Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species.
Definition
| Type of pesticide | Target pest group |
|---|---|
| Algicides or algaecides | Algae |
| Avicides | Birds |
| Bactericides | Bacteria |
| Fungicides | Fungi and oomycetes |
| Herbicides | Plant |
| Insecticides | Insects |
| Lampricides | Lampreys |
| Miticides or acaricides | Mites |
| Molluscicides | Snails |
| Nematicides | Nematodes |
| Rodenticides | Rodents |
| Slimicides | Algae, Bacteria, Fungi, and Slime molds |
| Virucides | Viruses |
The word pesticide derives from the Latin pestis (plague) and caedere (kill).
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has defined pesticide as:
- any substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, or controlling any pest, including vectors of human or animal disease, unwanted species of plants or animals, causing harm during or otherwise interfering with the production, processing, storage, transport, or marketing of food, agricultural commodities, wood and wood products or animal feedstuffs, or substances that may be administered to animals for the control of insects, arachnids, or other pests in or on their bodies. The term includes substances intended for use as a plant growth regulator, defoliant, desiccant, or agent for thinning fruit or preventing the premature fall of fruit. Also used as substances applied to crops either before or after harvest to protect the commodity from deterioration during storage and transport.
Classifications
Pesticides can be classified by target organism (e.g., herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, rodenticides, and pediculicides – see table),
Biopesticides according to the EPA include microbial pesticides, biochemical pesticides, and plant-incorporated protectants.
Pesticides can be classified into structural classes, with many structural classes developed for each of the target organisms listed in the table. A structural class is usually associated with a single mode of action, whereas a mode of action may encompass more than one structural class.
The pesticidal chemical (active ingredient) is mixed (formulated) with other components to form the product that is sold, and which is applied in various ways. Pesticides in gas form are fumigants.
Pesticides can be classified based upon their mode of action, which indicates the exact biological mechanism which the pesticide disrupts. The modes of action are important for resistance management, and are categorized and administered by the insecticide, herbicide, and fungicide resistance action committees.
Pesticides may be systemic or non-systemic. A systemic pesticide moves (translocates) inside the plant. Translocation may be upward in the xylem, or downward in the phloem or both. Non-systemic pesticides (contact pesticides) remain on the surface and act though direct contact with target organism. Pesticdes are more effective if they are systemic. Systemicity is a prerequisite for the pesticide to be used as a seed-treatment.
Pesticides can be classified as persistent (non-biodegradable) or non-persistent (biodegradable). A pesticide must be persistent enough to kill or control its target but must degrade fast enough not to accumulate in the environment or the food chain in order to be approved by the authorities. Persistent pesticides, including DDT, were banned decades ago, an exception being spraying in houses to combat malaria vectors.
History
From biblical times until the 1950s the pesticides used were inorganic compounds and plant extracts. The inorganic compounds were derivatives of copper, arsenic, mercury, sulfur, among others, and the plant extracts contained pyrethrum, nicotine, and rotenone among others. The less toxic of these are still in use in organic farming. In the 1940s the insecticide DDT, and the herbicide 2,4-D, were introduced. These synthetic organic (i.e. non inorganic) compounds were widely used and were very profitable. They were followed in the 1950s and 1960s by numerous other synthetic pesticides, which led to the growth of the pesticide industry. During this period, it became increasing evident that DDT, which had been sprayed widely in the environment to combat the vector, had accumulated in the food chain, and become a global pollutant, as summarised in the well-known book Silent Spring. Finally, DDT was banned in the 1970s in several countries, and subsequently all persistent pesticides were banned worldwide, an exception being spraying on interior walls for vector control.
Resistance to a pesticide was first seen in the 1920s with inorganic pesticides, and later it was found that development of resistance is to be expected, and measures to delay it are important. Integrated pest management (IPM) was introduced in the 1950s. By careful analysis and spraying only when an economical or biological threshold of crop damage is reached, pesticide application is reduced. This became in the 2020s the official policy of international organisations, industry, and many governments. With the introduction of high yielding varieties in the 1960s in the green revolution, more pesticides were used. Since the 1980s genetically modified crops were introduced, which resulted in lower amounts of insecticides used on them. Organic agriculture, which uses only non-synthetic pesticides, has grown and in 2020 represents about 1.5 per cent of the world’s total agricultural land.
Pesticides have become more effective. Application rates fell from 1,000–2,500 grams of active ingredient per hectare (g/ha) in the 1950s to 40–100 g/ha in the 2000s. Despite this, amounts used have increased. In high income countries over 20 years between the 1990s and 2010s amounts used increased 20%, while in the low income countries amounts increased 1623%.
Development of new pesticides
The aim is to find new compounds or agents with improved properties such as a new mode of action or lower application rate. Another aim is to replace older pesticides which have been banned for reasons of toxicity or environmental harm or have become less effective due to development of resistance.
The process starts with testing (screening) against target organisms such as insects, fungi or plants. Inputs are typically random compounds, natural products, compounds designed to disrupt a biochemical target, compounds described in patents or literature, or biocontrol organisms.
Compounds that are active in the screening process, known as hits or leads, cannot be used as pesticides, except for biocontrol organisms and some potent natural products. These lead compounds need to be optimised by a series of cycles of synthesis and testing of analogs. For approval by regulatory authorities for use as pesticides, the optimized compounds must meet several requirements. In addition to being potent (low application rate), they must show low toxicity, low environmental impact, and viable manufacturing cost. The cost of developing a pesticide in 2022 was estimated to be 350 million US dollars. It has become more difficult to find new pesticides. More than 100 new active ingredients were introduced in the 2000s and less than 40 in the 2010s. Biopesticides are cheaper to develop, since the authorities require less toxicological and environmental study. Since 2000 the rate of new biological product introduction has frequently exceeded that of conventional products.
More than 25% of existing chemical pesticides contain one or more chiral centres (stereogenic centres). Newer pesticides with lower application rates tend to have more complex structures, and thus more often contain chiral centres. In cases when most or all of the pesticidal activity in a new compound is found in one enantiomer (the eutomer), the registration and use of the compound as this single enantiomer is preferred. This reduces the total application rate and avoids the tedious environmental testing required when registering a racemate. However if a viable enantioselective manufacturing route cannot be found, then the racemate is registered and used.
Insecticides with systemic activity against sucking pests, which are safe to pollinators, are sought particularly in view of the partial bans on neonicotinoids. Revised 2023 guidance by registration authorities describes the bee testing that is required for new insecticides to be approved for commercial use.
Uses
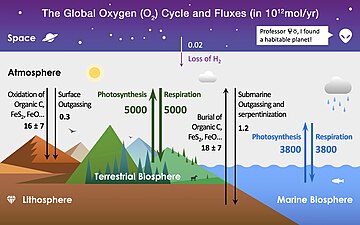
In addition to their main use in agriculture, pesticides have a number of other applications. Pesticides are used to control organisms that are considered to be harmful, or pernicious to their surroundings. For example, they are used to kill mosquitoes that can transmit potentially deadly diseases like West Nile virus, yellow fever, and malaria. They can also kill bees, wasps or ants that can cause allergic reactions. Insecticides can protect animals from illnesses that can be caused by parasites such as fleas. Pesticides can prevent sickness in humans that could be caused by moldy food or diseased produce. Herbicides can be used to clear roadside weeds, trees, and brush. They can also kill invasive weeds that may cause environmental damage. Herbicides are commonly applied in ponds and lakes to control algae and plants such as water grasses that can interfere with activities like swimming and fishing and cause the water to look or smell unpleasant. Uncontrolled pests such as termites and mold can damage structures such as houses. Pesticides are used in grocery stores and food storage facilities to manage rodents and insects that infest food such as grain. Pesticides are used on lawns and golf courses, partly for cosmetic reasons.
Integrated pest management, the use of multiple approaches to control pests, is becoming widespread and has been used with success in countries such as Indonesia, China, Bangladesh, the U.S., Australia, and Mexico. IPM attempts to recognize the more widespread impacts of an action on an ecosystem, so that natural balances are not upset.
Each use of a pesticide carries some associated risk. Proper pesticide use decreases these associated risks to a level deemed acceptable by pesticide regulatory agencies such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Pest Management Regulatory Agency (PMRA) of Canada.
DDT, sprayed on the walls of houses, is an organochlorine that has been used to fight malaria vectors (mosquitos) since the 1940s. The World Health Organization recommend this approach. It and other organochlorine pesticides have been banned in most countries worldwide because of their persistence in the environment and human toxicity. DDT has become less effective, as resistance was identified in Africa as early as 1955, and by 1972 nineteen species of mosquito worldwide were resistant to DDT.
Amount used
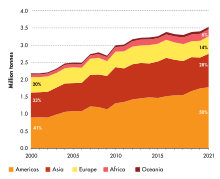
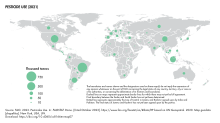
Total pesticides use in agriculture in 2021 was 3.54 million tonnes of active ingredients (Mt), a 4 percent increase with respect to 2020, a 11 percent increase in a decade, and a doubling since 1990. Pesticides use per area of cropland in 2021 was 2.26 kg per hectare (kg/ha), an increase of 4 percent with respect to 2020; use per value of agricultural production was 0.86 kg per thousand international dollar (kg/1000 I$) (+2%); and use per person was 0.45 kg per capita (kg/cap) (+3%). Between 1990 and 2021, these indicators increased by 85 percent, 3 percent, and 33 percent, respectively. Brazil was the world's largest user of pesticides in 2021, with 720 kt of pesticides applications for agricultural use, while USA (457 kt) was the second largest user.
Applications per cropland area in 2021 varied widely, from 10.9 kg/hectare in Brazil to 0.8 kg/ha in the Russian Federation. The level in Brazil was about twice as high as in Argentina (5.6 kg/ha) and Indonesia (5.3 kg/ha). Insecticide use in the US has declined by more than half since 1980 (0.6%/yr), mostly due to the near phase-out of organophosphates. In corn fields, the decline was even steeper, due to the switchover to transgenic Bt corn.
Benefits
Pesticides can save farmers' money by preventing crop losses to insects and other pests; in the U.S., farmers get an estimated fourfold return on money they spend on pesticides. One study found that not using pesticides reduced crop yields by about 10%. Another study, conducted in 1999, found that a ban on pesticides in the United States may result in a rise of food prices, loss of jobs, and an increase in world hunger.
There are two levels of benefits for pesticide use, primary and secondary. Primary benefits are direct gains from the use of pesticides and secondary benefits are effects that are more long-term.
Biological
Controlling pests and plant disease vectors
- Improved crop yields
- Improved crop/livestock quality
- Invasive species controlled
Controlling human/livestock disease vectors and nuisance organisms
- Human lives saved and disease reduced. Diseases controlled include malaria, with millions of lives having been saved or enhanced with the use of DDT alone.
- Animal lives saved and disease reduced
Controlling organisms that harm other human activities and structures
- Drivers view unobstructed
- Tree/brush/leaf hazards prevented
- Wooden structures protected
Monetary
In one study, it was estimated that for every dollar ($1) that is spent on pesticides for crops can yield up to four dollars ($4) in crops saved. This means based that, on the amount of money spent per year on pesticides, $10 billion, there is an additional $40 billion savings in crop that would be lost due to damage by insects and weeds. In general, farmers benefit from having an increase in crop yield and from being able to grow a variety of crops throughout the year. Consumers of agricultural products also benefit from being able to afford the vast quantities of produce available year-round.
Disadvantages
On the cost side of pesticide use there can be costs to the environment, costs to human health. Pesticides safety education and pesticide applicator regulation are designed to protect the public from pesticide misuse, but do not eliminate all misuse. Reducing the use of pesticides and choosing less toxic pesticides may reduce risks placed on society and the environment from pesticide use.
Health effects

Pesticides may affect health negatively, mimicking hormones causing reproductive problems, and also causing cancer. A 2007 systematic review found that "most studies on non-Hodgkin lymphoma and leukemia showed positive associations with pesticide exposure" and thus concluded that cosmetic use of pesticides should be decreased. There is substantial evidence of associations between organophosphate insecticide exposures and neurobehavioral alterations. Limited evidence also exists for other negative outcomes from pesticide exposure including neurological, birth defects, and fetal death.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends limiting exposure of children to pesticides and using safer alternatives:
Pesticides are also found in majority of U.S. households with 88 million out of the 121.1 million households indicating that they use some form of pesticide in 2012. As of 2007, there were more than 1,055 active ingredients registered as pesticides, which yield over 20,000 pesticide products that are marketed in the United States.
Owing to inadequate regulation and safety precautions, 99% of
pesticide-related deaths occur in developing countries that account for
only 25% of pesticide usage.
One study found pesticide self-poisoning the method of choice in one third of suicides worldwide, and recommended, among other things, more restrictions on the types of pesticides that are most harmful to humans.
A 2014 epidemiological review found associations between autism and exposure to certain pesticides, but noted that the available evidence was insufficient to conclude that the relationship was causal.
Occupational exposure among agricultural workers
The World Health Organization and the UN Environment Programme estimate that 3 million agricultural workers in the developing world experience severe poisoning from pesticides each year, resulting in 18,000 deaths. According to one study, as many as 25 million workers in developing countries may suffer mild pesticide poisoning yearly. Other occupational exposures besides agricultural workers, including pet groomers, groundskeepers, and fumigators, may also put individuals at risk of health effects from pesticides.
Pesticide use is widespread in Latin America, as around US$3 billion are spent each year in the region. Records indicate an increase in the frequency of pesticide poisonings over the past two decades. The most common incidents of pesticide poisoning is thought to result from exposure to organophosphate and carbamate insecticides. At-home pesticide use, use of unregulated products, and the role of undocumented workers within the agricultural industry makes characterizing true pesticide exposure a challenge. It is estimated that 50–80% of pesticide poisoning cases are unreported.
Underreporting of pesticide poisoning is especially common in areas where agricultural workers are less likely to seek care from a healthcare facility that may be monitoring or tracking the incidence of acute poisoning. The extent of unintentional pesticide poisoning may be much greater than available data suggest, particularly among developing countries. Globally, agriculture and food production remain one of the largest industries. In East Africa, the agricultural industry represents one of the largest sectors of the economy, with nearly 80% of its population relying on agriculture for income. Farmers in these communities rely on pesticide products to maintain high crop yields.
Some East Africa governments are shifting to corporate farming, and opportunities for foreign conglomerates to operate commercial farms have led to more accessible research on pesticide use and exposure among workers. In other areas where large proportions of the population rely on subsistence, small-scale farming, estimating pesticide use and exposure is more difficult.
Pesticide poisoning

Pesticides may exhibit toxic effects on humans and other non-target species, the severity of which depends on the frequency and magnitude of exposure. Toxicity also depends on the rate of absorption, distribution within the body, metabolism, and elimination of compounds from the body. Commonly used pesticides like organophosphates and carbamates act by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity, which prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine at the neural synapse. Excess acetylcholine can lead to symptoms like muscle cramps or tremors, confusion, dizziness and nausea. Studies show that farm workers in Ethiopia, Kenya, and Zimbabwe have decreased concentrations of plasma acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine acting on synapses throughout the nervous system. Other studies in Ethiopia have observed reduced respiratory function among farm workers who spray crops with pesticides. Numerous exposure pathways for farm workers increase the risk of pesticide poisoning, including dermal absorption walking through fields and applying products, as well as inhalation exposure.
Measuring exposure to pesticides
There are multiple approaches to measuring a person's exposure to pesticides, each of which provides an estimate of an individual's internal dose. Two broad approaches include measuring biomarkers and markers of biological effect. The former involves taking direct measurement of the parent compound or its metabolites in various types of media: urine, blood, serum. Biomarkers may include a direct measurement of the compound in the body before it's been biotransformed during metabolism. Other suitable biomarkers may include the metabolites of the parent compound after they've been biotransformed during metabolism. Toxicokinetic data can provide more detailed information on how quickly the compound is metabolized and eliminated from the body, and provide insights into the timing of exposure.
Markers of biological effect provide an estimation of exposure based on cellular activities related to the mechanism of action. For example, many studies investigating exposure to pesticides often involve the quantification of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme at the neural synapse to determine the magnitude of the inhibitory effect of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides.
Another method of quantifying exposure involves measuring, at the molecular level, the amount of pesticide interacting with the site of action. These methods are more commonly used for occupational exposures where the mechanism of action is better understood, as described by WHO guidelines published in "Biological Monitoring of Chemical Exposure in the Workplace". Better understanding of how pesticides elicit their toxic effects is needed before this method of exposure assessment can be applied to occupational exposure of agricultural workers.
Alternative methods to assess exposure include questionnaires to discern from participants whether they are experiencing symptoms associated with pesticide poisoning. Self-reported symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, nausea, joint pain, or respiratory symptoms.
Challenges in assessing pesticide exposure
Multiple challenges exist in assessing exposure to pesticides in the general population, and many others that are specific to occupational exposures of agricultural workers. Beyond farm workers, estimating exposure to family members and children presents additional challenges, and may occur through "take-home" exposure from pesticide residues collected on clothing or equipment belonging to parent farm workers and inadvertently brought into the home. Children may also be exposed to pesticides prenatally from mothers who are exposed to pesticides during pregnancy. Characterizing children's exposure resulting from drift of airborne and spray application of pesticides is similarly challenging, yet well documented in developing countries. Because of critical development periods of the fetus and newborn children, these non-working populations are more vulnerable to the effects of pesticides, and may be at increased risk of developing neurocognitive effects and impaired development.
While measuring biomarkers or markers of biological effects may provide more accurate estimates of exposure, collecting these data in the field is often impractical and many methods are not sensitive enough to detect low-level concentrations. Rapid cholinesterase test kits exist to collect blood samples in the field. Conducting large scale assessments of agricultural workers in remote regions of developing countries makes the implementation of these kits a challenge. The cholinesterase assay is a useful clinical tool to assess individual exposure and acute toxicity. Considerable variability in baseline enzyme activity among individuals makes it difficult to compare field measurements of cholinesterase activity to a reference dose to determine health risk associated with exposure. Another challenge researchers face in deriving a reference dose is identifying health endpoints that are relevant to exposure. More epidemiological research is needed to identify critical health endpoints, particularly among populations who are occupationally exposed.
Prevention
Minimizing harmful exposure to pesticides can be achieved by proper use of personal protective equipment, adequate reentry times into recently sprayed areas, and effective product labeling for hazardous substances as per FIFRA regulations. Training high-risk populations, including agricultural workers, on the proper use and storage of pesticides, can reduce the incidence of acute pesticide poisoning and potential chronic health effects associated with exposure. Continued research into the human toxic health effects of pesticides serves as a basis for relevant policies and enforceable standards that are health protective to all populations.
Environmental effects
Pesticide use raises a number of environmental concerns. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, including non-target species, air, water and soil. Pesticide drift occurs when pesticides suspended in the air as particles are carried by wind to other areas, potentially contaminating them. Pesticides are one of the causes of water pollution, and some pesticides were persistent organic pollutants (now banned), which contribute to soil and flower (pollen, nectar) contamination. Furthermore, pesticide use can adversely impact neighboring agricultural activity, as pests themselves drift to and harm nearby crops that have no pesticide used on them.
In addition, pesticide use reduces biodiversity, contributes to pollinator decline, destroys habitat (especially for birds), and threatens endangered species. Pests can develop a resistance to the pesticide (pesticide resistance), necessitating a new pesticide. Alternatively a greater dose of the pesticide can be used to counteract the resistance, although this will cause a worsening of the ambient pollution problem.
The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, banned all persistent pesticides, in particular DDT and other organochlorine pesticides, which were stable and lipophilic, and thus able to bioaccumulate in the body and the food chain. and which spread throughout the planet. Persistent pesticides are no longer used for agriculture, and will not be approved by the authorities. Because the half life in soil is long (for DDT 2–15 years) residues can still be detected in humans at levels 5 to 10 times lower than found in the 1970s.
Pesticides now have to be degradable in the environment. Such degradation of pesticides is due to both innate chemical properties of the compounds and environmental processes or conditions. For example, the presence of halogens within a chemical structure often slows down degradation in an aerobic environment. Adsorption to soil may retard pesticide movement, but also may reduce bioavailability to microbial degraders.
Pesticide contamination in the environment can be monitored through bioindicators such as bee pollinators.
Economics
| Harm | Annual US cost |
|---|---|
| Public health | $1.1 billion |
| Pesticide resistance in pest | $1.5 billion |
| Crop losses caused by pesticides | $1.4 billion |
| Bird losses due to pesticides | $2.2 billion |
| Groundwater contamination | $2.0 billion |
| Other costs | $1.4 billion |
| Total costs | $9.6 billion |
In one study, the human health and environmental costs due to pesticides in the United States was estimated to be $9.6 billion: offset by about $40 billion in increased agricultural production.
Additional costs include the registration process and the cost of purchasing pesticides: which are typically borne by agrichemical companies and farmers respectively. The registration process can take several years to complete (there are 70 different types of field tests) and can cost $50–70 million for a single pesticide. At the beginning of the 21st century, the United States spent approximately $10 billion on pesticides annually.
Resistance
The use of pesticides inherently entails the risk of resistance developing. Various techniques and procedures of pesticide application can slow the development of resistance, as can some natural features of the target population and surrounding environment.
Alternatives
Alternatives to pesticides are available and include methods of cultivation, use of biological pest controls (such as pheromones and microbial pesticides), genetic engineering (mostly of crops), and methods of interfering with insect breeding. Application of composted yard waste has also been used as a way of controlling pests.
These methods are becoming increasingly popular and often are safer than traditional chemical pesticides. In addition, EPA is registering reduced-risk pesticides in increasing numbers.
Cultivation practices
Cultivation practices include polyculture (growing multiple types of plants), crop rotation, planting crops in areas where the pests that damage them do not live, timing planting according to when pests will be least problematic, and use of trap crops that attract pests away from the real crop. Trap crops have successfully controlled pests in some commercial agricultural systems while reducing pesticide usage. In other systems, trap crops can fail to reduce pest densities at a commercial scale, even when the trap crop works in controlled experiments.
Use of other organisms
Release of other organisms that fight the pest is another example of an alternative to pesticide use. These organisms can include natural predators or parasites of the pests. Biological pesticides based on entomopathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses causing disease in the pest species can also be used.
Biological control engineering
Interfering with insects' reproduction can be accomplished by sterilizing males of the target species and releasing them, so that they mate with females but do not produce offspring. This technique was first used on the screwworm fly in 1958 and has since been used with the medfly, the tsetse fly, and the gypsy moth. This is a costly and slow approach that only works on some types of insects.
Other alternatives
Other alternatives include "laserweeding" – the use of novel agricultural robots for weed control using lasers.
Push pull strategy
The term "push-pull" was established in 1987 as an approach for integrated pest management (IPM). This strategy uses a mixture of behavior-modifying stimuli to manipulate the distribution and abundance of insects. "Push" means the insects are repelled or deterred away from whatever resource is being protected. "Pull" means that certain stimuli (semiochemical stimuli, pheromones, food additives, visual stimuli, genetically altered plants, etc.) are used to attract pests to trap crops where they will be killed. There are numerous different components involved in order to implement a Push-Pull Strategy in IPM.
Many case studies testing the effectiveness of the push-pull approach have been done across the world. The most successful push-pull strategy was developed in Africa for subsistence farming. Another successful case study was performed on the control of Helicoverpa in cotton crops in Australia. In Europe, the Middle East, and the United States, push-pull strategies were successfully used in the controlling of Sitona lineatus in bean fields.
Some advantages of using the push-pull method are less use of chemical or biological materials and better protection against insect habituation to this control method. Some disadvantages of the push-pull strategy are that if there is a lack of appropriate knowledge of the behavioral and chemical ecology of the host-pest interactions then this method becomes unreliable. Furthermore, because the push-pull method is not a very popular method of IPM operational and registration costs are higher.
Effectiveness
Some evidence shows that alternatives to pesticides can be equally effective as the use of chemicals. A study of Maize fields in northern Florida found that the application of composted yard waste with high carbon to nitrogen ratio to agricultural fields was highly effective at reducing the population of plant-parasitic nematodes and increasing crop yield, with yield increases ranging from 10% to 212%; the observed effects were long-term, often not appearing until the third season of the study. Additional silicon nutrition protects some horticultural crops against fungal diseases almost completely, while insufficient silicon sometimes leads to severe infection even when fungicides are used.
Pesticide resistance is increasing and that may make alternatives more attractive.
Types
Biopesticides
Biopesticides are certain types of pesticides derived from such natural materials as animals, plants, bacteria, and certain minerals. For example, canola oil and baking soda have pesticidal applications and are considered biopesticides. Biopesticides fall into three major classes:
- Microbial pesticides which consist of bacteria, entomopathogenic fungi or viruses (and sometimes includes the metabolites that bacteria or fungi produce). Entomopathogenic nematodes are also often classed as microbial pesticides, even though they are multi-cellular.
- Biochemical pesticides or herbal pesticides are naturally occurring substances that control (or monitor in the case of pheromones) pests and microbial diseases.
- Plant-incorporated protectants (PIPs) have genetic material from other species incorporated into their genetic material (i.e. GM crops). Their use is controversial, especially in many European countries.
By pest type
Pesticides that are related to the type of pests are:
| Type | Action |
|---|---|
| Algicides | Control algae in lakes, canals, swimming pools, water tanks, and other sites |
| Avicides | kill birds |
| Antifouling agents | Kill or repel organisms that attach to underwater surfaces, such as boat bottoms |
| Antimicrobials | Kill microorganisms (such as bacteria and viruses) |
| Attractants | Attract pests (for example, to lure an insect or rodent to a trap). |
| Bactericides | Kill bacteria |
| Biopesticides | Certain types of pesticides derived from such natural materials as animals, plants, bacteria, and certain minerals |
| Biocides | Kill microorganisms |
| Defoliants | Cause leaves or foliage to drop from a plant, usually to facilitate harvest. |
| Desiccants | Promote drying of living tissues, such as unwanted plant tops. |
| Disinfectants and sanitizers | Kill or inactivate disease-producing microorganisms on inanimate objects |
| Fungicides | Kill fungi (including blights, mildews, molds, and rusts) |
| Fumigants | Produce gas or vapor intended to destroy pests in buildings or soil |
| Gene drives | A genetic mechanism embedded into the genetic material of the target species, which can kill or suppress the reproductive of its descendants. |
| Herbicides | Kill weeds and other plants that grow where they are not wanted |
| Insect growth regulators | Disrupt the molting, maturing from pupal stage to adult, or other life processes of insects. |
| Insecticides | Kill insects and other arthropods |
| Lampricides | Kills Lampreys |
| Miticides or acaricides | Kill mites that feed on plants and animals |
| Microbial pesticides | Microorganisms that kill, inhibit, or out compete pests, including insects or other microorganisms |
| Molluscicides | Kill snails and slugs |
| Nematicides | Kill nematodes (microscopic, worm-like organisms that feed on plant roots) |
| Ovicides | Kill eggs of insects and mites |
| Pheromones | Biochemicals used to disrupt the mating behavior of insects |
| Piscicide | Kills fish |
| Plant growth regulators | Alter the expected growth, flowering or reproduction rate of plants (does not include fertilizers). |
| Plant Incorporated protectants | Substances that plants produce from genetic material that has been added to the plant. |
| Repellents | Repel pests, including insects (such as mosquitoes) and birds |
| Rodenticides | Control mice and other rodents |
| Slimicides | Kill slime-producing microorganisms such as algae, bacteria, fungi, and slime molds |
| Soil sterilant | Temporarily or permanently prevents the growth of all plants and animals |
| Virucides | Kills viruses. |
| Wood preservatives | Used to make wood resistant to insects, fungi, and other pests. |
Regulation
International
In many countries, pesticides must be approved for sale and use by a government agency.
Worldwide, 85% of countries have pesticide legislation for the proper storage of pesticides and 51% include provisions to ensure proper disposal of all obsolete pesticides.
Though pesticide regulations differ from country to country, pesticides, and products on which they were used are traded across international borders. To deal with inconsistencies in regulations among countries, delegates to a conference of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization adopted an International Code of Conduct on the Distribution and Use of Pesticides in 1985 to create voluntary standards of pesticide regulation for different countries. The Code was updated in 1998 and 2002. The FAO claims that the code has raised awareness about pesticide hazards and decreased the number of countries without restrictions on pesticide use.
Three other efforts to improve regulation of international pesticide trade are the United Nations London Guidelines for the Exchange of Information on Chemicals in International Trade and the United Nations Codex Alimentarius Commission. The former seeks to implement procedures for ensuring that prior informed consent exists between countries buying and selling pesticides, while the latter seeks to create uniform standards for maximum levels of pesticide residues among participating countries.
United States

In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is responsible for regulating pesticides under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) and the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA).
Studies must be conducted to establish the conditions in which the material is safe to use and the effectiveness against the intended pest(s). The EPA regulates pesticides to ensure that these products do not pose adverse effects to humans or the environment, with an emphasis on the health and safety of children. Pesticides produced before November 1984 continue to be reassessed in order to meet the current scientific and regulatory standards. All registered pesticides are reviewed every 15 years to ensure they meet the proper standards. During the registration process, a label is created. The label contains directions for proper use of the material in addition to safety restrictions. Based on acute toxicity, pesticides are assigned to a Toxicity Class. Pesticides are the most thoroughly tested chemicals after drugs in the United States; those used on food require more than 100 tests to determine a range of potential impacts.
Some pesticides are considered too hazardous for sale to the general public and are designated restricted use pesticides. Only certified applicators, who have passed an exam, may purchase or supervise the application of restricted use pesticides. Records of sales and use are required to be maintained and may be audited by government agencies charged with the enforcement of pesticide regulations. These records must be made available to employees and state or territorial environmental regulatory agencies.
In addition to the EPA, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) set standards for the level of pesticide residue that is allowed on or in crops. The EPA looks at what the potential human health and environmental effects might be associated with the use of the pesticide.
In addition, the U.S. EPA uses the National Research Council's four-step process for human health risk assessment: (1) Hazard Identification, (2) Dose-Response Assessment, (3) Exposure Assessment, and (4) Risk Characterization.
In 2013 Kaua'i County (Hawai'i) passed Bill No. 2491 to add an article to Chapter 22 of the county's code relating to pesticides and GMOs. The bill strengthens protections of local communities in Kaua'i where many large pesticide companies test their products.
The first legislation providing federal authority for regulating pesticides was enacted in 1910.
Canada
EU
EU legislation has been approved banning the use of highly toxic pesticides including those that are carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic to reproduction, those that are endocrine-disrupting, and those that are persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic (PBT) or very persistent and very bioaccumulative (vPvB) and measures have been approved to improve the general safety of pesticides across all EU member states.
In 2023 The Environment Committee of European Parliament approved a decision aiming to reduce pesticide use by 50% (the most hazardous by 65%) by the year 2030 and ensure sustainable use of pesticides (for example use them only as a last resort). The decision also includes measures for providing farmers with alternatives.
Residue
Pesticide residue refers to the pesticides that may remain on or in food after they are applied to food crops. The maximum residue limits (MRL) of pesticides in food are carefully set by the regulatory authorities to ensure, to their best judgement, no health impacts. Regulations such as pre-harvest intervals also often prevent harvest of crop or livestock products if recently treated in order to allow residue concentrations to decrease over time to safe levels before harvest. Exposure of the general population to these residues most commonly occurs through consumption of treated food sources, or being in close contact to areas treated with pesticides such as farms or lawns.
Persistent pesticides are no longer used for agriculture, and will not be approved by the authorities. Because the half life in soil is long (for DDT 2–15 years) residues can still be detected in humans at levels 5 to 10 times lower than found in the 1970s.
Residues are monitored by the authorities. In 2016, over 99% of samples of US produce had no pesticide residue or had residue levels well below the EPA tolerance levels for each pesticide.
![Figure 1. Relationship between formamide and other prebiotic feedstock molecules, such as HCN and ammonium formate.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f6/Figure1.tif/lossless-page1-330px-Figure1.tif.png)
![Figure 2. Main prebiotic building blocks that can be synthesized from formamide under plausible prebiotic conditions.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b0/Wikifig.tif/lossy-page1-440px-Wikifig.tif.jpg)