The thermoelectric effect refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric potential creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (converting temperature to current), Peltier effect (converting current to temperature), and Thomson effect
(conductor heating/cooling). While all materials have a nonzero
thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful.
However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong
thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) could be used in
applications including power generation and refrigeration. A commonly used thermoelectric material in such applications is bismuth telluride (Bi
2Te
3).
Thermoelectric materials are used in thermoelectric systems for cooling or heating in niche applications, and are being studied as a way to regenerate electricity from waste heat.
2Te
3).
Thermoelectric materials are used in thermoelectric systems for cooling or heating in niche applications, and are being studied as a way to regenerate electricity from waste heat.
Materials selection criteria
The usefulness of a material in thermoelectric systems is determined by the two factors device efficiency and power factor. These are determined by the material's electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, Seebeck coefficient and behavior under changing temperatures.
Device efficiency
The efficiency of a thermoelectric device for electricity generation is given by , defined as
The ability of a given material to efficiently produce thermoelectric power is related to its dimensionless figure of merit given by
- ,
which depends on the Seebeck coefficient S, thermal conductivity κ, electrical conductivity σ, and temperature T.
In an actual thermoelectric device, two materials are used. The maximum efficiency is then given by
where is the temperature at the hot junction and is the temperature at the surface being cooled.
is the modified dimensionless figure of merit, which takes into
consideration the thermoelectric capacity of both thermoelectric
materials being used in the device and, after geometrical optimization
regarding the legs sections, is defined as
where is the electrical resistivity,
is the average temperature between the hot and cold surfaces and the
subscripts n and p denote properties related to the n- and p-type
semiconducting thermoelectric materials, respectively. Since
thermoelectric devices are heat engines, their efficiency is limited by
the Carnot efficiency, hence the and terms in . Regardless, the coefficient of performance
of current commercial thermoelectric refrigerators ranges from 0.3 to
0.6, one-sixth the value of traditional vapor-compression refrigerators.
Power factor
To determine the usefulness of a material in a thermoelectric generator or a thermoelectric cooler the power factor is calculated by its Seebeck coefficient and its electrical conductivity under a given temperature difference:
where S is the Seebeck coefficient, and σ is the electrical conductivity.
Materials with a high power factor are able to 'generate' more
energy (move more heat or extract more energy from that temperature
difference) in a space-constrained application, but are not necessarily
more efficient in generating this energy.
Aspects of materials choice
For
good efficiency, materials with high electrical conductivity, low
thermal conductivity and high Seebeck coefficient are needed.
State density: metals vs semiconductors
The band structure of semiconductors offers better thermoelectric effects than the band structure of metals.
The Fermi energy is below the conduction band
causing the state density to be asymmetric around the Fermi energy.
Therefore, the average electron energy of the conduction band is higher
than the Fermi energy, making the system conducive for charge motion
into a lower energy state. By contrast, the Fermi energy lies in the
conduction band in metals. This makes the state density symmetric about
the Fermi energy so that the average conduction electron energy is close
to the Fermi energy, reducing the forces pushing for charge transport.
Therefore, semiconductors are ideal thermoelectric materials. Due to the small Seebeck coefficient metals have a very limited performance and the main materials of interest are Semiconductors.
Conductivity
In the efficiency equations above, thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity compete.
The thermal conductivity κ has mainly two components:
- κ = κ electron + κ phonon
According to the Wiedemann–Franz law, the higher the electrical conductivity, the higher κ electron becomes.
Thus in metals the ratio of thermal to electrical conductivity is about
fixed, as the electron part dominates.
In semiconductors, the phonon part is important and can not be
neglected. It reduces the efficiency. For good efficiency a low ratio of
κ phonon / κ electron is desired.
Therefore, it is necessary to minimize κ phonon and keep the electrical conductivity high. Thus semiconductors should be highly doped.
G. A. Slack proposed that in order to optimize the figure of merit, phonons, which are responsible for thermal conductivity must experience the material as a glass (experiencing a high degree of phonon scattering—lowering thermal conductivity) while electrons must experience it as a crystal (experiencing very little scattering—maintaining electrical conductivity). The figure of merit can be improved through the independent adjustment of these properties.
Quality Factor (detailed theory on semiconductors)
The maximum of a material is given by the material's Quality Factor:
where is the Boltzmann constant, is the reduced Planck constant, is the number of degenerated valleys for the band, is the average longitudinal elastic moduli, is the inertial effective mass, is the deformation potential coefficient, is the lattice thermal conduction, and is temperature. The figure of merit, , depends on doping concentration and temperature of the material of interest. The material Quality Factor: is useful because it allows for an intrinsic comparisons of possible efficiency between different materials. This relation shows that improving the electronic component ,
which primarily affects the Seebeck coefficient, will increase the
quality factor of a material. A large density of states can be created
due to a large number of conducting bands () or by flat bands giving a high band effective mass (). For isotropic materials . Therefore, it is desirable for thermoelectric materials to have high valley degeneracy in a very sharp band structure.
Other complex features of the electronic structure are important. These
can be partially quantified using an electronic fitness function.
Materials of interest
Strategies to improve thermoelectrics include both advanced bulk materials and the use of low-dimensional systems. Such approaches to reduce lattice thermal conductivity fall under three general material types: (1) Alloys: create point defects, vacancies, or rattling structures (heavy-ion species with large vibrational amplitudes contained within partially filled structural sites) to scatter phonons within the unit cell crystal; (2) Complex crystals: separate the phonon glass from the electron crystal using approaches similar to those for superconductors
(the region responsible for electron transport should be an electron
crystal of a high-mobility semiconductor, while the phonon glass should
ideally house disordered structures and dopants without disrupting the electron crystal, analogous to the charge reservoir in high-Tc superconductors); (3) Multiphase nanocomposites: scatter phonons at the interfaces of nanostructured materials, be they mixed composites or thin film superlattices.
Materials under consideration for thermoelectric device applications include:
Bismuth chalcogenides and their nanostructures
Materials such as Bi
2Te
3 and Bi
2Se
3 comprise some of the best performing room temperature thermoelectrics with a temperature-independent figure-of-merit, ZT, between 0.8 and 1.0. Nanostructuring these materials to produce a layered superlattice structure of alternating Bi
2Te
3 and Sb
2Te
3 layers produces a device within which there is good electrical conductivity but perpendicular to which thermal conductivity is poor. The result is an enhanced ZT (approximately 2.4 at room temperature for p-type). Note that this high value of ZT has not been independently confirmed due to the complicated demands on the growth of such superlattices and device fabrication; however the material ZT values are consistent with the performance of hot-spot coolers made out of these materials and validated at Intel Labs.
2Te
3 and Bi
2Se
3 comprise some of the best performing room temperature thermoelectrics with a temperature-independent figure-of-merit, ZT, between 0.8 and 1.0. Nanostructuring these materials to produce a layered superlattice structure of alternating Bi
2Te
3 and Sb
2Te
3 layers produces a device within which there is good electrical conductivity but perpendicular to which thermal conductivity is poor. The result is an enhanced ZT (approximately 2.4 at room temperature for p-type). Note that this high value of ZT has not been independently confirmed due to the complicated demands on the growth of such superlattices and device fabrication; however the material ZT values are consistent with the performance of hot-spot coolers made out of these materials and validated at Intel Labs.
Bismuth telluride and its solid solutions are good thermoelectric
materials at room temperature and therefore suitable for refrigeration
applications around 300 K. The Czochralski method has been used to grow
single crystalline bismuth telluride compounds. These compounds are
usually obtained with directional solidification from melt or powder
metallurgy processes. Materials produced with these methods have lower
efficiency than single crystalline ones due to the random orientation of
crystal grains, but their mechanical properties are superior and the
sensitivity to structural defects and impurities is lower due to high
optimal carrier concentration.
The required carrier concentration is obtained by choosing a
nonstoichiometric composition, which is achieved by introducing excess
bismuth or tellurium atoms to primary melt or by dopant impurities. Some
possible dopants are halogens and group IV and V atoms. Due to the small bandgap (0.16 eV) Bi2Te3
is partially degenerate and the corresponding Fermi-level should be
close to the conduction band minimum at room temperature. The size of
the band-gap means that Bi2Te3 has high intrinsic
carrier concentration. Therefore, minority carrier conduction cannot be
neglected for small stoichiometric deviations. Use of telluride
compounds is limited by the toxicity and rarity of tellurium.
Lead telluride
Heremans et al. (2008) demonstrated that thallium-doped lead telluride alloy (PbTe) achieves a ZT of 1.5 at 773 K. Later, Snyder et al. (2011) reported ZT~1.4 at 750 K in sodium-doped PbTe, and ZT~1.8 at 850 K in sodium-doped PbTe1−xSex alloy. Snyder's group determined that both thallium and sodium alter the electronic structure of the crystal increasing electronic conductivity. They also claim that selenium increases electric conductivity and reduces thermal conductivity.
In 2012 another team used lead telluride to convert 15 to 20
percent of waste heat to electricity, reaching a ZT of 2.2, which they
claimed was the highest yet reported.
Inorganic clathrates
Inorganic clathrates have the general formula AxByC46-y (type I) and AxByC136-y (type II), where B and C are group III and IV elements, respectively, which form the framework where “guest” A atoms (alkali or alkaline earth metal) are encapsulated in two different polyhedra facing each other. The differences between types I and II come from the number and size of voids present in their unit cells. Transport properties depend on the framework's properties, but tuning is possible by changing the “guest” atoms.
The most direct approach to synthesize and optimize the
thermoelectric properties of semiconducting type I clathrates is
substitutional doping, where some framework atoms are replaced with
dopant atoms. In addition, powder metallurgical and crystal growth
techniques have been used in clathrate synthesis. The structural and
chemical properties of clathrates enable the optimization of their
transport properties as a function of stoichiometry.
The structure of type II materials allows a partial filling of the
polyhedra, enabling better tuning of the electrical properties and
therefore better control of the doping level. Partially filled variants
can be synthesized as semiconducting or even insulating.
Blake et al. have predicted ZT~0.5 at room temperature and ZT~1.7 at 800 K for optimized compositions. Kuznetsov et al.
measured electrical resistance and Seebeck coefficient for three
different type I clathrates above room temperature and by estimating
high temperature thermal conductivity from the published low temperature
data they obtained ZT~0.7 at 700 K for Ba8Ga16Ge30 and ZT~0.87 at 870 K for Ba8Ga16Si30.
Magnesium group IV compounds
Mg2BIV (BIV=Si,
Ge, Sn) compounds and their solid solutions are good thermoelectric
materials and their ZT values are comparable with those of established
materials. The appropriate production methods are based on direct
co-melting, but mechanical alloying has also been used. During
synthesis, magnesium losses due to evaporation and segregation of
components (especially for Mg2Sn) need to be taken into
account. Directed crystallization methods can produce single crystalline
material. Solid solutions and doped compounds have to be annealed in
order to produce homogeneous samples - with the same properties
throughout. At 800 K, Mg2Si0.55−xSn0.4Ge0.05Bix has been reported to have a figure of merit about 1.4, the highest ever reported for these compounds.
Silicides
Higher
silicides display ZT levels with current materials. They are
mechanically and chemically strong and therefore can often be used in
harsh environments without protection. Possible fabrication methods
include Czochralski and floating zone for single crystals and hot pressing and sintering for polycrystalline.
Skutterudite thermoelectrics
Recently, skutterudite materials have sparked the interest of researchers in search of new thermoelectrics. These structures are of the form (Co,Ni,Fe)(P,Sb,As)
3 and are cubic with space group Im3. Unfilled, these materials contain voids into which low-coordination ions (usually rare-earth elements) can be inserted in order to alter thermal conductivity by producing sources for lattice phonon scattering and decrease thermal conductivity due to the lattice without reducing electrical conductivity. Such qualities make these materials exhibit PGEC behavior. However, recently Khan et al. (2017) showed that it is possible to reduce the thermal conductivity without filling these voids and enhance the figure of merit by 100%, with special architecture containing nano and micro pores.
3 and are cubic with space group Im3. Unfilled, these materials contain voids into which low-coordination ions (usually rare-earth elements) can be inserted in order to alter thermal conductivity by producing sources for lattice phonon scattering and decrease thermal conductivity due to the lattice without reducing electrical conductivity. Such qualities make these materials exhibit PGEC behavior. However, recently Khan et al. (2017) showed that it is possible to reduce the thermal conductivity without filling these voids and enhance the figure of merit by 100%, with special architecture containing nano and micro pores.
Skutterudites have the chemical formula LM4X12, where L is a rare-earth metal, M a transition metal and X a metalloid, a group V element or pnictogen whose properties lie between those of a metal and nonmetal such as phosphorus, antimony, or arsenic.
These materials could be potential in multistage thermoelectric devices
as it has been shown that they have ZT>1.0, but their properties are
not well known.
Oxide thermoelectrics
Homologous oxide compounds (such as those of the form (SrTiO
3)n(SrO)
m—the Ruddlesden-Popper phase) have layered superlattice structures that make them promising candidates for use in high-temperature thermoelectric devices. These materials exhibit low thermal conductivity perpendicular to the layers while maintaining good electronic conductivity within the layers. ZT values are relatively low (~0.34 at 1,000K), but their enhanced thermal stability, as compared to conventional high-ZT bismuth compounds, makes them superior for use in high-temperature applications.
3)n(SrO)
m—the Ruddlesden-Popper phase) have layered superlattice structures that make them promising candidates for use in high-temperature thermoelectric devices. These materials exhibit low thermal conductivity perpendicular to the layers while maintaining good electronic conductivity within the layers. ZT values are relatively low (~0.34 at 1,000K), but their enhanced thermal stability, as compared to conventional high-ZT bismuth compounds, makes them superior for use in high-temperature applications.
Interest in oxides as thermoelectric materials was reawakened in 1997 when NaxCoO2
was found to exhibit good thermoelectric behavior. In addition to their
thermal stability, other advantages of oxides are their non-toxicity
and high oxidation resistance. Simultaneously controlling both the
electric and phonon systems may require nanostructured materials. Some
layered oxide materials are thought to have ZT~2.7 at 900 K.
If the layers in a given material have the same stoichiometry, they
will be stacked so that the same atoms will not be positioned on top of
each other, impeding phonon conductivity perpendicular to the layers.
Recently, oxide thermoelectrics have gained a lot of attention so that
the range of promising phases increased drastically. Novel members of
this family include ZnO, MnO2, and NbO2, to name but a few.
Half Heusler alloys
Half
Heusler alloys have a great potential for high- temperature power
generation applications. Half-Heusler (HH) are alloys with a Formula ABX
. Examples of Half-Heusler include NbFeSb, NbCoSn and VFeSb. HH
possesses cubic MgAgAs type structure, forming three interpenetrating
face-centered-cubic (FCC). The ability to substitute any of these three
sublattices opens the door for wide variety of HH compounds to be
synthesized. A and B sites substitutions are employed to reduce the
thermal conductivity, while the X site substitution is used to enhance
the carrier concentration and thus the electrical conductivity.
Previously, ZT could not peak more than 0.5 for p-type and 0.8
for n-type HH compound. However, in the past few years, researchers were
able to achieve ZT≈1 for both n-type and p-type.
Nano-sized grains is one of the approaches used to lower the thermal
conductivity via grain boundaries- assisted phonon scattering.
Other approach was to utilize the principles of nanocomposites, by
which certain combination of metals were favored on others due to the
atomic size difference. For instance, Hf and Ti is more effective than
Hf and Zr, when reduction of thermal conductivity is of concern, since
the atomic size difference between the former is larger than that of the
latter.
Electrically conducting organic materials
Some
electrically conducting organic materials may have a higher figure of
merit than existing inorganic materials. Seebeck coefficient can be even
millivolts per Kelvin but electrical conductivity is usually low,
resulting in small ZT values. Quasi-one-dimensional organic crystals are
formed from linear chains or stacks of molecules that are packed into a
3D crystal. Under certain conditions some Q1D organic crystals may have
ZT~20 at room temperature for both p- and n-type materials. This has
been credited to an unspecified interference between two main
electron-phonon interactions leading to the formation of narrow strip of
states in the conduction band with a significantly reduced scattering rate as the mechanism compensate each other, yielding high ZT.
Silicon-germanium
Silicon-germanium alloys are currently the best thermoelectric materials around 1000 ℃ and are therefore used in some radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG) (notably the MHW-RTG and GPHS-RTG) and some other high temperature applications, such as waste heat recovery. Usability of silicon-germanium alloys is limited by their price and mid-range ZT (~0.7).
Sodium cobaltate
Experiments on crystals of sodium cobaltate, using X-ray and neutron scattering experiments carried out at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility
(ESRF) and the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) in Grenoble were able to
suppress thermal conductivity by a factor of six compared to
vacancy-free sodium cobaltate. The experiments agreed with corresponding
density functional calculations. The technique involved large anharmonic displacements of Na
0.8CoO
2 contained within the crystals.
0.8CoO
2 contained within the crystals.
Amorphous materials
In
2002, Nolas and Goldsmid have come up with a suggestion that systems
with the phonon mean free path larger than the charge carrier mean free
path can exhibit an enhanced thermoelectric efficiency.
This can be realized in amorphous thermoelectrics and soon they became a
focus of many studies. This ground-breaking idea was accomplished in
Cu-Ge-Te, NbO2, In-Ga-Zn-O, Zr-Ni-Sn, Si-Au, and Ti-Pb-V-O
amorphous systems. It should be mentioned that modelling of transport
properties is challenging enough without breaking the long-range order
so that design of amorphous thermoelectrics is at its infancy.
Naturally, amorphous thermoelectrics give rise to extensive phonon
scattering, which is still a challenge for crystalline thermoelectrics. A
bright future is expected for these materials.
Functionally graded materials
Functionally graded materials
make it possible to improve the conversion efficiency of existing
thermoelectrics. These materials have a non-uniform carrier
concentration distribution and in some cases also solid solution
composition. In power generation applications the temperature difference
can be several hundred degrees and therefore devices made from
homogeneous materials have some part that operates at the temperature
where ZT is substantially lower than its maximum value. This problem can
be solved by using materials whose transport properties vary along
their length thus enabling substantial improvements to the operating
efficiency over large temperature differences. This is possible with
functionally graded materials as they have a variable carrier
concentration along the length of the material, which is optimized for
operations over specific temperature range.
Nanomaterials and superlattices
In addition to nanostructured Bi
2Te
3/Sb
2Te
3 superlattice thin films, other nanostructured materials, including nanowires, nanotubes and quantum dots show potential in improving thermoelectric properties.
2Te
3/Sb
2Te
3 superlattice thin films, other nanostructured materials, including nanowires, nanotubes and quantum dots show potential in improving thermoelectric properties.
PbTe/PbSeTe quantum dot superlattice
Another example of a superlattice involves a PbTe/PbSeTe quantum dot
superlattices provides an enhanced ZT (approximately 1.5 at room
temperature) that was higher than the bulk ZT value for either PbTe or
PbSeTe (approximately 0.5).
Nanocrystal stability and thermal conductivity
Not
all nanocrystalline materials are stable, because the crystal size can
grow at high temperatures, ruining the materials' desired
characteristics.
Nanocrystalline materials have many interfaces between crystals, which Physics of SASER scatter phonons so the thermal conductivity is reduced. Phonons are confined to the grain, if their mean free path is larger than the material grain size.
Measured lattice thermal conductivity in nanowires is known to depend on roughness, the method of synthesis and properties of the source material.
Nanocrystalline transition metal silicides
Nanocrystalline
transition metal silicides are a promising material group for
thermoelectric applications, because they fulfill several criteria that
are demanded from the commercial applications point of view. In some
nanocrystalline transition metal silicides the power factor is higher
than in the corresponding polycrystalline material but the lack of
reliable data on thermal conductivity prevents the evaluation of their
thermoelectric efficiency.
Nanostructured skutterudites
Skutterudites, a cobalt arsenide mineral with variable amounts of nickel and iron, can be produced artificially, and are candidates for better thermoelectric materials.
One advantage of nanostructured skutterudites
over normal skutterudites is their reduced thermal conductivity, caused
by grain boundary scattering. ZT values of ~0.65 and > 0.4 have been
achieved with CoSb3 based samples; the former values were 2.0 for Ni and 0.75 for Te-doped material at 680 K and latter for Au-composite at T > 700 K.
Even greater performance improvements can be achieved by using
composites and by controlling the grain size, the compaction conditions
of polycrystalline samples and the carrier concentration.
Graphene
Graphene is known for its high electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient at room temperature.
However, from thermoelectric perspective, its thermal conductivity is
notably high, which in turn limits its ZT. Several approaches were
suggested to reduce the thermal conductivity of graphene without
altering much its electrical conductivity. These include, but not
limited to, the following:
1- Doping with carbon isotopes to form isotopic
heterojunction such as that of 12C and 13C. Basically, those isotopes
possess different phonon frequency mismatch, which ultimately lead to
the scattering of the heat carriers (the phonons). Fortunately, this
approach has been shown to not affecting neither the power factor nor
the electrical conductivity.
2- Wrinkles and cracks in the graphene structure were
shown to contribute to the reduction in the thermal conductivity.
Reported values of thermal conductivity of suspended graphene of size
3.8 µm show a wide spread from 1500 to 5000 W/mK. A recent study
attributed that to the microstructural defects present in graphene, such
as wrinkles and cracks, which can drop the thermal conductivity by 27%. These defects help scatter phonons.
3- Introduction of defects with techniques such as oxygen plasma treatment: a more systemic way of introducing defects in graphene structure is done through O2
plasma treatment. Ultimately, the graphene sample will contain
prescribed-holes spaced and numbered according to the plasma intensity.
People were able to improve ZT of graphene from 1 to a value of 2.6 when
the defect density is raised from 0.04 to 2.5 (this number is an index
of defect density and usually understood when compared to the
corresponding value of the un-treated graphene, 0.04 in our case).
Nevertheless, this technique would lower the electrical conductivity as
well, which can be kept unchanged if the plasma processing parameters
are optimized.
4- Functionalization of graphene by oxygen: the thermal
behavior of graphene oxide has not been investigated extensively as
compared to its counterpart; graphene. However, it was shown
theoretically by Density Functional Theory (DFT) model that adding
oxygen into the lattice of graphene reduces a lot its thermal
conductivity due to phonon scattering effect. Scattering of phonons
result from both acoustic mismatch and reduced symmetry in graphene
structure after doping with oxygen. The reduction of thermal
conductivity can easily exceed 50% with this approach.
Superlattices and roughness
Superlattices
- nano structured thermocouples, are considered a good candidate for
better thermoelectric device manufacturing, with materials that can be
used in manufacturing this structure.
Their production is expensive for general-use due to fabrication
processes based on expensive thin-film growth methods. However, since
the amount of thin-film materials required for device fabrication with
superlattices, is so much less than thin-film materials in bulk
thermoelectric materials (almost by a factor of 1/10,000) the long-term
cost advantage is indeed favorable.
This is particularly true given the limited availability of
tellurium causing competing solar applications for thermoelectric
coupling systems to rise.
Superlattice structures also allow the independent manipulation
of transport parameters by adjusting the structure itself, enabling
research for better understanding of the thermoelectric phenomena in
nanoscale, and studying the phonon-blocking electron-transmitting structures - explaining the changes in electric field and conductivity due to the material's nano-structure.
Many strategies exist to decrease the superlattice thermal
conductivity that are based on engineering of phonon transport. The
thermal conductivity along the film plane and wire axis can be reduced
by creating diffuse interface scattering and by reducing the interface separation distance, both which are caused by interface roughness.
Interface roughness can naturally occur or may be artificially induced.
In nature, roughness is caused by the mixing of atoms of foreign
elements. Artificial roughness can be created using various structure
types, such as quantum dot interfaces and thin-films on step-covered substrates.
Problems in superlattices
Reduced electrical conductivity: reduced phonon-scattering interface structures often also exhibit a decrease in electrical conductivity.
The thermal conductivity in the cross-plane direction of the lattice is usually very low, but depending on the type of superlattice, the thermoelectric coefficient may increase because of changes to the band structure.
Low thermal conductivity in superlattices is usually due
to strong interface scattering of phonons. Minibands are caused by the
lack of quantum confinement within a well. The mini-band structure
depends on the superlattice period so that with a very short period
(~1 nm) the band structure approaches the alloy limit and with a long
period (≥ ~60 nm) minibands become so close to each other that they can
be approximated with a continuum.
Superlatice structure countermeasures: counter measures can be taken which practically eliminate the problem of
decreased electrical conductivity in a reduced phonon-scattering
interface. These measures include the proper choice of superlattice
structure, taking advantage of mini-band conduction across superlattices, and avoiding quantum-confinement.
It has been shown that because electrons and phonons have different
wavelengths, it is possible to engineer the structure in such a way that
phonons are scattered more diffusely at the interface than electrons.
Phonon confinement countermeasures: another approach to overcome the decrease in electrical conductivity in reduced phonon-scattering structures is to increase phonon reflectivity and therefore decrease the thermal conductivity perpendicular to the interfaces. This can be achieved by increasing the mismatch between the materials in adjacent layers, including density, group velocity, specific heat, and the phonon-spectrum.
Interface roughness causes diffuse phonon scattering, which
either increases or decreases the phonon reflectivity at the interfaces.
A mismatch between bulk dispersion relations confines phonons, and the
confinement becomes more favorable as the difference in dispersion
increases.
The amount of confinement is currently unknown as only some
models and experimental data exist. As with a previous method, the
effects on the electrical conductivity have to be considered.
Attempts to Localize long wavelength phonons by aperiodic
superlattices or composite superlattices with different periodicities
have been made. In addition, defects, especially dislocations, can be
used to reduce thermal conductivity in low dimensional systems.
Parasitic heat: parasitic heat
conduction in the barrier layers could cause significant performance
loss. It has been proposed but not tested that this can be overcome by
choosing a certain correct distance between the quantum wells.
The Seebeck coefficient can change its sign in superlattice
nanowires due to the existence of minigaps as Fermi energy varies. This
indicates that superlattices can be tailored to exhibit n or p-type
behavior by using the same dopants as those that are used for
corresponding bulk materials by carefully controlling Fermi energy or
the dopant concentration. With nanowire arrays, it is possible to
exploit semimetal-semiconductor
transition due to the quantum confinement and use materials that
normally would not be good thermoelectric materials in bulk form. Such
elements are for example bismuth. The Seebeck effect could also be used
to determine the carrier concentration and Fermi energy in nanowires.
In quantum dot thermoelectrics, unconventional or nonband
transport behavior (e.g. tunneling or hopping) is necessary to utilize
their special electronic band structure in the transport direction. It
is possible to achieve ZT>2 at elevated temperatures with quantum dot
superlattices, but they are almost always unsuitable for mass
production.
However, in superlattices, where quantum-effects are not involved, with film thickness of only a few micrometers (µm) to about 15 µm, Bi2Te3/Sb2Te3 superlattice material has been made into high-performance microcoolers and other devices. The performance of hot-spot coolers are consistent with the reported ZT~2.4 of superlattice materials at 300 K.
Nanocomposites are promising material class for bulk
thermoelectric devices, but several challenges have to be overcome to
make them suitable for practical applications. It is not well understood
why the improved thermoelectric properties appear only in certain
materials with specific fabrication processes.
SrTe nanocrystals can be embedded in a bulk PbTe matrix so that
rocksalt lattices of both materials are completely aligned (endotaxy)
with optimal molar concentration for SrTe only 2%. This can cause strong
phonon scattering but would not affect charge transport. In such case,
ZT~1.7 can be achieved at 815 K for p-type material.
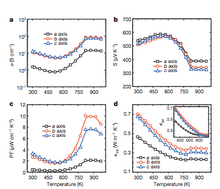
Tin selenide
In
2014, researchers at Northwestern University discovered that tin
selenide (SnSe) has a ZT of 2.6 along the b axis of the unit cell.
This is the highest value reported to date. This high ZT figure of
merit has been attributed to an extremely low thermal conductivity found
in the SnSe lattice. Specifically, SnSe demonstrated a lattice thermal
conductivity of 0.23 W·m−1·K−1, which is much lower than previously reported values of 0.5 W·m−1·K−1 and greater.
This SnSe material also exhibited a ZT of 2.3±0.3 along the c-axis and 0.8±0.2
along the a-axis. These excellent figures of merit were obtained by
researchers working at elevated temperatures, specifically 923 K
(650 °C). As shown by the figures below, SnSe performance metrics were
found to significantly improve at higher temperatures; this is due to a
structural change that is discussed below. Power factor, conductivity,
and thermal conductivity all reach their optimal values at or above
750 K, and appear to plateau at higher temperatures. However, these
reports have become controversial as reported in Nature because other
groups have not been able to reproduce the reported bulk thermal
conductivity data.
SnSe Performance Metrics
Although it exists at room temperature in an orthorhombic structure
with space group Pnma, SnSe has been shown to undergo a transition to a
structure with higher symmetry, space group Cmcm, at higher
temperatures.
This structure consists of Sn-Se planes that are stacked upwards in the
a-direction, which accounts for the poor performance out-of-plane
(along a-axis). Upon transitioning to the Cmcm structure, SnSe
maintains its low thermal conductivity but exhibits higher carrier
mobilities, leading to its excellent ZT value.
One particular impediment to further development of SnSe is that it has a relatively low carrier concentration: approximately 1017 cm−3. Further compounding this issue is the fact that SnSe has been reported to have low doping efficiency.
However, such single crystalline materials suffer from inability
to make useful devices due to their brittleness as well as narrow range
of temperatures, where ZT is reported to be high. Further,
polycrystalline materials made out of these compounds by several
investigators have not confirmed the high ZT of these materials.
Production methods
Production
methods for these materials can be divided into powder and crystal
growth based techniques. Powder based techniques offer excellent ability
to control and maintain desired carrier distribution. In crystal growth
techniques dopants are often mixed with melt, but diffusion from
gaseous phase can also be used. In the zone melting techniques disks of
different materials are stacked on top of others and then materials are
mixed with each other when a traveling heater causes melting. In powder
techniques, either different powders are mixed with a varying ratio
before melting or they are in different layers as a stack before
pressing and melting.
There are applications, such as cooling of electronic circuits,
where thin films are required. Therefore, thermoelectric materials can
also be synthesized using physical vapor deposition techniques. Another reason to utilize these methods is to design these phases and provide guidance for bulk applications.
Significant improvement on 3D printing skills makes it possible
for thermoelectric materials prepared from 3D printing inks, which are
usually synthesized by dispersing inorganic powders to organic solvent
or making a suspension.
Thermoelectric products are made from special materials that absorb
heat and create electricity. The requirement of having complex
geometries that fit in tightly constrained spaces, makes 3D printing the
ideal manufacturing technique.
Also, printable materials that demonstrate good mechanical flexibility
could be utilized for wearable thermoelectrics, which convert body
energy to electricity.
Applications
Refrigeration
Thermoelectric materials can be used as refrigerators, called "thermoelectric coolers", or "Peltier coolers" after the Peltier effect that controls their operation. As a refrigeration technology, Peltier cooling is far less common than vapor-compression refrigeration. The main advantages of a Peltier cooler (compared to a vapor-compression refrigerator) are its lack of moving parts or refrigerant, and its small size and flexible shape (form factor).
The main disadvantage of Peltier coolers is low
efficiency. It is estimated that materials with ZT>3 (about 20–30%
Carnot efficiency) would be required to replace traditional coolers in
most applications. Today, Peltier coolers are only used in niche applications, especially small scale, where efficiency is not important.
Power generation
Thermoelectric efficiency depends on the figure of merit, ZT. There is no theoretical upper limit to ZT, and as ZT approaches infinity, the thermoelectric efficiency approaches the Carnot limit. However, no known thermoelectrics have a ZT greater than 3.
As of 2010, thermoelectric generators serve application niches where
efficiency and cost are less important than reliability, light weight,
and small size.
Internal combustion engines capture 20–25% of the energy released during fuel combustion.
Increasing the conversion rate can increase mileage and provide more
electricity for on-board controls and creature comforts (stability
controls, telematics, navigation systems, electronic braking, etc.)
It may be possible to shift energy draw from the engine (in certain
cases) to the electrical load in the car, e.g. electrical power steering
or electrical coolant pump operation.
Cogeneration
power plants use the heat produced during electricity generation for
alternative purposes. Thermoelectrics may find applications in such
systems or in solar thermal energy generation.








![Z\bar{T} = {(S_p - S_n)^2 \bar{T} \over [(\rho_n \kappa_n)^{1/2} + (\rho_p \kappa_p)^{1/2}]^2}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0744744f68a10d8207f953c0712eb3388479fae7)