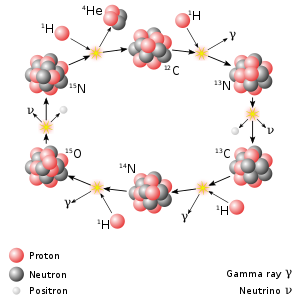Star
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the planet's energy. Some other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points due to their immense distance. Historically, the most prominent stars were grouped into constellations and asterisms, and the brightest stars gained proper names. Extensive catalogues of stars have been assembled by astronomers, which provide standardized star designations.
For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core, releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Once the hydrogen in the core of a star is nearly exhausted, almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime and, for some stars, by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the principal determinant of its evolution and eventual fate.
Other characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement. A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities, known as a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram), allows the age and evolutionary state of a star to be determined.
A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Once the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily converted into helium through nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the process.[1] The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the core through a combination of radiative and convective processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing further under its own gravity. Once the hydrogen fuel at the core is exhausted, a star with at least 0.4 times the mass of the Sun[2] expands to become a red giant, in some cases fusing heavier elements at the core or in shells around the core. The star then evolves into a degenerate form, recycling a portion of its matter into the interstellar environment, where it will contribute to the formation of a new generation of stars with a higher proportion of heavy elements.[3] Meanwhile, the core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or (if it is sufficiently massive) a black hole.
Binary and multi-star systems consist of two or more stars that are gravitationally bound, and generally move around each other in stable orbits. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can have a significant impact on their evolution.[4] Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy.
Observation history

People have seen patterns in the stars since ancient times.[5] This 1690 depiction of the constellation of Leo, the lion, is by Johannes Hevelius.[6]

The constellation of Leo as it can be seen by the naked eye. Lines have been added.
Historically, stars have been important to civilizations throughout the world. They have been part of religious practices and used for celestial navigation and orientation. Many ancient astronomers believed that stars were permanently affixed to a heavenly sphere, and that they were immutable. By convention, astronomers grouped stars into constellations and used them to track the motions of the planets and the inferred position of the Sun.[5] The motion of the Sun against the background stars (and the horizon) was used to create calendars, which could be used to regulate agricultural practices.[7]
The Gregorian calendar, currently used nearly everywhere in the world, is a solar calendar based on the angle of the Earth's rotational axis relative to its local star, the Sun.
The oldest accurately dated star chart appeared in ancient Egyptian astronomy in 1534 BC.[8] The earliest known star catalogues were compiled by the ancient Babylonian astronomers of Mesopotamia in the late 2nd millennium BC, during the Kassite Period (ca. 1531–1155 BC).[9]
The first star catalogue in Greek astronomy was created by Aristillus in approximately 300 BC, with the help of Timocharis.[10] The star catalog of Hipparchus (2nd century BC) included 1020 stars and was used to assemble Ptolemy's star catalogue.[11] Hipparchus is known for the discovery of the first recorded nova (new star).[12] Many of the constellations and star names in use today derive from Greek astronomy.
In spite of the apparent immutability of the heavens, Chinese astronomers were aware that new stars could appear.[13] In 185 AD, they were the first to observe and write about a supernova, now known as the SN 185.[14] The brightest stellar event in recorded history was the SN 1006 supernova, which was observed in 1006 and written about by the Egyptian astronomer Ali ibn Ridwan and several Chinese astronomers.[15] The SN 1054 supernova, which gave birth to the Crab Nebula, was also observed by Chinese and Islamic astronomers.[16][17][18]
Medieval Islamic astronomers gave Arabic names to many stars that are still used today, and they invented numerous astronomical instruments that could compute the positions of the stars. They built the first large observatory research institutes, mainly for the purpose of producing Zij star catalogues.[19] Among these, the Book of Fixed Stars (964) was written by the Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi, who observed a number of stars, star clusters (including the Omicron Velorum and Brocchi's Clusters) and galaxies (including the Andromeda Galaxy).[20] According to A. Zahoor, in the 11th century, the Persian polymath scholar Abu Rayhan Biruni described the Milky Way galaxy as a multitude of fragments having the properties of nebulous stars, and also gave the latitudes of various stars during a lunar eclipse in 1019.[21]
According to Josep Puig, the Andalusian astronomer Ibn Bajjah proposed that the Milky Way was made up of many stars which almost touched one another and appeared to be a continuous image due to the effect of refraction from sublunary material, citing his observation of the conjunction of Jupiter and Mars on 500 AH (1106/1107 AD) as evidence.[22] Early European astronomers such as Tycho Brahe identified new stars in the night sky (later termed novae), suggesting that the heavens were not immutable. In 1584 Giordano Bruno suggested that the stars were like the Sun, and may have other planets, possibly even Earth-like, in orbit around them,[23] an idea that had been suggested earlier by the ancient Greek philosophers, Democritus and Epicurus,[24] and by medieval Islamic cosmologists[25] such as Fakhr al-Din al-Razi.[26] By the following century, the idea of the stars being the same as the Sun was reaching a consensus among astronomers. To explain why these stars exerted no net gravitational pull on the Solar System, Isaac Newton suggested that the stars were equally distributed in every direction, an idea prompted by the theologian Richard Bentley.[27]
The Italian astronomer Geminiano Montanari recorded observing variations in luminosity of the star Algol in 1667. Edmond Halley published the first measurements of the proper motion of a pair of nearby "fixed" stars, demonstrating that they had changed positions from the time of the ancient Greek astronomers Ptolemy and Hipparchus.[23]
William Herschel was the first astronomer to attempt to determine the distribution of stars in the sky. During the 1780s, he performed a series of gauges in 600 directions, and counted the stars observed along each line of sight. From this he deduced that the number of stars steadily increased toward one side of the sky, in the direction of the Milky Way core. His son John Herschel repeated this study in the southern hemisphere and found a corresponding increase in the same direction.[28] In addition to his other accomplishments, William Herschel is also noted for his discovery that some stars do not merely lie along the same line of sight, but are also physical companions that form binary star systems.
The science of stellar spectroscopy was pioneered by Joseph von Fraunhofer and Angelo Secchi. By comparing the spectra of stars such as Sirius to the Sun, they found differences in the strength and number of their absorption lines—the dark lines in a stellar spectra due to the absorption of specific frequencies by the atmosphere. In 1865 Secchi began classifying stars into spectral types.[29] However, the modern version of the stellar classification scheme was developed by Annie J. Cannon during the 1900s.
The first direct measurement of the distance to a star (61 Cygni at 11.4 light-years) was made in 1838 by Friedrich Bessel using the parallax technique. Parallax measurements demonstrated the vast separation of the stars in the heavens.[23] Observation of double stars gained increasing importance during the 19th century. In 1834, Friedrich Bessel observed changes in the proper motion of the star Sirius, and inferred a hidden companion. Edward Pickering discovered the first spectroscopic binary in 1899 when he observed the periodic splitting of the spectral lines of the star Mizar in a 104-day period. Detailed observations of many binary star systems were collected by astronomers such as William Struve and S. W. Burnham, allowing the masses of stars to be determined from computation of the orbital elements. The first solution to the problem of deriving an orbit of binary stars from telescope observations was made by Felix Savary in 1827.[30] The twentieth century saw increasingly rapid advances in the scientific study of stars. The photograph became a valuable astronomical tool. Karl Schwarzschild discovered that the color of a star, and hence its temperature, could be determined by comparing the visual magnitude against the photographic magnitude. The development of the photoelectric photometer allowed very precise measurements of magnitude at multiple wavelength intervals. In 1921 Albert A. Michelson made the first measurements of a stellar diameter using an interferometer on the Hooker telescope.[31]
Important theoretical work on the physical structure of stars occurred during the first decades of the twentieth century. In 1913, the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram was developed, propelling the astrophysical study of stars. Successful models were developed to explain the interiors of stars and stellar evolution. Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin first proposed that stars were made primarily of hydrogen and helium in her 1925 PhD thesis.[32] The spectra of stars were further understood through advances in quantum physics. This allowed the chemical composition of the stellar atmosphere to be determined.[33]
With the exception of supernovae, individual stars have primarily been observed in our Local Group of galaxies,[34] and especially in the visible part of the Milky Way (as demonstrated by the detailed star catalogues available for our galaxy).[35] But some stars have been observed in the M100 galaxy of the Virgo Cluster, about 100 million light years from the Earth.[36] In the Local Supercluster it is possible to see star clusters, and current telescopes could in principle observe faint individual stars in the Local Cluster[37] (see Cepheids). However, outside the Local Supercluster of galaxies, neither individual stars nor clusters of stars have been observed. The only exception is a faint image of a large star cluster containing hundreds of thousands of stars located at a distance of one billion light years[38]—ten times further than the most distant star cluster previously observed.
Designations

This view contains blue stars known as "Blue stragglers", for their apparent location on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
The concept of the constellation was known to exist during the Babylonian period. Ancient sky watchers imagined that prominent arrangements of stars formed patterns, and they associated these with particular aspects of nature or their myths. Twelve of these formations lay along the band of the ecliptic and these became the basis of astrology.[39] Many of the more prominent individual stars were also given names, particularly with Arabic or Latin designations.
As well as certain constellations and the Sun itself, individual stars have their own myths.[40] To the Ancient Greeks, some "stars", known as planets (Greek πλανήτης (planētēs), meaning "wanderer"), represented various important deities, from which the names of the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn were taken.[40] (Uranus and Neptune were also Greek and Roman gods, but neither planet was known in Antiquity because of their low brightness. Their names were assigned by later astronomers.)
Circa 1600, the names of the constellations were used to name the stars in the corresponding regions of the sky. The German astronomer Johann Bayer created a series of star maps and applied Greek letters as designations to the stars in each constellation. Later a numbering system based on the star's right ascension was invented and added to John Flamsteed's star catalogue in his book "Historia coelestis Britannica" (the 1712 edition), whereby this numbering system came to be called Flamsteed designation or Flamsteed numbering.[41][42]
The only internationally recognized authority for naming celestial bodies is the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[43] A number of private companies sell names of stars, which the British Library calls an unregulated commercial enterprise.[44][45] However, the IAU has disassociated itself from this commercial practice, and these names are neither recognized by the IAU nor used by them.[46] One such star naming company is the International Star Registry, which, during the 1980s, was accused of deceptive practice for making it appear that the assigned name was official. This now-discontinued ISR practice was informally labeled a scam and a fraud,[47][48][49][50] and the New York City Department of Consumer Affairs issued a violation against ISR for engaging in a deceptive trade practice.[51][52]
Units of measurement
Although stellar parameters can be expressed in SI units or CGS units, it is often most convenient to express mass, luminosity, and radii in solar units, based on the characteristics of the Sun:solar mass: M⊙ = 1.9891 × 1030 kg[53] solar luminosity: L⊙ = 3.827 × 1026 watts[53] solar radius R⊙ = 6.960 × 108 m[54]
Formation and evolution
Stars form within extended regions of higher density in the interstellar medium, although the density is still lower than the inside of a vacuum chamber. These regions - known as molecular clouds - consist mostly of hydrogen, with about 23 to 28 percent helium and a few percent heavier elements.One example of such a star-forming region is the Orion Nebula.[55] As massive stars form from molecular clouds, they powerfully illuminate those clouds. They also ionize the hydrogen, creating an H II region.
All stars spend the majority of their existence as main sequence stars, fueled primarily by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium within their cores. However, stars of different masses have markedly different properties at various stages of their development. The ultimate fate of more massive stars differs from that of less massive stars, as do their luminosity and the impact they have on their environment. Accordingly, astronomers often group stars by their mass:[56]
- Very low mass stars with masses below 0.5 solar masses do not enter the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) but evolve directly into white dwarfs
- Low mass stars (including the Sun) with a mass above about 0.5 and below about 1.8–2.2 solar masses (depending on composition) do enter the AGB, where they develop a degenerate helium core
- Intermediate-mass stars undergo helium fusion and develop a degenerate carbon-oxygen core. Massive stars have a minimum mass of 7–10 solar masses, but this may be as low as 5–6 solar masses. These stars undergo carbon fusion, with their lives ending in a core-collapse supernova explosion.
Protostar formation
The formation of a star begins with gravitational instability within a molecular cloud, caused by regions of higher density - often triggered by shock-waves from nearby supernovae (massive stellar explosions), the collision of different molecular clouds, or the collision of galaxies (as in a starburst galaxy). Once a region reaches a sufficient density of matter to satisfy the criteria for Jeans instability, it begins to collapse under its own gravitational force.[57]
Artist's conception of the birth of a star within a dense molecular cloud. NASA image
As the cloud collapses, individual conglomerations of dense dust and gas form "Bok globules". As a globule collapses and the density increases, the gravitational energy converts into heat and the temperature rises. When the protostellar cloud has approximately reached the stable condition of hydrostatic equilibrium, a protostar forms at the core.[58] These pre–main sequence stars are often surrounded by a protoplanetary disk and powered mainly by the release of gravitational energy. The period of gravitational contraction lasts about 10 to 15 million years.
Early stars of less than 2 solar masses are called T Tauri stars, while those with greater mass are Herbig Ae/Be stars. These newly-formed stars emit jets of gas along their axis of rotation, which may reduce the angular momentum of the collapsing star and result in small patches of nebulosity known as Herbig–Haro objects.[59][60] These jets, in combination with radiation from nearby massive stars, may help to drive away the surrounding cloud from which the star was formed.[61]
Early in their development, T Tauri stars follow the Hayashi track—they contract and decrease in luminosity while remaining at roughly the same temperature. Less massive T Tauri stars follow this track to the main sequence, while more massive stars turn onto the Henyey track.
Main sequence
Stars spend about 90% of their existence fusing hydrogen into helium in high-temperature and high-pressure reactions near the core. Such stars are said to be on the main sequence and are called dwarf stars. Starting at zero-age main sequence, the proportion of helium in a star's core will steadily increase, the rate of nuclear fusion at the core will slowly increase, as will the star's temperature and luminosity.[62] The Sun, for example, is estimated to have increased in luminosity by about 40% since it reached the main sequence 4.6 billion (4.6 × 109) years ago.[63]Every star generates a stellar wind of particles that causes a continual outflow of gas into space. For most stars, the mass lost is negligible. The Sun loses 10−14 solar masses every year,[64] or about 0.01% of its total mass over its entire lifespan. However, very massive stars can lose 10−7 to 10−5 solar masses each year, significantly affecting their evolution.[65] Stars that begin with more than 50 solar masses can lose over half their total mass while on the main sequence.[66]

An example of a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram for a set of stars that includes the Sun (center). (See "Classification" below.)
The duration that a star spends on the main sequence depends primarily on the amount of fuel it has to fuse and the rate at which it fuses that fuel, i.e. its initial mass and its luminosity. For the Sun, its life is estimated to be about 10 billion (1010) years. Massive stars consume their fuel very rapidly and are short-lived. Low mass stars consume their fuel very slowly. Stars less massive than 0.25 solar masses, called red dwarfs, are able to fuse nearly all of their mass as fuel while stars of about 1 solar mass can only use about 10% of their mass as fuel. The combination of their slow fuel-consumption and relatively large usable fuel supply allows stars about 0.25 times the mass of the Sun to last for about one trillion (1012) years according to stellar-evolution calculations, while the least-massive hydrogen-fusing stars (0.08 solar masses) will last for about 12 trillion years.[67] At the end of their lives, red dwarfs simply become dimmer and dimmer.[2] However, since the lifespan of such stars is greater than the current age of the universe (13.8 billion years), no stars under about 0.85 solar masses[68] are expected to have moved off the main sequence.
Besides mass, the elements heavier than helium can play a significant role in the evolution of stars. Astronomers consider all elements heavier than helium "metals", and call the chemical concentration of these elements the metallicity. The metallicity can influence the duration that a star will burn its fuel, control the formation of magnetic fields[69] and modify the strength of the stellar wind.[70] Older, population II stars have substantially less metallicity than the younger, population I stars due to the composition of the molecular clouds from which they formed. Over time these clouds become increasingly enriched in heavier elements as older stars die and shed portions of their atmospheres.
Post-main sequence
As stars of at least 0.4 solar masses[2] exhaust their supply of hydrogen at their core, their outer layers expand greatly and cool to form a red giant. In about 5 billion years, when the Sun enters this phase, it will expand to a maximum radius of roughly 1 astronomical unit (150 million kilometres), 250 times its present size. As a giant, the Sun will lose roughly 30% of its current mass.[63][71]In a red giant of up to 2.25 solar masses, hydrogen fusion proceeds in a shell surrounding the core.[72] Eventually the core is compressed enough to start helium fusion, and the star now gradually shrinks in radius and its surface temperature increases. For larger stars, the core region transitions directly from fusing hydrogen to fusing helium.[4]
After the star has consumed the helium at the core, fusion continues in a shell around a hot core of carbon and oxygen. The star then follows an evolutionary path that parallels the original red giant phase, but at a higher surface-temperature.
Massive stars
During their helium-burning phase, very high-mass stars with more than nine solar masses expand to form red supergiants. Once this fuel is exhausted at the core, they continue to fuse elements heavier than helium.The core contracts until the temperature and pressure suffice to fuse carbon (see carbon burning process). This process continues, with the successive stages being fueled by neon (see neon burning process), oxygen (see oxygen burning process), and silicon (see silicon burning process). Near the end of the star's life, fusion continues along a series of onion-layer shells within the star. Each shell fuses a different element, with the outermost shell fusing hydrogen; the next shell fusing helium, and so forth.[73]
The final stage occurs when a massive star begins producing iron. Since iron nuclei are more tightly bound than any heavier nuclei, any fusion beyond iron does not produce a net release of energy—the process would, on the contrary, consume energy. Likewise, since they are more tightly bound than all lighter nuclei, energy cannot be released by fission.[72] In relatively old, very massive stars, a large core of inert iron will accumulate in the center of the star. The heavier elements in these stars can work their way to the surface, forming evolved objects known as Wolf-Rayet stars that have a dense stellar wind which sheds the outer atmosphere.
Collapse
As a star's core shrinks, the intensity of radiation from that surface increases, creating such radiation pressure on the outer shell of gas that it will push those layers away, forming a planetary nebula. If what remains after the outer atmosphere has been shed is less than 1.4 solar masses, it shrinks to a relatively tiny object about the size of Earth, known as a white dwarf. White dwarfs lack the mass for further gravitational compression to take place.[74] The electron-degenerate matter inside a white dwarf is no longer a plasma, even though stars are generally referred to as being spheres of plasma.Eventually, white dwarfs fade into black dwarfs over a very long period of time.
In larger stars, fusion continues until the iron core has grown so large (more than 1.4 solar masses) that it can no longer support its own mass. This core will suddenly collapse as its electrons are driven into its protons, forming neutrons, neutrinos and gamma rays in a burst of electron capture and inverse beta decay. The shockwave formed by this sudden collapse causes the rest of the star to explode in a supernova. Supernovae become so bright that they may briefly outshine the star's entire home galaxy. When they occur within the Milky Way, supernovae have historically been observed by naked-eye observers as "new stars" where none seemingly existed before.[75]
Supernova explosions blow away most of their stars' matter (forming nebulae such as the Crab Nebula).[75] There remains a neutron star (which sometimes manifests itself as a pulsar or X-ray burster) or, in the case of the largest stars (large enough to leave a remnant greater than roughly 4 solar masses), a black hole.[76] In a neutron star the matter is in a state known as neutron-degenerate matter, with a more exotic form of degenerate matter, QCD matter, possibly present in the core. Within a black hole the matter is in a state that is not currently understood.
The blown-off outer layers of dying stars include heavy elements, which may be recycled during the formation of new stars. These heavy elements allow the formation of rocky planets. The outflow from supernovae and the stellar wind of large stars play an important part in shaping the interstellar medium.[75]
Distribution
In addition to isolated stars, a multi-star system can consist of two or more gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. The simplest and most common multi-star system is a binary star, but systems of three or more stars are also found. For reasons of orbital stability, such multi-star systems are often organized into hierarchical sets of binary stars.[77] Larger groups called star clusters also exist. These range from loose stellar associations with only a few stars, up to enormous globular clusters with hundreds of thousands of stars.
It has been a long-held assumption that the majority of stars occur in gravitationally bound, multiple-star systems. This is particularly true for very massive O and B class stars, where 80% of the stars are believed to be part of multiple-star systems. However the proportion of single star systems increases for smaller stars, so that only 25% of red dwarfs are known to have stellar companions. As 85% of all stars are red dwarfs, most stars in the Milky Way are likely single from birth.[78]
Stars are not spread uniformly across the universe, but are normally grouped into galaxies along with interstellar gas and dust. A typical galaxy contains hundreds of billions of stars, and there are more than 100 billion (1011) galaxies in the observable universe.[79] A 2010 star count estimate was 300 sextillion (3 × 1023) in the observable universe.[80] While it is often believed that stars only exist within galaxies, intergalactic stars have been discovered.[81]
The nearest star to the Earth, apart from the Sun, is Proxima Centauri, which is 39.9 trillion kilometres, or 4.2 light-years away. Travelling at the orbital speed of the Space Shuttle (8 kilometres per second—almost 30,000 kilometres per hour), it would take about 150,000 years to get there.[82]
Distances like this are typical inside galactic discs, including in the vicinity of the solar system.[83] Stars can be much closer to each other in the centres of galaxies and in globular clusters, or much farther apart in galactic halos.
Due to the relatively vast distances between stars outside the galactic nucleus, collisions between stars are thought to be rare. In denser regions such as the core of globular clusters or the galactic center, collisions can be more common.[84] Such collisions can produce what are known as blue stragglers. These abnormal stars have a higher surface temperature than the other main sequence stars with the same luminosity in the cluster.[85]
Characteristics
Almost everything about a star is determined by its initial mass, including essential characteristics such as luminosity and size, as well as its evolution, lifespan, and eventual fate.
Age
Most stars are between 1 billion and 10 billion years old. Some stars may even be close to 13.8 billion years old—the observed age of the universe. The oldest star yet discovered, HD 140283, nicknamed Methuselah star, is an estimated 14.46 ± 0.8 billion years old.[86] (Due to the uncertainty in the value, this age for the star does not conflict with the age of the Universe, determined by the Planck satellite as 13.798 ± 0.037.[86])The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily because massive stars have greater pressure on their cores, causing them to burn hydrogen more rapidly. The most massive stars last an average of a few million years, while stars of minimum mass (red dwarfs) burn their fuel very slowly and can last tens to hundreds of billions of years.[87][88]
Chemical composition
“From a chemist’s point of view, the surface or interior of a star…is boring—there are no molecules there.”--Roald Hoffmann[89]When stars form in the present Milky Way galaxy they are composed of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium,[90] as measured by mass, with a small fraction of heavier elements. Typically the portion of heavy elements is measured in terms of the iron content of the stellar atmosphere, as iron is a common element and its absorption lines are relatively easy to measure. Because the molecular clouds where stars form are steadily enriched by heavier elements, a measurement of the chemical composition of a star can be used to infer its age.[91][dubious ] The portion of heavier elements may also be an indicator of the likelihood that the star has a planetary system.[92]
The star with the lowest iron content ever measured is the dwarf HE1327-2326, with only 1/200,000th the iron content of the Sun.[93] By contrast, the super-metal-rich star μ Leonis has nearly double the abundance of iron as the Sun, while the planet-bearing star 14 Herculis has nearly triple the iron.[94] There also exist chemically peculiar stars that show unusual abundances of certain elements in their spectrum; especially chromium and rare earth elements.[95]
Diameter
Due to their great distance from the Earth, all stars except the Sun appear to the unaided eye as shining points in the night sky that twinkle because of the effect of the Earth's atmosphere. The Sun is also a star, but it is close enough to the Earth to appear as a disk instead, and to provide daylight. Other than the Sun, the star with the largest apparent size is R Doradus, with an angular diameter of only 0.057 arcseconds.[96]
The disks of most stars are much too small in angular size to be observed with current ground-based optical telescopes, and so interferometer telescopes are required to produce images of these objects. Another technique for measuring the angular size of stars is through occultation. By precisely measuring the drop in brightness of a star as it is occulted by the Moon (or the rise in brightness when it reappears), the star's angular diameter can be computed.[97]
Stars range in size from neutron stars, which vary anywhere from 20 to 40 km (25 mi) in diameter, to supergiants like Betelgeuse in the Orion constellation, which has a diameter approximately 650 times that of the Sun—about 900,000,000 km (559,234,073 mi). Betelgeuse, however, has a much lower density than the Sun.[98]
Kinematics

The Pleiades, an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Taurus. These stars share a common motion through space.[99] NASA photo
The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding galaxy. The components of motion of a star consist of the radial velocity toward or away from the Sun, and the traverse angular movement, which is called its proper motion.
Radial velocity is measured by the doppler shift of the star's spectral lines, and is given in units of km/s. The proper motion of a star is determined by precise astrometric measurements in units of milli-arc seconds (mas) per year. By determining the parallax of a star, the proper motion can then be converted into units of velocity. Stars with high rates of proper motion are likely to be relatively close to the Sun, making them good candidates for parallax measurements.[100]
Once both rates of movement are known, the space velocity of the star relative to the Sun or the galaxy can be computed. Among nearby stars, it has been found that younger population I stars have generally lower velocities than older, population II stars. The latter have elliptical orbits that are inclined to the plane of the galaxy.[101] A comparison of the kinematics of nearby stars has also led to the identification of stellar associations. These are most likely groups of stars that share a common point of origin in giant molecular clouds.[102]
Magnetic field

Surface magnetic field of SU Aur (a young star of T Tauri type), reconstructed by means of Zeeman-Doppler imaging
The magnetic field of a star is generated within regions of the interior where convective circulation occurs. This movement of conductive plasma functions like a dynamo, generating magnetic fields that extend throughout the star. The strength of the magnetic field varies with the mass and composition of the star, and the amount of magnetic surface activity depends upon the star's rate of rotation. This surface activity produces starspots, which are regions of strong magnetic fields and lower than normal surface temperatures. Coronal loops are arching magnetic fields that reach out into the corona from active regions. Stellar flares are bursts of high-energy particles that are emitted due to the same magnetic activity.[103]
Young, rapidly rotating stars tend to have high levels of surface activity because of their magnetic field. The magnetic field can act upon a star's stellar wind, functioning as a brake to gradually slow the rate of rotation with time. Thus, older stars such as the Sun have a much slower rate of rotation and a lower level of surface activity. The activity levels of slowly rotating stars tend to vary in a cyclical manner and can shut down altogether for periods of time.[104] During the Maunder minimum, for example, the Sun underwent a 70-year period with almost no sunspot activity.
Mass
One of the most massive stars known is Eta Carinae,[105] which, with 100–150 times as much mass as the Sun, will have a lifespan of only several million years. A study of the Arches cluster suggests that 150 solar masses is the upper limit for stars in the current era of the universe.[106] The reason for this limit is not precisely known, but it is partially due to the Eddington luminosity which defines the maximum amount of luminosity that can pass through the atmosphere of a star without ejecting the gases into space. However, a star named R136a1 in the Large Magellanic Cloud, RMC 136a star cluster has been measured at 265 solar masses, which puts this limit into question.[107] A study determined that stars larger than 150 solar masses in R136 were created through the collision and merger of massive stars in close binary systems, providing a way to sidestep the 150 solar mass limit.[108]
The reflection nebula NGC 1999 is brilliantly illuminated by V380 Orionis (center), a variable star with about 3.5 times the mass of the Sun. The black patch of sky is a vast hole of empty space and not a dark nebula as previously thought. NASA image
The first stars to form after the Big Bang may have been larger, up to 300 solar masses or more,[109] due to the complete absence of elements heavier than lithium in their composition. This generation of supermassive, population III stars is long extinct, however, and currently only theoretical.
With a mass only 93 times that of Jupiter, AB Doradus C, a companion to AB Doradus A, is the smallest known star undergoing nuclear fusion in its core.[110] For stars with similar metallicity to the Sun, the theoretical minimum mass the star can have, and still undergo fusion at the core, is estimated to be about 75 times the mass of Jupiter.[111][112] When the metallicity is very low, however, a recent study of the faintest stars found that the minimum star size seems to be about 8.3% of the solar mass, or about 87 times the mass of Jupiter.[112][113] Smaller bodies are called brown dwarfs, which occupy a poorly defined grey area between stars and gas giants.
The combination of the radius and the mass of a star determines the surface gravity. Giant stars have a much lower surface gravity than main sequence stars, while the opposite is the case for degenerate, compact stars such as white dwarfs. The surface gravity can influence the appearance of a star's spectrum, with higher gravity causing a broadening of the absorption lines.[33]
Rotation
The rotation rate of stars can be determined through spectroscopic measurement, or more exactly determined by tracking the rotation rate of starspots. Young stars can have a rapid rate of rotation greater than 100 km/s at the equator. The B-class star Achernar, for example, has an equatorial rotation velocity of about 225 km/s or greater, causing its equator to be slung outward and giving it an equatorial diameter that is more than 50% larger than the distance between the poles. This rate of rotation is just below the critical velocity of 300 km/s where the star would break apart.[114] By contrast, the Sun only rotates once every 25 – 35 days, with an equatorial velocity of 1.994 km/s. The star's magnetic field and the stellar wind serve to slow a main sequence star's rate of rotation by a significant amount as it evolves on the main sequence.[115]Degenerate stars have contracted into a compact mass, resulting in a rapid rate of rotation. However they have relatively low rates of rotation compared to what would be expected by conservation of angular momentum—the tendency of a rotating body to compensate for a contraction in size by increasing its rate of spin. A large portion of the star's angular momentum is dissipated as a result of mass loss through the stellar wind.[116] In spite of this, the rate of rotation for a pulsar can be very rapid. The pulsar at the heart of the Crab nebula, for example, rotates 30 times per second.[117] The rotation rate of the pulsar will gradually slow due to the emission of radiation.
Temperature
The surface temperature of a main sequence star is determined by the rate of energy production at the core and by its radius, and is often estimated from the star's color index.[118] The temperature is normally given as the effective temperature, which is the temperature of an idealized black body that radiates its energy at the same luminosity per surface area as the star. Note that the effective temperature is only a representative value, as the temperature increases toward the core.[119] The temperature in the core region of a star is several million kelvins.[120]The stellar temperature will determine the rate of ionization of various elements, resulting in characteristic absorption lines in the spectrum. The surface temperature of a star, along with its visual absolute magnitude and absorption features, is used to classify a star (see classification below).[33]
Massive main sequence stars can have surface temperatures of 50,000 K. Smaller stars such as the Sun have surface temperatures of a few thousand K. Red giants have relatively low surface temperatures of about 3,600 K; but they also have a high luminosity due to their large exterior surface area.[121]
Radiation
The energy produced by stars, as a product of nuclear fusion, radiates into space as both electromagnetic radiation and particle radiation. The particle radiation emitted by a star is manifested as the stellar wind,[122] which streams from the outer layers as free protons, and electrically charged alpha, and beta particles. Although almost massless there also exists a steady stream of neutrinos emanating from the star's core.The production of energy at the core is the reason stars shine so brightly: every time two or more atomic nuclei fuse together to form a single atomic nucleus of a new heavier element, gamma ray photons are released from the nuclear fusion product. This energy is converted to other forms of electromagnetic energy of lower frequency, such as visible light, by the time it reaches the star's outer layers.
The color of a star, as determined by the most intense frequency of the visible light, depends on the temperature of the star's outer layers, including its photosphere.[123] Besides visible light, stars also emit forms of electromagnetic radiation that are invisible to the human eye. In fact, stellar electromagnetic radiation spans the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from the longest wavelengths of radio waves through infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, to the shortest of X-rays, and gamma rays. From the standpoint of total energy emitted by a star, not all components of stellar electromagnetic radiation are significant, but all frequencies provide insight into the star's physics.
Using the stellar spectrum, astronomers can also determine the surface temperature, surface gravity, metallicity and rotational velocity of a star. If the distance of the star is known, such as by measuring the parallax, then the luminosity of the star can be derived. The mass, radius, surface gravity, and rotation period can then be estimated based on stellar models. (Mass can be calculated for stars in binary systems by measuring their orbital velocities and distances. Gravitational microlensing has been used to measure the mass of a single star.[124]) With these parameters, astronomers can also estimate the age of the star.[125]
Luminosity
The luminosity of a star is the amount of light and other forms of radiant energy it radiates per unit of time. It has units of power. The luminosity of a star is determined by the radius and the surface temperature. However, many stars do not radiate a uniform flux (the amount of energy radiated per unit area) across their entire surface. The rapidly rotating star Vega, for example, has a higher energy flux at its poles than along its equator.[126]Surface patches with a lower temperature and luminosity than average are known as starspots. Small, dwarf stars such as our Sun generally have essentially featureless disks with only small starspots. Larger, giant stars have much larger, more obvious starspots,[127] and they also exhibit strong stellar limb darkening. That is, the brightness decreases towards the edge of the stellar disk.[128] Red dwarf flare stars such as UV Ceti may also possess prominent starspot features.[129]
Magnitude
The apparent brightness of a star is expressed in terms of its apparent magnitude, which is the brightness of a star and is a function of the star's luminosity, distance from Earth, and the altering of the star's light as it passes through Earth's atmosphere. Intrinsic or absolute magnitude is directly related to a star's luminosity and is what the apparent magnitude a star would be if the distance between the Earth and the star were 10 parsecs (32.6 light-years).| Apparent magnitude | Number of Stars[130] |
|---|---|
| 0 | 4 |
| 1 | 15 |
| 2 | 48 |
| 3 | 171 |
| 4 | 513 |
| 5 | 1,602 |
| 6 | 4,800 |
| 7 | 14,000 |
Both the apparent and absolute magnitude scales are logarithmic units: one whole number difference in magnitude is equal to a brightness variation of about 2.5 times[131] (the 5th root of 100 or approximately 2.512). This means that a first magnitude star (+1.00) is about 2.5 times brighter than a second magnitude (+2.00) star, and approximately 100 times brighter than a sixth magnitude star (+6.00). The faintest stars visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions are about magnitude +6.
On both apparent and absolute magnitude scales, the smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star; the larger the magnitude number, the fainter. The brightest stars, on either scale, have negative magnitude numbers. The variation in brightness (ΔL) between two stars is calculated by subtracting the magnitude number of the brighter star (mb) from the magnitude number of the fainter star (mf), then using the difference as an exponent for the base number 2.512; that is to say:
The Sun has an apparent magnitude of −26.7, but its absolute magnitude is only +4.83. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky as seen from Earth, is approximately 23 times more luminous than the Sun, while Canopus, the second brightest star in the night sky with an absolute magnitude of −5.53, is approximately 14,000 times more luminous than the Sun. Despite Canopus being vastly more luminous than Sirius, however, Sirius appears brighter than Canopus. This is because Sirius is merely 8.6 light-years from the Earth, while Canopus is much farther away at a distance of 310 light-years.
As of 2006, the star with the highest known absolute magnitude is LBV 1806-20, with a magnitude of −14.2. This star is at least 5,000,000 times more luminous than the Sun.[132] The least luminous stars that are currently known are located in the NGC 6397 cluster. The faintest red dwarfs in the cluster were magnitude 26, while a 28th magnitude white dwarf was also discovered. These faint stars are so dim that their light is as bright as a birthday candle on the Moon when viewed from the Earth.[133]
Classification
| Class | Temperature | Sample star |
|---|---|---|
| O | 33,000 K or more | Zeta Ophiuchi |
| B | 10,500–30,000 K | Rigel |
| A | 7,500–10,000 K | Altair |
| F | 6,000–7,200 K | Procyon A |
| G | 5,500–6,000 K | Sun |
| K | 4,000–5,250 K | Epsilon Indi |
| M | 2,600–3,850 K | Proxima Centauri |
Stars are given a single-letter classification according to their spectra, ranging from type O, which are very hot, to M, which are so cool that molecules may form in their atmospheres. The main classifications in order of decreasing surface temperature are: O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. A variety of rare spectral types have special classifications. The most common of these are types L and T, which classify the coldest low-mass stars and brown dwarfs. Each letter has 10 sub-divisions, numbered from 0 to 9, in order of decreasing temperature. However, this system breaks down at extreme high temperatures: class O0 and O1 stars may not exist.[137]
In addition, stars may be classified by the luminosity effects found in their spectral lines, which correspond to their spatial size and is determined by the surface gravity. These range from 0 (hypergiants) through III (giants) to V (main sequence dwarfs); some authors add VII (white dwarfs).
Most stars belong to the main sequence, which consists of ordinary hydrogen-burning stars. These fall along a narrow, diagonal band when graphed according to their absolute magnitude and spectral type.[137] The Sun is a main sequence G2V yellow dwarf of intermediate temperature and ordinary size.
Additional nomenclature, in the form of lower-case letters, can follow the spectral type to indicate peculiar features of the spectrum. For example, an "e" can indicate the presence of emission lines; "m" represents unusually strong levels of metals, and "var" can mean variations in the spectral type.[137]
White dwarf stars have their own class that begins with the letter D. This is further sub-divided into the classes DA, DB, DC, DO, DZ, and DQ, depending on the types of prominent lines found in the spectrum. This is followed by a numerical value that indicates the temperature index.[138]
Variable stars
Variable stars have periodic or random changes in luminosity because of intrinsic or extrinsic properties. Of the intrinsically variable stars, the primary types can be subdivided into three principal groups.
During their stellar evolution, some stars pass through phases where they can become pulsating variables. Pulsating variable stars vary in radius and luminosity over time, expanding and contracting with periods ranging from minutes to years, depending on the size of the star. This category includes Cepheid and cepheid-like stars, and long-period variables such as Mira.[139]
Eruptive variables are stars that experience sudden increases in luminosity because of flares or mass ejection events.[139] This group includes protostars, Wolf-Rayet stars, and Flare stars, as well as giant and supergiant stars.
Cataclysmic or explosive variable stars are those that undergo a dramatic change in their properties. This group includes novae and supernovae. A binary star system that includes a nearby white dwarf can produce certain types of these spectacular stellar explosions, including the nova and a Type 1a supernova.[4] The explosion is created when the white dwarf accretes hydrogen from the companion star, building up mass until the hydrogen undergoes fusion.[140] Some novae are also recurrent, having periodic outbursts of moderate amplitude.[139]
Stars can also vary in luminosity because of extrinsic factors, such as eclipsing binaries, as well as rotating stars that produce extreme starspots.[139] A notable example of an eclipsing binary is Algol, which regularly varies in magnitude from 2.3 to 3.5 over a period of 2.87 days.
Structure

Internal structures of main sequence stars, convection zones with arrowed cycles and radiative zones with red flashes. To the left a low-mass red dwarf, in the center a mid-sized yellow dwarf and at the right a massive blue-white main sequence star.
The interior of a stable star is in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium: the forces on any small volume almost exactly counterbalance each other. The balanced forces are inward gravitational force and an outward force due to the pressure gradient within the star. The pressure gradient is established by the temperature gradient of the plasma; the outer part of the star is cooler than the core. The temperature at the core of a main sequence or giant star is at least on the order of 107 K. The resulting temperature and pressure at the hydrogen-burning core of a main sequence star are sufficient for nuclear fusion to occur and for sufficient energy to be produced to prevent further collapse of the star.[141][142]
As atomic nuclei are fused in the core, they emit energy in the form of gamma rays. These photons interact with the surrounding plasma, adding to the thermal energy at the core. Stars on the main sequence convert hydrogen into helium, creating a slowly but steadily increasing proportion of helium in the core. Eventually the helium content becomes predominant and energy production ceases at the core. Instead, for stars of more than 0.4 solar masses, fusion occurs in a slowly expanding shell around the degenerate helium core.[143]
In addition to hydrostatic equilibrium, the interior of a stable star will also maintain an energy balance of thermal equilibrium. There is a radial temperature gradient throughout the interior that results in a flux of energy flowing toward the exterior. The outgoing flux of energy leaving any layer within the star will exactly match the incoming flux from below.
The radiation zone is the region within the stellar interior where radiative transfer is sufficiently efficient to maintain the flux of energy. In this region the plasma will not be perturbed and any mass motions will die out. If this is not the case, however, then the plasma becomes unstable and convection will occur, forming a convection zone. This can occur, for example, in regions where very high energy fluxes occur, such as near the core or in areas with high opacity as in the outer envelope.[142]
The occurrence of convection in the outer envelope of a main sequence star depends on the mass. Stars with several times the mass of the Sun have a convection zone deep within the interior and a radiative zone in the outer layers. Smaller stars such as the Sun are just the opposite, with the convective zone located in the outer layers.[144] Red dwarf stars with less than 0.4 solar masses are convective throughout, which prevents the accumulation of a helium core.[2] For most stars the convective zones will also vary over time as the star ages and the constitution of the interior is modified.[142]

This diagram shows a cross-section of the Sun. NASA image
The portion of a star that is visible to an observer is called the photosphere. This is the layer at which the plasma of the star becomes transparent to photons of light. From here, the energy generated at the core becomes free to propagate out into space. It is within the photosphere that sun spots, or regions of lower than average temperature, appear.
Above the level of the photosphere is the stellar atmosphere. In a main sequence star such as the Sun, the lowest level of the atmosphere is the thin chromosphere region, where spicules appear and stellar flares begin. This is surrounded by a transition region, where the temperature rapidly increases within a distance of only 100 km (62 mi). Beyond this is the corona, a volume of super-heated plasma that can extend outward to several million kilometres.[145] The existence of a corona appears to be dependent on a convective zone in the outer layers of the star.[144] Despite its high temperature, the corona emits very little light. The corona region of the Sun is normally only visible during a solar eclipse.
From the corona, a stellar wind of plasma particles expands outward from the star, propagating until it interacts with the interstellar medium. For the Sun, the influence of its solar wind extends throughout the bubble-shaped region of the heliosphere.[146]
Nuclear fusion reaction pathways
A variety of different nuclear fusion reactions take place inside the cores of stars, depending upon their mass and composition, as part of stellar nucleosynthesis. The net mass of the fused atomic nuclei is smaller than the sum of the constituents. This lost mass is released as electromagnetic energy, according to the mass-energy equivalence relationship E = mc2.[1]
The hydrogen fusion process is temperature-sensitive, so a moderate increase in the core temperature will result in a significant increase in the fusion rate. As a result the core temperature of main sequence stars only varies from 4 million kelvin for a small M-class star to 40 million kelvin for a massive O-class star.[120]
In the Sun, with a 10-million-kelvin core, hydrogen fuses to form helium in the proton-proton chain reaction:[147]
These reactions result in the overall reaction:
- 41H → 4He + 2e+ + 2γ + 2νe (26.7 MeV)
| Element | Solar masses |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 0.01 |
| Helium | 0.4 |
| Carbon | 5[148] |
| Neon | 8 |
In more massive stars, helium is produced in a cycle of reactions catalyzed by carbon—the carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle.[147]
In evolved stars with cores at 100 million kelvin and masses between 0.5 and 10 solar masses, helium can be transformed into carbon in the triple-alpha process that uses the intermediate element beryllium:[147]
For an overall reaction of:
- 34He → 12C + γ + 7.2 MeV
The example below shows the amount of time required for a star of 20 solar masses to consume all of its nuclear fuel. As an O-class main sequence star, it would be 8 times the solar radius and 62,000 times the Sun's luminosity.[149]
| Fuel material | Temperature (million kelvins) | Density (kg/cm3) | Burn duration (τ in years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 37 | 0.0045 | 8.1 million |
| He | 188 | 0.97 | 1.2 million |
| C | 870 | 170 | 976 |
| Ne | 1,570 | 3,100 | 0.6 |
| O | 1,980 | 5,550 | 1.25 |
| S/Si | 3,340 | 33,400 | 0.0315[150] |