Black light test of Dawn's triple-junction gallium arsenide solar cells
Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells are solar cells with multiple p–n junctions made of different semiconductor materials. Each material's p-n junction will produce electric current in response to different wavelengths of light. The use of multiple semiconducting materials
allows the absorbance of a broader range of wavelengths, improving the
cell's sunlight to electrical energy conversion efficiency.
Traditional single-junction cells have a maximum theoretical efficiency of 33.16%. Theoretically, an infinite number of junctions would have a limiting efficiency of 86.8% under highly concentrated sunlight.
Currently, the best lab examples of traditional crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cells have efficiencies between 20% and 25%, while lab examples of multi-junction cells have demonstrated performance over 46% under concentrated sunlight. Commercial examples of tandem cells are widely available at 30% under one-sun illumination,
and improve to around 40% under concentrated sunlight. However, this
efficiency is gained at the cost of increased complexity and
manufacturing price. To date, their higher price and higher price-to-performance ratio have limited their use to special roles, notably in aerospace where their high power-to-weight ratio is desirable. In terrestrial applications, these solar cells are emerging in concentrator photovoltaics (CPV), with a growing number of installations around the world.
Tandem fabrication techniques have been used to improve the
performance of existing designs. In particular, the technique can be
applied to lower cost thin-film solar cells using amorphous silicon,
as opposed to conventional crystalline silicon, to produce a cell with
about 10% efficiency that is lightweight and flexible. This approach has
been used by several commercial vendors, but these products are currently limited to certain niche roles, like roofing materials.
Description
Basics of solar cells
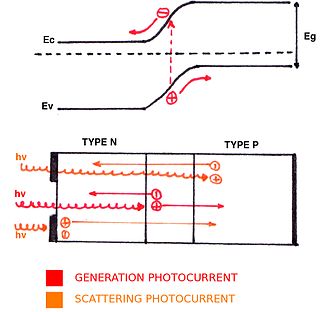
Figure A. Band diagram illustration of the photovoltaic effect. Photons give their energy to electrons in the depletion or quasi-neutral regions. These move from the valence band to the conduction band. Depending on the location, electrons and holes are accelerated by Edrift, which gives generation photocurrent, or by Escatt, which gives scattering photocurrent.
Traditional photovoltaic cells are commonly composed of doped silicon
with metallic contacts deposited on the top and bottom. The doping is
normally applied to a thin layer on the top of the cell, producing a pn-junction with a particular bandgap energy, Eg.
Photons
that hit the top of the solar cell are either reflected or transmitted
into the cell. Transmitted photons have the potential to give their
energy, hν, to an electron if hν ≥ Eg, generating an electron-hole pair. In the depletion region, the drift electric field Edrift
accelerates both electrons and holes towards their respective n-doped
and p-doped regions (up and down, respectively). The resulting current Ig is called the generated photocurrent. In the quasi-neutral region, the scattering electric field Escatt accelerates holes (electrons) towards the p-doped (n-doped) region, which gives a scattering photocurrent Ipscatt (Inscatt). Consequently, due to the accumulation of charges, a potential V and a photocurrent Iph appear. The expression for this photocurrent is obtained by adding generation and scattering photocurrents: Iph = Ig + Inscatt + Ipscatt.
The J-V characteristics (J is current density, i.e.
current per unit area) of a solar cell under illumination are obtained
by shifting the J-V characteristics of a diode in the dark downward by Iph. Since solar cells are designed to supply power and not absorb it, the power P = V·Iph must be negative. Hence, the operating point (Vm, Jm) is located in the region where V>0 and Iph<0 a="" and="" chosen="" href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absolute_value" maximize="" the="" title="Absolute value" to="">absolute value
of the power |P|.
Loss mechanisms
The Shockley-Queisser limit
for the efficiency of a single-junction solar cell. It is essentially
impossible for a single-junction solar cell, under unconcentrated
sunlight, to have more than ~34% efficiency. A multi-junction cell,
however, can exceed that limit.
The theoretical performance of a solar cell was first studied in depth in the 1960s, and is today known as the Shockley–Queisser limit. The limit describes several loss mechanisms that are inherent to any solar cell design.
The first are the losses due to blackbody radiation, a loss mechanism that affects any material object above absolute zero. In the case of solar cells at standard temperature and pressure, this loss accounts for about 7% of the power. The second is an effect known as "recombination", where the electrons created by the photoelectric effect meet the electron holes left behind by previous excitations. In silicon, this accounts for another 10% of the power.
However, the dominant loss mechanism is the inability of a solar cell to extract all of the power in the light,
and the associated problem that it cannot extract any power at all from
certain photons. This is due to the fact that the photons must have
enough energy to overcome the bandgap of the material.
If the photon has less energy than the bandgap, it is not
collected at all. This is a major consideration for conventional solar
cells, which are not sensitive to most of the infrared
spectrum, although that represents almost half of the power coming from
the sun. Conversely, photons with more energy than the bandgap, say
blue light, initially eject an electron to a state high above the
bandgap, but this extra energy is lost through collisions in a process
known as "relaxation". This lost energy turns into heat in the cell,
which has the side-effect of further increasing blackbody losses.
Combining all of these factors, the maximum efficiency for a
single-bandgap material, like conventional silicon cells, is about 34%.
That is, 66% of the energy in the sunlight hitting the cell will be
lost. Practical concerns further reduce this, notably reflection off the
front surface or the metal terminals, with modern high-quality cells at
about 22%.
Lower, also called narrower, bandgap materials will convert
longer wavelength, lower energy photons. Higher, or wider bandgap
materials will convert shorter wavelength, higher energy light. An
analysis of the AM1.5
spectrum, shows the best balance is reached at about 1.1 eV (about
1100 nm, in the near infrared), which happens to be very close to the
natural bandgap in silicon and a number of other useful semiconductors.
Multi-junction cells
Cells
made from multiple materials layers can have multiple bandgaps and will
therefore respond to multiple light wavelengths, capturing and
converting some of the energy that would otherwise be lost to relaxation
as described above.
For instance, if one had a cell with two bandgaps in it, one
tuned to red light and the other to green, then the extra energy in
green, cyan and blue light would be lost only to the bandgap of the
green-sensitive material, while the energy of the red, yellow and orange
would be lost only to the bandgap of the red-sensitive material.
Following analysis similar to those performed for single-bandgap
devices, it can be demonstrated that the perfect bandgaps for a two-gap
device are at 1.1 eV and 1.8 eV.
Conveniently, light of a particular wavelength does not interact
strongly with materials that are of bigger bandgap. This means that you
can make a multi-junction cell by layering the different materials on
top of each other, shortest wavelengths (biggest bandgap) on the "top"
and increasing through the body of the cell. As the photons have to pass
through the cell to reach the proper layer to be absorbed, transparent conductors need to be used to collect the electrons being generated at each layer.
Figure
C. (a) The structure of an MJ solar cell. There are six important types
of layers: pn junctions, back surface field (BSF) layers, window
layers, tunnel junctions, anti-reflective coating and metallic contacts. (b) Graph of spectral irradiance E vs. wavelength λ over the AM1.5
solar spectrum, together with the maximum electricity conversion
efficiency for every junction as a function of the wavelength.
Producing a tandem cell is not an easy task, largely due to the
thinness of the materials and the difficulties extracting the current
between the layers. The easy solution is to use two mechanically
separate thin film solar cells and then wire them together separately outside the cell. This technique is widely used by amorphous silicon solar cells, Uni-Solar's
products use three such layers to reach efficiencies around 9%. Lab
examples using more exotic thin-film materials have demonstrated
efficiencies over 30%.
The more difficult solution is the "monolithically integrated"
cell, where the cell consists of a number of layers that are
mechanically and electrically connected. These cells are much more
difficult to produce because the electrical characteristics of each
layer have to be carefully matched. In particular, the photocurrent
generated in each layer needs to be matched, otherwise electrons will be
absorbed between layers. This limits their construction to certain
materials, best met by the III-V semiconductors.
Material choice
The
choice of materials for each sub-cell is determined by the requirements
for lattice-matching, current-matching, and high performance
opto-electronic properties.
For optimal growth and resulting crystal quality, the crystal lattice constant a
of each material must be closely matched, resulting in lattice-matched
devices. This constraint has been relaxed somewhat in recently developed
metamorphic solar cells
which contain a small degree of lattice mismatch. However, a greater
degree of mismatch or other growth imperfections can lead to crystal
defects causing a degradation in electronic properties.
Since each sub-cell is connected electrically in series, the same
current flows through each junction. The materials are ordered with
decreasing bandgaps, Eg, allowing sub-bandgap light (hc/λ < e·Eg)
to transmit to the lower sub-cells. Therefore, suitable bandgaps must
be chosen such that the design spectrum will balance the current
generation in each of the sub-cells, achieving current matching. Figure
C(b) plots spectral irradiance E(λ), which is the source power density at a given wavelength
λ. It is plotted together with the maximum conversion efficiency for
every junction as a function of the wavelength, which is directly
related to the number of photons available for conversion into
photocurrent.
Finally, the layers must be electrically optimal for high
performance. This necessitates usage of materials with strong absorption
coefficients α(λ), high minority carrier lifetimes τminority, and high mobilities µ.
The favorable values in the table below justify the choice of materials typically used for multi-junction solar cells: InGaP for the top sub-cell (Eg = 1.8 − 1.9 eV), InGaAs for the middle sub-cell (Eg = 1.4 eV), and Germanium for the bottom sub-cell (Eg = 0.67 eV). The use of Ge is mainly due to its lattice constant, robustness, low cost, abundance, and ease of production.
Because the different layers are closely lattice-matched, the fabrication of the device typically employs metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). This technique is preferable to the molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) because it ensures high crystal quality and large scale production.
| Material | Eg, eV | a, nm | absorption (λ = 0.8 μm), 1/µm |
µn, cm2/(V·s) | τp, µs | Hardness (Mohs) |
α, µm/K | S, m/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c-Si | 1.12 | 0.5431 | 0.102 | 1400 | 1 | 7 | 2.6 | 0.1–60 |
| InGaP | 1.86 | 0.5451 | 2 | 500 | – | 5 | 5.3 | 50 |
| GaAs | 1.4 | 0.5653 | 0.9 | 8500 | 3 | 4–5 | 6 | 50 |
| Ge | 0.65 | 0.5657 | 3 | 3900 | 1000 | 6 | 7 | 1000 |
| InGaAs | 1.2 | 0.5868 | 30 | 1200 | – | – | 5.66 | 100–1000 |
Structural elements
Metallic contacts
The metallic contacts are low-resistivity electrodes that make contact with the semiconductor layers. They are often aluminum.
This provides an electrical connection to a load or other parts of a
solar cell array. They are usually on two sides of the cell. And are
important to be on the back face so that shadowing on the lighting
surface is reduced.
Anti-reflective coating
Anti-reflective (AR) coating is generally composed of several layers in the case of MJ solar cells. The top AR layer has usually a NaOH surface texturation with several pyramids in order to increase the transmission coefficient T,
the trapping of the light in the material (because photons cannot
easily get out the MJ structure due to pyramids) and therefore, the path
length of photons in the material.
On the one hand, the thickness of each AR layer is chosen to get
destructive interferences. Therefore, the reflection coefficient R decreases to 1%. In the case of two AR layers L1 (the top layer, usually SiO
2) and L2 (usually TiO
2), there must be to have the same amplitudes for reflected fields and nL1dL1 = 4λmin,nL2dL2 = λmin/4 to have opposite phase for reflected fields. On the other hand, the thickness of each AR layer is also chosen to minimize the reflectance at wavelengths for which the photocurrent is the lowest. Consequently, this maximizes JSC by matching currents of the three subcells. As example, because the current generated by the bottom cell is greater than the currents generated by the other cells, the thickness of AR layers is adjusted so that the infrared (IR) transmission (which corresponds to the bottom cell) is degraded while the ultraviolet transmission (which corresponds to the top cell) is upgraded. Particularly, an AR coating is very important at low wavelengths because, without it, T would be strongly reduced to 70%.
2) and L2 (usually TiO
2), there must be to have the same amplitudes for reflected fields and nL1dL1 = 4λmin,nL2dL2 = λmin/4 to have opposite phase for reflected fields. On the other hand, the thickness of each AR layer is also chosen to minimize the reflectance at wavelengths for which the photocurrent is the lowest. Consequently, this maximizes JSC by matching currents of the three subcells. As example, because the current generated by the bottom cell is greater than the currents generated by the other cells, the thickness of AR layers is adjusted so that the infrared (IR) transmission (which corresponds to the bottom cell) is degraded while the ultraviolet transmission (which corresponds to the top cell) is upgraded. Particularly, an AR coating is very important at low wavelengths because, without it, T would be strongly reduced to 70%.
Tunnel junctions
Figure D: Layers and band diagram of the tunnel junction. Because the length of the depletion region is narrow and the band gap is high, electrons can tunnel.
The main goal of tunnel junctions is to provide a low electrical resistance and optically low-loss connection between two subcells.
Without it, the p-doped region of the top cell would be directly
connected with the n-doped region of the middle cell. Hence, a pn
junction with opposite direction to the others would appear between the
top cell and the middle cell. Consequently, the photovoltage would be lower than if there would be no parasitic diode. In order to decrease this effect, a tunnel junction is used. It is simply a wide band gap, highly doped diode. The high doping reduces the length of the depletion region because
Hence, electrons can easily tunnel through the depletion region. The
J-V characteristic of the tunnel junction is very important because it
explains why tunnel junctions can be used to have a low electrical
resistance connection between two pn junctions. Figure D shows three
different regions: the tunneling region, the negative differential
resistance region and the thermal diffusion region. The region where
electrons can tunnel through the barrier is called the tunneling region.
There, the voltage must be low enough so that energy of some electrons
who are tunneling is equal to energy states available on the other side
of the barrier. Consequently, current density through the tunnel
junction is high (with maximum value of ,
the peak current density) and the slope near the origin is therefore
steep. Then, the resistance is extremely low and consequently, the voltage too.
This is why tunnel junctions are ideal for connecting two pn junctions
without having a voltage drop. When voltage is higher, electrons cannot
cross the barrier because energy states are no longer available for
electrons. Therefore, the current density decreases and the differential
resistance is negative. The last region, called thermal diffusion
region, corresponds to the J-V characteristic of the usual diode:
In order to avoid the reduction of the MJ solar cell performances,
tunnel junctions must be transparent to wavelengths absorbed by the next
photovoltaic cell, the middle cell, i.e. EgTunnel > EgMiddleCell.
Window layer and back-surface field
Figure E: (a) Layers and band diagram
of a window layer. The surface recombination is reduced. (b) Layers and
band diagram of a BSF layer. The scattering of carriers is reduced.
A window layer is used in order to reduce the surface recombination velocity S.
Similarly, a back-surface field (BSF) layer reduces the scattering of
carriers towards the tunnel junction. The structure of these two layers
is the same: it is a heterojunction which catches electrons (holes). Indeed, despite the electric field Ed,
these cannot jump above the barrier formed by the heterojunction
because they don't have enough energy, as illustrated in figure E.
Hence, electrons (holes) cannot recombine with holes (electrons) and
cannot diffuse through the barrier. By the way, window and BSF layers
must be transparent to wavelengths absorbed by the next pn junction i.e.
EgWindow > EgEmitter and EgBSF > EgEmitter. Furthermore, the lattice constant must be close to the one of InGaP and the layer must be highly doped (n ≥ 1018 cm−3).
J-V characteristic
For
maximum efficiency, each subcell should be operated at its optimal J-V
parameters, which are not necessarily equal for each subcell. If they
are different, the total current through the solar cell is the lowest of
the three. By approximation, it results in the same relationship for the short-circuit current of the MJ solar cell: JSC = min (JSC1, JSC2, JSC3) where JSCi(λ) is the short-circuit current density at a given wavelength λ for the subcell i.
Because of the impossibility to obtain JSC1, JSC2, JSC3 directly from the total J-V characteristic, the quantum efficiency QE(λ)
is utilized. It measures the ratio between the amount of electron-hole
pairs created and the incident photons at a given wavelength λ. Let φi(λ) be the photon flux of corresponding incident light in subcell iandQEi(λ) be the quantum efficiency of the subcell i. By definition, this equates to:
The value of is obtained by linking it with the absorption coefficient ,
i.e. the number of photons absorbed per unit of length by a material.
If it is assumed that each photon absorbed by a subcell creates an
electron/hole pair (which is a good approximation), this leads to where di is the thickness of the subcell i and is the percentage of incident light which is not absorbed by the subcell i.
Similarly, because
- , the following approximation can be used: .
The values of are then given by the J-V diode equation:
Theoretical limiting efficiency
We
can estimate the limiting efficiency of ideal infinite multi-junction
solar cells using the graphical quantum-efficiency (QE) analysis
invented by C. H. Henry.
To fully take advantage of Henry's method, the unit of the AM1.5
spectral irradiance should be converted to that of photon flux (i.e.,
number of photons/m2/s). To do that, it is necessary to carry
out an intermediate unit conversion from the power of electromagnetic
radiation incident per unit area per photon energy to the photon flux
per photon energy (i.e., from [W/m2/eV] to [number of photons/m2/s/eV]).
For this intermediate unit conversion, the following points have to be
considered: A photon has a distinct energy which is defined as follows:
(1): Eph = h∙f = h∙(c/λ)
where Eph is photon energy, h is Planck's constant (h = 6.626*10−34 [J∙s]), c is speed of light (c = 2.998*108 [m/s]), f is frequency [1/s], and λ is wavelength [nm].
(1): Eph = h∙f = h∙(c/λ)
where Eph is photon energy, h is Planck's constant (h = 6.626*10−34 [J∙s]), c is speed of light (c = 2.998*108 [m/s]), f is frequency [1/s], and λ is wavelength [nm].
Then the photon flux per photon energy, dnph/dhν, with respect to certain irradiance E [W/m2/eV] can be calculated as follows:
(2): = E/{h∙(c/λ)} = E[W/(m2∙eV)]∙λ∙(10−9 [m])/(1.998∙10−25 [J∙s∙m/s]) = E∙λ∙5.03∙1015 [(# of photons)/(m2∙s∙eV)]
As a result of this intermediate unit conversion, the AM1.5 spectral irradiance is given in unit of the photon flux per photon energy, [number of photons/m2/s/eV], as shown in Figure 1.
(2): = E/{h∙(c/λ)} = E[W/(m2∙eV)]∙λ∙(10−9 [m])/(1.998∙10−25 [J∙s∙m/s]) = E∙λ∙5.03∙1015 [(# of photons)/(m2∙s∙eV)]
As a result of this intermediate unit conversion, the AM1.5 spectral irradiance is given in unit of the photon flux per photon energy, [number of photons/m2/s/eV], as shown in Figure 1.
Based on the above result from the intermediate unit conversion, we
can derive the photon flux by numerically integrating the photon flux
per photon energy with respect to photon energy. The numerically
integrated photon flux is calculated using the Trapezoidal rule, as
follows:
(3):
(3):
As a result of this numerical integration, the AM1.5 spectral
irradiance is given in unit of the photon flux, [number of
photons/m2/s], as shown in Figure 2.
It is should be noted that there are no photon flux data in the small
photon energy range from 0 eV to 0.3096 eV because the standard (AM1.5)
solar energy spectrum for hν < 0.31 eV are not available. Regardless
of this data unavailability, however, the graphical QE analysis can be
done using the only available data with a reasonable assumption that
semiconductors are opaque for photon energies greater than their bandgap
energy, but transparent for photon energies less than their bandgap
energy. This assumption accounts for the first intrinsic loss in the
efficiency of solar cells, which is caused by the inability of
single-junction solar cells to properly match the broad solar energy
spectrum.
However, the current graphical QE analysis still cannot reflect the
second intrinsic loss in the efficiency of solar cells, radiative
recombination. To take the radiative recombination into account, we need
to evaluate the radiative current density, Jrad, first. According to Shockley and Queisser method,
Jrad can be approximated as follows:
(4):
(5):
where Eg is in electron volts and n is evaluated to be 3.6, the value for GaAs. The incident absorbed thermal radiation Jth is given by Jrad with V = 0.
(6):
(6):
The current density delivered to the load is the difference of
the current densities due to absorbed solar and thermal radiation and
the current density of radiation emitted from the top surface or
absorbed in the substrate. Defining Jph = enph, we have:
(7): J = Jph + Jth − Jrad
The second term, Jth, is negligible compared to Jph for all semiconductors with Eg. ≥ 0.3 eV, as can be shown by evaluation of the above Jth equation. Thus, we will neglect this term to simplify the following discussion. Then we can express J as follows:
(8):
The open-circuit voltage is found by setting J = 0.
(9):
(8):
The open-circuit voltage is found by setting J = 0.
(9):
The maximum power point (Jm, Vm) is found by stetting the derivative . The familiar result of this calculation is:
(10):
(10):
(11):
Finally, the maximum work (Wm) done per absorbed photon, Wm is given by:
(12):
(12):
Combining the last three equations, we have:
(13):
(13):
Figure 3. Maximum work by ideal infinite multi-junction solar cells under standard AM1.5 spectral irradiance.
Now, we can fully use Henry's graphical QE analysis, taking into
account the two major intrinsic losses in the efficiency of solar cells.
The two main intrinsic losses are radiative recombination, and the
inability of single junction solar cells to properly match the broad
solar energy spectrum. The shaded area under the red line represents the
maximum work done by ideal infinite multi-junction solar cells. Hence,
the limiting efficiency of ideal infinite multi-junction solar cells is
evaluated to be 68.8% by comparing the shaded area defined by the red
line with the total photon-flux area determined by the black line. (This
is why this method is called "graphical" QE analysis.) Although this
limiting efficiency value is consistent with the values published by
Parrott and Vos in 1979: 64% and 68.2% respectively,
there is a small gap between the estimated value in this report and
literature values. This minor difference is most likely due to the
different ways how to approximate the photon flux from 0 eV to 0.3096
eV. Here, we approximated the photon flux from 0 eV to 0.3096 eV as the
same as the photon flux at 0.31 eV.
Materials
The
majority of multi-junction cells that have been produced to date use
three layers (although many tandem a-Si:H/mc-Si modules have been
produced and are widely available). However, the triple junction cells
require the use of semiconductors that can be tuned to specific
frequencies, which has led to most of them being made of gallium arsenide (GaAs) compounds, often germanium for the bottom-, GaAs for the middle-, and GaInP2 for the top-cell.
Gallium arsenide substrate
Dual junction cells can be made on Gallium arsenide wafers. Alloys of Indium gallium phosphide in the range In.5Ga.5P through In.53Ga.47P
serve as the high band gap alloy. This alloy range provides for the
ability to have band gaps in the range of 1.92eV to 1.87eV. The lower GaAs junction has a band gap of 1.42eV.
Germanium substrate
Triple junction cells consisting of indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs) or indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) and germanium
(Ge) can be fabricated on germanium wafers. Early cells used straight
gallium arsenide in the middle junction. Later cells have utilized In0.015Ga0.985As, due to the better lattice match to Ge, resulting in a lower defect density.
Due to the huge band gap difference between GaAs (1.42eV), and Ge
(0.66eV), the current match is very poor, with the Ge junction operated
significantly current limited.
Current efficiencies for commercial InGaP/GaAs/Ge cells approach 40% under concentrated sunlight. Lab cells (partly using additional junctions between the GaAs and Ge junction) have demonstrated efficiencies above 40%.
Indium phosphide substrate
Indium phosphide
may be used as a substrate to fabricate cells with band gaps between
1.35eV and 0.74eV. Indium Phosphide has a band gap of 1.35eV. Indium gallium arsenide (In0.53Ga0.47As)
is lattice matched to Indium Phosphide with a band gap of 0.74eV. A
quaternary alloy of Indium gallium arsenide phosphide can be lattice
matched for any band gap in between the two.
Indium phosphide-based cells have the potential to work in tandem
with gallium arsenide cells. The two cells can be optically connected
in series (with the InP cell below the GaAs cell), or in parallel
through the use of spectra splitting using a Dichroic filter.
Indium gallium nitride substrate
Indium gallium nitride
(InGaN) is a semiconductor material made of a mix of gallium nitride
(GaN) and indium nitride (InN). It is a ternary group III/V direct bandgap
semiconductor. Its bandgap can be tuned by varying the amount of indium
in the alloy from 0.7 eV to 3.4 eV, thus making it an ideal material
for solar cells.
However, its conversion efficiencies because of technological factors
unrelated to bandgap are still not high enough to be competitive in the
market.
Performance improvements
Structure
Many MJ photovoltaic cells use III-V semiconductor
materials. GaAsSb-based heterojunction tunnel diodes, instead of
conventional InGaP highly doped tunnel diodes described above, have a
lower tunneling distance. Indeed, in the heterostructure formed by
GaAsSb and InGaAs, the valence band of GaAsSb is higher than the valence band of the adjoining p-doped layer. Consequently, the tunneling distance dtunnel is reduced and so the tunneling current, which exponentially depends of dtunnel, is increased. Hence, the voltage is lower than that of the InGaP tunnel junction.
GaAsSb heterojunction tunnel diodes offer other advantages. The same current can be achieved by using a lower doping.
Secondly, because the lattice constant is larger for GaAsSb than Ge,
one can use a wider range of materials for the bottom cell because more
materials are lattice-matched to GaAsSb than to Ge.
Chemical components can be added to some layers. Adding about one percent of indium in each layer better matches lattice constants of the different layers.
Without it, there is about 0.08 percent of mismatching between layers,
which inhibits performance. Adding aluminium to the top cell increases
its band gap to 1.96 eV, covering a larger part of the solar spectrum and obtain a higher open-circuit voltage VOC.
The theoretical efficiency of MJ solar cells is 86.8% for an infinite number of pn junctions,
implying that more junctions increase efficiency. The maximum
theoretical efficiency is 37, 50, 56, 72% for 1, 2, 3, 36 pn junctions,
respectively, with the number of junctions increasing exponentially to
achieve equal efficiency increments.
The exponential relationship implies that as the cell approaches the
limit of efficiency, the increase cost and complexity grow rapidly.
Decreasing the thickness of the top cell increases the transmission
coefficient T.
Finally, an InGaP hetero-layer between the p-Ge layer and the
InGaAs layer can be added in order to create automatically the n-Ge
layer by scattering during MOCVD growth and increase significantly the
quantum efficiency QE(λ) of the bottom cell. InGaP is advantageous because of its high scattering coefficient and low solubility in Ge.
Spectral variations
Solar
spectrum at the Earth surface changes constantly depending on the
weather and sun position. This results in the variation of φ(λ), QE(λ), α(λ) and thus the short-circuit currents JSCi. As a result, the current densities Ji
are not necessarily matched and the total current becomes lower. These
variations can be quantified using the average photon energy (APE) which
is the ratio between the spectral irradiance G(λ) (the power density of
the light source in a specific wavelength λ) and the total photon flux
density. It can be shown that a high (low) value for APE means low
(high) wavelengths spectral conditions and higher (lower) efficiencies.
Thus APE is a good indicator for quantifying the effects of the solar
spectrum variations on performances and has the added advantage of being
independent of the device structure and the absorption profile of the
device.
Use of light concentrators
Light
concentrators increase efficiencies and reduce the cost/efficiency
ratio. The three types of light concentrators in use are refractive
lenses like Fresnel lenses, reflective dishes (parabolic or cassegraine), and light guide
optics. Thanks to these devices, light arriving on a large surface can
be concentrated on a smaller cell. The intensity concentration ratio (or
“suns”) is the average intensity of the focused light divided by 1 kW/m2 (reasonable value related to solar constant). If its value is X then the MJ current becomes X higher under concentrated illumination.
Using concentrations on the order of 500 to 1000, meaning that a 1 cm2 cell can use the light collected from 0.1 m2 (as 1 m2 equal 10000 cm2),
produces the highest efficiencies seen to date. Three-layer cells are
fundamentally limited to 63%, but existing commercial prototypes have
already demonstrated over 40%.
These cells capture about 2/3 of their theoretical maximum performance,
so assuming the same is true for a non-concentrated version of the same
design, one might expect a three-layer cell of 30% efficiency. This is
not enough of an advantage over traditional silicon designs to make up
for their extra production costs. For this reason, almost all
multi-junction cell research for terrestrial use is dedicated to
concentrator systems, normally using mirrors or fresnel lenses.
Using a concentrator also has the added benefit that the number
of cells needed to cover a given amount of ground area is greatly
reduced. A conventional system covering 1 m2 would require 625 16 cm2
cells, but for a concentrator system only a single cell is needed,
along with a concentrator. The argument for concentrated Multi-junction
cells has been that the high cost of the cells themselves would be more
than offset by the reduction in total number of cells. However, the
downside of the concentrator approach is that efficiency drops off very
quickly under lower lighting conditions. In order to maximize its
advantage over traditional cells and thus be cost competitive, the
concentrator system has to track the sun as it moves to keep the light
focused on the cell and maintain maximum efficiency as long as possible.
This requires a solar tracker system, which increases yield, but also cost.
Fabrication
As of 2014 multi-junction cells were expensive to produce, using techniques similar to semiconductor device fabrication, usually metalorganic vapour phase epitaxy but on "chip" sizes on the order of centimeters.
A new technique was announced that year that allowed such cells
to use a substrate of glass or steel, lower-cost vapors in reduced
quantities that was claimed to offer costs competitive with conventional
silicon cells.
Comparison with other technologies
There are four main categories of photovoltaic cells: conventional mono and multi crystalline silicon (c-Si) cells, thin film solar cells (a-Si, CIGS and CdTe), and multi-junction (MJ) solar cells. The fourth category, emerging photovoltaics, contains technologies that are still in the research or development phase and are not listed in the table below.
| Categories | Technology | η (%) | VOC (V) | ISC (A) | W/m2 | t (µm) | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystalline silicon cells | Monocrystalline | 24.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 63 | 100 |
|
| Polysilicon | 20.3 | 0.615 | 8.35 | 211 | 200 |
| |
| Thin film solar cells | Amorphous silicon | 11.1 | 0.63 | 0.089 | 33 | 1 |
|
| CdTe | 16.5 | 0.86 | 0.029 | – | 5 |
| |
| CIGS | 19.5 | – | – | – | 1 |
| |
| Multi-junction cells | MJ | 40.7 | 2.6 | 1.81 | 476 | 140 |
|
MJ solar cells and other photovoltaic devices have significant differences (see the table above). Physically, the main property of a MJ solar cell is having more than
one pn junction in order to catch a larger photon energy spectrum while
the main property of the thin film solar cell is to use thin films instead of thick layers in order to decrease the cost efficiency ratio. As of 2010,
MJ solar panels are more expensive than others. These differences imply
different applications: MJ solar cells are preferred in space and c-Si
solar cells for terrestrial applications.
National Renewable Energy Laboratory graph of solar cell efficiency over time.
The efficiencies of solar cells and Si solar technology are
relatively stable, while the efficiency of solar modules and
multi-junction technology are progressing.
Measurements on MJ solar cells are usually made in laboratory,
using light concentrators (this is often not the case for the other
cells) and under standard test conditions (STCs). STCs prescribe, for
terrestrial applications, the AM1.5 spectrum as the reference. This air
mass (AM) corresponds to a fixed position of the sun in the sky of 48°
and a fixed power of 833 W/m2. Therefore, spectral variations of incident light and environmental parameters are not taken into account under STC.
Consequently, performance of MJ solar cells in terrestrial
environment is inferior to that achieved in laboratory. Moreover, MJ
solar cells are designed such that currents are matched under STC, but
not necessarily under field conditions. One can use QE(λ) to compare performances of different technologies, but QE(λ)
contains no information on the matching of currents of subcells. An
important comparison point is rather the output power per unit area
generated with the same incident light.
Applications
As
of 2010, the cost of MJ solar cells was too high to allow use outside
of specialized applications. The high cost is mainly due to the complex
structure and the high price of materials. Nevertheless, with light
concentrators under illumination of at least 400 suns, MJ solar panels become practical.
As less expensive multi-junction materials become available other applications involve bandgap engineering for microclimates with varied atmospheric conditions.
MJ cells are currently being utilized in the Mars rover missions.
The environment in space is quite different. Because there is no
atmosphere, the solar spectrum is different (AM0). The cells have a poor
current match due to a greater photon flux of photons above 1.87eV vs.
those between 1.87eV and 1.42eV. This results in too little current in
the GaAs junction, and hampers the overall efficiency since the InGaP
junction operates below MPP current and the GaAs junction operates above
MPP current. To improve current match, the InGaP layer is
intentionally thinned to allow additional photons to penetrate to the
lower GaAs layer.
In terrestrial concentrating applications, the scatter of blue
light by the atmosphere reduces the photon flux above 1.87eV, better
balancing the junction currents. Radiation particles that are no longer
filtered can damage the cell. There are two kinds of damage: ionization and atomic displacement. Still, MJ cells offer higher radiation resistance, higher efficiency and a lower temperature coefficient.




























![W_{{m}}=E_{g}-kT[ln({\frac {A}{en_{{ph}}}})+ln(1+{\frac {eV_{{m}}}{kT}})+1]\,](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/73bc6a4b637d3efa4857c79bae7b9c82fffb8a25)



