Phonons play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter, like thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics.
The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name phonon comes from the Greek word φωνή (phonē), which translates to sound or voice because long-wavelength phonons give rise to sound. The name is based on the word photon.
Shorter-wavelength higher-frequency phonons are responsible for the majority of the thermal capacity of solids.
The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name phonon comes from the Greek word φωνή (phonē), which translates to sound or voice because long-wavelength phonons give rise to sound. The name is based on the word photon.
Shorter-wavelength higher-frequency phonons are responsible for the majority of the thermal capacity of solids.
Definition
A phonon is the quantum mechanical description of an elementary vibrational motion in which a lattice of atoms or molecules uniformly oscillates at a single frequency. In classical mechanics this designates a normal mode of vibration. Normal modes are important because any arbitrary lattice vibration can be considered to be a superposition of these elementary vibration modes. While normal modes are wave-like phenomena in classical mechanics, phonons have particle-like properties too, in a way related to the wave–particle duality of quantum mechanics.
Lattice dynamics
The equations in this section do not use axioms of quantum mechanics but instead use relations for which there exists a direct correspondence in classical mechanics.
For example: a rigid regular, crystalline (not amorphous), lattice is composed of N particles. These particles may be atoms or molecules. N is a large number, say of the order of 1023, or on the order of Avogadro's number for a typical sample of a solid. Since the lattice is rigid, the atoms must be exerting forces on one another to keep each atom near its equilibrium position. These forces may be Van der Waals forces, covalent bonds, electrostatic attractions, and others, all of which are ultimately due to the electric force. Magnetic and gravitational forces are generally negligible. The forces between each pair of atoms may be characterized by a potential energy function V
that depends on the distance of separation of the atoms. The potential
energy of the entire lattice is the sum of all pairwise potential
energies multiplied by a factor of 1/2 to avoid double counting:
where ri is the position of the ith atom, and V is the potential energy between two atoms.
It is difficult to solve this many-body problem explicitly in either classical or quantum mechanics. In order to simplify the task, two important approximations
are usually imposed. First, the sum is only performed over neighboring
atoms. Although the electric forces in real solids extend to infinity,
this approximation is still valid because the fields produced by distant
atoms are effectively screened. Secondly, the potentials V are treated as harmonic potentials. This is permissible as long as the atoms remain close to their equilibrium positions. Formally, this is accomplished by Taylor expanding V about its equilibrium value to quadratic order, giving V proportional to the displacement x2 and the elastic force simply proportional to x. The error in ignoring higher order terms remains small if x remains close to the equilibrium position.
The resulting lattice may be visualized as a system of balls
connected by springs. The following figure shows a cubic lattice, which
is a good model for many types of crystalline solid. Other lattices
include a linear chain, which is a very simple lattice which we will
shortly use for modeling phonons.
The potential energy of the lattice may now be written as
Here, ω is the natural frequency of the harmonic potentials, which are assumed to be the same since the lattice is regular. Ri is the position coordinate of the ith atom, which we now measure from its equilibrium position. The sum over nearest neighbors is denoted (nn).
Lattice waves
Phonon propagating through a square lattice (atom displacements greatly exaggerated)
Due to the connections between atoms, the displacement of one or more
atoms from their equilibrium positions gives rise to a set of vibration
waves propagating through the lattice. One such wave is shown in the figure to the right. The amplitude of the wave is given by the displacements of the atoms from their equilibrium positions. The wavelength λ is marked.
There is a minimum possible wavelength, given by twice the equilibrium separation a between atoms. Any wavelength shorter than this can be mapped onto a wavelength longer than 2a, due to the periodicity of the lattice. This can be thought as one consequence of Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, the lattice points are viewed as the "sampling points" of a continuous wave.
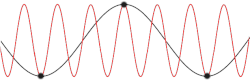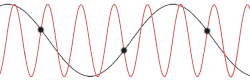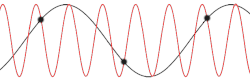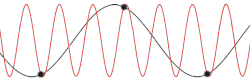
Not every possible lattice vibration has a well-defined wavelength and frequency. However, the normal modes do possess well-defined wavelengths and frequencies.
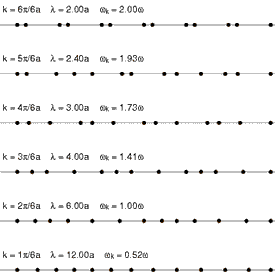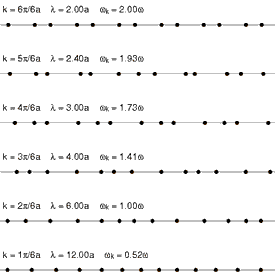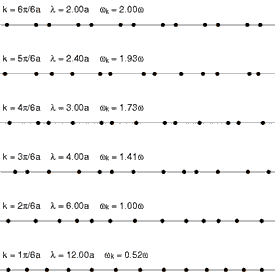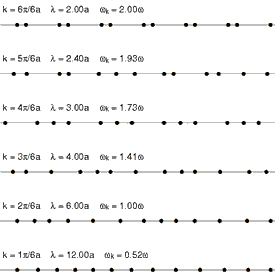
One-dimensional lattice
Animation
showing the first 6 normal modes of a one-dimensional lattice: a linear
chain of particles. The shortest wavelength is at top, with
progressively longer wavelengths below. In the lowest lines the motion
of the waves to the right can be seen.
In order to simplify the analysis needed for a 3-dimensional lattice
of atoms, it is convenient to model a 1-dimensional lattice or linear
chain. This model is complex enough to display the salient features of
phonons.
Classical treatment
The
forces between the atoms are assumed to be linear and
nearest-neighbour, and they are represented by an elastic spring. Each
atom is assumed to be a point particle and the nucleus and electrons
move in step (adiabatic approximation):
···o++++++o++++++o++++++o++++++o++++++o++++++o++++++o++++++o++++++o···
→→ → →→→
where n labels the nth atom out of a total of N, a is the distance between atoms when the chain is in equilibrium, and un the displacement of the nth atom from its equilibrium position.
If C is the elastic constant of the spring and m the mass of the atom, then the equation of motion of the nth atom is
This is a set of coupled equations. Since the solutions are expected to be oscillatory, new coordinates are defined by a discrete Fourier transform, in order to decouple them.
Put
Here, na corresponds and devolves to the continuous variable x of scalar field theory. The Qk are known as the normal coordinates, continuum field modes φk. Substitution into the equation of motion produces the following decoupled equations (this requires a significant manipulation using the orthonormality and completeness relations of the discrete Fourier transform
These are the equations for harmonic oscillators which have the solution
Each normal coordinate Qk represents an independent vibrational mode of the lattice with wavenumber k which is known as a normal mode.
The second equation, for ωk, is known as the dispersion relation between the angular frequency and the wavenumber. In the continuum limit, a→0, N→∞, with Na held fixed, un → φ(x), a scalar field, and . This amounts to free scalar classical field theory.
Quantum treatment
A one-dimensional quantum mechanical harmonic chain consists of N
identical atoms. This is the simplest quantum mechanical model of a
lattice that allows phonons to arise from it. The formalism for this
model is readily generalizable to two and three dimensions.
In some contrast to the previous section, the positions of the masses are not denoted by ui, but, instead, by x1, x2…, as measured from their equilibrium positions (i.e. xi = 0 if particle i is at its equilibrium position.) In two or more dimensions, the xi are vector quantities. The Hamiltonian for this system is
where m is the mass of each atom (assuming it is equal for all), and xi and pi are the position and momentum operators, respectively, for the ith
atom and the sum is made over the nearest neighbors (nn). However one
expects that in a lattice there could also appear waves that behave like
particles. It is customary to deal with waves in Fourier space which uses normal modes of the wavevector as variables instead coordinates of particles. The number of normal modes is same as the number of particles. However, the Fourier space is very useful given the periodicity of the system.
A set of N "normal coordinates" Qk may be introduced, defined as the discrete Fourier transforms of the xk and N "conjugate momenta" Πk defined as the Fourier transforms of the pk:
This choice retains the desired commutation relations in either real space or wavevector space
From the general result
The potential energy term is
where
The Hamiltonian may be written in wavevector space as
The couplings between the position variables have been transformed away; if the Q and Π were Hermitian (which they are not), the transformed Hamiltonian would describe N uncoupled harmonic oscillators.
The form of the quantization depends on the choice of boundary conditions; for simplicity, periodic boundary conditions are imposed, defining the (N + 1)th
atom as equivalent to the first atom. Physically, this corresponds to
joining the chain at its ends. The resulting quantization is
The upper bound to n comes from the minimum wavelength, which is twice the lattice spacing a, as discussed above.
The harmonic oscillator eigenvalues or energy levels for the mode ωk are:
The levels are evenly spaced at:
An exact amount of energy ħω must be supplied to the harmonic oscillator lattice to push it to the next energy level. In comparison to the photon case when the electromagnetic field is quantized, the quantum of vibrational energy is called a phonon.
All quantum systems show wavelike and particlelike properties
simultaneously. The particle-like properties of the phonon are best
understood using the methods of second quantization and operator techniques described later.
Three-dimensional lattice
This may be generalized to a three-dimensional lattice. The wavenumber k is replaced by a three-dimensional wavevector k. Furthermore, each k is now associated with three normal coordinates.
The new indices s = 1, 2, 3 label the polarization
of the phonons. In the one-dimensional model, the atoms were restricted
to moving along the line, so the phonons corresponded to longitudinal waves.
In three dimensions, vibration is not restricted to the direction of
propagation, and can also occur in the perpendicular planes, like transverse waves.
This gives rise to the additional normal coordinates, which, as the
form of the Hamiltonian indicates, we may view as independent species of
phonons.
Dispersion relation
Dispersion curves in linear diatomic chain
Optical and acoustic vibrations in linear diatomic chain.
Dispersion relation ω = ω(k) for some waves corresponding to lattice vibrations in GaAs.
For a one-dimensional alternating array of two types of ion or atom of mass m1, m2 repeated periodically at a distance a, connected by springs of spring constant K, two modes of vibration result:
where k is the wavevector of the vibration related to its wavelength by
.
The connection between frequency and wavevector, ω = ω(k), is known as a dispersion relation. The plus sign results in the so-called optical mode, and the minus sign to the acoustic mode. In the optical mode two adjacent different atoms move against each other, while in the acoustic mode they move together.
The speed of propagation of an acoustic phonon, which is also the speed of sound in the lattice, is given by the slope of the acoustic dispersion relation, ∂ωk/∂k (see group velocity.) At low values of k (i.e. long wavelengths), the dispersion relation is almost linear, and the speed of sound is approximately ωa,
independent of the phonon frequency. As a result, packets of phonons
with different (but long) wavelengths can propagate for large distances
across the lattice without breaking apart. This is the reason that sound
propagates through solids without significant distortion. This behavior
fails at large values of k, i.e. short wavelengths, due to the microscopic details of the lattice.
For a crystal that has at least two atoms in its primitive cell, the dispersion relations
exhibit two types of phonons, namely, optical and acoustic modes
corresponding to the upper blue and lower red curve in the diagram,
respectively. The vertical axis is the energy or frequency of phonon,
while the horizontal axis is the wavevector. The boundaries at −π/a and π/a are those of the first Brillouin zone. A crystal with N ≥ 2 different atoms in the primitive cell exhibits three acoustic modes: one longitudinal acoustic mode and two transverse acoustic modes. The number of optical modes is 3N – 3. The lower figure shows the dispersion relations for several phonon modes in GaAs as a function of wavevector k in the principal directions of its Brillouin zone.
Many phonon dispersion curves have been measured by neutron scattering.
The physics of sound in fluids
differs from the physics of sound in solids, although both are density
waves: sound waves in fluids only have longitudinal components, whereas
sound waves in solids have longitudinal and transverse components. This
is because fluids can't support shear stresses (but see viscoelastic fluids, which only apply to high frequencies).
Interpretation of phonons using second quantization techniques
In fact, the above-derived Hamiltonian looks like the classical Hamiltonian function, but if it is interpreted as an operator, then it describes a quantum field theory of non-interacting bosons.
The energy spectrum of this Hamiltonian is easily obtained by the method of ladder operators, similar to the quantum harmonic oscillator problem. We introduce a set of ladder operators defined by:
By direct insertion on the Hamiltonian, it is readily verified that
As with the quantum harmonic oscillator, one can show that bk† and bk respectively create and destroy one excitation of energy ħωk. These excitations are phonons.
Two important properties of phonons may be deduced. Firstly, phonons are bosons, since any number of identical excitations can be created by repeated application of the creation operator bk†.
Secondly, each phonon is a "collective mode" caused by the motion of
every atom in the lattice. This may be seen from the fact that the
ladder operators contain sums over the position and momentum operators
of every atom.
It is not a priori obvious that these excitations generated by the b operators are literally waves of lattice displacement, but one may convince oneself of this by calculating the position–position correlation function. Let |k⟩ denote a state with a single quantum of mode k excited, i.e.
One can show that, for any two atoms j and l,
which has the form of a lattice wave with frequency ωk and wavenumber k.
In three dimensions the Hamiltonian has the form
Acoustic and optical phonons
Solids with more than one atom in the smallest unit cell, exhibit two types of phonons: acoustic phonons and optical phonons.
Acoustic phonons are coherent movements of atoms of the
lattice out of their equilibrium positions. If the displacement is in
the direction of propagation, then in some areas the atoms will be
closer, in others farther apart, as in a sound wave in air (hence the
name acoustic). Displacement perpendicular to the propagation direction
is comparable to waves on a string. If the wavelength of acoustic
phonons goes to infinity, this corresponds to a simple displacement of
the whole crystal, and this costs zero deformation energy. Acoustic
phonons exhibit a linear relationship between frequency and phonon
wavevector for long wavelengths. The frequencies of acoustic phonons
tend to zero with longer wavelength. Longitudinal and transverse
acoustic phonons are often abbreviated as LA and TA phonons,
respectively.
Optical phonons are out-of-phase movements of the atoms in
the lattice, one atom moving to the left, and its neighbor to the
right. This occurs if the lattice basis consists of two or more atoms.
They are called optical because in ionic crystals, like sodium chloride, they are excited by infrared radiation.
The electric field of the light will move every positive sodium ion in
the direction of the field, and every negative chloride ion in the other
direction, sending the crystal vibrating.
Optical phonons have a non-zero frequency at the Brillouin zone
center and show no dispersion near that long wavelength limit. This is
because they correspond to a mode of vibration where positive and
negative ions at adjacent lattice sites swing against each other,
creating a time-varying electrical dipole moment. Optical phonons that interact in this way with light are called infrared active. Optical phonons that are Raman active can also interact indirectly with light, through Raman scattering.
Optical phonons are often abbreviated as LO and TO phonons, for the
longitudinal and transverse modes respectively; the splitting between LO
and TO frequencies is often described accurately by the Lyddane–Sachs–Teller relation.
When measuring optical phonon energy by experiment, optical phonon frequencies are sometimes given in spectroscopic wavenumber notation, where the symbol ω represents ordinary frequency (not angular frequency), and is expressed in units of cm−1. The value is obtained by dividing the frequency by the speed of light in vacuum. In other words, the frequency in cm−1 units corresponds to the inverse of the wavelength of a photon in vacuum, that has the same frequency as the measured phonon. The cm−1 is a unit of energy used frequently in the dispersion relations of both acoustic and optical phonons, see units of energy for more details and uses.
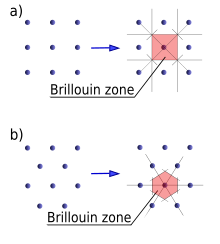
Crystal momentum
k-vectors
exceeding the first Brillouin zone (red) do not carry any more
information than their counterparts (black) in the first Brillouin zone.
By analogy to photons and matter waves, phonons have been treated with wavevector k as though it has a momentum ħk, however, this is not strictly correct, because ħk is not actually a physical momentum; it is called the crystal momentum or pseudomomentum. This is because k is only determined up to addition of constant vectors (the reciprocal lattice vectors and integer multiples thereof). For example, in the one-dimensional model, the normal coordinates Q and Π are defined so that
where
for any integer n. A phonon with wavenumber k is thus equivalent to an infinite family of phonons with wavenumbers k ± 2π/a, k ± 4π/a,
and so forth. Physically, the reciprocal lattice vectors act as
additional chunks of momentum which the lattice can impart to the
phonon. Bloch electrons obey a similar set of restrictions.
Brillouin zones, (a) in a square lattice, and (b) in a hexagonal lattice
It is usually convenient to consider phonon wavevectors k which have the smallest magnitude |k| in their "family". The set of all such wavevectors defines the first Brillouin zone. Additional Brillouin zones may be defined as copies of the first zone, shifted by some reciprocal lattice vector.
Thermodynamics
The thermodynamic
properties of a solid are directly related to its phonon structure. The
entire set of all possible phonons that are described by the above
phonon dispersion relations combine in what is known as the phonon density of states which determines the heat capacity of a crystal.
At absolute zero temperature, a crystal lattice lies in its ground state, and contains no phonons. A lattice at a nonzero temperature has an energy that is not constant, but fluctuates randomly about some mean value.
These energy fluctuations are caused by random lattice vibrations,
which can be viewed as a gas of phonons. (The random motion of the atoms
in the lattice is what we usually think of as heat.) Because these
phonons are generated by the temperature of the lattice, they are
sometimes designated thermal phonons.
Unlike the atoms which make up an ordinary gas, thermal phonons
can be created and destroyed by random energy fluctuations. In the
language of statistical mechanics this means that the chemical potential
for adding a phonon is zero. This behavior is an extension of the
harmonic potential, mentioned earlier, into the anharmonic regime. The
behavior of thermal phonons is similar to the photon gas produced by an electromagnetic cavity,
wherein photons may be emitted or absorbed by the cavity walls. This
similarity is not coincidental, for it turns out that the
electromagnetic field behaves like a set of harmonic oscillators; see Black-body radiation. Both gases obey the Bose–Einstein statistics:
in thermal equilibrium and within the harmonic regime, the probability
of finding phonons (or photons) in a given state with a given angular
frequency is:
where ωk,s is the frequency of the phonons (or photons) in the state, kB is Boltzmann's constant, and T is the temperature.
Heat flow in nanometer-wide gaps
The idea of quantum tunneling applied to phonons produces the idea of phonon tunneling, where across nanometer-wide gaps, heat can transfer between materials from phonon that "tunnel" between the two materials. The type of heat transfer works between distances too large for conduction to occur but too small for radiation to occur.
Operator formalism
The phonon Hamiltonian is given by
In terms of the operators, these are given by
Here, in expressing the Hamiltonian in operator formalism, we have not taken into account the 1/2ħωq term, since if we take an infinite lattice or, for that matter a continuum, the 1/2ħωq terms will add up giving an infinity. Hence, it is "renormalized" by putting the factor of 1/2ħωq to 0 arguing that the difference in energy is what we measure and not the absolute value of it. Hence, the 1/2ħωq factor is absent in the operator formalised expression for the Hamiltonian.
The ground state also called the "vacuum state" is the state
composed of no phonons. Hence, the energy of the ground state is 0.
When, a system is in state |n1n2n3…⟩, we say there are nα phonons of type α. The nα are called the occupation number of the phonons. Energy of a single phonon of type α being ħωq, the total energy of a general phonon system is given by n1ħω1 + n2ħω2 +…. In other words, the phonons are non-interacting. The action of creation and annihilation operators are given by
and,
i.e. aα† creates a phonon of type α while aα annihilates. Hence, they are respectively the creation and annihilation operator for phonons. Analogous to the quantum harmonic oscillator case, we can define particle number operator as
The number operator commutes with a string of products of the creation and annihilation operators if, the number of a are equal to number of a†.
Nonlinearity
As well as photons, phonons can interact via parametric down conversion and form squeezed coherent states.
Predicted properties
Even though phonons are often used as a quasiparticle, some popular research has shown that phonons and rotons may indeed have some kind of mass and be affected by gravity as standard particles are. In particular, phonons are predicted to have a kind of negative mass and negative gravity.
This can be shown in how phonons are known to travel faster in denser
materials. Because the part of a material pointing towards a
gravitational source is closer to the object, it becomes denser on that
end. From this, it is predicted that phonons would deflect away as it
detects the difference in densities, exhibiting the qualities of a
negative gravitational field. Although the effect would be too small to measure, it is possible that future equipment could lead to successful results.
Phonons have also been predicted play a key role in superconductivity in materials and the prediction of superconductive compounds.










![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\left[x_{l},p_{m}\right]&=i\hbar \delta _{l,m}\\\left[Q_{k},\Pi _{k'}\right]&={\frac {1}{N}}\sum _{l,m}e^{ikal}e^{-ik'am}\left[x_{l},p_{m}\right]\\&={\frac {i\hbar }{N}}\sum _{l}e^{ial\left(k-k'\right)}=i\hbar \delta _{k,k'}\\\left[Q_{k},Q_{k'}\right]&=\left[\Pi _{k},\Pi _{k'}\right]=0\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1829b425a1c6cb72b77a83ed8f279de7279fa4db)