By examining DNA sequences
in different populations, scientists can determine the closeness of
relationships between populations (or within populations). Certain
similarities in genetic makeup let molecular anthropologists determine
whether or not different groups of people belong to the same haplogroup, and thus if they share a common geographical origin. This is significant because it allows anthropologists to trace patterns of migration and settlement, which gives helpful insight as to how contemporary populations have formed and progressed over time.
Molecular anthropology has been extremely useful in establishing the evolutionary tree of humans and other primates, including closely related species like chimps and gorillas. While there are clearly many morphological similarities between humans and chimpanzees, for example, certain studies also have concluded that there is roughly a 98 percent commonality between the DNA of both species. However, more recent studies have modified the commonality of 98 percent to a commonality of 94 percent, showing that the genetic gap between humans and chimps is larger than originally thought. Such information is useful in searching for common ancestors and coming to a better understanding of how humans evolved.
Molecular anthropology has been extremely useful in establishing the evolutionary tree of humans and other primates, including closely related species like chimps and gorillas. While there are clearly many morphological similarities between humans and chimpanzees, for example, certain studies also have concluded that there is roughly a 98 percent commonality between the DNA of both species. However, more recent studies have modified the commonality of 98 percent to a commonality of 94 percent, showing that the genetic gap between humans and chimps is larger than originally thought. Such information is useful in searching for common ancestors and coming to a better understanding of how humans evolved.
Haploid loci in molecular anthropology
Image
of mitochondrion. There are many mitochondria within a cell, and DNA in
them replicates independently of the chromosomes in the nucleus.
There are two continuous linkage groups in humans that are carried by a single sex. The first is the Y chromosome,
which is passed from father to son. Anatomical females carry a Y
chromosome only rarely, as a result of genetic defect. The other linkage
group is the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). MtDNA is almost always only
passed to the next generation by females, but under highly exceptional
circumstances mtDNA can be passed through males.
The non-recombinant portion of the Y chromosome and the mtDNA, under
normal circumstances, do not undergo productive recombination. Part of
the Y chromosome can undergo recombination with the X chromosome and
within ape history the boundary has changed. Such recombinant changes in
the non-recombinant region of Y are extremely rare.
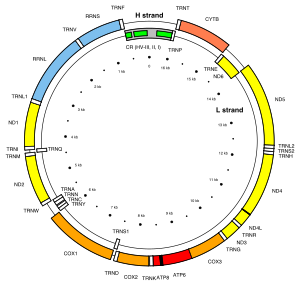
Mitochondrial DNA
Illustration of the human mitochondrial DNA with the control region (CR, in grey) containing hypervariable sequences I and II.
Mitochondrial DNA became an area of research in phylogenetics in the
late 1970s. Unlike genomic DNA, it offered advantages in that it did not
undergo recombination. The process of recombination, if frequent
enough, corrupts the ability to create parsimonious trees because of
stretches of amino acid subsititions (SNPs).
When looking between distantly related species, recombination is less
of a problem since recombination between branches from common ancestors
is prevented after true speciation occurs. When examining closely
related species, or branching within species, recombination creates a
large number of 'irrelevant SNPs' for cladistic analysis. MtDNA,
through the process of organelle division, became clonal over time; very
little, or often none, of that paternal mtDNA is passed. While
recombination may occur in mtDNA, there is little risk that it will be
passed to the next generation. As a result, mtDNA become clonal copies
of each other, except when a new mutation arises. As a result, mtDNA
does not have pitfalls of autosomal loci when studied in interbreeding
groups. Another advantage of mtDNA is that the hyper-variable regions
evolve very quickly; this shows that certain regions of mitochondrial
DNA approach neutrality. This allowed the use of mitochondrial DNA to
determine that the relative age of the human population was small,
having gone through a recent constriction at about 150,000 years ago.
Mitochondrial DNA has also been used to verify the proximity of
chimpanzees to humans relative to gorillas, and to verify the
relationship of these three species relative to the orangutan.
A
population bottleneck, as illustrated was detected by intrahuman mtDNA
phylogenetic studies; the length of the bottleneck itself is
indeterminate per mtDNA.
More recently,
the mtDNA genome has been used to estimate branching patterns in
peoples around the world, such as when the new world was settled and
how. The problem with these studies have been that they rely heavily on
mutations in the coding region. Researchers have increasingly discovered
that as humans moved from Africa's south-eastern regions, that more
mutations accumulated in the coding region than expected, and in passage
to the new world some groups are believed
to have passed from the Asian tropics to Siberia to an ancient land
region called Beringia and quickly migrated to South America. Many of
the mtDNA have far more mutations and at rarely mutated coding sites
relative to expectations of neutral mutations.
Mitochondrial DNA offers another advantage over autosomal DNA.
There are generally 2 to 4 copies of each chromosome in each cell (1 to 2
from each parent chromosome). For mtDNA there can be dozens to hundreds
in each cell. This increases the amount of each mtDNA loci by at least a
magnitude. For ancient DNA, in which the DNA is highly degraded, the
number of copies of DNA is helpful in extending and bridging short
fragments together, and decreases the amount of bone extracted from
highly valuable fossil/ancient remains. Unlike Y chromosome, both male
and female remains carry mtDNA in roughly equal quantities.
Schematic of typical animal cell, showing subcellular components. Organelles: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (9) mitochondria
Y chromosome
Illustration of human Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is found in the nucleus of normal cells (nuclear DNA).
Unlike mtDNA, it has mutations in the non-recombinant portion (NRY) of
the chromosome spaced widely apart, so far apart that finding the
mutations on new Y chromosomes is labor-intensive compared with mtDNA.
Many studies rely on tandem repeats; however, tandem repeats can expand
and retract rapidly and in some predictable patterns. The Y chromosome
only tracks male lines, and is not found in females, whereas mtDNA can
be traced in males even though they fail to pass on mtDNA. In addition,
it has been estimated that effective male populations in the
prehistoric period were typically two females per male, and recent
studies show that cultural hegemony plays a large role in the passage of Y. This has created discordance between males and females for the Time to the Most Recent Common Ancestor
(TMRCA). The estimates for Y TMRCA range from 1/4 to less than 1/2 that
of mtDNA TMRCA. It is unclear whether this is due to high
male-to-female ratios in the past coupled with repeat migrations from
Africa, as a result of mutational rate change, or as some have even
proposed that females of the LCA between chimps and humans continued to
pass DNA millions after males ceased to pass DNA. At present the best
evidence suggests that in migration the male to female ratio in humans
may have declined, causing a trimming of Y diversity on multiple
occasions within and outside of Africa.
Diagram of human X chromosome showing genetic map
For short-range molecular phylogenetics and molecular clocking, the Y
chromosome is highly effective and creates a second perspective. One
argument that arose was that the Maori
by mtDNA appear to have migrated from Eastern China or Taiwan, by Y
chromosome from the Papua New Guinea region. When HLA haplotypes were
used to evaluate the two hypotheses, it was uncovered that both were
right, that the Maori were an admixed population. Such admixtures appear
to be common in the human population and thus the use of a single
haploid loci can give a biased perspective.
X-linked studies
The
X-chromosome is also a form of nuclear DNA. Since it is found as 1 copy
in males and 2 non-identical chromosomes in females it has a ploidy
of 1.5. However, in humans the effective ploidy is somewhat higher,
~1.7, as females in the breeding population have tended to outnumber
males by 2:1 during a large portion of human prehistory. Like mtDNA,
X-linked DNA tends to over emphasize female population history much more
than male. There have been several studies of loci on X chromosome, in
total 20 sites have been examined. These include PDHA1, PDHA1, Xq21.3,
Xq13.3, Zfx,
Fix, Il2rg, Plp, Gk, Ids, Alas2, Rrm2p4, AmeIX, Tnfsf5, Licam, and
Msn. The time to most recent common ancestor (TMRCA) ranges from fixed
to ~1.8 million years, with a median around 700ky. These studies roughly
plot to the expected fixation distribution of alleles, given linkage
disequilibrium between adjacent sites. For some alleles the point of
origin is elusive, for others, the point of origin points toward
Sub-Saharan Africa. There are some distinctions within SSA that suggest a
smaller region, but there is not adequate enough sample size and
coverage to define a place of most recent common ancestor. The TMRCA is
consistent with and extends the bottleneck implied by mtDNA,
confidently to about 500,000 years.
Autosomal loci
Diagram of human karyotype
Ancient DNA sequencing
Krings
Neandertal mtDNA have been sequenced, and sequence similarity indicates
an equally recent origin from a small population on the Neanderthal
branch of late hominids. The MCR1 gene has also been sequenced but the
results are controversial, with one study claiming that contamination
issues cannot be resolved from human Neandertal similarities.
Critically, however, no DNA sequence has been obtained from Homo
erectus, Homo floriensis, or any of the other late hominids. Some of the
ancient sequences obtained have highly probable errors, and proper
control to avoid contamination.
Comparison of differences between human and Neanderthal mtDNA
Causes of errors
The
molecular phylogenetics is based on quantification substitutions and
then comparing sequence with other species, there are several points in
the process which create errors. The first and greatest challenge is
finding "anchors" that allow the research to calibrate the system. In
this example, there are 10 mutations between chimp and humans, but the
researcher has no known fossils that are agreeably ancestral to both but
not ancestral to the next species in the tree, gorilla. However, there
are fossils believed to be ancestral to Orangutans and Humans, from
about 14 million years ago. So that the researcher can use Orangutan and
Human comparison and comes up with a difference of 24. Using this he
can estimate (24/(14*2, the "2" is for the length of the branch to Human
(14my) and the branch to Orangutan (14 my) from their last common
ancestor (LCA). The mutation rate at 0.857 for a stretch of sequence.
Mutation rates are given, however, as rate per nucleotide(nt)-site, so
if the sequence were say 100 nt in length that rate would be 0.00857/nt
per million years. Ten mutations*100nt/(0.00857*2) = 5.8 million years.
Problem of calibration
There
are several problems not seen in the above. First, mutations occur as
random events. Second, the chance that any site in the genome varies is
different from the next site, a very good example is the codons for
amino acids, the first two nt in a codon may mutate at 1 per billion
years, but the third nt may mutate 1 per million years. Unless scientist
study the sequence of a great many animals, particularly those close to
the branch being examined, they generally do not know what the rate of
mutation for a given site. Mutations do occur at 1st and 2nd positions
of codons, but in most cases these mutations are under negative
selection and so are removed from the population over small periods of
time. In defining the rate of evolution in the anchor one has the
problem that random mutation creates. For example, a rate of .005 or
.010 can also explain 24 mutations according to the binomial probability distribution.
Some of the mutations that did occur between the two have reverted,
hiding an initially higher rate. Selection may play into this, a rare
mutation may be selective at point X in time, but later climate may
change or the species migrates and it is not longer selective, and
pressure exerted on new mutations that revert the change, and sometimes
the reversion of a nt can occur, the greater the distance between two
species the more likely this is going to occur. In addition, from that
ancestral species both species may randomly mutate a site to the same
nucleotide. Many times this can be resolved by obtaining DNA samples
from species in the branches, creating a parsimonious tree in which the
order of mutation can be deduced, creating branch-length diagram. This
diagram will then produce a more accurate estimate of mutations between
two species. Statistically one can assign variance based on the problem
of randomness, back mutations, and parallel mutations (homoplasies) in
creating an error range.
There is another problem in calibration however that has defied
statistical analysis. There is a true/false designation of a fossil to a
least common ancestor. In reality the odds of having the least common
ancestor of two extant species as an anchor is low, often that fossil
already lies in one branch (underestimating the age), lies in a third
branch (underestimating the age) or in the case of being within the LCA
species, may have been millions of years older than the branch. To date
the only way to assess this variance is to apply molecular phylogenetics
on species claimed to be branch points. This only, however identifies
the 'outlying' anchor points. And since it is more likely the more
abundant fossils are younger than the branch point the outlying fossil
may simply be a rare older representative. These unknowns create
uncertainty that is difficult to quantify, and often not attempted.
Recent papers have been able to estimate, roughly, variance. The
general trend as new fossils are discovered, is that the older fossils
underestimated the age of the branch point. In addition to this dating
of fossils has had a history of errors and there have been many revised
datings. The age assigned by researchers to some major branch points
have almost doubled in age over the last 30 years. An excellent example
of this is the debate over LM3 (Mungo lake 3) in Australia. Originally
it was dated to around 30 ky by carbon dating, carbon dating has
problems, however, for sampled over 20ky in age, and severe problems for
samples around 30ky in age. Another study looked at the fossil and
estimated the age to be 62 ky in age.
At the point one has an estimation of mutation rate, given the
above there must be two sources of variance that need to be
cross-multiplied to generate an overall variance. This is infrequently
done in the literature.
Problems in estimating TMRCA
Time to most recent common ancestor (TMRCA) combines the errors in calibration with errors in determining the age of a local branch.
History
Protein era
Structure of human hemoglobin. Hemoglobins from dozens of animals and even plants were sequenced in the 1960s and early 1970s
With DNA newly discovered as the genetic material, in the early 1960s protein sequencing was beginning to take off. Protein sequencing began on cytochrome C and Hemoglobin. Gerhard Braunitzer sequenced hemoglobin and myoglobin, in total more than hundreds of sequences from wide ranging species were done. In 1967 A.C. Wilson began to promote the idea of a "molecular clock". By 1969 molecular clocking was applied to anthropoid evolution and V. Sarich and A.C. Wilson found that albumin and hemoglobin has comparable rates of evolution, indicating chimps and humans split about 4 to 5 million years ago. In 1970, Louis Leakey confronted this conclusion with arguing for improper calibration of molecular clocks. By 1975 protein sequencing and comparative serology combined were used to propose that humans closest living relative (as a species) was the chimpanzee. In hindsight, the last common ancestor (LCA) from humans and chimps appears to older than the Sarich and Wilson
estimate, but not as old as Leakey claimed, either. However, Leakey was
correct in the divergence of old and new world monkeys, the value
Sarich and wilson used was a significant underestimate. This error in
prediction capability highlights a common theme.
DNA era
Restriction
fragment length polymorphisms studies the cutting of mtDNA into
fragments, Later the focus of PCR would be on the D 'control'-loop, at
the top of the circle
RLFP and DNA hybridization
In 1979, W.M.Brown and Wilson began looking at the evolution of mitochodrial DNA in animals, and found they were evolving rapidly. The technique they used was restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP),
which was more affordable at the time compared to sequencing. In 1980,
W.M. Brown, looking at the relative variation between human and other
species, recognized there was a recent constriction (180,000 years ago) in the human population.
A year later Brown and Wilson were looking at RFLP fragments and
determined the human population expanded more recently than other ape
populations. In 1984 the first DNA sequence from an extinct animal was done.
Sibley and Ahlquist apply DNA-DNA hybridization technology to
anthropoid phylogeny, and see pan/human split closer than gorilla/pan or
gorilla/human split, a highly controversial claim. However, in 1987 they were able to support their claim.
In 1987, Cann, Stoneking and Wilson suggest, by RFLP analysis of human
mitochondrial DNA, that humans evolved from a constrict in Africa of a
single female in a small population, ~10,00 individuals, 200,000 years
ago.
Era of PCR
PCR could rapidly amplify DNA from one molecule to billions, allowing sequencing from human hairs or ancient DNA.
In 1987, PCR-amplification of mtDNA was first used to determine sequences.
In 1991 Vigilante et al. published the seminal work on mtDNA phylogeny
implicating sub-saharan Africa as the place of humans most recent common
ancestors for all mtDNAs.
The war between out-of-Africa and multiregionalism, already simmering
with the critiques of Allan Templeton, soon escalated with the
paleoanthropologist, like Milford Wolpoff, getting involved.
In 1995, F. Ayala published his critical Science article "The Myth about Eve", which relied on HLA-DR sequence.
At the time, however Ayala was not aware of rapid evolution of HLA loci
via recombinatory process. In 1996, Parham and Ohta published their
finds on the rapid evolution of HLA by short-distance recombination
('gene conversion' or 'abortive recombination'), weakening Ayala's claim
(Parham had actually written a review a year earlier, but this had gone
unnoticed). A stream of papers would follow from both sides, many with highly flawed methods and sampling. One of the more interesting
was Harris and Hey, 1998 which showed that the TMCRA (time to most
recent common ancestor) for the PDHA1 gene was well in excess of 1
million years. Given a ploidy
at this locus of 1.5 (3 fold higher than mtDNA) the TMRCA was more than
double the expectation. While this falls into the 'fixation curve' of
1.5 ploidy (averaging 2 female and 1 male) the suggested age of 1.8 my
is close a significantly deviant p-value for the population size,
possibly indicating that the human population shrank or split off of
another population. Oddly, the next X-linked loci they examined, Factor IX, showed a TMRCA of less than 300,000 years.
Cross-linked DNA extracted from the 4,000-year-old liver of an Ancient Egyptian priest called Nekht-Ankh
Ancient DNA
Ancient
DNA sequencing had been conducted on a limited scale up to the late
1990s when the staff at the Max Planck Institute shocked the
anthropology world by sequencing DNA from an estimated 40,000-year-old Neanderthal.
The result of that experiment is that the differences between humans
living in Europe, many of which were derived from haplogroup H (CRS),
Neandertals branched from humans more than 300,000 years before
haplogroup H reached Europe. While the mtDNA and other studies continued
to support a unique recent African origin, this new study basically
answered critiques from the Neanderthal side.
Genomic sequencing
Significant
progress has been made in genomic sequencing since Ingman and colleague
published their finding on mitochondrial genome.
Several papers on genomic mtDNA have been published; there is
considerable variability in the rate of evolution, and rate variation
and selection are evident at many sites. In 2007, Gonder et al. proposed
that a core population of humans, with greatest level of diversity and
lowest selection, once lived in the region of Tanzania and proximal
parts of southern Africa, since humans left this part of Africa,
mitochondria have been selectively evolving to new regions.
Critical progress
Critical in the history of molecular anthropology:
- That molecular phylogenetics could compete with comparative anthropology for determining the proximity of species to humans.
- Wilson and King realized in 1975, that while there was equity between the level of molecular evolution branching from chimp to human to putative LCA, that there was an inequity in morphological evolution. Comparative morphology based on fossils could be biased by different rates of change.
- Realization that in DNA there are multiple independent comparisons. Two techniques, mtDNA and hybridization converge on a single answer, chimps as a species are most closely related to humans.
- The ability to resolve population sizes based on the 2N rule, proposed by Kimura in the 1950s. To use that information to compare relative sizes of population and come to a conclusion about abundance that contrasted observations based on the paleontological record. While human fossils in the early and middle stone age are far more abundant than chimpanzee or gorilla, there are few unambiguous chimpanzee or gorilla fossils from the same period.
Loci that have been used in molecular phylogenetics:
- Cytochrome C
- Serum albumin
- Hemoglobin - Braunitizer, 1960s, Harding et al. 1997
- Mitochondrial D-loop - Wilson group, 1980, 1981, 1984, 1987, 1989, 1991(posthumously) - TMRCA about 170 kya.
- Y-chromosome
- HLA-DR - Ayala 1995 - TMRCA for locus is 60 million years.
- CD4 (Intron) - Tishkoff, 1996 - most of the diversity is in Africa.
- PDHA1 (X-linked) Harris and Hey - TMRCA for locus greater than 1.5 million years.
Xlinked loci: PDHA1, Xq21.3, Xq13.3, Zfx, Fix, Il2rg, Plp, Gk, Ids, Alas2, Rrm2p4, AmeIX, Tnfsf5, Licam, and Msn
Autosomal:Numerous.