Galileo Galilei
Condensed from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
His contributions to observational astronomy include the telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, the discovery of the four largest satellites of Jupiter (named the Galilean moons in his honour), and the observation and analysis of sunspots. Galileo also worked in applied science and technology, inventing an improved military compass and other instruments.
Galileo's championing of heliocentrism was controversial within his lifetime, a time when most subscribed to either geocentrism or the Tychonic system.[9] He met with opposition from astronomers, who doubted heliocentrism due to the absence of an observed stellar parallax.[9] The matter was investigated by the Roman Inquisition in 1615, which concluded that heliocentrism was false and contrary to scripture, placing works advocating the Copernican system on the index of banned books and forbidding Galileo from advocating heliocentrism.[9][10] Galileo later defended his views in Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, which appeared to attack Pope Urban VIII, thus alienating not only the Pope but also the Jesuits, both of whom had supported Galileo up until this point.[9] He was tried by the Holy Office, then found "vehemently suspect of heresy", was forced to recant, and spent the rest of his life under house arrest.[11][12] It was while Galileo was under house arrest that he wrote one of his finest works, Two New Sciences, in which he summarised the work he had done some forty years earlier, on the two sciences now called kinematics and strength of materials.[13][14]
Career as a scientist
Although he seriously considered the priesthood as a young man, at his father's urging he instead enrolled at the University of Pisa for a medical degree.[22] In 1581, when he was studying medicine, he noticed a swinging chandelier, which air currents shifted about to swing in larger and smaller arcs.It seemed, by comparison with his heartbeat, that the chandelier took the same amount of time to swing back and forth, no matter how far it was swinging. When he returned home, he set up two pendulums of equal length and swung one with a large sweep and the other with a small sweep and found that they kept time together. It was not until Christiaan Huygens almost one hundred years later that the tautochrone nature of a swinging pendulum was used to create an accurate timepiece.[23] Up to this point, he had deliberately been kept away from mathematics (since a physician earned so much more than a mathematician), but upon accidentally attending a lecture on geometry, he talked his reluctant father into letting him study mathematics and natural philosophy instead of medicine.[23] He created a thermoscope (forerunner of the thermometer) and in 1586 published a small book on the design of a hydrostatic balance he had invented (which first brought him to the attention of the scholarly world). Galileo also studied disegno, a term encompassing fine art, and in 1588 obtained the position of instructor in the Accademia delle Arti del Disegno in Florence, teaching perspective and chiaroscuro. Being inspired by the artistic tradition of the city and the works of the Renaissance artists, Galileo acquired an aesthetic mentality. While a young teacher at the Accademia, he began a lifelong friendship with the Florentine painter Cigoli, who included Galileo's lunar observations in one of his paintings.[24][25]
In 1589, he was appointed to the chair of mathematics in Pisa. In 1591, his father died, and he was entrusted with the care of his younger brother Michelagnolo. In 1592, he moved to the University of Padua where he taught geometry, mechanics, and astronomy until 1610.[26] During this period, Galileo made significant discoveries in both pure fundamental science (for example, kinematics of motion and astronomy) as well as practical applied science (for example, strength of materials and improvement of the telescope). His multiple interests included the study of astrology, which at the time was a discipline tied to the studies of mathematics and astronomy.[27]
Galileo, Kepler and theories of tides

Galileo Galilei. Portrait by Leoni
Cardinal Bellarmine had written in 1615 that the Copernican system could not be defended without "a true physical demonstration that the sun does not circle the earth but the earth circles the sun".[28] Galileo considered his theory of the tides to provide the required physical proof of the motion of the earth. This theory was so important to him that he originally intended to entitle his Dialogue on the Two Chief World Systems the Dialogue on the Ebb and Flow of the Sea.[29] The reference to tides was removed by order of the Inquisition.
For Galileo, the tides were caused by the sloshing back and forth of water in the seas as a point on the Earth's surface sped up and slowed down because of the Earth's rotation on its axis and revolution around the Sun. He circulated his first account of the tides in 1616, addressed to Cardinal Orsini.[30] His theory gave the first insight into the importance of the shapes of ocean basins in the size and timing of tides; he correctly accounted, for instance, for the negligible tides halfway along the Adriatic Sea compared to those at the ends. As a general account of the cause of tides, however, his theory was a failure.
If this theory were correct, there would be only one high tide per day. Galileo and his contemporaries were aware of this inadequacy because there are two daily high tides at Venice instead of one, about twelve hours apart. Galileo dismissed this anomaly as the result of several secondary causes including the shape of the sea, its depth, and other factors.[31] Against the assertion that Galileo was deceptive in making these arguments, Albert Einstein expressed the opinion that Galileo developed his "fascinating arguments" and accepted them uncritically out of a desire for physical proof of the motion of the Earth.[32] Galileo dismissed the idea, held by his contemporary Johannes Kepler, that the moon caused the tides.[33] He also refused to accept Kepler's elliptical orbits of the planets,[34] considering the circle the "perfect" shape for planetary orbits.
Controversy over comets and The Assayer
In 1619, Galileo became embroiled in a controversy with Father Orazio Grassi, professor of mathematics at the Jesuit Collegio Romano. It began as a dispute over the nature of comets, but by the time Galileo had published The Assayer (Il Saggiatore) in 1623, his last salvo in the dispute, it had become a much wider argument over the very nature of science itself. Because The Assayer contains such a wealth of Galileo's ideas on how science should be practised, it has been referred to as his scientific manifesto.[35] Early in 1619, Father Grassi had anonymously published a pamphlet, An Astronomical Disputation on the Three Comets of the Year 1618, [36] which discussed the nature of a comet that had appeared late in November of the previous year. Grassi concluded that the comet was a fiery body which had moved along a segment of a great circle at a constant distance from the earth,[37] and since it moved in the sky more slowly than the moon, it must be farther away than the moon.Grassi's arguments and conclusions were criticised in a subsequent article, Discourse on the Comets,[38] published under the name of one of Galileo's disciples, a Florentine lawyer named Mario Guiducci although it had been largely written by Galileo himself.[39] Galileo and Guiducci offered no definitive theory of their own on the nature of comets[40] although they did present some tentative conjectures that are now known to be mistaken. In its opening passage, Galileo and Guiducci's Discourse gratuitously insulted the Jesuit Christopher Scheiner,[41] and various uncomplimentary remarks about the professors of the Collegio Romano were scattered throughout the work.[42] The Jesuits were offended,[43] and Grassi soon replied with a polemical tract of his own, The Astronomical and Philosophical Balance,[44] under the pseudonym Lothario Sarsio Sigensano,[45] purporting to be one of his own pupils.
The Assayer was Galileo's devastating reply to the Astronomical Balance.[46] It has been widely regarded as a masterpiece of polemical literature,[47] in which "Sarsi's" arguments are subjected to withering scorn.[48] It was greeted with wide acclaim, and particularly pleased the new pope, Urban VIII, to whom it had been dedicated.[49] Galileo's dispute with Grassi permanently alienated many of the Jesuits who had previously been sympathetic to his ideas,[50] and Galileo and his friends were convinced that these Jesuits were responsible for bringing about his later condemnation.[51] The evidence for this is at best equivocal, however.[52]
Controversy over heliocentrism
In the Catholic world prior to Galileo's conflict with the Church, the majority of educated people subscribed to the Aristotelian geocentric view that the earth was the center of the universe and that all heavenly bodies revolved around the Earth,[53] despite the use of Copernican theories to reform the calendar in 1582.[54] Biblical references Psalm 93:1, 96:10, and 1 Chronicles 16:30 include text stating that "the world is firmly established, it cannot be moved." In the same manner, Psalm 104:5 says, "the Lord set the earth on its foundations; it can never be moved." Further, Ecclesiastes 1:5 states that "And the sun rises and sets and returns to its place."[55]
Galileo defended heliocentrism, and in his Letter to the Grand Duchess Christina argued that it was not contrary to biblical texts. He took the Augustinian position that poetry, songs, instructions or historical statements in biblical texts need not always be interpreted literally. Galileo argued that the authors wrote from the perspective of the terrestrial world in which the sun does rise and set, and discussed a different kind of "movement" of the earth, not rotations.[56][citation needed]
By 1615 Galileo's writings on heliocentrism had been submitted to the Roman Inquisition, and his efforts to interpret the Bible were seen as a violation of the Council of Trent.[57] Attacks on the ideas of Copernicus had reached a head, and Galileo went to Rome to defend himself and Copernican ideas. In 1616, an Inquisitorial commission unanimously declared heliocentrism to be "foolish and absurd in philosophy, and formally heretical since it explicitly contradicts in many places the sense of Holy Scripture." The Inquisition found that the idea of the Earth's movement "receives the same judgement in philosophy and... in regard to theological truth it is at least erroneous in faith."[58] (The original document from the Inquisitorial commission was made widely available in 2014.[59])
Pope Paul V instructed Cardinal Bellarmine to deliver this finding to Galileo, and to order him to abandon the Copernican opinions. On February 26, Galileo was called to Bellarmine's residence and ordered
…to abstain completely from teaching or defending this doctrine and opinion or from discussing it... to abandon completely... the opinion that the sun stands still at the center of the world and the earth moves, and henceforth not to hold, teach, or defend it in any way whatever, either orally or in writing.The decree of the Congregation of the Index banned Copernicus's De Revolutionibus and other heliocentric works until correction.[60] Bellarmine's instructions did not prohibit Galileo from discussing heliocentrism as a mathematical fiction.[61]
— The Inquisition's injunction against Galileo, 1616.[60]
For the next decade, Galileo stayed well away from the controversy. He revived his project of writing a book on the subject, encouraged by the election of Cardinal Maffeo Barberini as Pope Urban VIII in 1623. Barberini was a friend and admirer of Galileo, and had opposed the condemnation of Galileo in 1616. Galileo's resulting book, Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, was published in 1632, with formal authorization from the Inquisition and papal permission.[62]
Earlier, Pope Urban VIII had personally asked Galileo to give arguments for and against heliocentrism in the book, and to be careful not to advocate heliocentrism. He made another request, that his own views on the matter be included in Galileo's book. Only the latter of those requests was fulfilled by Galileo.
Whether unknowingly or deliberately, Simplicio, the defender of the Aristotelian geocentric view in Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, was often caught in his own errors and sometimes came across as a fool. Indeed, although Galileo states in the preface of his book that the character is named after a famous Aristotelian philosopher (Simplicius in Latin, Simplicio in Italian), the name "Simplicio" in Italian also has the connotation of "simpleton".[63] This portrayal of Simplicio made Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems appear as an advocacy book: an attack on Aristotelian geocentrism and defence of the Copernican theory. Unfortunately for his relationship with the Pope, Galileo put the words of Urban VIII into the mouth of Simplicio.
Most historians agree Galileo did not act out of malice and felt blindsided by the reaction to his book.[64] However, the Pope did not take the suspected public ridicule lightly, nor the Copernican advocacy.
Galileo had alienated one of his biggest and most powerful supporters, the Pope, and was called to Rome to defend his writings[65] in September 1632. He finally arrived in February 1633 and was brought before inquisitor Vincenzo Maculani to be charged. Throughout his trial Galileo steadfastly maintained that since 1616 he had faithfully kept his promise not to hold any of the condemned opinions, and initially he denied even defending them. However, he was eventually persuaded to admit that, contrary to his true intention, a reader of his Dialogue could well have obtained the impression that it was intended to be a defence of Copernicanism. In view of Galileo's rather implausible denial that he had ever held Copernican ideas after 1616 or ever intended to defend them in the Dialogue, his final interrogation, in July 1633, concluded with his being threatened with torture if he did not tell the truth, but he maintained his denial despite the threat.[66]
The sentence of the Inquisition was delivered on June 22. It was in three essential parts:
- Galileo was found "vehemently suspect of heresy", namely of having held the opinions that the Sun lies motionless at the centre of the universe, that the Earth is not at its centre and moves, and that one may hold and defend an opinion as probable after it has been declared contrary to Holy Scripture. He was required to "abjure, curse and detest" those opinions.[67]
- He was sentenced to formal imprisonment at the pleasure of the Inquisition.[68] On the following day this was commuted to house arrest, which he remained under for the rest of his life.
- His offending Dialogue was banned; and in an action not announced at the trial, publication of any of his works was forbidden, including any he might write in the future.[69]

Tomb of Galileo Galilei, Santa Croce
According to popular legend, after recanting his theory that the Earth moved around the Sun, Galileo allegedly muttered the rebellious phrase And yet it moves. A 1640s painting by the Spanish painter Bartolomé Esteban Murillo or an artist of his school, in which the words were hidden until restoration work in 1911, depicts an imprisoned Galileo apparently pointing to the words "Eppur si muove" written on the wall of his dungeon. The earliest known written account of the legend dates to a century after his death, but Drake writes "there is no doubt now that the famous words were already attributed to Galileo before his death"..[70]
After a period with the friendly Ascanio Piccolomini (the Archbishop of Siena), Galileo was allowed to return to his villa at Arcetri near Florence in 1634, where he spent the remainder of his life under house arrest. Galileo was ordered to read the seven penitential psalms once a week for the next three years. However, his daughter Maria Celeste relieved him of the burden after securing ecclesiastical permission to take it upon herself.[71]
It was while Galileo was under house arrest that he dedicated his time to one of his finest works, Two New Sciences. Here he summarised work he had done some forty years earlier, on the two sciences now called kinematics and strength of materials, published in Holland to avoid the censor. This book has received high praise from Albert Einstein.[72] As a result of this work, Galileo is often called the "father of modern physics". He went completely blind in 1638 and was suffering from a painful hernia and insomnia, so he was permitted to travel to Florence for medical advice.[13][14]
Author Dava Sobel argues that prior to Galileo's 1633 trial and judgement for heresy, Pope Urban VIII had become preoccupied with court intrigue and problems of state, and began to fear persecution or threats to his own life. In this context, Sobel argues that the problem of Galileo was presented to the pope by court insiders and enemies of Galileo. Having been accused of weakness in defending the church, Urban reacted against Galileo out of anger and fear.[73]
Death
Galileo continued to receive visitors until 1642, when, after suffering fever and heart palpitations, he died on 8 January 1642, aged 77.[13][74] The Grand Duke of Tuscany, Ferdinando II, wished to bury him in the main body of the Basilica of Santa Croce, next to the tombs of his father and other ancestors, and to erect a marble mausoleum in his honour.[75] These plans were dropped, however, after Pope Urban VIII and his nephew, Cardinal Francesco Barberini, protested,[76] because Galileo had been condemned by the Catholic Church for "vehement suspicion of heresy".[77] He was instead buried in a small room next to the novices' chapel at the end of a corridor from the southern transept of the basilica to the sacristy.[78] He was reburied in the main body of the basilica in 1737 after a monument had been erected there in his honour;[79] during this move, three fingers and a tooth were removed from his remains.[80] One of these fingers, the middle finger from Galileo's right hand, is currently on exhibition at the Museo Galileo in Florence, Italy.[81]Scientific methods
Galileo made original contributions to the science of motion through an innovative combination of experiment and mathematics.[82] More typical of science at the time were the qualitative studies of William Gilbert, on magnetism and electricity. Galileo's father, Vincenzo Galilei, a lutenist and music theorist, had performed experiments establishing perhaps the oldest known non-linear relation in physics: for a stretched string, the pitch varies as the square root of the tension.[83] These observations lay within the framework of the Pythagorean tradition of music, well-known to instrument makers, which included the fact that subdividing a string by a whole number produces a harmonious scale. Thus, a limited amount of mathematics had long related music and physical science, and young Galileo could see his own father's observations expand on that tradition.[84]Galileo was one of the first modern thinkers to clearly state that the laws of nature are mathematical. In The Assayer he wrote "Philosophy is written in this grand book, the universe ... It is written in the language of mathematics, and its characters are triangles, circles, and other geometric figures;...."[85]
His mathematical analyses are a further development of a tradition employed by late scholastic natural philosophers, which Galileo learned when he studied philosophy.[86] He displayed a peculiar ability to ignore established authorities, most notably Aristotelianism. In broader terms, his work marked another step towards the eventual separation of science from both philosophy and religion; a major development in human thought. He was often willing to change his views in accordance with observation. In order to perform his experiments, Galileo had to set up standards of length and time, so that measurements made on different days and in different laboratories could be compared in a reproducible fashion. This provided a reliable foundation on which to confirm mathematical laws using inductive reasoning.
Galileo showed a remarkably modern appreciation for the proper relationship between mathematics, theoretical physics, and experimental physics. He understood the parabola, both in terms of conic sections and in terms of the ordinate (y) varying as the square of the abscissa (x). Galilei further asserted that the parabola was the theoretically ideal trajectory of a uniformly accelerated projectile in the absence of friction and other disturbances. He conceded that there are limits to the validity of this theory, noting on theoretical grounds that a projectile trajectory of a size comparable to that of the Earth could not possibly be a parabola,[87] but he nevertheless maintained that for distances up to the range of the artillery of his day, the deviation of a projectile's trajectory from a parabola would be only very slight.[88]
Astronomy
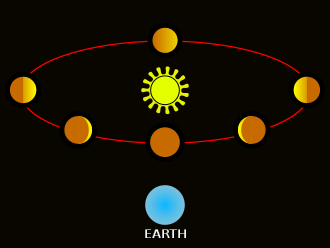
The phases of Venus, observed by Galileo in 1610
Based only on uncertain descriptions of the first practical telescope which Hans Lippershey tried to patent in the Netherlands in 1608,[89] Galileo, in the following year, made a telescope with about 3x magnification. He later made improved versions with up to about 30x magnification.[90] With a Galilean telescope, the observer could see magnified, upright images on the earth—it was what is commonly known as a terrestrial telescope or a spyglass. He could also use it to observe the sky; for a time he was one of those who could construct telescopes good enough for that purpose. On 25 August 1609, he demonstrated one of his early telescopes, with a magnification of about 8 or 9, to Venetian lawmakers. His telescopes were also a profitable sideline for Galileo, who sold them to merchants who found them useful both at sea and as items of trade. He published his initial telescopic astronomical observations in March 1610 in a brief treatise entitled Sidereus Nuncius (Starry Messenger).[91]
Kepler's supernova
According to Walusinsky,[92] Galileo's fame as an astronomer dates to his observation and discussion of Kepler's supernova in 1604. Since this new star displayed no detectable diurnal parallax, Galileo concluded that it was a distant star, and therefore disproved the Aristotelian belief in the immutability of the heavens. His public advocacy of this view met with strong opposition.[93]Jupiter
On 7 January 1610, Galileo observed with his telescope what he described at the time as "three fixed stars, totally invisible[94] by their smallness", all close to Jupiter, and lying on a straight line through it.[95] Observations on subsequent nights showed that the positions of these "stars" relative to Jupiter were changing in a way that would have been inexplicable if they had really been fixed stars. On 10 January, Galileo noted that one of them had disappeared, an observation which he attributed to its being hidden behind Jupiter. Within a few days, he concluded that they were orbiting Jupiter:[96] he had discovered three of Jupiter's four largest satellites (moons). He discovered the fourth on 13 January. Galileo named the group of four the Medicean stars, in honour of his future patron, Cosimo II de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, and Cosimo's three brothers.[97] Later astronomers, however, renamed them Galilean satellites in honour of their discoverer. These satellites are now called Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.His observations of the satellites of Jupiter caused a revolution in astronomy: a planet with smaller planets orbiting it did not conform to the principles of Aristotelian cosmology, which held that all heavenly bodies should circle the Earth,[98] and many astronomers and philosophers initially refused to believe that Galileo could have discovered such a thing.[99] His observations were confirmed by the observatory of Christopher Clavius and he received a hero's welcome when he visited Rome in 1611.[100] Galileo continued to observe the satellites over the next eighteen months, and by mid-1611, he had obtained remarkably accurate estimates for their periods—a feat which Kepler had believed impossible.[101]
Venus, Saturn, and Neptune
From September 1610, Galileo observed that Venus exhibited a full set of phases similar to that of the Moon. The heliocentric model of the solar system developed by Nicolaus Copernicus predicted that all phases would be visible since the orbit of Venus around the Sun would cause its illuminated hemisphere to face the Earth when it was on the opposite side of the Sun and to face away from the Earth when it was on the Earth-side of the Sun. On the other hand, in Ptolemy's geocentric model it was impossible for any of the planets' orbits to intersect the spherical shell carrying the Sun.Traditionally the orbit of Venus was placed entirely on the near side of the Sun, where it could exhibit only crescent and new phases. It was, however, also possible to place it entirely on the far side of the Sun, where it could exhibit only gibbous and full phases. After Galileo's telescopic observations of the crescent, gibbous and full phases of Venus, therefore, this Ptolemaic model became untenable. Thus in the early 17th century as a result of his discovery the great majority of astronomers converted to one of the various geo-heliocentric planetary models,[102] such as the Tychonic, Capellan and Extended Capellan models,[103] each either with or without a daily rotating Earth. These all had the virtue of explaining the phases of Venus without the vice of the 'refutation' of full heliocentrism's prediction of stellar parallax. Galileo's discovery of the phases of Venus was thus arguably his most empirically practically influential contribution to the two-stage transition from full geocentrism to full heliocentrism via geo-heliocentrism.
Galileo observed the planet Saturn, and at first mistook its rings for planets, thinking it was a three-bodied system. When he observed the planet later, Saturn's rings were directly oriented at Earth, causing him to think that two of the bodies had disappeared. The rings reappeared when he observed the planet in 1616, further confusing him.[104]
Galileo also observed the planet Neptune in 1612. It appears in his notebooks as one of many unremarkable dim stars. He did not realise that it was a planet, but he did note its motion relative to the stars before losing track of it.[105]
Sunspots
Galileo was one of the first Europeans to observe sunspots, although Kepler had unwittingly observed one in 1607, but mistook it for a transit of Mercury. He also reinterpreted a sunspot observation from the time of Charlemagne, which formerly had been attributed (impossibly) to a transit of Mercury.The very existence of sunspots showed another difficulty with the unchanging perfection of the heavens as posited in orthodox Aristotelian celestial physics. And the annual variations in sunspots' motions, discovered by Francesco Sizzi and others in 1612–1613,[106] provided a powerful argument against both the Ptolemaic system and the geoheliocentric system of Tycho Brahe.[107] A dispute over priority in the discovery of sunspots, and in their interpretation, led Galileo to a long and bitter feud with the Jesuit Christoph Scheiner; in fact, there is little doubt that both of them were beaten by David Fabricius and his son Johannes. Scheiner quickly adopted Kepler's 1615 proposal of the modern telescope design, which gave larger magnification at the cost of inverted images; Galileo apparently never changed to Kepler's design.
Moon
Prior to Galileo's construction of his version of a telescope, Thomas Harriot, an English mathematician and explorer, had already used what he dubbed a "perspective tube" to observe the moon. Reporting his observations, Harriot noted only "strange spottednesse" in the waning of the crescent, but was ignorant to the cause. Galileo, due in part to his artistic training[25] and the knowledge of chiaroscuro,[24] had understood the patterns of light and shadow were in fact topographical markers. While not being the only one to observe the moon through a telescope,Galileo was the first to deduce the cause of the uneven waning as light occlusion from lunar mountains and craters. In his study he also made topographical charts, estimating the heights of the mountains. The moon was not what was long thought to have been a translucent and perfect sphere, as Aristotle claimed, and hardly the first "planet", an "eternal pearl to magnificently ascend into the heavenly empyrian", as put forth by Dante.
Milky Way and stars
Galileo observed the Milky Way, previously believed to be nebulous, and found it to be a multitude of stars packed so densely that they appeared from Earth to be clouds. He located many other stars too distant to be visible with the naked eye. He observed the double star Mizar in Ursa Major in 1617.[108]In the Starry Messenger, Galileo reported that stars appeared as mere blazes of light, essentially unaltered in appearance by the telescope, and contrasted them to planets, which the telescope revealed to be discs. But shortly thereafter, in his letters on sunspots, he reported that the telescope revealed the shapes of both stars and planets to be "quite round". From that point forward, he continued to report that telescopes showed the roundness of stars, and that stars seen through the telescope measured a few seconds of arc in diameter.[109] He also devised a method for measuring the apparent size of a star without a telescope. As described in his Dialogue Concerning the two Chief World Systems, his method was to hang a thin rope in his line of sight to the star and measure the maximum distance from which it would wholly obscure the star. From his measurements of this distance and of the width of the rope, he could calculate the angle subtended by the star at his viewing point.[110] In his Dialogue, he reported that he had found the apparent diameter of a star of first magnitude to be no more than 5 arcseconds, and that of one of sixth magnitude to be about 5/6 arcseconds. Like most astronomers of his day, Galileo did not recognise that the apparent sizes of stars that he measured were spurious, caused by diffraction and atmospheric distortion (see seeing disk or Airy disk), and did not represent the true sizes of stars. However, Galileo's values were much smaller than previous estimates of the apparent sizes of the brightest stars, such as those made by Tycho Brahe (see Magnitude) and enabled Galileo to counter anti-Copernican arguments such as those made by Tycho that these stars would have to be absurdly large for their annual parallaxes to be undetectable.[111] Other astronomers such as Simon Marius, Giovanni Battista Riccioli, and Martinus Hortensius made similar measurements of stars, and Marius and Riccioli concluded the smaller sizes were not small enough to answer Tycho's argument.[112]
Engineering

Galileo's geometrical and military compass, thought to have been made c. 1604 by his personal instrument-maker Marc'Antonio Mazzoleni
Galileo made a number of contributions to what is now known as engineering, as distinct from pure physics. This is not the same distinction as made by Aristotle, who would have considered all Galileo's physics as techne or useful knowledge, as opposed to episteme, or philosophical investigation into the causes of things. Between 1595 and 1598, Galileo devised and improved a Geometric and Military Compass suitable for use by gunners and surveyors. This expanded on earlier instruments designed by Niccolò Tartaglia and Guidobaldo del Monte. For gunners, it offered, in addition to a new and safer way of elevating cannons accurately, a way of quickly computing the charge of gunpowder for cannonballs of different sizes and materials. As a geometric instrument, it enabled the construction of any regular polygon, computation of the area of any polygon or circular sector, and a variety of other calculations. Under Galileo's direction, instrument maker Marc'Antonio Mazzoleni produced more than 100 of these compasses, which Galileo sold (along with an instruction manual he wrote) for 50 lire and offered a course of instruction in the use of the compasses for 120 lire.[113]
In about 1593, Galileo constructed a thermometer, using the expansion and contraction of air in a bulb to move water in an attached tube.

A replica of the earliest surviving telescope attributed to Galileo Galilei, on display at the Griffith Observatory.
In 1609, Galileo was, along with Englishman Thomas Harriot and others, among the first to use a refracting telescope as an instrument to observe stars, planets or moons. The name "telescope" was coined for Galileo's instrument by a Greek mathematician, Giovanni Demisiani,[114] at a banquet held in 1611 by Prince Federico Cesi to make Galileo a member of his Accademia dei Lincei.[115] The name was derived from the Greek tele = 'far' and skopein = 'to look or see'. In 1610, he used a telescope at close range to magnify the parts of insects.[116] By 1624 Galileo had used[117] a compound microscope. He gave one of these instruments to Cardinal Zollern in May of that year for presentation to the Duke of Bavaria,[118] and in September he sent another to Prince Cesi.[119] The Linceans played a role again in naming the "microscope" a year later when fellow academy member Giovanni Faber coined the word for Galileo's invention from the Greek words μικρόν (micron) meaning "small", and σκοπεῖν (skopein) meaning "to look at". The word was meant to be analogous with "telescope".[120][121] Illustrations of insects made using one of Galileo's microscopes, and published in 1625, appear to have been the first clear documentation of the use of a compound microscope.[122]
In 1612, having determined the orbital periods of Jupiter's satellites, Galileo proposed that with sufficiently accurate knowledge of their orbits, one could use their positions as a universal clock, and this would make possible the determination of longitude. He worked on this problem from time to time during the remainder of his life; but the practical problems were severe. The method was first successfully applied by Giovanni Domenico Cassini in 1681 and was later used extensively for large land surveys; this method, for example, was used to survey France, and later by Zebulon Pike of the midwestern United States in 1806. For sea navigation, where delicate telescopic observations were more difficult, the longitude problem eventually required development of a practical portable marine chronometer, such as that of John Harrison.[123] In his last year, when totally blind, he designed an escapement mechanism for a pendulum clock (called Galileo's escapement), a vectorial model of which may be seen here. The first fully operational pendulum clock was made by Christiaan Huygens in the 1650s.
Physics
Galileo's theoretical and experimental work on the motions of bodies, along with the largely independent work of Kepler and René Descartes, was a precursor of the classical mechanics developed by Sir Isaac Newton. Galileo conducted several experiments with pendulums. It is popularly believed (thanks to the biography by Vincenzo Viviani) that these began by watching the swings of the bronze chandelier in the cathedral of Pisa, using his pulse as a timer. Later experiments are described in his Two New Sciences. Galileo claimed that a simple pendulum is isochronous, i.e. that its swings always take the same amount of time, independently of the amplitude. In fact, this is only approximately true,[124] as was discovered by Christiaan Huygens. Galileo also found that the square of the period varies directly with the length of the pendulum. Galileo's son, Vincenzo, sketched a clock based on his father's theories in 1642. The clock was never built and, because of the large swings required by its verge escapement, would have been a poor timekeeper. (See Technology above.)
Galileo is lesser known for, yet still credited with, being one of the first to understand sound frequency. By scraping a chisel at different speeds, he linked the pitch of the sound produced to the spacing of the chisel's skips, a measure of frequency. In 1638, Galileo described an experimental method to measure the speed of light by arranging that two observers, each having lanterns equipped with shutters, observe each other's lanterns at some distance. The first observer opens the shutter of his lamp, and, the second, upon seeing the light, immediately opens the shutter of his own lantern. The time between the first observer's opening his shutter and seeing the light from the second observer's lamp indicates the time it takes light to travel back and forth between the two observers.
Galileo reported that when he tried this at a distance of less than a mile, he was unable to determine whether or not the light appeared instantaneously.[125] Sometime between Galileo's death and 1667, the members of the Florentine Accademia del Cimento repeated the experiment over a distance of about a mile and obtained a similarly inconclusive result.[126] We now know that the speed of light is far too fast to be measured by such methods (with human shutter-openers on Earth).
Galileo put forward the basic principle of relativity, that the laws of physics are the same in any system that is moving at a constant speed in a straight line, regardless of its particular speed or direction. Hence, there is no absolute motion or absolute rest. This principle provided the basic framework for Newton's laws of motion and is central to Einstein's special theory of relativity.
Falling bodies
A biography by Galileo's pupil Vincenzo Viviani stated that Galileo had dropped balls of the same material, but different masses, from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that their time of descent was independent of their mass.[127] This was contrary to what Aristotle had taught: that heavy objects fall faster than lighter ones, in direct proportion to weight.[128] While this story has been retold in popular accounts, there is no account by Galileo himself of such an experiment, and it is generally accepted by historians that it was at most a thought experiment which did not actually take place.[129] An exception is Drake,[130] who argues that the experiment did take place, more or less as Viviani described it. The experiment described was actually performed by Simon Stevin (commonly known as Stevinus),[23] although the building used was actually the church tower in Delft in 1586.[131]However most of his experiments with falling bodies were carried out using inclined planes where both the issues of timing and wind resistance were much reduced.
In his 1638 Discorsi, Galileo's character Salviati, widely regarded as Galileo's spokesman, held that all unequal weights would fall with the same finite speed in a vacuum. But this had previously been proposed by Lucretius[132] and Simon Stevin.[133] Cristiano Banti's Salviati also held it could be experimentally demonstrated by the comparison of pendulum motions in air with bobs of lead and of cork which had different weight but which were otherwise similar.
Galileo proposed that a falling body would fall with a uniform acceleration, as long as the resistance of the medium through which it was falling remained negligible, or in the limiting case of its falling through a vacuum.[134] He also derived the correct kinematical law for the distance travelled during a uniform acceleration starting from rest—namely, that it is proportional to the square of the elapsed time ( d ∝ t 2 ).[135] Prior to Galileo, Nicole Oresme, in the 14th century, had derived the times-squared law for uniformly accelerated change,[136] and Domingo de Soto had suggested in the 16th century that bodies falling through a homogeneous medium would be uniformly accelerated.[137] Galileo expressed the time-squared law using geometrical constructions and mathematically precise words, adhering to the standards of the day. (It remained for others to re-express the law in algebraic terms).
He also concluded that objects retain their velocity unless a force—often friction—acts upon them, refuting the generally accepted Aristotelian hypothesis that objects "naturally" slow down and stop unless a force acts upon them. Philosophical ideas relating to inertia had been proposed by John Philoponus centuries earlier, as had Jean Buridan, and according to Joseph Needham, Mo Tzu had proposed it centuries before either of them; nevertheless, Galileo was the first to express it mathematically, verify it experimentally, and introduce the idea of frictional force, the key breakthrough in validating the concept. Galileo's Principle of Inertia stated: "A body moving on a level surface will continue in the same direction at constant speed unless disturbed." This principle was incorporated into Newton's laws of motion (first law).

Dome of the Cathedral of Pisa with the "lamp of Galileo"
See also: Equations for a falling body
Mathematics
While Galileo's application of mathematics to experimental physics was innovative, his mathematical methods were the standard ones of the day. The analysis and proofs relied heavily on the Eudoxian theory of proportion, as set forth in the fifth book of Euclid's Elements. This theory had become available only a century before, thanks to accurate translations by Tartaglia and others; but by the end of Galileo's life, it was being superseded by the algebraic methods of Descartes.Galileo produced some mathematics: Galileo's paradox, which shows that there are as many perfect squares as there are whole numbers, even though most numbers are not perfect squares.
His writings

Statue outside the Uffizi, Florence
Galileo's early works describing scientific instruments include the 1586 tract entitled The Little Balance (La Billancetta) describing an accurate balance to weigh objects in air or water[138] and the 1606 printed manual Le Operazioni del Compasso Geometrico et Militare on the operation of a geometrical and military compass.[139]
His early works in dynamics, the science of motion and mechanics were his 1590 Pisan De Motu (On Motion) and his circa 1600 Paduan Le Meccaniche (Mechanics). The former was based on Aristotelian–Archimedean fluid dynamics and held that the speed of gravitational fall in a fluid medium was proportional to the excess of a body's specific weight over that of the medium, whereby in a vacuum, bodies would fall with speeds in proportion to their specific weights. It also subscribed to the Hipparchan-Philoponan impetus dynamics in which impetus is self-dissipating and free-fall in a vacuum would have an essential terminal speed according to specific weight after an initial period of acceleration.
Galileo's 1610 The Starry Messenger (Sidereus Nuncius) was the first scientific treatise to be published based on observations made through a telescope. It reported his discoveries of:
- the Galilean moons;
- the roughness of the Moon's surface;
- the existence of a large number of stars invisible to the naked eye, particularly those responsible for the appearance of the Milky Way; and
- differences between the appearances of the planets and those of the fixed stars—the former appearing as small discs, while the latter appeared as unmagnified points of light.
In 1623, Galileo published The Assayer—Il Saggiatore, which attacked theories based on Aristotle's authority and promoted experimentation and the mathematical formulation of scientific ideas. The book was highly successful and even found support among the higher echelons of the Christian church.[144] Following the success of The Assayer, Galileo published the Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems (Dialogo sopra i due massimi sistemi del mondo) in 1632. Despite taking care to adhere to the Inquisition's 1616 instructions, the claims in the book favouring Copernican theory and a non Geocentric model of the solar system led to Galileo being tried and banned on publication. Despite the publication ban, Galileo published his Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences (Discorsi e Dimostrazioni Matematiche, intorno a due nuove scienze) in 1638 in Holland, outside the jurisdiction of the Inquisition.
Summary of Galileo's published written works
Galileo's main written works are as follows:- The Little Balance (1586)
- On Motion (1590)[145]
- Mechanics (ca. 1600)
- The Starry Messenger (1610; in Latin, Sidereus Nuncius)
- Discourse on Floating Bodies (1612)
- Letters on Sunspots (1613)
- Letter to the Grand Duchess Christina (1615; published in 1636)
- Discourse on the Tides (1616; in Italian, Discorso del flusso e reflusso del mare)
- Discourse on the Comets (1619; in Italian, Discorso Delle Comete)
- The Assayer (1623; in Italian, Il Saggiatore)
- Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems (1632; in Italian Dialogo dei due massimi sistemi del mondo)
- Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences (1638; in Italian, Discorsi e Dimostrazioni Matematiche, intorno a due nuove scienze)
Legacy
Church reassessments of Galileo in later centuries
The Inquisition's ban on reprinting Galileo's works was lifted in 1718 when permission was granted to publish an edition of his works (excluding the condemned Dialogue) in Florence.[146] In 1741 Pope Benedict XIV authorised the publication of an edition of Galileo's complete scientific works[147] which included a mildly censored version of the Dialogue.[148] In 1758 the general prohibition against works advocating heliocentrism was removed from the Index of prohibited books, although the specific ban on uncensored versions of the Dialogue and Copernicus's De Revolutionibus remained.[149] All traces of official opposition to heliocentrism by the church disappeared in 1835 when these works were finally dropped from the Index.[150]In 1939 Pope Pius XII, in his first speech to the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, within a few months of his election to the papacy, described Galileo as being among the "most audacious heroes of research... not afraid of the stumbling blocks and the risks on the way, nor fearful of the funereal monuments".[151] His close advisor of 40 years, Professor Robert Leiber, wrote: "Pius XII was very careful not to close any doors (to science) prematurely. He was energetic on this point and regretted that in the case of Galileo."[152]
On 15 February 1990, in a speech delivered at the Sapienza University of Rome,[153] Cardinal Ratzinger (later to become Pope Benedict XVI) cited some current views on the Galileo affair as forming what he called "a symptomatic case that permits us to see how deep the self-doubt of the modern age, of science and technology goes today".[154] Some of the views he cited were those of the philosopher Paul Feyerabend, whom he quoted as saying "The Church at the time of Galileo kept much more closely to reason than did Galileo himself, and she took into consideration the ethical and social consequences of Galileo's teaching too. Her verdict against Galileo was rational and just and the revision of this verdict can be justified only on the grounds of what is politically opportune."[154] The Cardinal did not clearly indicate whether he agreed or disagreed with Feyerabend's assertions. He did, however, say "It would be foolish to construct an impulsive apologetic on the basis of such views."[154]
On 31 October 1992, Pope John Paul II expressed regret for how the Galileo affair was handled, and issued a declaration acknowledging the errors committed by the Catholic Church tribunal that judged the scientific positions of Galileo Galilei, as the result of a study conducted by the Pontifical Council for Culture.[155][156] In March 2008 the head of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Nicola Cabibbo, announced a plan to honour Galileo by erecting a statue of him inside the Vatican walls.[157] In December of the same year, during events to mark the 400th anniversary of Galileo's earliest telescopic observations, Pope Benedict XVI praised his contributions to astronomy.[158] A month later, however, the head of the Pontifical Council for Culture, Gianfranco Ravasi, revealed that the plan to erect a statue of Galileo in the grounds of the Vatican had been suspended.[159]
Impact on modern science
According to Stephen Hawking, Galileo probably bears more of the responsibility for the birth of modern science than anybody else,[160] and Albert Einstein called him the father of modern science.[161][162]Galileo's astronomical discoveries and investigations into the Copernican theory have led to a lasting legacy which includes the categorisation of the four large moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo (Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto) as the Galilean moons. Other scientific endeavours and principles are named after Galileo including the Galileo spacecraft,[163] the first spacecraft to enter orbit around Jupiter, the proposed Galileo global satellite navigation system, the transformation between inertial systems in classical mechanics denoted Galilean transformation and the Gal (unit), sometimes known as the Galileo, which is a non-SI unit of acceleration.
Partly because 2009 was the fourth centenary of Galileo's first recorded astronomical observations with the telescope, the United Nations scheduled it to be the International Year of Astronomy.[164] A global scheme was laid out by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), also endorsed by UNESCO—the UN body responsible for Educational, Scientific and Cultural matters. The International Year of Astronomy 2009 was intended to be a global celebration of astronomy and its contributions to society and culture, stimulating worldwide interest not only in astronomy but science in general, with a particular slant towards young people.
Asteroid 697 Galilea is named in his honour.
In artistic and popular media
Galileo is mentioned several times in the "opera" section of the Queen song, "Bohemian Rhapsody".[165] He features prominently in the song "Galileo" performed by the Indigo Girls and Amy Grant's Galileo on her Heart in Motion album.Twentieth-century plays have been written on Galileo's life, including Life of Galileo (1943) by the German playwright Bertolt Brecht, with a film adaptation (1975) of it, and Lamp At Midnight (1947) by Barrie Stavis,[166] as well as the 2008 play "Galileo Galilei".[167]
Kim Stanley Robinson wrote a science fiction novel entitled Galileo's Dream (2009), in which Galileo is brought into the future to help resolve a crisis of scientific philosophy; the story moves back and forth between Galileo's own time and a hypothetical distant future, and contains a great deal of biographical information.[168]
Galileo Galilei was recently selected as a main motif for a high value collectors' coin: the €25 International Year of Astronomy commemorative coin, minted in 2009. This coin also commemorates the 400th anniversary of the invention of Galileo's telescope. The obverse shows a portion of his portrait and his telescope. The background shows one of his first drawings of the surface of the moon. In the silver ring other telescopes are depicted: the Isaac Newton Telescope, the observatory in Kremsmünster Abbey, a modern telescope, a radio telescope and a space telescope. In 2009, the Galileoscope was also released. This is a mass-produced, low-cost educational 2-inch (51 mm) telescope with relatively high quality.
Timeline
- 1543 – Nicolaus Copernicus publishes De revolutionibus orbium coelestium as an alternative world system to the Ptolemy's geocentric model causing subsequent questions to be raised about Aristotelian physics following Copernicus' death
- 1563 – Parents Vincenzo Galilei and Giulia Ammannati marry
- 1564 – Birth in Pisa, Italy
- ~1570 – Thomas Digges publishes Pantometria describing a telescope built between 1540–1559 by his father Leonard Digges
- 1573 – Tycho Brahe publishes De nova stella (On the new star) refuting Aristotelian belief in immutable celestial spheres and an eternal, unchanging, more perfect heavenly realm of celestial aether above the moon
- 1576 – Giuseppe Moletti Galileo's predecessor in the mathematics chair at Padua, reports falling bodies of the same shape fall at the same speed, regardless of material[169]
- 1581 – His father, Vincenzo Galilei publishes Dialogo della musica antica et moderna formulating musical theories[170]
- 1581 – Enrols as medical student at University of Pisa
- 1582 – Attends mathematics lecture by Ostilio Ricci and decides to study math and science
- 1585 – Leaves University of Pisa without degree and works as tutor
- 1586 – Invents hydrostatic balance; wrote La Balancitta (The little balance)
- 1586 – Simon Stevin publishes results for dropping lead weights from 10 meters
- 1588 – Tycho Brahe publishes work on comets containing a description of the Tychonic system of the world[171]
- 1589 – Appointed to Mathematics Chair, University of Pisa
- 1590 – Partially completes De Motu (On Motion), which is never published
- 1591 – Death of his father, Vicenzo Galilei
- 1592 – Appointed professor of mathematics at University of Padua, remains 18 years
- ~1593 – Invents early thermometer that unfortunately depended on both temperature and pressure
- ~1595 – Invents improved ballistics calculation geometric and military compass, which he later improves for surveying and general calculations and earns income from tutoring on its use
- 1597 – Letter to Kepler indicates his belief in the Copernican System
- 1600 – First child, Virginia is born; ~1600 Le Meccaniche (Mechanics)
- 1600 – William Gilbert publishes On the Magnet and Magnetic Bodies, and on That Great Magnet the Earth with arguments supporting the Copernican system
- 1600 – Roman Inquisition finds Giordano Bruno, Copernican system supporter, guilty of heresy for opinions on pantheism and the eternal plurality of worlds, and for denial of the Trinity, divinity of Christ, virginity of Mary, and Transubstantiation; burned at the stake by civil authorities
- 1601 – Daughter Livia is born
- 1604 – Measures supernova position indicating no parallax for the new star
- 1605 – Sued by brothers-in-law for nonpayment of sisters' dowries
- 1606 – Son Vincenzo born
- 1606 – Publishes manual for his calculating compass
- 1607 – Rotilio Orlandini attempts to assassinate Galileo's friend, Friar Paolo Sarpi
- 1608 – Hans Lippershey invents a refracting telescope
- 1609 – Independently invents and improves telescopes based on description of invention by Hans Lippershey
- 1609 – Kepler publishes Astronomia nova containing his first two laws and for the first time demonstrates the Copernican model is more accurate than the Ptolemaic for uses such as navigation and prediction
- 1609 – Thomas Harriot sketches the Moon from telescopic observations made four months before Galileo's
- 1610 – Publishes Sidereus Nuncius (Starry Messenger); views our moon's mountains and craters and brightest 4 of Jupiter's moons
- 1610 - Martin Horky publishes Brevissima Peregrinatio Contra Nuncium Sidereum, opposing Galileo
- 1610 – Kepler requests one of Galileo's telescopes or lenses, but Galileo replies he is too busy to build one and has no extras[172]
- 1610 – Lifetime appointment to mathematics position at University of Padua, and as mathematician and philosopher for Cosimo II, Grand Duke of Tuscany
- 1611 – Discovers phases of Venus; granted audience with Pope; made member of Lincean Academy
- 1611 – David Fabricius publishes Narration on Spots Observed on the Sun and their Apparent Rotation with the Sun prior to Christoph Scheiner and Galileo's published works on the subject
- 1612 – Proposed Jupiter's moons could be used as a universal clock for possible determination of longitude
- ~1612 or 1613 – Francesco Sizzi discovers annual variations in sunspots' motions
- 1613 – Letters on Sunspots
- 1615 – Letter to Grand Duchess Christina (not published until 1636)
- 1616 – Officially warned by the Church not to hold or defend the Copernican System
- 1616 – The Catholic Church places De revolutionibus orbium coelestium on the List of Prohibited Books, pending correction
- 1616 – Private letter Discourse on the Tides
- 1617 – Moves into Bellosguardo, west of Florence, near his daughters' convent; observes double star Mizar in Ursa Major
- 1619 – Kepler publishes Harmonices Mundi which introduces his third law
- 1619 – Discourse on the Comets
- 1621 – Maffeo Barberini becomes Pope Urban VIII
- 1623 – Publishes The Assayer
- 1624 – Visits Pope who praises and honours him, leaving with assumed permission to publish work on the Copernican vs. Ptolemaic Systems; used a compound microscope
- 1625 – Illustrations of insects made using one of Galileo's microscopes published
- 1630 – Completes Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems and subsequently receives approval of Church censor
- 1632 – Publishes Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems
- 1633 – sentenced by the Inquisition to imprisonment, commuted to house arrest, for vehement suspicion of heresy in violating the 1616 injunction
- 1633 – Catholic Church places Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems on the List of Prohibited Books
- 1638 – Publishes Dialogues Concerning Two New Sciences
- 1642 – death in Arcetri, Italy
- 1668 – Newton builds his reflecting telescope
- 1687 – Isaac Newton publishes Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica deriving Kepler's laws from the Universal Law of Gravitation and the Laws of Motion, uniting the heavens and earth under the same natural laws











