their ability, and children
who live in a rural area are affected more than children who are live in
an urban area.. In the Democratic Republic of Congo, about 33% of households is food insecure; it is 60% in eastern provinces. .
A study showed the correlation of food insecurity negatively affecting
at-risk HIV adults in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
In 2007-2008 grain prices increased and the people in the
Democratic Republic of the Congo went to civil unrest, there were riots
and protest. Hunger is frequent in this country, but sometimes it is to
the extreme that many families cannot afford to eat every day. Bushmeat trade was used to measure the trend of food security. The
trend signifies the amount of consumption in urban and rural areas.
Urban areas mainly consume bushmeat because they cannot afford other
types of meat.
Feed the Future
In 2010 the government of the United States began the Feed the Future Initiative.
This initiative is expected to work on the basis of country-led
priorities that call for consistent support by the governments, donor
organizations, the private sector, and the civil society to accomplish
its long-term goals.
World Summit on Food Security
The
World Summit on Food Security, held in Rome in 1996, aimed to renew a
global commitment to the fight against hunger. The Food and Agriculture
Organization of the United Nations (FAO) called the summit in response
to widespread under-nutrition and growing concern about the capacity of
agriculture to meet future food needs. The conference produced two key
documents, the Rome Declaration on World Food Security and the World
Food Summit Plan of Action.
The Rome Declaration called for the members of the United Nations
to work to halve the number of chronically undernourished people on the
Earth by the year 2015. The Plan of Action set a number of targets for
government and non-governmental organizations for achieving food
security, at the individual, household, national, regional and global
levels.
Another World Summit on Food Security took place at the FAO's headquarters in Rome between November 16 and 18, 2009. The decision to convene the summit was taken by the Council of FAO in June 2009, at the proposal of FAO Director-General Dr Jacques Diouf. Heads of state and government attended this summit.
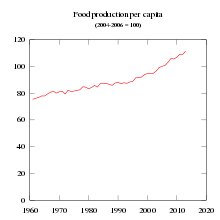
Pillars of food security
Growth in food production has been greater than population growth. Food per person increased since 1961. Data source: Food and Agriculture Organization.
Growth of World Food Supply (caloric base) per capita
The WHO states that there are three pillars that determine food
security: food availability, food access, and food use and misuse. The FAO adds a fourth pillar: the stability of the first three dimensions of food security over time.
In 2009, the World Summit on Food Security stated that the "four
pillars of food security are availability, access, utilization, and
stability".
Availability
Food availability relates to the supply of food through production, distribution, and exchange. Food production is determined by a variety of factors including land ownership and use; soil management; crop selection, breeding, and management; livestock breeding and management; and harvesting. Crop production can be affected by changes in rainfall and temperatures. The use of land, water, and energy to grow food often competes with other uses, which can affect food production.
Land used for agriculture can be used for urbanization or lost to
desertification, salinization, and soil erosion due to unsustainable
agricultural practices.
Crop production is not required for a country to achieve food security.
Nations don't have to have the natural resources required to produce
crops in order to achieve food security, as seen in the examples of
Japan and Singapore.
Because food consumers outnumber producers in every country, food must be distributed to different regions or nations.
Food distribution involves the storage, processing, transport, packaging, and marketing of food.
Food-chain infrastructure and storage technologies on farms can also
affect the amount of food wasted in the distribution process.
Poor transport infrastructure can increase the price of supplying water
and fertilizer as well as the price of moving food to national and
global markets.
Around the world, few individuals or households are continuously
self-reliant for food. This creates the need for a bartering, exchange,
or cash economy to acquire food. The exchange of food requires efficient trading systems and market institutions, which can affect food security.
Per capita world food supplies are more than adequate to provide food
security to all, and thus food accessibility is a greater barrier to
achieving food security.
Access
Goats
are an important part of the solution to global food security because
they are fairly low-maintenance and easy to raise and farm.
Food access refers to the affordability and allocation of food, as well as the preferences of individuals and households. The UN Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights noted that the causes of hunger and malnutrition are often not a scarcity of food but an inability to access available food, usually due to poverty. Poverty can limit access to food, and can also increase how vulnerable an individual or household is to food price spikes.
Access depends on whether the household has enough income to purchase
food at prevailing prices or has sufficient land and other resources to
grow its own food. Households with enough resources can overcome unstable harvests and local food shortages and maintain their access to food.
There are two distinct types of access to food: direct access, in
which a household produces food using human and material resources, and
economic access, in which a household purchases food produced
elsewhere. Location can affect access to food and which type of access a family will rely on.
The assets of a household, including income, land, products of labor,
inheritances, and gifts can determine a household's access to food. However, the ability to access sufficient food may not lead to the purchase of food over other materials and services.
Demographics and education levels of members of the household as well
as the gender of the household head determine the preferences of the
household, which influences the type of food that are purchased.
A household's access to enough and nutritious food may not assure
adequate food intake of all household members, as intrahousehold food
allocation may not sufficiently meet the requirements of each member of
the household. The USDA
adds that access to food must be available in socially acceptable ways,
without, for example, resorting to emergency food supplies, scavenging,
stealing, or other coping strategies.
Utilization
The next pillar of food security is food utilization, which refers to the metabolism of food by individuals.
Once food is obtained by a household, a variety of factors affect the
quantity and quality of food that reaches members of the household. In
order to achieve food security, the food ingested must be safe and must
be enough to meet the physiological requirements of each individual. Food safety affects food utilization, and can be affected by the preparation, processing, and cooking of food in the community and household. Nutritional values of the household determine food choice, and whether food meets cultural preferences is important to utilization in terms of psychological and social well-being.
Access to healthcare is another determinant of food utilization, since
the health of individuals controls how the food is metabolized. For example, intestinal parasites can take nutrients from the body and decrease food utilization. Sanitation can also decrease the occurrence and spread of diseases that can affect food utilization. Education about nutrition and food preparation can affect food utilization and improve this pillar of food security.
Stability
Food stability refers to the ability to obtain food over time. Food insecurity can be transitory, seasonal, or chronic. In transitory food insecurity, food may be unavailable during certain periods of time. At the food production level, natural disasters and drought result in crop failure and decreased food availability. Civil conflicts can also decrease access to food.
Instability in markets resulting in food-price spikes can cause
transitory food insecurity. Other factors that can temporarily cause
food insecurity are loss of employment or productivity, which can be
caused by illness. Seasonal food insecurity can result from the regular pattern of growing seasons in food production.
Chronic (or permanent) food insecurity is defined as the long-term, persistent lack of adequate food.
In this case, households are constantly at risk of being unable to
acquire food to meet the needs of all members.
Chronic and transitory food insecurity are linked, since the
reoccurrence of transitory food security can make households more
vulnerable to chronic food insecurity.
Effects of food insecurity
Famine
and hunger are both rooted in food insecurity. Chronic food insecurity
translates into a high degree of vulnerability to famine and hunger;
ensuring food security presupposes elimination of that vulnerability.
Stunting and chronic nutritional deficiencies
Children with symptoms of low calorie and protein intake and a nurse attendant at a Nigerian orphanage in the late 1960s
Many countries experience ongoing food shortages and distribution
problems. These result in chronic and often widespread hunger amongst
significant numbers of people. Human populations can respond to chronic hunger and malnutrition by decreasing body size, known in medical terms as stunting or stunted growth. This process starts in utero
if the mother is malnourished and continues through approximately the
third year of life. It leads to higher infant and child mortality, but
at rates far lower than during famines.
Once stunting has occurred, improved nutritional intake after the age
of about two years is unable to reverse the damage. Stunting itself can
be viewed as a coping mechanism, bringing body size into alignment with
the calories available during adulthood in the location where the child
is born. Limiting body size as a way of adapting to low levels of energy (calories) adversely affects health in three ways:
- Premature failure of vital organs during adulthood. For example, a 50-year-old individual might die of heart failure because his/her heart suffered structural defects during early development;
- Stunted individuals suffer a higher rate of disease and illness than those who have not undergone stunting;
- Severe malnutrition in early childhood often leads to defects in cognitive development. It therefore creates disparity among children who did not experience severe malnutrition and those who experience it.
Challenges to achieving food security
Global water crisis
Irrigation canals have opened dry desert areas of Egypt to agriculture.
Water deficits, which are already spurring heavy grain imports in numerous smaller countries, may soon do the same in larger countries, such as China or India. The water tables are falling in scores of countries (including northern China, the US, and India) due to widespread over pumping
using powerful diesel and electric pumps. Other countries affected
include Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran. This will eventually lead to water scarcity and cutbacks in grain harvest. Even with the overpumping of its aquifers, China is developing a grain deficit.
When this happens, it will almost certainly drive grain prices upward.
Most of the 3 billion people projected to be born worldwide by
mid-century will be born in countries already experiencing water shortages.
After China and India, there is a second tier of smaller countries with
large water deficits – Afghanistan, Algeria, Egypt, Iran, Mexico, and
Pakistan. Four of these already import a large share of their grain.
Only Pakistan remains self-sufficient. But with a population expanding
by 4 million a year, it will likely soon turn to the world market for
grain.
Regionally, Sub-Saharan Africa
has the largest number of water-stressed countries of any place on the
globe, as of an estimated 800 million people who live in Africa, 300
million live in a water-stressed environment. It is estimated that by 2030, 75 million to 250 million people in Africa
will be living in areas of high water stress, which will likely
displace anywhere between 24 million and 700 million people as
conditions become increasingly unlivable.
Because the majority of Africa remains dependent on an agricultural
lifestyle and 80 to 90 percent of all families in rural Africa rely upon
producing their own food, water scarcity translates to a loss of food security.
Multimillion-dollar investments beginning in the 1990s by the World Bank have reclaimed desert and turned the Ica Valley in Peru, one of the driest places on earth, into the largest supplier of asparagus
in the world. However, the constant irrigation has caused a rapid drop
in the water table, in some places as much as eight meters per year, one
of the fastest rates of aquifer depletion in the world. The wells of
small farmers and local people are beginning to run dry and the water
supply for the main city in the valley is under threat. As a cash crop,
asparagus has provided jobs for local people, but most of the money goes
to the buyers, mainly the British. A 2010 report concluded that the
industry is not sustainable and accuses investors, including the World
Bank, of failing to take proper responsibility for the effect of their
decisions on the water resources of poorer countries. Diverting water from the headwaters of the Ica River to asparagus fields has also led to a water shortage in the mountain region of Huancavelica, where indigenous communities make a marginal living herding.
Land degradation
Intensive farming often leads to a vicious cycle of exhaustion of soil fertility and decline of agricultural yields. Approximately 40 percent of the world's agricultural land is seriously degraded.
In Africa, if current trends of soil degradation continue, the
continent might be able to feed just 25 percent of its population by
2025, according to UNU's Ghana-based Institute for Natural Resources in Africa.
Climate change
Extreme events, such as droughts and floods, are forecast to increase as climate change and global warming takes hold.
Ranging from overnight floods to gradually worsening droughts, these
will have a range of effects on the agricultural sector. According to
the Climate & Development Knowledge Network report Managing Climate Extremes and Disasters in the Agriculture Sectors: Lessons from the IPCC SREX Report,
the effects will include changing productivity and livelihood patterns,
economic losses, and effects on infrastructure, markets and food
security. Food security in future will be linked to our ability to adapt
agricultural systems to extreme events. An example of a shifting
weather pattern would be a rise in temperatures. As temperatures rise
due to climate change there is a risk of a diminished food supply due to
heat damage.
Approximately 2.4 billion people live in the drainage basin of the Himalayan rivers. India, China, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Myanmar could experience floods followed by severe droughts in coming decades. In India alone, the Ganges provides water for drinking and farming for more than 500 million people. The west coast of North America, which gets much of its water from glaciers in mountain ranges such as the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada, also would be affected. Glaciers aren't the only worry that the developing nations have; sea level is reported to rise as climate change progresses, reducing the amount of land available for agriculture.
In other parts of the world, a big effect will be low yields of
grain according to the World Food Trade Model, specifically in the low
latitude regions where much of the developing world is located. From
this the price of grain will rise, along with the developing nations
trying to grow the grain. Due to this, every 2–2.5% price hike will
increase the number of hungry people by 1%.
Low crop yields are just one of the problem facing farmers in the low
latitudes and tropical regions. The timing and length of the growing
seasons, when farmers plant their crops, are going to be changing
dramatically, per the USDA, due to unknown changes in soil temperature
and moisture conditions.
Another way of thinking about food security and climate change comes from Evan Fraser, a geographer working at the University of Guelph in Ontario Canada. His approach is to explore the vulnerability of food systems
to climate change and he defines vulnerability to climate change as
situations that occur when relatively minor environmental problems cause
major effects on food security. Examples of this include the Irish Potato Famine, which was caused by a rainy year that created ideal conditions for the fungal blight to spread in potato fields, or the Ethiopian Famine in the early 1980s.
Three factors stand out as common in such cases, and these three
factors act as a diagnostic "tool kit" through which to identify cases
where food security may be vulnerable to climate change. These factors
are: (1) specialized agro-ecosystems;
(2) households with very few livelihood options other than farming; (3)
situations where formal institutions do not provide adequate safety
nets to protect people.
"The International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) estimates
that an additional US$ 7.1–7.3 billion per year are needed in
agricultural investments to offset the negative effect of climate change on nutrition for children by 2050 (Table 6)."
“Results show that climate change is likely to reduce
agricultural production, thus reducing food availability” (Brown etal.,
2008.) “The food security threat posed by climate change is greatest for
Africa, where agricultural yields and per capita food production has
been steadily declining, and where population growth will double the
demand for food, water, and livestock forage in the next 30 years”
(Devereux et al., 2004).In 2060, the hungry population could range from
641 million to 2087 million with climate change (Chen et al., 1994). By
the year 2030, Cereal crops will decrease from 15 to 19 percent,
temperatures are estimated to rise from 1 degrees Celsius to 2. 75
degrees Celsius, which will lead to less rainfall, which will all result
in an increase in food insecurity in 2030 (Devereux etal, 2004). In
prediction farming countries will be the worst sectors hit, hot
countries and drought countries will reach even higher temperatures and
richer countries will be hit the least as they have more access to more
resources (Devereux et al. 2004). From a food security perspective,
climate change is the dominant rationale to the increase in recent years
and predicted years to come.
Agricultural diseases
Diseases
affecting livestock or crops can have devastating effects on food
availability especially if there are no contingency plans in place.
For example, Ug99, a lineage of wheat stem rust which can cause up to 100% crop losses, is present in wheat fields in several countries in Africa and the Middle East
and is predicted to spread rapidly through these regions and possibly
further afield, potentially causing a wheat production disaster that
would affect food security worldwide.
The genetic diversity of the crop wild relatives of wheat can be used to improve modern varieties to be more resistant to rust. In their centers of origin
wild wheat plants are screened for resistance to rust, then their
genetic information is studied and finally wild plants and modern
varieties are crossed through means of modern plant breeding in order to transfer the resistance genes from the wild plants to the modern varieties.
Food versus fuel
Farmland and other agricultural resources have long been used to produce non-food crops including industrial materials such as cotton, flax, and rubber; drug crops such as tobacco and opium, and biofuels such as firewood,
etc. In the 21st century the production of fuel crops has increased,
adding to this diversion. However technologies are also developed to
commercially produce food from energy such as natural gas and electrical energy with tiny water and land foot print.
Politics
Nobel Prize winning economist Amartya Sen observed that "there is no such thing as an apolitical food problem."
While drought and other naturally occurring events may trigger famine
conditions, it is government action or inaction that determines its
severity, and often even whether or not a famine will occur. The 20th
century has examples of governments, as in Collectivization in the Soviet Union or the Great Leap Forward in the People's Republic of China undermining the food security of their own nations. Mass starvation is frequently a weapon of war, as in the blockade of Germany, the Battle of the Atlantic, and the blockade of Japan during World War I and World War II and in the Hunger Plan enacted by Nazi Germany.
Governments sometimes have a narrow base of support, built upon cronyism and patronage. Fred Cuny
pointed out in 1999 that under these conditions: "The distribution of
food within a country is a political issue. Governments in most
countries give priority to urban areas, since that is where the most
influential and powerful families and enterprises are usually located.
The government often neglects subsistence farmers and rural areas in
general. The more remote and underdeveloped the area the less likely the
government will be to effectively meet its needs. Many agrarian
policies, especially the pricing of agricultural commodities,
discriminate against rural areas. Governments often keep prices of basic
grains at such artificially low levels that subsistence producers
cannot accumulate enough capital to make investments to improve their
production. Thus, they are effectively prevented from getting out of
their precarious situation."
Dictators and warlords
have used food as a political weapon, rewarding supporters while
denying food supplies to areas that oppose their rule. Under such
conditions food becomes a currency with which to buy support and famine
becomes an effective weapon against opposition.
Governments with strong tendencies towards kleptocracy
can undermine food security even when harvests are good. When
government monopolizes trade, farmers may find that they are free to
grow cash crops for export, but under penalty of law only able to sell
their crops to government buyers at prices far below the world market
price. The government then is free to sell their crop on the world market at full price, pocketing the difference.
When the rule of law is absent, or private property is non-existent, farmers have little incentive to improve their productivity.
If a farm becomes noticeably more productive than neighboring farms, it
may become the target of individuals well connected to the government.
Rather than risk being noticed and possibly losing their land, farmers
may be content with the perceived safety of mediocrity.
As pointed out by William Bernstein in The Birth of Plenty:
"Individuals without property are susceptible to starvation, and it is
much easier to bend the fearful and hungry to the will of the state. If a
[farmer's] property can be arbitrarily threatened by the state, that
power will inevitably be employed to intimidate those with divergent
political and religious opinions."
Food sovereignty
The approach known as food sovereignty views the business practices of multinational corporations as a form of neocolonialism.
It contends that multinational corporations have the financial
resources available to buy up the agricultural resources of impoverished
nations, particularly in the tropics. They also have the political
clout to convert these resources to the exclusive production of cash crops for sale to industrialized nations outside of the tropics, and in the process to squeeze the poor off of the more productive lands. Under this view subsistence farmers
are left to cultivate only lands that are so marginal in terms of
productivity as to be of no interest to the multinational corporations.
Likewise, food sovereignty holds it to be true that communities should
be able to define their own means of production and that food is a basic
human right. With several multinational corporations now pushing
agricultural technologies on developing countries, technologies that
include improved seeds, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides, crop
production has become an increasingly analyzed and debated issue. Many
communities calling for food sovereignty are protesting the imposition
of Western technologies on to their indigenous systems and agency.
Food waste
Food waste may be diverted for alternative human consumption when
economic variables allow for it. The waste of consumable food is even
gaining attention from large food conglomerates. For instance, due to
low food prices, simply discarding irregular carrots has typically been
more cost-effective than spending money on the extra labor or machinery
necessary to handle them. A juice factory in the Netherlands, however,
has developed a process to efficiently divert and use previously
rejected carrots, and its parent company is expanding this innovation to
plants in Great Britain.
In recent years, France has worked to combat food insecurity, in
part by addressing food waste; since 2013 the country has passed laws
prohibiting grocery stores from discarding unsold food items, requiring
that they instead donate the food to designated charities. Nevertheless, according to the Economist’s Global Food Security Index,
overall food insecurity remains more severe in France than the United
States despite higher nation-wide estimates of food waste in the U.S.
Local efforts, such as the Greater Franklin Food Council
in Farmington, Maine, certainly can – and do – directly help regional
food security, particularly when residents become mindful of the
juxtaposition of food insecurity in their communities with their own
food waste at home. Learning that the average family of four throws away
$1,500 worth of food per year while neighbors may be going hungry can
provide the motivation to waste less and give more: waste less money at
the grocery store and give more to the food pantry.
Risks to food security
Population growth
A family planning placard in Ethiopia. It shows some negative effects of having too many children.
Current UN projections show a continued increase in population in the
future (but a steady decline in the population growth rate), with the
global population expected to reach 9.8 billion in 2050 and 11.2 billion
by 2100. Estimates by the UN Population Division for the year 2150 range between 3.2 and 24.8 billion; mathematical modeling supports the lower estimate.
Some analysts have questioned the sustainability of further world
population growth, highlighting the growing pressures on the
environment, global food supplies, and energy resources. Solutions for
feeding the extra billions in the future are being studied and
documented. One out of every seven people on our planet go to sleep hungry. People are suffering due to overpopulation, 25,000 people die of malnutrition and hunger related diseases everyday.
Fossil fuel dependence
While agricultural output has increased, energy consumption to
produce a crop has also increased at a greater rate, so that the ratio
of crops produced to energy input has decreased over time. Green Revolution techniques also heavily rely on chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides, many of which are petroleum products, making agriculture increasingly reliant on petroleum.
Between 1950 and 1984, as the Green Revolution transformed
agriculture around the globe, world grain production increased by 250%.
The energy for the Green Revolution was provided by fossil fuels in the form of fertilizers (natural gas), pesticides (oil), and hydrocarbon fueled irrigation.
David Pimentel, professor of ecology and agriculture at Cornell University,
and Mario Giampietro, senior researcher at the National Research
Institute on Food and Nutrition (NRIFN), place in their study Food, Land, Population and the U.S. Economy the maximum U.S. population for a sustainable economy
at 210 million. To achieve a sustainable economy and avert disaster,
the United States must reduce its population by at least one-third, and
world population will have to be reduced by two-thirds, says the study.
The authors of this study believe that the mentioned agricultural
crisis will only begin to affect us after 2020, and will not become
critical until 2050. The oncoming peaking of global oil
production (and subsequent decline of production), along with the peak
of North American natural gas production will very likely precipitate
this agricultural crisis much sooner than expected. Geologist Dale Allen Pfeiffer claims that coming decades could see spiraling food prices without relief and massive starvation on a global level such as never experienced before.
Homogeneity in the global food supply
A small number of major crops, e.g. Soybean,
have formed an increasing share of the food energy, protein, fat, and
food weight eaten by the world's population over the past 50 years
Since 1961, human diets across the world have become more diverse in
the consumption of major commodity staple crops, with a corollary
decline in consumption of local or regionally important crops, and thus
have become more homogeneous globally.
The differences between the foods eaten in different countries were
reduced by 68% between 1961 and 2009. The modern "global standard"
diet contains an increasingly large percentage of a relatively small
number of major staple commodity crops, which have increased
substantially in the share of the total food energy (calories), protein,
fat, and food weight that they provide to the world's human population,
including wheat, rice, sugar, maize, soybean (by +284%), palm oil (by +173%), and sunflower (by +246%).
Whereas nations used to consume greater proportions of locally or
regionally important crops, wheat has become a staple in over 97% of
countries, with the other global staples showing similar dominance
worldwide. Other crops have declined sharply over the same period,
including rye, yam, sweet potato (by −45%), cassava (by −38%), coconut, sorghum (by −52%) and millets (by −45%).
Such crop diversity change in the human diet is associated with mixed
effects on food security, improving under-nutrition in some regions but
contributing to the diet-related diseases caused by over-consumption of
macronutrients.
Price setting
On April 30, 2008, Thailand, one of the world's biggest rice exporters, announced the creation of the Organisation of Rice Exporting Countries
with the potential to develop into a price-fixing cartel for rice. It
is a project to organize 21 rice exporting countries to create a
homonymous organisation to control the price of rice. The group is
mainly made up of Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar. The
organization attempts to serve the purpose of making a "contribution to
ensuring food stability, not just in an individual country but also to
address food shortages in the region and the world". However, it is
still questionable whether this organization will serve its role as an
effective rice price fixing cartel, that is similar to OPEC's mechanism
for managing petroleum. Economic analysts and traders said the proposal
would go nowhere because of the inability of governments to cooperate
with each other and control farmers' output. Moreover, countries that
are involved expressed their concern, that this could only worsen the
food security.
Land use change
China
needs not less than 120 million hectares of arable land for its food
security. China has recently reported a surplus of 15 million hectares.
On the other side of the coin, some 4 million hectares of conversion to
urban use and 3 million hectares of contaminated land have been reported
as well. Furthermore, a survey found that 2.5% of China's arable land is too contaminated to grow food without harm.
In Europe, the conversion of agricultural soil implied a net loss of
potential. But the rapid loss in the area of arable soils appears to be
economically meaningless because EU is perceived to be dependent on
internal food supply anymore. During the period 2000–2006 the European
Union lost 0.27% of its cropland and 0.26% of its crop productive
potential. The loss of agricultural land during the same time was the
highest in the Netherlands, which lost 1.57% of its crop production
potential within six years. The figures are quite alarming for Cyprus
(0.84%), Ireland (0.77%) and Spain (0.49%) as well.
In Italy, in the Emilia-Romagna plain (ERP), the conversion of 15,000
hectare of agricultural soil (period 2003-2008) implied a net loss of
109,000 Mg per year of wheat, which accounts for the calories needed by
14% of ERP population (425,000 people). Such a loss in wheat production
is just 0.02% of gross domestic product (GDP) of the Emilia-Romagna
region which is actually a minor effect in financial terms.
Additionally, the income from the new land use is often much higher than
the one guaranteed by agriculture, as in the case of urbanisation or
extraction of raw materials.
Global catastrophic risks
As anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions reduce the stability of the global climate, abrupt climate change could become more intense. The impact of an asteroid or comet larger than about 1 km diameter has the potential to block the sun globally, causing impact winter. Particles in the troposphere would quickly rain out, but particles in the stratosphere, especially sulfate, could remain there for years. Similarly, a supervolcanic eruption would reduce the potential of agricultural production from solar photosynthesis, causing volcanic winter. The Toba super volcanic eruption approximately 70,000 years ago may have nearly caused the extinction of humans. Again, primarily sulfate particles could block the sun for years. Solar blocking is not limited to natural causes as nuclear winter
is also possible, which refers to the scenario involving widespread
nuclear war and burning of cities that release soot into the
stratosphere that would stay there for about 10 years.
The high stratospheric temperatures produced by soot absorbing solar
radiation would create near-global ozone hole conditions even for a
regional nuclear conflict.
A sufficiently powerful geomagnetic storm
could result in the sudden absence of access to electricity in large
areas of the world. Because industrial farming is increasingly dependent
on constant access to electricity, for example in precision livestock farming, a geomagnetic storm could potentially have devastating effects to the food production.
Agricultural subsidies in the United States
Agricultural subsidies
are paid to farmers and agribusinesses to supplement their income,
manage the supply of their commodities and influence the cost and supply
of those commodities. In the United States, the main crops the government subsidizes contribute to the obesity problem; since 1995, $300 billion have gone to crops that are used to create junk food.
Taxpayers heavily subsidize corn and soy, which are main
ingredients in processed foods and fatty foods which the government does
not encourage,
and used to fatten livestock. Half of farmland is devoted to corn and
soy, the rest is wheat. Soy and corn can be found in sweeteners like high fructose corn syrup. Over $19 billion during the prior 18 years to 2013 was spent to incent farmers to grow these crops,
raising the price of fruits and vegetables by about 40% and lowering
the price of dairy and other animal products. Little land is used for
fruit and vegetable farming.
Corn, a pillar of American agriculture for years, is now mainly used for ethanol, high fructose corn syrup and bio-based plastics. About 40 percent of corn is used for ethanol and 36% is used as animal feed.
Only a tiny fraction of corn is used as a food source, much of that
fraction is used for high-fructose corn syrup, which is a main
ingredient in processed, unhealthy junk food.
People who ate the most subsidized food had a 37% higher risk of
being obese compared to people who ate the least amount of subsidized
food.
This brings up the concern that minority communities are more prone to
risks of obesity due to financial limitations. The subsidies result in
those commodities being cheap to the public, compared to those
recommended by dietary guidelines.
President Trump proposed a 21% cut to government discretionary spending in the agriculture sector, which has met partisan resistance.
This budget proposal would also reduce spending on the Special
Supplement Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children, albeit
less than President Obama did.
Children and food security
Bengali famine, 1943. The Japanese conquest of Burma cut off India's main supply of rice imports.
On April 29, 2008, a UNICEF UK report found that the world's poorest and most vulnerable children are being hit the hardest by climate change.
The report, "Our Climate, Our Children, Our Responsibility: The
Implications of Climate Change for the World's Children", says that
access to clean water and food supplies will become more difficult,
particularly in Africa and Asia.
In the United States
By
way of comparison, in one of the largest food producing countries in
the world, the United States, approximately one out of six people are
"food insecure", including 17 million children, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture. A 2012 study in the Journal of Applied Research on Children
found that rates of food security varied significantly by race, class
and education. In both kindergarten and third grade, 8% of the children
were classified as food insecure, but only 5% of white children were
food insecure, while 12% and 15% of black and Hispanic children were
food insecure, respectively. In third grade, 13% of black and 11% of
Hispanic children are food insecure compared to 5% of white children.
There are also striking regional variations in food security.
Although food insecurity can be difficult to measure, 45% of elementary
and secondary students in Maine qualify for free or reduced-price school
lunch; by some measures Maine has been declared the most food-insecure
of the New England states.
Transportation challenges and distance are common barriers to families
in rural areas who seek food assistance. Social stigma is another
important consideration, and for children, sensitively administering
in-school programs can make the difference between success and failure.
For instance, when John Woods, co-founder of Full Plates, Full
Potential,
learned that embarrassed students were shying away from the free
breakfasts being distributed at a school he was working with, he made
arrangements to provide breakfast free of charge to all of the students
there.
According to a 2015 Congressional Budget Office report on child
nutrition programs, it is more likely that food insecure children will
participate in school nutrition programs than children from food secure
families. School nutrition programs, such as the National School Lunch Program (NSLP) and the School Breakfast Program (SBP)
have provided millions of children access to healthier lunch and
breakfast meals, since their inceptions in the mid-1900s. According to
the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NSLP has served over 300
million, while SBP has served about 10 million students each day.
Nevertheless, far too many qualifying students still fail to receive
these benefits simply due to not submitting the necessary paperwork.
Multiple studies have reported that school nutrition programs play an
important role in ensuring students are accessing healthy meals.
Students who ate school lunches provided by NLSP showed higher diet
quality than if they had their own lunches.
Even more, the USDA improved standards for school meals, which
ultimately lead to positive impacts on children’s food selection and
eating habits.
Countless partnerships have emerged in the quest for food
security. A number of federal nutrition programs exist to provide food
specifically for children, including the Summer Food Service Program, Special Milk Program (SMP) and Child and Adult Care Food Program (CACFP),
and community and state organizations often network with these
programs. The Summer Food Program in Bangor, Maine, is run by the Bangor
Housing Authority and sponsored by Good Shepherd Food Bank.
In turn, Waterville Maine's Thomas College, for example, is among the
organizations holding food drives to collect donations for Good
Shepherd. Children whose families qualify for Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) or Women, Infants, and Children (WIC)
may also receive food assistance. WIC alone served approximately 7.6
million participants, 75% of which are children and infants.
Despite the sizable populations served by these programs, Conservatives have regularly targeted these programs for defunding.
Conservatives' arguments against school nutrition programs include fear
of wasting food and fraud from applications. On January 23, 2017,
H.R.610 was introduced to the House by Republican Representative Steve
King. The bill seeks to repeal a rule set by the Food and Nutrition
Service of the Department of Agriculture, which mandates schools to
provide more nutritious and diverse foods across the food plate. Two months later, the Trump administration released a preliminary 2018 budget that proposed a $2 billion cut from WIC.
Food insecurity in children can lead to developmental impairments
and long term consequences such as weakened physical, intellectual and
emotional development.
Food insecurity also related to obesity for people living in
neighborhoods where nutritious food are unavailable or unaffordable.
Gender and food security
A Kenyan woman farmer at work in the Mount Kenya region
Gender inequality
both leads to and is a result of food insecurity. According to
estimates women and girls make up 60% of the world's chronically hungry
and little progress has been made in ensuring the equal right to food for women enshrined in the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women. Women face discrimination
both in education and employment opportunities and within the
household, where their bargaining power is lower. Women’s employment is
essential for not only advancing gender equality within the workforce,
but ensuring a sustainable future as it means less pressure for high
birth rates and net migration. On the other hand, gender equality is described as instrumental to ending malnutrition and hunger.
Women tend to be responsible for food preparation and childcare within
the family and are more likely to spend their income on food and their
children's needs.
Women also play an important role in food production, processing,
distribution and marketing. They often work as unpaid family workers,
are involved in subsistence farming and represent about 43% of the
agricultural labor force in developing countries, varying from 20% in
Latin America to 50% in Eastern and Southeastern Asia and Sub-Saharan
Africa. However, women face discrimination in access to land, credit,
technologies, finance and other services. Empirical studies suggest that
if women had the same access to productive resources as men, women
could boost their yields by 20–30%; raising the overall agricultural
output in developing countries by 2.5 to 4%. While those are rough
estimates, the significant benefit of closing the gender gap on
agricultural productivity cannot be denied.
The gendered aspects of food security are visible along the four
pillars of food security: availability, access, utilization and
stability, as defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization.
The number of people affected by hunger is extremely high, with enormous effects on women and girls. Making this trend disappear "must be a top priority for governments and international institutions".
Actions governments take must take into consideration that food
insecurity is an issue regarding "equality, rights and social justice".
"Food and nutrition insecurity is a political and economic phenomenon fuelled by inequitable global and national processes".
Factors like capitalism, exploration of Indigenous lands all contribute
to food insecurity for minorities and the people who are the most
oppressed in various countries (women being one of these oppressed
groups). To emphasis, "food and nutrition insecurity is a gender justice
issue".
The facts that women and girls are the most oppressed by "the
inequitable global economic processes that govern food systems and by
global trends such as climate change", shows how institutions continue
to place women in positions of disadvantage and impoverishment to make
money and thrive on capitalizing the food system.
When the government withholds food by raising its prices to amounts
only privileged people can afford, they both benefit and are able to
control the "lower-class"/ marginalized people via the food market.
An interesting fact is that "despite rapid economic growth in India,
thousands of women and girls still lack food and nutrition security as a
direct result of their lower status compared with men and boys".
"Such inequalities are compounded by women and girls' often limited
access to productive resources, education and decision-making, by the
'normalised' burden of unpaid work – including care work – and by the
endemic problems of gender-based violence (GBV), HIV and AIDS".
Use of genetically modified (GM) crops
One of the most up-and-coming techniques to ensuring global food security is the use of genetically modified (GM) crops.
The genome of these crops can be altered to address one or more aspects
of the plant that may be preventing it from being grown in various
regions under certain conditions. Many of these alterations can address
the challenges that were previously mentioned above, including the water
crisis, land degradation, and the ever-changing climate.
In agriculture and animal husbandry, the Green Revolution popularized the use of conventional hybridization to increase yield by creating "high-yielding varieties".
Often the handful of hybridized breeds originated in developed
countries and were further hybridized with local varieties in the rest
of the developing world to create high yield strains resistant to local
climate and diseases.
The area sown to genetically engineered crops in developing
countries is rapidly catching up with the area sown in industrial
nations. According to the International Service for the Acquisition of
Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA), GM crops were grown by approximately
8.5 million farmers in 21 countries in 2005; up from 8.25 million
farmers in 17 countries in 2004. However, the ISAAA is funded by
organisations including prominent agricultural biotechnology
corporations, such as Monsanto and Bayer, and there have been several challenges made to the accuracy of ISAAA's global figures.
Opposition to GM crops
Some scientists question the safety of biotechnology as a panacea; agroecologists Miguel Altieri and Peter Rosset have enumerated ten reasons why biotechnology will not ensure food security, protect the environment, or reduce poverty. Reasons include:
- There is no relationship between the prevalence of hunger in a given country and its population
- Most innovations in agricultural biotechnology have been profit-driven rather than need-driven
- Ecological theory predicts that the large-scale landscape homogenization with transgenic crops will exacerbate the ecological problems already associated with monoculture agriculture
- And, that much of the needed food can be produced by small farmers located throughout the world using existing agroecological technologies.
Based on evidence from previous attempts, there is a likely lack of
transferability of one type of GM crop from one region to another. For
example, modified crops that have proven successful in Asia from the
Green Revolution have failed when tried in regions of Africa. More research must be done regarding the specific requirements of growing a specific crop in a specific region.
There is also a drastic lack of education given to governments,
farmers, and the community about the science behind GM crops, as well as
suitable growing practices. In most relief programs, farmers are given
seeds with little explanation and little attention is paid to the
resources available to them or even laws that prohibit them from
distributing produce. Governments are often not advised on the economic
and health implications that come with growing GM crops, and are then
left to make judgments on their own. Because they have so little
information regarding these crops, they usually shy away from allowing
them or do not take the time and effort required to regulate their use.
Members of the community that will then consume the produce from these
crops are also left in the dark about what these modifications mean and
are often scared off by their 'unnatural' origins. This has resulted in
failure to properly grow crops as well as strong opposition to the
unknown practices.
A study published in June 2016 evaluated the status of the implementation of Golden Rice,
which was first developed in the 1990s to produce higher levels of
Vitamin A than its non-GMO counterparts. This strain of rice was
designed so that malnourished women and children in third world
countries who were more susceptible to deficiencies could easily improve
their Vitamin A intake levels and prevent blindness, which is a common
result. Golden Rice production was centralized to the Philippines, yet
there have been many hurdles to jump in order to get production moving.
The study showed that the project is far behind schedule and is not
living up to its expectations. Although research on Golden Rice still
continues, the country has moved forward with other non-GMO initiatives
to address the Vitamin A deficiency problem which is so prevasive in
that region.
Many anti-GMO activists argue that the use of GM crops decreases biodiversity
amongst plants. Livestock biodiversity is also threatened by the
modernization of agriculture and the focus on more productive major
breeds. Therefore, efforts have been made by governments and
non-governmental organizations to conserve livestock biodiversity
through strategies such as Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources.
Support of GM crops
Many
GM crop success stories exist, primarily in developed nations like the
USA, China, and various countries in Europe. Common GM crops include
cotton, maize, and soybeans, all of which are grown throughout North and
South America as well as regions of Asia.
Modified cotton crops, for example, have been altered such that they
are resistant to pests, can grown in more extreme heat, cold, or
drought, and produce longer, stronger fibers to be used in textile
production.
One of the biggest threats to rice, which is a staple food crop especially in India and other countries within Asia, is blast disease which is a fungal infection that causes lesions to form on all parts of the plant.
A genetically engineered strain of rice has been developed so that it
is resistant to blast, greatly improving the crop yield of farmers and
allowing rice to be more accessible to everyone.
Some other crops have been modified such that they produce higher
yields per plant or that they require less land for growing. The latter
can be helpful in extreme climates with little arable land and also
decreases deforestation, as fewer trees need to be cut down in order to
make room for crop fields.
Others yet have been altered such that they do not require the use of
insecticides or fungicides. This addresses various health concerns
associated with such pesticides and can also work to improve
biodiversity within the area in which these crops are grown.
In a review of Borlaug's 2000 publication entitled Ending world hunger: the promise of biotechnology and the threat of antiscience zealotry, the authors argued that Borlaug's warnings were still true in 2010,
GM crops are as natural and safe as today's bread wheat, opined Dr. Borlaug, who also reminded agricultural scientists of their moral obligation to stand up to the antiscience crowd and warn policy makers that global food insecurity will not disappear without this new technology and ignoring this reality global food insecurity would make future solutions all the more difficult to achieve.
— Rozwadowski and Kagale
Research conducted by the GMO Risk Assessment and
Communication of Evidence (GRACE) program through the EU between 2007
and 2013 focused on many uses of GM crops and evaluated many facets of
their effects on human, animal, and environmental health.
The body of scientific evidence concluding that GM foods are safe
to eat and do not pose environmental risks is wide. Findings from the
International Council of Scientists (2003) that analyzed a selection of
approximately 50 science-based reviews concluded that “currently
available genetically modified foods are safe to eat,” and “there is no
evidence of any deleterious environmental effects having occurred from
the trait/species combinations currently available.”
The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) supported
the same consensus a year later in addition to recommending the
extension of biotechnology to the developing world.
Similarly, the Royal Society (2003) and British Medical Association
(2004) found no adverse health effects of consuming genetically modified
foods.
These findings supported the conclusions of earlier studies by the
European Union Research Directorate, a compendium of 81 scientific
studies conducted by more than 400 research teams did not show “any new
risks to human health or the environment, beyond the usual uncertainties
of conventional plant breeding.”
Likewise, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development in
Europe (OECD) and the Nuffield Council on Bioethics (1999) did not find
that genetically modified foods posed a health risk.
Approaches
A liquid manure spreader is used to increase agricultural productivity.
By the United Nations
The UN Millennium Development Goals
are one of the initiatives aimed at achieving food security in the
world. The first Millennium Development Goal states that the UN "is to
eradicate extreme hunger and poverty" by 2015.
Olivier De Schutter, the UN Special Rapporteur on the Right to Food,
advocates for a multidimensional approach to food security challenges.
This approach emphasizes the physical availability of food; the social,
economic and physical access people have to food; and the nutrition,
safety and cultural appropriateness or adequacy of food.
By the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations stated in The State of Food Insecurity in the World 2003 that countries that have reduced hunger often had rapid economic growth, specifically in their agricultural sectors. These countries were also characterized as having slower population growth, lower HIV rates, and higher rankings in the Human Development Index. At that time, the FAO considered addressing agriculture and population growth vital to achieving food security. In The State of Food Insecurity in the World 2012, the FAO restated its focus on economic growth
and agricultural growth to achieve food security and added a focus on
the poor and on "nutrition-sensitive" growth. For example, economic
growth should be used by governments to provide public services to
benefit poor and hungry populations. The FAO also cited smallholders,
including women, as groups that should be involved in agricultural
growth to generate employment for the poor. For economic and
agricultural growth to be "nutrition-sensitive", resources should be
utilized to improve access to diverse diets for the poor as well as
access to a safe water supply and to healthcare.
The FAO has proposed a "twin track" approach to fight food insecurity
that combines sustainable development and short-term hunger relief.
Development approaches include investing in rural markets and rural
infrastructure.
In general, the FAO proposes the use of public policies and programs
that promote long-term economic growth that will benefit the poor. To
obtain short-term food security, vouchers for seeds, fertilizer,
or access to services could promote agricultural production. The use of
conditional or unconditional food or cash transfers was another
approach the FAO noted. Conditional transfers could include school feeding programs, while unconditional transfers could include general food distribution, emergency food aid or cash transfers. A third approach is the use of subsidies
as safety nets to increase the purchasing power of households. The FAO
stated that "approaches should be human rights-based, target the poor,
promote gender equality, enhance long-term resilience and allow
sustainable graduation out of poverty."
The FAO noted that some countries have been successful in
fighting food insecurity and decreasing the number of people suffering
from undernourishment. Bangladesh is an example of a country that has
met the Millennium Development Goal hunger target. The FAO credited
growth in agricultural productivity and macroeconomic stability for the
rapid economic growth in the 1990s that resulted in an increase in food
security. Irrigation systems were established through infrastructure development programs. Two programs, HarvestPlus and the Golden Rice Project, provided biofortified crops in order to decrease micronutrient deficiencess.
World Food Day
was established on October 16, in honor of the date that the FAO was
founded in 1945. On this day, the FAO hosts a variety of event at the
headquarters in Rome and around the world, as well as seminars with UN
officials.
By the World Food Programme
Fight Hunger: Walk the World campaign is a United Nations World Food Programme initiative.
The World Food Programme (WFP) is an agency of the United Nations that uses food aid
to promote food security and eradicate hunger and poverty. In
particular, the WFP provides food aid to refugees and to others
experiencing food emergencies. It also seeks to improve nutrition and
quality of life to the most vulnerable populations and promote
self-reliance.
An example of a WFP program is the "Food For Assets" program in which
participants work on new infrastructure, or learn new skills, that will
increase food security, in exchange for food.
The WFP and the Government of Kenya have partnered in the Food For
Assets program in hopes of increasing the resilience of communities to
shocks.
Global partnerships to achieve food security and end hunger
In April 2012, the Food Assistance Convention was signed, the world's first legally binding international agreement on food aid. The May 2012 Copenhagen Consensus
recommended that efforts to combat hunger and malnutrition should be
the first priority for politicians and private sector philanthropists
looking to maximize the effectiveness of aid spending. They put this
ahead of other priorities, like the fight against malaria and AIDS.
The main global policy to reduce hunger and poverty are the recently approved Sustainable Development Goals.
In particular Goal 2: Zero Hunger sets globally agreed targets to end
hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote
sustainable agriculture by 2030.
A number of organizations have formed initiatives with the more
ambitious goal to achieve this outcome in only 10 years, by 2025:
- In 2013 Caritas International started a Caritas-wide initiative aimed at ending systemic hunger by 2025. The One human family, food for all campaign focuses on awareness raising, improving the effect of Caritas programs and advocating the implementation of the Right to Food.
- The partnership Compact2025, led by IFPRI with the involvement of UN organisations, NGOs and private foundations develops and disseminates evidence-based advice to politicians and other decision-makers aimed at ending hunger and undernutrition in the coming 10 years, by 2025. It bases its claim that hunger can be ended by 2025 on a report by Shenggen Fan and Paul Polman that analyzed the experiences from China, Vietnam, Brazil and Thailand and concludes that eliminating hunger and undernutrition was possible by 2025.
- In June 2015, the European Union and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation have launched a partnership to combat undernutrition especially in children. The program will initiatilly be implemented in Bangladesh, Burundi, Ethiopia, Kenya, Laos and Niger and will help these countries to improve information and analysis about nutrition so they can develop effective national nutrition policies.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN has created a partnership that will act through the African Union's CAADP framework aiming to end hunger in Africa by 2025. It includes different interventions including support for improved food production, a strengthening of social protection and integration of the Right to Food into national legislation.
By the United States Agency for International Development
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) proposes several key steps to increasing agricultural productivity which is in turn key to increasing rural income and reducing food insecurity. They include:
- Boosting agricultural science and technology. Current agricultural yields are insufficient to feed the growing populations. Eventually, the rising agricultural productivity drives economic growth.
- Securing property rights and access to finance
- Enhancing human capital through education and improved health
- Conflict prevention and resolution mechanisms and democracy and governance based on principles of accountability and transparency in public institutions and the rule of law are basic to reducing vulnerable members of society.
Since the 1960s, the U.S. has been implementing a food stamp program
(now called the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program) to directly
target consumers who lack the income to purchase food. According to Tim
Josling, a Senior Fellow at the Freeman Spogli Institute for
International Studies, Stanford University,
food stamps or other methods of distribution of purchasing power
directly to consumers might fit into the range of international programs
under consideration to tackle food insecurity.
Improving agricultural productivity to benefit the rural poor
There are strong, direct relationships between agricultural
productivity, hunger, poverty, and sustainability. Three-quarters of the
world's poor live in rural areas and make their living from
agriculture. Hunger and child malnutrition
are greater in these areas than in urban areas. Moreover, the higher
the proportion of the rural population that obtains its income solely
from subsistence farming (without the benefit of pro-poor technologies
and access to markets), the higher the incidence of malnutrition.
Therefore, improvements in agricultural productivity aimed at
small-scale farmers will benefit the rural poor first. Food and feed
crop demand is likely to double in the next 50 years, as the global
population approaches nine billion. Growing sufficient food will require
people to make changes such as increasing productivity in areas
dependent on rainfed agriculture; improving soil fertility management; expanding cropped areas; investing in irrigation;
conducting agricultural trade between countries; and reducing gross
food demand by influencing diets and reducing post-harvest losses.
According to the Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture, a major study led by the International Water Management Institute
(IWMI), managing rainwater and soil moisture more effectively, and
using supplemental and small-scale irrigation, hold the key to helping
the greatest number of poor people. It has called for a new era of water
investments and policies for upgrading rainfed agriculture that would
go beyond controlling field-level soil and water to bring new freshwater
sources through better local management of rainfall and runoff.
Increased agricultural productivity enables farmers to grow more food,
which translates into better diets and, under market conditions that
offer a level playing field, into higher farm incomes. With more money,
farmers are more likely to diversify production and grow higher-value
crops, benefiting not only themselves but the economy as a whole."
Researchers suggest forming an alliance between the emergency food program and community-supported agriculture, as some countries' food stamps cannot be used at farmer's markets and places where food is less processed and grown locally.
The gathering of wild food plants appears to be an efficient alternative
method of subsistence in tropical countries, which may play a role in
poverty alleviation.
Large-scale food stockpiling
The minimum annual global wheat storage is approximately two months. To counteract the severe food security issues caused by global catastrophic risks, years of food storage has been proposed.
Though this could ameliorate smaller scale problems like regional
conflict and drought, it would exacerbate current food insecurity by
raising food prices.
Agricultural insurances
Insurance
is a financial instrument, which allows exposed individuals to pool
resources to spread their risk. They do so by contributing premium to an
insurance fund, which will indemnify those who suffer insured loss.
This procedure reduces the risk for an individual by spreading his/her
risk among the multiple fund contributors. Insurance can be designed to
protect many types of individuals and assets against single or multiple
perils and buffer insured parties against sudden and dramatic income or
asset loss.
Crop insurance is purchased by agricultural producers to protect
themselves against either the loss of their crops due to natural
disasters. Two type of insurances are available:
(1) claim-based insurances, and (2) index-based insurances. In
particular in poor countries facing food security problems, index-based
insurances offer some interesting advantages: (1) indices can be derived
from globally available satellite images that correlate well with what
is insured; (2) these indices can be delivered at low cost; and (3) the
insurance products open up new markets that are not served by
claim-based insurances.
An advantage of index-based insurance is that it can potentially
be delivered at lower cost. A significant barrier that hinders uptake of
claim-based insurance is the high transaction cost for searching for
prospective policyholders, negotiating and administering contracts,
verifying losses and determining payouts. Index insurance eliminates the
loss verification step, thereby mitigating a significant transaction
cost. A second advantage of index-based insurance is that, because it
pays an indemnity based on the reading of an index rather than
individual losses, it eliminates much of the fraud, moral hazard and
adverse selection, which are common in classical claim-based insurance. A
further advantage of index insurance is that payments based on a
standardized and indisputable index also allow for a fast indemnity
payment. The indemnity payment could be automated, further reducing
transaction costs.
Basis risk is a major disadvantage of index-based insurance. It
is the situation where an individual experiences a loss without
receiving payment or vice versa. Basis risk is a direct result of the
strength of the relation between the index that estimates the average
loss by the insured group and the loss of insured assets by an
individual. The weaker this relation the higher the basis risk. High
basis risk undermines the willingness of potential clients to purchase
insurance. It thus challenges insurance companies to design insurances
such as to minimize basis risk.
Food Justice Movement
The Food Justice Movement has been seen as a unique and multifaceted
movement with relevance to the issue of food security. It has been
described as a movement about social-economic and political problems in
connection to environmental justice,
improved nutrition and health, and activism. Today, a growing number of
individuals and minority groups are embracing the Food Justice due to
the perceived increase in hunger within nations such as the United
States as well as the amplified effect of food insecurity on many
minority communities, particularly the Black and Latino communities.
A number of organizations have either championed the Food Justice Cause
or greatly impacted the Food Justice space. An example of a prominent
organization within the food justice movement has been the Coalition of Immokalee Workers,
which is a worker-based human rights organization that has been
recognized globally for its accomplishments in the areas of human
trafficking, social responsibility and gender-based violence at work.
The Coalition of Immoaklee Workers most prominent accomplishment related
to the food justice space has been its part in implementing the Fair Food Program
which increased the pay and bettered working conditions of farm workers
in the tomato industry who had been exploited for generations. This
accomplishment provided over 30,000 workers more income and the ability
to access better and more healthy foods for themselves and their
families. Another organization in the food justice space is the Fair
Food Network, an organization that has embraced the mission of helping
familIes who need healthy food to gain access to it while also
increasing the livelihoold for farmers in America and growing local
economies. Started by Oran B. Hesterma,
the Fair Food Network has invested over $200 million in various
projects and initiatives, such as the Double Up Food Bucks program, to
help low-income and minority communities access healthier food.
Bees
Bees and
other pollinating insects are currently improving the food production of
2 billion small farmers worldwide, helping to ensure food security for
the world's population. Research shows that if pollination is managed
well on small diverse farms, with all other factors being equal, crop
yields can increase by a significant median of 24 percent.
How animal pollinators positively affect fruit condition and nutrient content is still being discovered.
Criticism
As of 2015 the concept of food security has mostly focused on food calories rather than the quality and nutrition
of food. The concept of nutrition security evolved over time. In 1995,
it has been defined as "adequate nutritional status in terms of protein,
energy, vitamins, and minerals for all household members at all times".