| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Antimony | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery lustrous gray | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Sb) | 121.760(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Antimony in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 51 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | metalloid | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell
| 2, 8, 18, 18, 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 903.78 K (630.63 °C, 1167.13 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1908 K (1635 °C, 2975 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 6.697 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.53 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 19.79 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 193.43 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.23 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −3, −2, −1, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5 (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.05 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 140 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 139±5 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 206 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of antimony | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | rhombohedral | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 3420 m/s (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 11 µm/(m·K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 24.4 W/(m·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 417 nΩ·m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | −99.0·10−6 cm3/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 55 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 20 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 42 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 3.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 294–384 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-36-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | before 800 CE | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of antimony | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Antimony is a chemical element with symbol Sb (from Latin: stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name, kohl. Metallic antimony was also known, but it was erroneously identified as lead upon its discovery. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio.
For some time, China has been the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony are roasting and reduction with carbon or direct reduction of stibnite with iron.
The largest applications for metallic antimony is an alloy with lead and tin and the lead antimony plates in lead–acid batteries. Alloys of lead and tin with antimony have improved properties for solders, bullets, and plain bearings. Antimony compounds are prominent additives for chlorine and bromine-containing fire retardants found in many commercial and domestic products. An emerging application is the use of antimony in microelectronics.
Characteristics
Properties
A vial containing the black allotrope of antimony
Native antimony with oxidation products
Crystal structure common to Sb, AsSb and gray As
Antimony is a member of group 15 of the periodic table, one of the elements called pnictogens, and has an electronegativity of 2.05. In accordance with periodic trends, it is more electronegative than tin or bismuth, and less electronegative than tellurium or arsenic. Antimony is stable in air at room temperature, but reacts with oxygen if heated to produce antimony trioxide, Sb2O3.
Antimony is a silvery, lustrous gray metalloid with a Mohs scale hardness of 3, which is too soft to make hard objects; coins of antimony were issued in China's Guizhou province in 1931 but the durability was poor and the minting was soon discontinued. Antimony is resistant to attack by acids.
Four allotropes
of antimony are known: a stable metallic form and three metastable
forms (explosive, black and yellow). Elemental antimony is a brittle, silver-white shiny metalloid. When slowly cooled, molten antimony crystallizes in a trigonal cell, isomorphic with the gray allotrope of arsenic. A rare explosive form of antimony can be formed from the electrolysis of antimony trichloride. When scratched with a sharp implement, an exothermic
reaction occurs and white fumes are given off as metallic antimony
forms; when rubbed with a pestle in a mortar, a strong detonation
occurs. Black antimony is formed upon rapid cooling of antimony vapor.
It has the same crystal structure as red phosphorus
and black arsenic, it oxidizes in air and may ignite spontaneously. At
100 °C, it gradually transforms into the stable form. The yellow
allotrope of antimony is the most unstable. It has only been generated
by oxidation of stibine (SbH3) at −90 °C. Above this temperature and in ambient light, this metastable allotrope transforms into the more stable black allotrope.
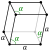
Elemental antimony adopts a layered structure (space group R3m
No. 166) in which layers consist of fused, ruffled, six-membered rings.
The nearest and next-nearest neighbors form an irregular octahedral
complex, with the three atoms in each double layer slightly closer than
the three atoms in the next. This relatively close packing leads to a
high density of 6.697 g/cm3, but the weak bonding between the layers leads to the low hardness and brittleness of antimony.
Isotopes
Antimony has two stable isotopes: 121Sb with a natural abundance of 57.36% and 123Sb with a natural abundance of 42.64%. It also has 35 radioisotopes, of which the longest-lived is 125Sb with a half-life of 2.75 years. In addition, 29 metastable states have been characterized. The most stable of these is 120m1Sb with a half-life of 5.76 days. Isotopes that are lighter than the stable 123Sb tend to decay by β+ decay, and those that are heavier tend to decay by β− decay, with some exceptions.
Occurrence
The abundance of antimony in the Earth's crust is estimated to be 0.2 to 0.5 parts per million, comparable to thallium at 0.5 parts per million and silver at 0.07 ppm. Even though this element is not abundant, it is found in more than 100 mineral species. Antimony is sometimes found natively (e.g. on Antimony Peak), but more frequently it is found in the sulfide stibnite (Sb2S3) which is the predominant ore mineral.
Compounds
Antimony compounds are often classified according to their oxidation state: Sb(III) and Sb(V). The +5 oxidation state is more stable.
Oxides and hydroxides
Antimony trioxide is formed when antimony is burnt in air. In the gas phase, the molecule of the compound is Sb
4O
6, but it polymerizes upon condensing. Antimony pentoxide (Sb
4O
10) can be formed only by oxidation with concentrated nitric acid. Antimony also forms a mixed-valence oxide, antimony tetroxide (Sb
2O
4), which features both Sb(III) and Sb(V). Unlike oxides of phosphorus and arsenic, these oxides are amphoteric, do not form well-defined oxoacids, and react with acids to form antimony salts.
4O
6, but it polymerizes upon condensing. Antimony pentoxide (Sb
4O
10) can be formed only by oxidation with concentrated nitric acid. Antimony also forms a mixed-valence oxide, antimony tetroxide (Sb
2O
4), which features both Sb(III) and Sb(V). Unlike oxides of phosphorus and arsenic, these oxides are amphoteric, do not form well-defined oxoacids, and react with acids to form antimony salts.
Antimonous acid Sb(OH)
3 is unknown, but the conjugate base sodium antimonite ([Na
3SbO
3]
4) forms upon fusing sodium oxide and Sb
4O
6. Transition metal antimonites are also known. Antimonic acid exists only as the hydrate HSb(OH)
6, forming salts as the antimonate anion Sb(OH)−
6. When a solution containing this anion is dehydrated, the precipitate contains mixed oxides.
3 is unknown, but the conjugate base sodium antimonite ([Na
3SbO
3]
4) forms upon fusing sodium oxide and Sb
4O
6. Transition metal antimonites are also known. Antimonic acid exists only as the hydrate HSb(OH)
6, forming salts as the antimonate anion Sb(OH)−
6. When a solution containing this anion is dehydrated, the precipitate contains mixed oxides.
Many antimony ores are sulfides, including stibnite (Sb
2S
3), pyrargyrite (Ag
3SbS
3), zinkenite, jamesonite, and boulangerite. Antimony pentasulfide is non-stoichiometric and features antimony in the +3 oxidation state and S-S bonds. Several thioantimonides are known, such as [Sb
6S
10]2− and [Sb
8S
13]2−.
2S
3), pyrargyrite (Ag
3SbS
3), zinkenite, jamesonite, and boulangerite. Antimony pentasulfide is non-stoichiometric and features antimony in the +3 oxidation state and S-S bonds. Several thioantimonides are known, such as [Sb
6S
10]2− and [Sb
8S
13]2−.
Halides
Antimony forms two series of halides: SbX
3 and SbX
5. The trihalides SbF
3, SbCl
3, SbBr
3, and SbI
3 are all molecular compounds having trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry.
3 and SbX
5. The trihalides SbF
3, SbCl
3, SbBr
3, and SbI
3 are all molecular compounds having trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry.
- Sb
2O
3 + 6 HF → 2 SbF
3 + 3 H
2O
It is Lewis acidic and readily accepts fluoride ions to form the complex anions SbF−
4 and SbF2−
5. Molten SbF
3 is a weak electrical conductor. The trichloride SbCl
3 is prepared by dissolving Sb
2S
3 in hydrochloric acid:
4 and SbF2−
5. Molten SbF
3 is a weak electrical conductor. The trichloride SbCl
3 is prepared by dissolving Sb
2S
3 in hydrochloric acid:
- Sb
2S
3 + 6 HCl → 2 SbCl
3 + 3 H
2S
Structure of gaseous SbF5
The pentahalides SbF
5 and SbCl
5 have trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry in the gas phase, but in the liquid phase, SbF
5 is polymeric, whereas SbCl
5 is monomeric. SbF
5 is a powerful Lewis acid used to make the superacid fluoroantimonic acid ("H2SbF7").
5 and SbCl
5 have trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry in the gas phase, but in the liquid phase, SbF
5 is polymeric, whereas SbCl
5 is monomeric. SbF
5 is a powerful Lewis acid used to make the superacid fluoroantimonic acid ("H2SbF7").
Oxyhalides are more common for antimony than for arsenic and phosphorus. Antimony trioxide dissolves in concentrated acid to form oxoantimonyl compounds such as SbOCl and (SbO)
2SO
4.
2SO
4.
Antimonides, hydrides, and organoantimony compounds
Compounds in this class generally are described as derivatives of Sb3−. Antimony forms antimonides with metals, such as indium antimonide (InSb) and silver antimonide (Ag
3Sb). The alkali metal and zinc antimonides, such as Na3Sb and Zn3Sb2, are more reactive. Treating these antimonides with acid produces the highly unstable gas stibine, SbH
3:
3Sb). The alkali metal and zinc antimonides, such as Na3Sb and Zn3Sb2, are more reactive. Treating these antimonides with acid produces the highly unstable gas stibine, SbH
3:
- Sb3− + 3 H+ → SbH
3
Stibine can also be produced by treating Sb3+ salts with hydride reagents such as sodium borohydride. Stibine decomposes spontaneously at room temperature. Because stibine has a positive heat of formation, it is thermodynamically unstable and thus antimony does not react with hydrogen directly.
Organoantimony compounds are typically prepared by alkylation of antimony halides with Grignard reagents.
A large variety of compounds are known with both Sb(III) and Sb(V)
centers, including mixed chloro-organic derivatives, anions, and
cations. Examples include Sb(C6H5)3 (triphenylstibine), Sb2(C6H5)4 (with an Sb-Sb bond), and cyclic [Sb(C6H5)]n. Pentacoordinated organoantimony compounds are common, examples being Sb(C6H5)5 and several related halides.
History
One of the alchemical symbols for antimony
Antimony(III) sulfide, Sb2S3, was recognized in predynastic Egypt as an eye cosmetic (kohl) as early as about 3100 BC, when the cosmetic palette was invented.
An artifact, said to be part of a vase, made of antimony dating to about 3000 BC was found at Telloh, Chaldea (part of present-day Iraq), and a copper object plated with antimony dating between 2500 BC and 2200 BC has been found in Egypt. Austen, at a lecture by Herbert Gladstone in 1892
commented that "we only know of antimony at the present day as a highly
brittle and crystalline metal, which could hardly be fashioned into a
useful vase, and therefore this remarkable 'find' (artifact mentioned
above) must represent the lost art of rendering antimony malleable."
Moorey was unconvinced the artifact was indeed a vase, mentioning
that Selimkhanov, after his analysis of the Tello object (published in
1975), "attempted to relate the metal to Transcaucasian natural
antimony" (i.e. native metal) and that "the antimony objects from
Transcaucasia are all small personal ornaments." This weakens the evidence for a lost art "of rendering antimony malleable."
The Roman scholar Pliny the Elder described several ways of preparing antimony sulfide for medical purposes in his treatise Natural History.
Pliny the Elder also made a distinction between "male" and "female"
forms of antimony; the male form is probably the sulfide, while the
female form, which is superior, heavier, and less friable, has been
suspected to be native metallic antimony.
The Greek naturalist Pedanius Dioscorides
mentioned that antimony sulfide could be roasted by heating by a
current of air. It is thought that this produced metallic antimony.
The Italian metallurgist Vannoccio Biringuccio produced the first known description of a procedure to isolate antimony.
The first description of a procedure for isolating antimony is in the 1540 book De la pirotechnia by Vannoccio Biringuccio, predating the more famous 1556 book by Agricola, De re metallica. In this context Agricola has been often incorrectly credited with the discovery of metallic antimony. The book Currus Triumphalis Antimonii
(The Triumphal Chariot of Antimony), describing the preparation of
metallic antimony, was published in Germany in 1604. It was purported to
be written by a Benedictine monk, writing under the name Basilius Valentinus in the 15th century; if it were authentic, which it is not, it would predate Biringuccio.
The metal antimony was known to German chemist Andreas Libavius in 1615 who obtained it by adding iron to a molten mixture of antimony sulfide, salt and potassium tartrate. This procedure produced antimony with a crystalline or starred surface.
With the advent of challenges to phlogiston theory, it was recognized that antimony is an element forming sulfides, oxides, and other compounds, as do other metals.
The first discovery of naturally occurring pure antimony in the Earth's crust was described by the Swedish scientist and local mine district engineer Anton von Swab in 1783; the type-sample was collected from the Sala Silver Mine in the Bergslagen mining district of Sala, Västmanland, Sweden.
Etymology
The medieval Latin form, from which the modern languages and late Byzantine Greek take their names for antimony, is antimonium. The origin of this is uncertain; all suggestions have some difficulty either of form or interpretation. The popular etymology, from ἀντίμοναχός anti-monachos or French antimoine, still has adherents; this would mean "monk-killer", and is explained by many early alchemists being monks, and antimony being poisonous.
Another popular etymology is the hypothetical Greek word ἀντίμόνος antimonos, "against aloneness", explained as "not found as metal", or "not found unalloyed". Lippmann conjectured a hypothetical Greek word ανθήμόνιον anthemonion,
which would mean "floret", and cites several examples of related Greek
words (but not that one) which describe chemical or biological efflorescence.
The early uses of antimonium include the translations, in 1050–1100, by Constantine the African of Arabic medical treatises. Several authorities believe antimonium is a scribal corruption of some Arabic form; Meyerhof derives it from ithmid; other possibilities include athimar, the Arabic name of the metalloid, and a hypothetical as-stimmi, derived from or parallel to the Greek.
The standard chemical symbol for antimony (Sb) is credited to Jöns Jakob Berzelius, who derived the abbreviation from stibium.
The ancient words for antimony mostly have, as their chief meaning, kohl, the sulfide of antimony.
The Egyptians called antimony mśdmt; in hieroglyphs, the vowels are uncertain, but the Coptic form of the word is ⲥⲧⲏⲙ (stēm). The Greek word, στίμμι stimmi, is probably a loan word from Arabic or from Egyptian stm
|
and is used by Attic tragic poets of the 5th century BC. Later Greeks also used στἰβι stibi, as did Celsus and Pliny, writing in Latin, in the first century AD. Pliny also gives the names stimi [sic], larbaris, alabaster, and the "very common" platyophthalmos, "wide-eye" (from the effect of the cosmetic). Later Latin authors adapted the word to Latin as stibium. The Arabic word for the substance, as opposed to the cosmetic, can appear as إثمد ithmid, athmoud, othmod, or uthmod. Littré suggests the first form, which is the earliest, derives from stimmida, an accusative for stimmi.
Production
World antimony output in 2010
World production trend of antimony
Top producers and production volumes
The British Geological Survey
(BGS) reported that in 2005 China was the top producer of antimony with
approximately 84% of the world share, followed at a distance by South
Africa, Bolivia and Tajikistan. Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan province has the largest deposits in China with an estimated deposit of 2.1 million metric tons.
In 2016, according to the US Geological Survey, China accounted for 76.9% of total antimony production, followed in second place by Russia with 6.9% and Tajikistan with 6.2%.
| Country | Tonnes | % of total |
|---|---|---|
| 100,000 | 76.9 | |
| 9,000 | 6.9 | |
| 8,000 | 6.2 | |
| 4,000 | 3.1 | |
| 3,500 | 2.7 | |
| Top 5 | 124,500 | 95.8 |
| Total world | 130,000 | 100.0 |
Chinese production of antimony is expected to decline in the future
as mines and smelters are closed down by the government as part of
pollution control. Especially due to a new environmental protection law
having gone into effect on January 2015
and revised “Emission Standards of Pollutants for Stanum, Antimony, and
Mercury” having gone into effect, hurdles for economic production are
higher. According to the National Bureau of Statistics in China, by
September 2015 50% of antimony production capacity in the Hunan province
(the province with biggest antimony reserves in China) had not been
used.
Reported production of antimony in China has fallen and is
unlikely to increase in the coming years, according to the Roskill
report. No significant antimony deposits in China have been developed
for about ten years, and the remaining economic reserves are being
rapidly depleted.
The world's largest antimony producers, according to Roskill, are listed below:
| Country | Company | Capacity (tonnes per year) |
|---|---|---|
| Mandalay Resources | 2,750 | |
| various | 5,460 | |
| Beaver Brook | 6,000 | |
| Hsikwangshan Twinkling Star | 55,000 | |
| Hunan Chenzhou Mining | 20,000 | |
| China Tin Group | 20,000 | |
| Shenyang Huachang Antimony | 15,000 | |
| Kazzinc | 1,000 | |
| Kadamdzhai | 500 | |
| SRS | 500 | |
| US Antimony | 70 | |
| various | 6,000 | |
| GeoProMining | 6,500 | |
| Consolidated Murchison | 6,000 | |
| Unzob | 5,500 | |
| unknown | 600 | |
| Cengiz & Özdemir Antimuan Madenleri | 2,400 |
Reserves
According
to statistics from the USGS, current global reserves of antimony will
be depleted in 13 years. However, the USGS expects more resources will
be found.
| Country | Reserves (tonnes of antimony content) |
% of total |
|---|---|---|
| 950,000 | 47.81 | |
| 350,000 | 17.61 | |
| 310,000 | 15.60 | |
| 140,000 | 7.05 | |
| 60,000 | 3.02 | |
| 50,000 | 2.52 | |
| 27,000 | 1.36 | |
| Other countries | 100,000 | 5.03 |
| Total world | 1,987,000 | 100.0 |
Production process
The
extraction of antimony from ores depends on the quality and composition
of the ore. Most antimony is mined as the sulfide; lower-grade ores are
concentrated by froth flotation, while higher-grade ores are heated to 500–600 °C, the temperature at which stibnite melts and separates from the gangue minerals. Antimony can be isolated from the crude antimony sulfide by reduction with scrap iron:
- Sb
2S
3 + 3 Fe → 2 Sb + 3 FeS
The sulfide is converted to an oxide; the product is then roasted,
sometimes for the purpose of vaporizing the volatile antimony(III)
oxide, which is recovered. This material is often used directly for the main applications, impurities being arsenic and sulfide. Antimony is isolated from the oxide by a carbothermal reduction:
- 2 Sb
2O
3 + 3 C → 4 Sb + 3 CO
2
The lower-grade ores are reduced in blast furnaces while the higher-grade ores are reduced in reverberatory furnaces.
Supply risk and critical mineral rankings
Antimony has consistently been ranked high in European and US risk lists concerning criticality of the element
indicating the relative risk to the supply of chemical elements or
element groups required to maintain the current economy and lifestyle.
With most of the antimony imported into Europe and the US coming
from China, Chinese production is critical to supply. As China is
revising and increasing environmental control standards, antimony
production is becoming increasingly restricted. Additionally Chinese
export quotas for antimony have been decreasing in the past years. These
two factors increase supply risk for both Europe and US.
Europe
According
to the BGS Risk List 2015, antimony is ranked second highest (after
rare earth elements) on the relative supply risk index.
This indicates that it has currently the second highest supply risk for
chemical elements or element groups which are of economic value to the
British economy and lifestyle.
Furthermore, antimony was identified as one of 20 critical raw materials
for the EU in a report published in 2014 (which revised the initial
report published in 2011). As seen in Figure xxx antimony maintains high
supply risk relative to its economic importance. 92% of the antimony is
imported from China, which is a significantly high concentration of
production.
U.S.
Much analysis
has been conducted in the U.S. toward defining which metals should be
called strategic or critical to the nation's security. Exact definitions
do not exist, and views as to what constitutes a strategic or critical
mineral to U.S. security diverge.
In 2015, no antimony was mined in the U.S. The metal is imported
from foreign countries. From 2011-2014 68% of America's antimony came
from China, 14% from India, 4% from Mexico, and 14% from other sources.
There are no publicly known government stockpiles in place currently.
The U.S. “Subcommittee on Critical and Strategic Mineral Supply
Chains” has screened 78 mineral resources from 1996-2008. It found that a
small subset of minerals including antimony has fallen into the
category of potentially critical minerals consistently. In the future, a
second assessment will be made of the found subset of minerals to
identify which should be defined of significant risk and critical to
U.S. interests.
Applications
About 60% of antimony is consumed in flame retardants, and 20% is used in alloys for batteries, plain bearings, and solders.
Flame retardants
Antimony is mainly used as the trioxide for flame-proofing compounds,
always in combination with halogenated flame retardants except in
halogen-containing polymers. The flame retarding effect of antimony
trioxide is produced by the formation of halogenated antimony compounds, which react with hydrogen atoms, and probably also with oxygen atoms and OH radicals, thus inhibiting fire.
Markets for these flame-retardants include children's clothing, toys,
aircraft, and automobile seat covers. They are also added to polyester resins in fiberglass composites
for such items as light aircraft engine covers. The resin will burn in
the presence of an externally generated flame, but will extinguish when
the external flame is removed.
Alloys
Antimony forms a highly useful alloy with lead,
increasing its hardness and mechanical strength. For most applications
involving lead, varying amounts of antimony are used as alloying metal.
In lead–acid batteries, this addition improves plate strength and charging characteristics. It is used in antifriction alloys (such as Babbitt metal), in bullets and lead shot, electrical cable sheathing, type metal (for example, for linotype printing machines), solder (some "lead-free" solders contain 5% Sb), in pewter, and in hardening alloys with low tin content in the manufacturing of organ pipes.
Other applications
Three other applications consume nearly all the rest of the world's supply. One application is as a stabilizer and catalyst for the production of polyethylene terephthalate. Another is as a fining agent to remove microscopic bubbles in glass, mostly for TV screens; antimony ions interact with oxygen, suppressing the tendency of the latter to form bubbles. The third application is pigments.
Antimony is increasingly being used in semiconductors as a dopant in n-type silicon wafers for diodes, infrared detectors, and Hall-effect devices. In the 1950s, the emitters and collectors of n-p-n alloy junction transistors were doped with tiny beads of a lead-antimony alloy. Indium antimonide is used as a material for mid-infrared detectors.
Biology and medicine have few uses for antimony. Treatments containing antimony, known as antimonials, are used as emetics. Antimony compounds are used as antiprotozoan drugs. Potassium antimonyl tartrate, or tartar emetic, was once used as an anti-schistosomal drug from 1919 on. It was subsequently replaced by praziquantel. Antimony and its compounds are used in several veterinary preparations, such as anthiomaline and lithium antimony thiomalate, as a skin conditioner in ruminants. Antimony has a nourishing or conditioning effect on keratinized tissues in animals.
Antimony-based drugs, such as meglumine antimoniate, are also considered the drugs of choice for treatment of leishmaniasis in domestic animals. Unfortunately, besides having low therapeutic indices, the drugs have minimal penetration of the bone marrow, where some of the Leishmania amastigotes reside, and curing the disease – especially the visceral form – is very difficult. Elemental antimony as an antimony pill was once used as a medicine. It could be reused by others after ingestion and elimination.
Antimony(III) sulfide is used in the heads of some safety matches.
Antimony sulfides help to stabilize the friction coefficient in automotive brake pad materials.
Antimony-124 is used together with beryllium in neutron sources; the gamma rays emitted by antimony-124 initiate the photodisintegration of beryllium. The emitted neutrons have an average energy of 24 keV. Natural antimony is used in startup neutron sources.
Precautions
The
effects of antimony and its compounds on human and environmental health
differ widely. Elemental antimony metal does not affect human and
environmental health. Inhalation of antimony trioxide (and similar
poorly soluble Sb(III) dust particles such as antimony dust) is
considered harmful and suspected of causing cancer. However, these
effects are only observed with female rats and after long-term exposure
to high dust concentrations. The effects are hypothesized to be
attributed to inhalation of poorly soluble Sb particles leading to
impaired lung clearance, lung overload, inflammation and ultimately
tumour formation, not to exposure to antimony ions (OECD, 2008).
Antimony chlorides are corrosive to skin. The effects of antimony are
not comparable to those of arsenic; this might be caused by the
significant differences of uptake, metabolism, and excretion between
arsenic and antimony.
For oral absorption, ICRP (1994) has recommended values of 10%
for tartar emetic and 1% for all other antimony compounds. Dermal
absorption for metals is estimated to be at most 1% (HERAG, 2007).
Inhalation absorption of antimony trioxide and other poorly soluble
Sb(III) substances (such as antimony dust) is estimated at 6.8% (OECD,
2008), whereas a value less than 1% is derived for Sb(V) substances.
Antimony(V) is not quantitatively reduced to antimony(III) in the cell,
and both species exist simultaneously.
Antimony is mainly excreted from the human body via urine.
Antimony and its compounds do not cause acute human health effects, with
the exception of antimony potassium tartrate ("tartar emetic"), a prodrug that is intentionally used to treat leishmaniasis patients.
Prolonged skin contact with antimony dust may cause dermatitis.
However, it was agreed at the European Union level that the skin rashes
observed are not substance-specific, but most probably due to a physical
blocking of sweat ducts (ECHA/PR/09/09, Helsinki, 6 July 2009).
Antimony dust may also be explosive when dispersed in the air; when in a
bulk solid it is not combustible.
Antimony is incompatible with strong acids, halogenated acids, and oxidizers; when exposed to newly formed hydrogen it may form stibine (SbH3).
The 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) is set at 0.5 mg/m3 by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists and by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) as a legal permissible exposure limit (PEL) in the workplace. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 0.5 mg/m3 as an 8 hour TWA.
Antimony compounds are used as catalysts for polyethylene terephthalate
(PET) production. Some studies report minor antimony leaching from PET
bottles into liquids, but levels are below drinking water guidelines.
Antimony concentrations in fruit juice concentrates were somewhat higher
(up to 44.7 µg/L of antimony), but juices do not fall under the
drinking water regulations. The drinking water guidelines are:
- World Health Organization: 20 µg/L
- Japan: 15 µg/L
- United States Environmental Protection Agency, Health Canada and the Ontario Ministry of Environment: 6 µg/L
- EU and German Federal Ministry of Environment: 5 µg/L
The TDI proposed by WHO is 6 µg antimony per kilogram of body weight. The IDLH (immediately dangerous to life and health) value for antimony is 50 mg/m3.
Toxicity
Certain compounds of antimony appear to be toxic, particularly antimony trioxide and antimony potassium tartrate. Effects may be similar to arsenic poisoning.
Occupational exposure may cause respiratory irritation, pneumoconiosis,
antimony spots on the skin, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac
arrhythmias. In addition, antimony trioxide is potentially carcinogenic
to humans.
Adverse health effects have been observed in humans and animals
following inhalation, oral, or dermal exposure to antimony and antimony
compounds.
Antimony toxicity typically occurs either due to occupational exposure,
during therapy or from accidental ingestion. It is unclear if antimony
can enter the body through the skin.